Acidic bath for electrolytically depositing a copper deposit containing halogenated or pseudohalogenated monomeric phenazinium compounds
An onium compound and halide technology, applied in the field of halogenated or pseudo-halogenated monomeric phenazinium compounds, can solve the problems of product quality change, time-consuming reaction, high cost, long reaction time, moderate stability and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
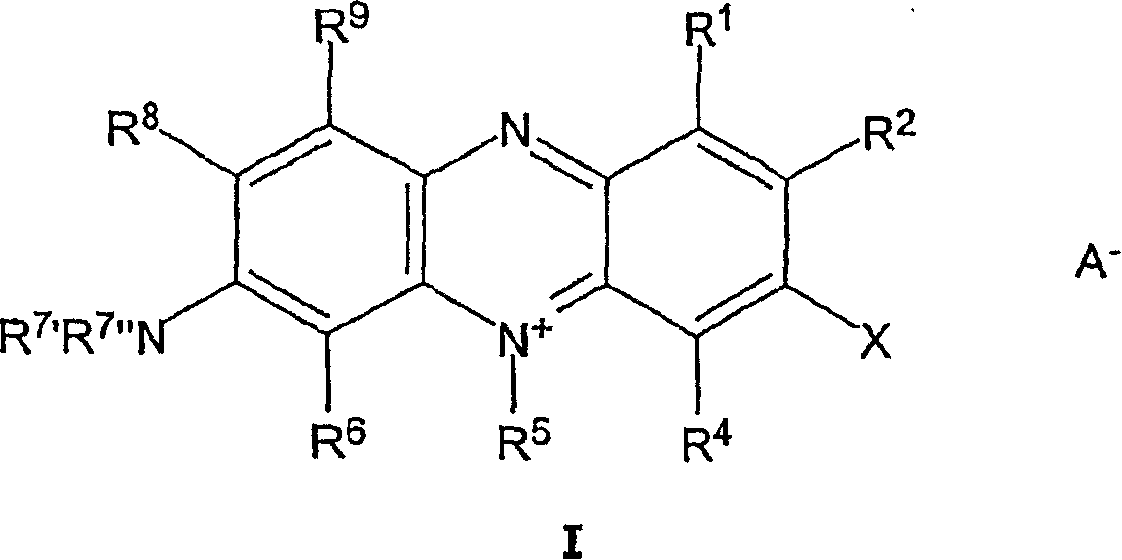
[0056] A novel preparation method was used to synthesize halogenated or pseudohalogenated monomeric phenazinium compounds. In conventional methods, in the first synthetic step, the diazonium compound is formed by diazotizing a monomeric phenazinium compound in a first synthetic vessel in the presence of a mineral acid and a diazotizing agent, followed by a second synthetic step , and only after transferring the diazo compound to a second synthesis vessel, react the diazo compound in the presence of a mineral acid and a halogenated or pseudohalogenated cuprous(I) halide to form the halogenated or pseudohalogenated monomeric phen Azinium compounds, compared to conventional methods, the method according to the invention involves first and second reaction steps, both of which are carried out in the presence of monomeric phenazinium compounds, mineral acids, diazotizing agents and halides or pseudohalides in a single container (one-pot method).
[0057] Thus, the one-pot method is...
preparation Embodiment 1
[0085] Preparative Example 1: No additional halide added
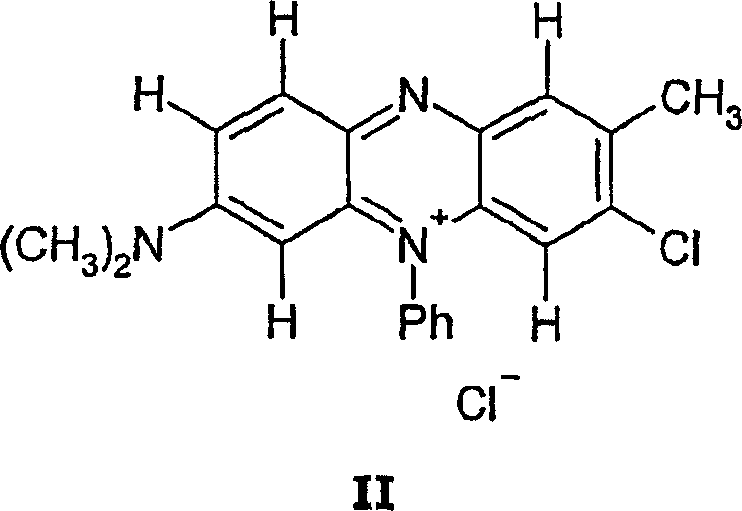
[0086] 3-Chloro-7-N,N-dimethylamino-2-methyl-5-phenyl-phenazinium chloride
[0087] Suspend 1 g of 3-amino-7-N,N-dimethylamino-2-methyl-5-phenyl-phenazinium chloride in 15 ml of 35% by weight hydrochloric acid and heat it to 50 °C . Next, saturated aqueous sodium nitrite solution (454 mg in 6 ml of water) was slowly added dropwise, and then stirred at this temperature for one hour. The reaction formulation was cooled to room temperature, and the resulting dark blue solid material was filtered off and dried. Yield 615 mg (58.5% of theory).
[0088] After quantitative analysis by mass spectrometry, the purity of the obtained material was found to be 94 mole %, ie only 6 mole % of the material used was not composed of the monomeric compound.
preparation Embodiment 2
[0089] Preparative Example 2: Addition of Additional Halide
[0090] 3-Chloro-7-N,N-dimethylamino-2-methyl-5-phenyl-phenazinium chloride
[0091] Suspend 1 g of 3-amino-7-N,N-dimethylamino-2-methyl-5-phenyl-phenazinium chloride in 15 ml of 35% by weight hydrochloric acid and heat it to 50 °C . Next, 347 mg of nickel(II) chloride was added, and a saturated aqueous sodium nitrite solution (454 mg in 6 ml of water) was slowly added dropwise, followed by stirring at this temperature for one hour. The reaction formulation was cooled to room temperature, and the resulting dark blue solid material was filtered off and dried. Yield 724 mg (69.0% of theory).
[0092] After quantitative analysis by mass spectrometry, it was found that the purity of the obtained material was 90 mol%, ie only 10 mol% of the used material was not composed of the monomeric compound.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com