A bionic liver tissue engineering scaffold and forming process thereof
A tissue engineering scaffold, bionic liver technology, applied in tissue cell/virus culture devices, biochemical instruments, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as poor controllability, difficult to build structures, and complexity, and improve porosity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
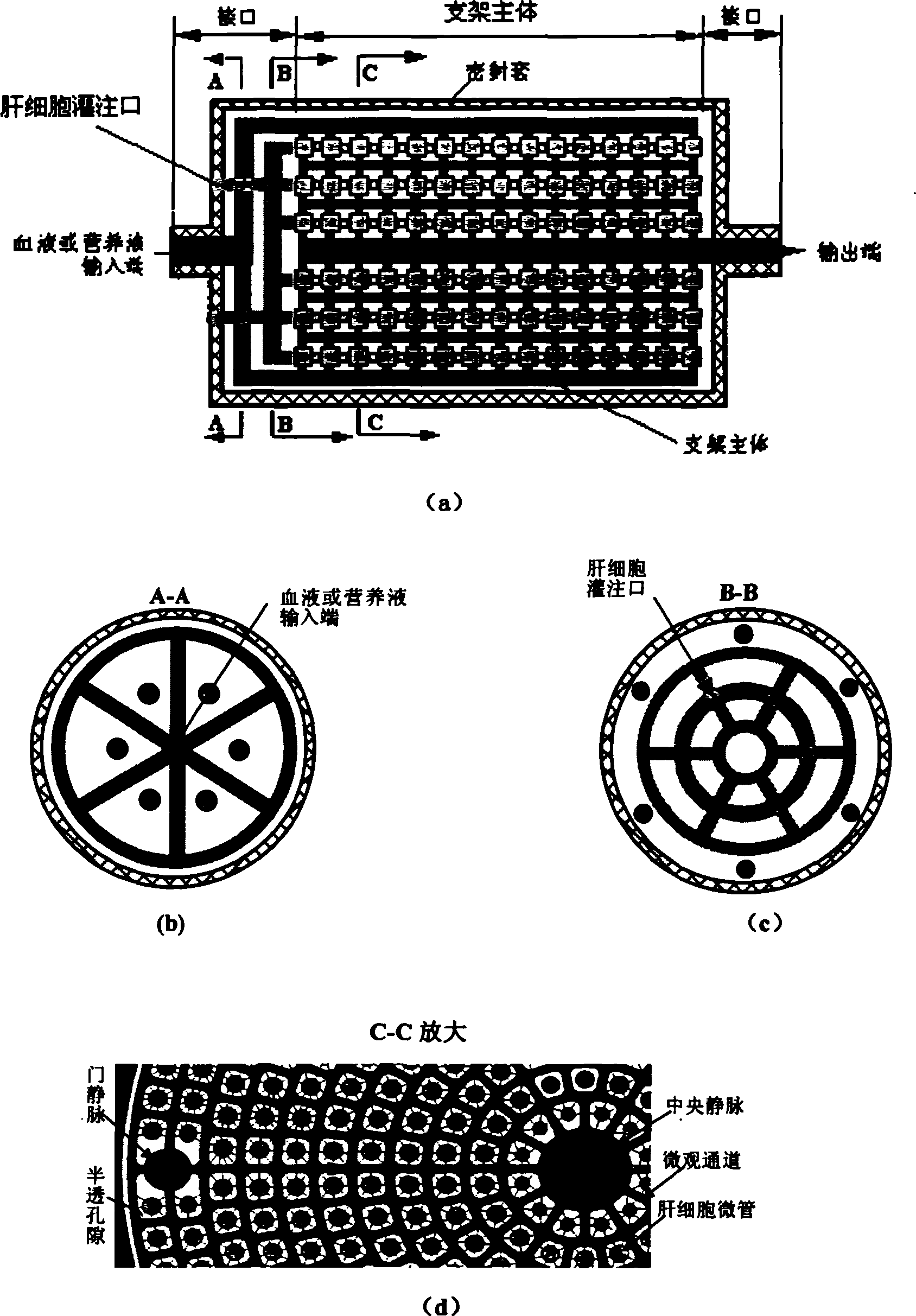
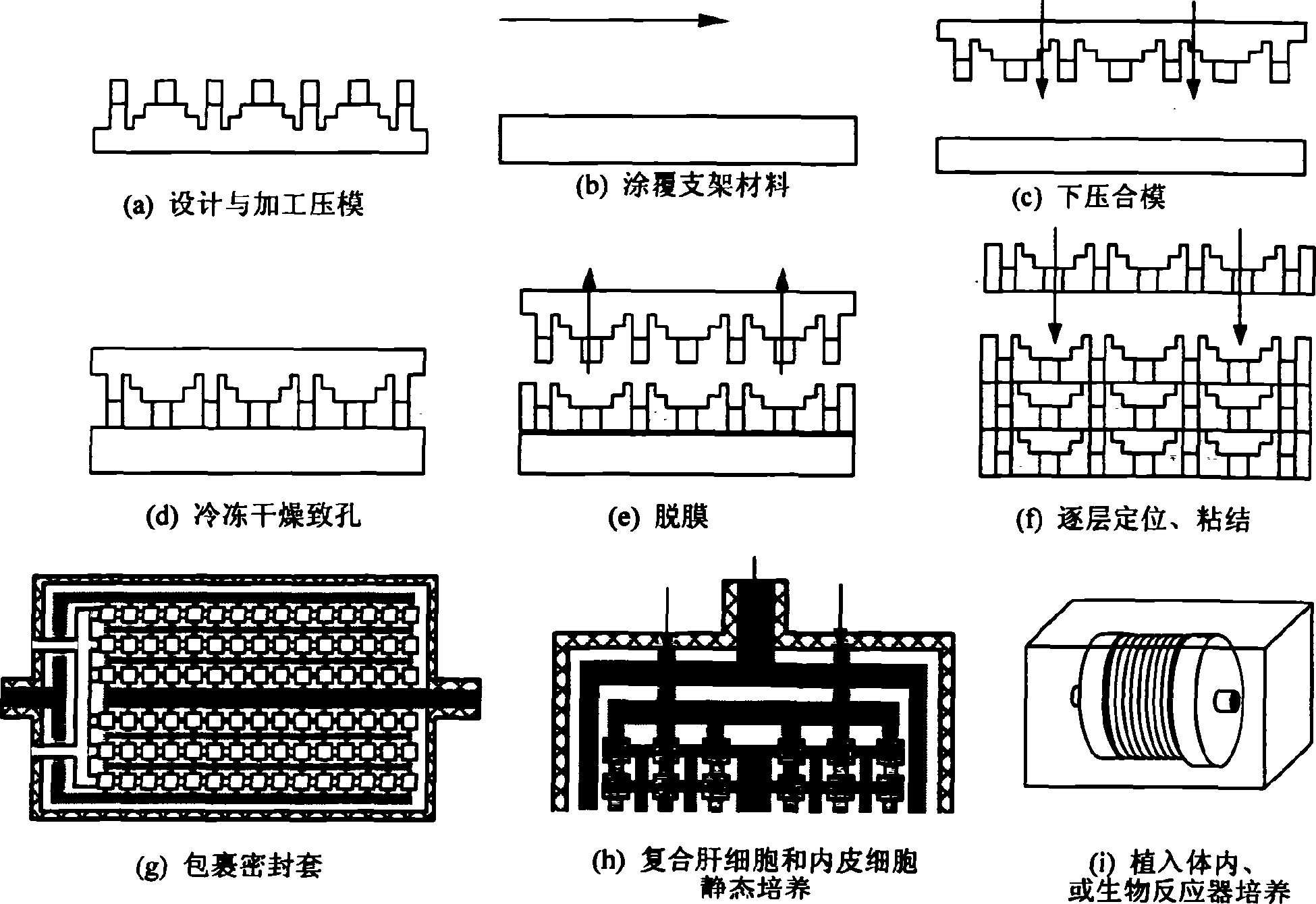
[0026] figure 1 It is the basic structure diagram of bionic bracket and interface. The scaffold and the interface simulate the hepatic lobule structure of the natural liver. The scaffold has two sets of independent microscopic piping systems that simulate the hepatic lobular structure, and are connected to the interfaces at both ends, respectively, for the microchannel structure of endothelial cells and hepatocyte growth ; There is no conduction between the two sets of pipelines, but they penetrate through the bracket material and exchange substances. The interfaces at both ends can be used for perfusing hepatocytes and connecting with blood vessels or nutrient solution delivery tubes respectively. The specific structure is detailed as follows.
[0027] Such as figure 1 As shown in (a): the shape of the bionic liver tissue engineering scaffold and the interface is cylindrical, which is composed of the main body of the bracket and the interface (including the sealing sleeve)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com