Directional freeze method for TiAl-based alloy plate
A technology of directional solidification and directional solidification furnace, which is applied in the field of continuous casting directional solidification, and can solve problems such as unsuitable plate processing and unsuitable TiAl-based alloy material processing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
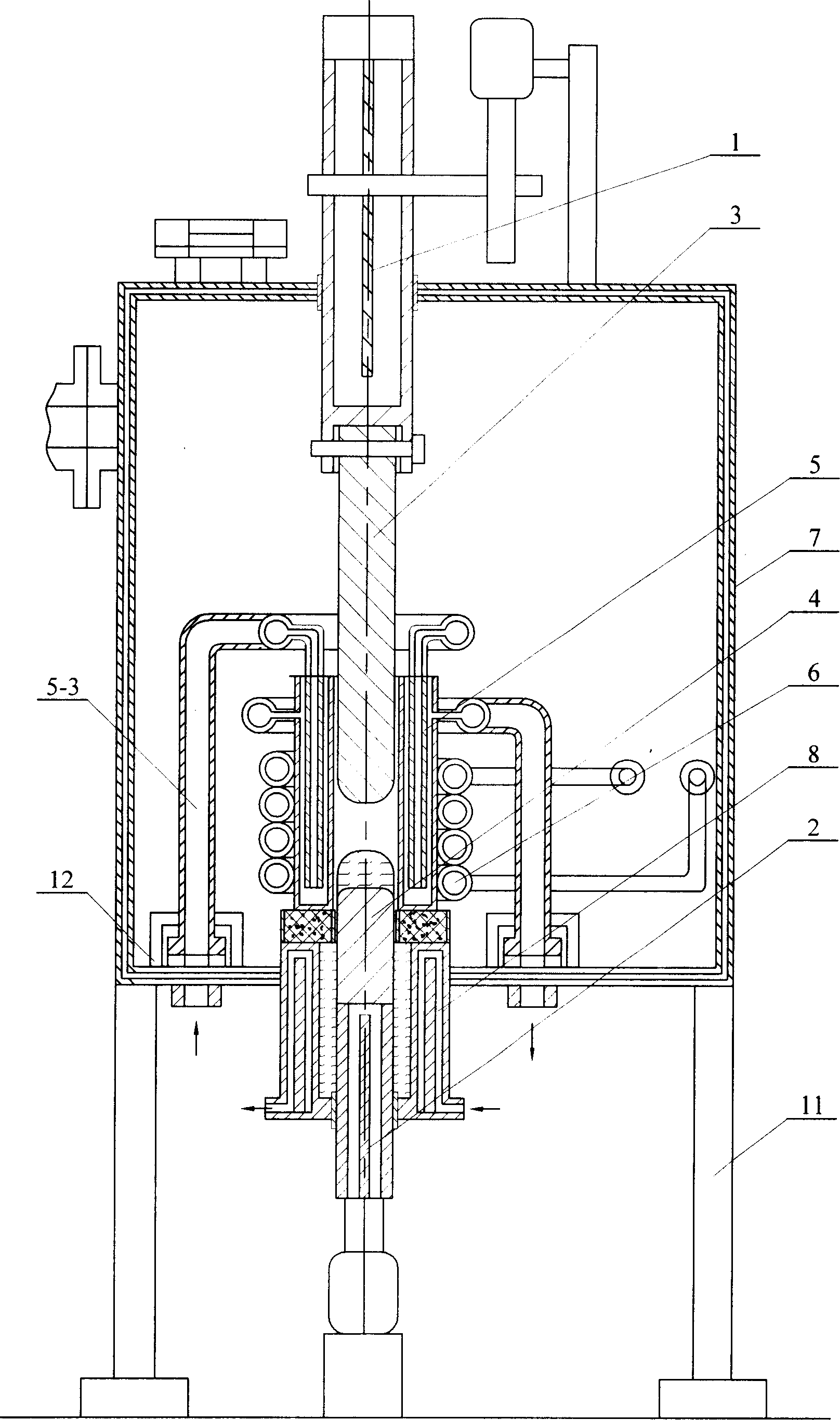
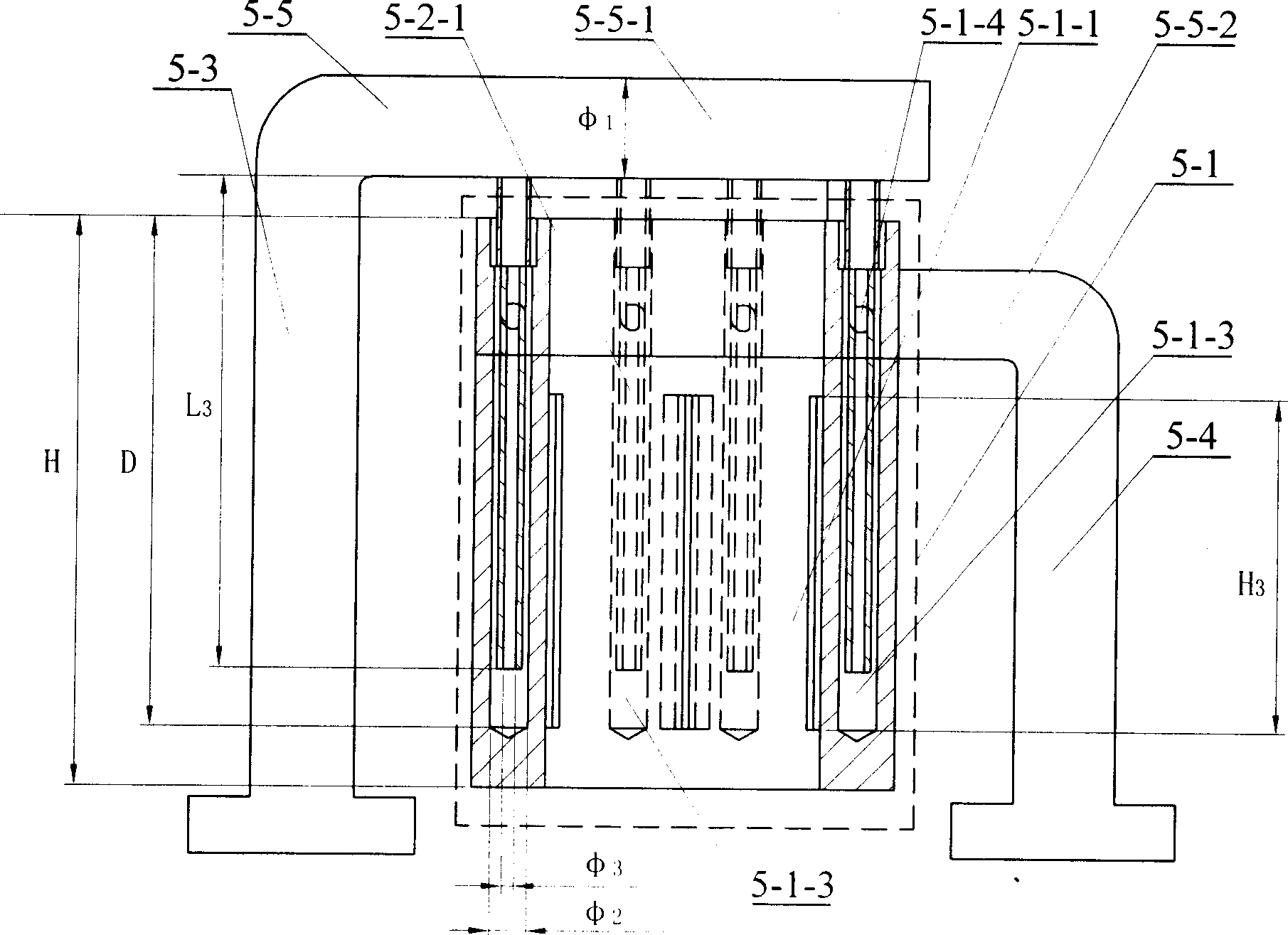
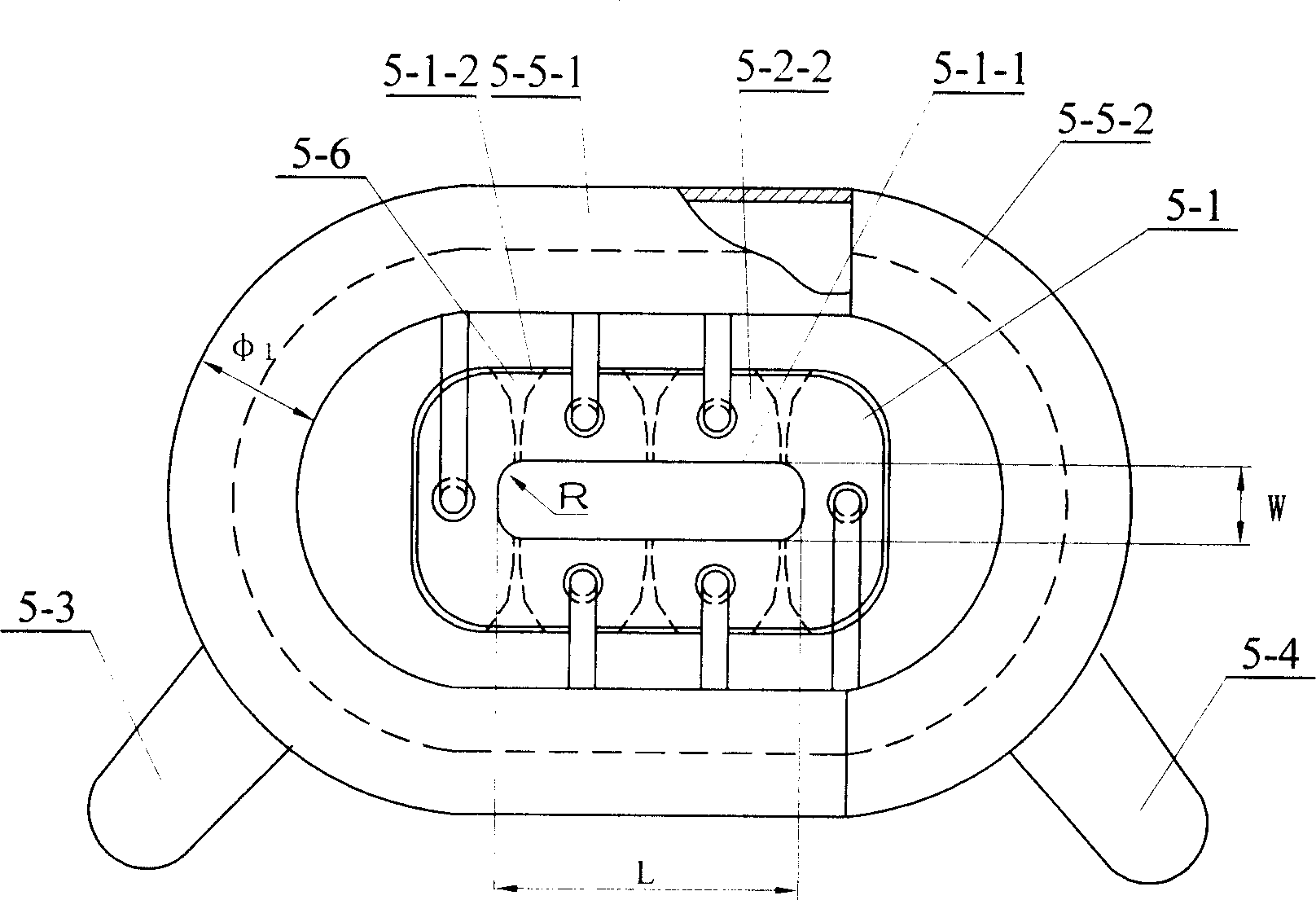
[0005] Specific embodiment one: the directional solidification method of the TiAl-based alloy sheet in this embodiment is to install a furnace 7 with the functions of constraining molten alloy and controlling the distribution of magnetic field in the electromagnetic constrained forming and directional solidification furnace 7 with the functions of electromagnetic constrained forming and directional solidification Cold crucible 5, the cross section of the cavity 5-1-1 of the cold crucible 5 is rectangular, 2 to 8 turns of induction coil 6 are fixed outside the cold crucible 5, and then in the cavity 5-1-1 of the cold crucible 5 A dummy ingot 4 whose upper end is fixedly connected to the upper feeding mechanism 1 and a TiAl-based alloy material rod 3 whose lower end is fixedly connected to the lower drawing mechanism 2 are provided. The TiAl-based alloy material rod 3 is arranged directly above the dummy ingot 4, and the The ratio of the width W, length L, and height H of the cha...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0015] Specific embodiment two: the structure of the slits 5-6 that can ensure the uniform distribution of the magnetic field in the crucible is six straight slits, or four oblique slits and two straight slits, or four oblique slits slits and four straight slits, filling the slits with low-conductivity materials to electrically insulate both ends of the slits; the cross-sectional shape of any of the slits 5-6 is: two widths W near the inside of the crucible 1 It is a parallel straight line 5-6-1 of 0.1 ~ 0.5mm, and its radially outward length L 1 2-4 mm, the parallel straight line 5-6-1 transitions to the outer surface 5-1-2 of the crucible body 5-1 through the straight line 5-6-2 or arc 5-6-3. It has been proved by experiments that the position and structure of the slits can well ensure the uniform distribution of the magnetic field in the crucible, so that the melting temperature of each position of the metal is consistent, so as to better realize the electromagnetic confine...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0016] Specific Embodiment Three: The coil 6 in this embodiment is a single coil, the coil 6 in this embodiment is connected to a single-phase power supply with a power of 75-90kW, and the width W, length L, and height H of the cavity 5-1-1 are The ratio between them is 1:2.2-3.2:10-15, and under the same conditions as those in Embodiment 1, a rectangular blank with an aspect ratio of 2-3 can be obtained. Control the power of the single-phase power supply within this range, so that the upper feeding material can be fully melted and a certain degree of superheat can be maintained. When the ingot moves downward and is constrained to form, it has sufficient binding force to ensure the integrity of the ingot shape and obtain orientation. For the solidification structure, since the aspect ratio of the cast ingot is required to be small in this embodiment, there is no need to use the heat preservation jacket 10, see FIG. 13 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com