Solid state image pickup device and camera using the same
A technology of solid-state imaging devices and pixel parts, which is applied to electrical components, image communication, and color TV components, etc., which can solve the problems of increased chip area and cost, and achieve low power consumption, improved linearity, and reduced noise.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
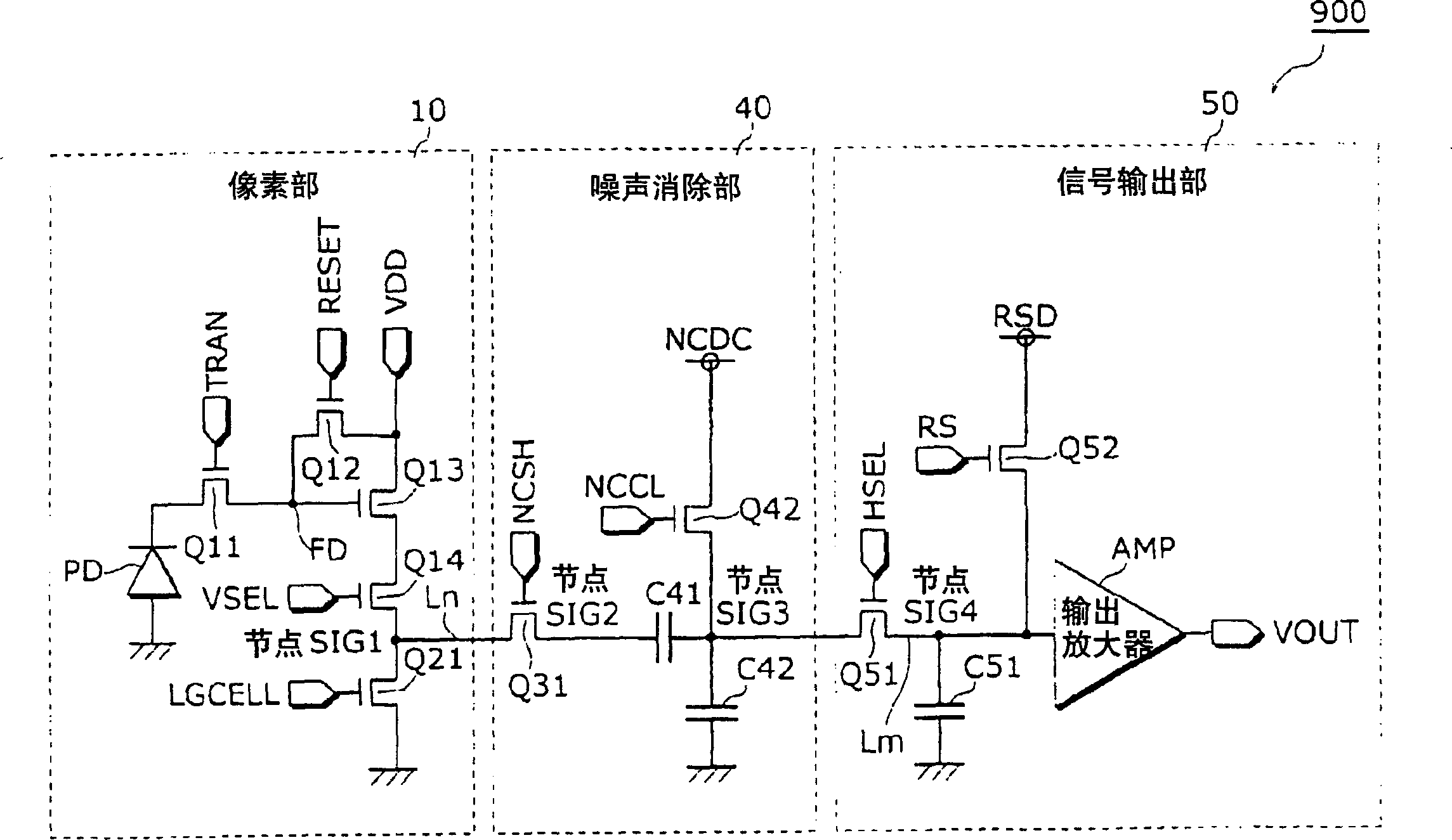
[0119] image 3 It is a schematic circuit diagram of a circuit composed only of N-type MOSs in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, which prevents deterioration of pixel characteristics due to heat treatment in the P-type MOS formation process. where, in this figure, for the figure 1 Components corresponding to the illustrated solid-state imaging device 900 are assigned the same reference numerals, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
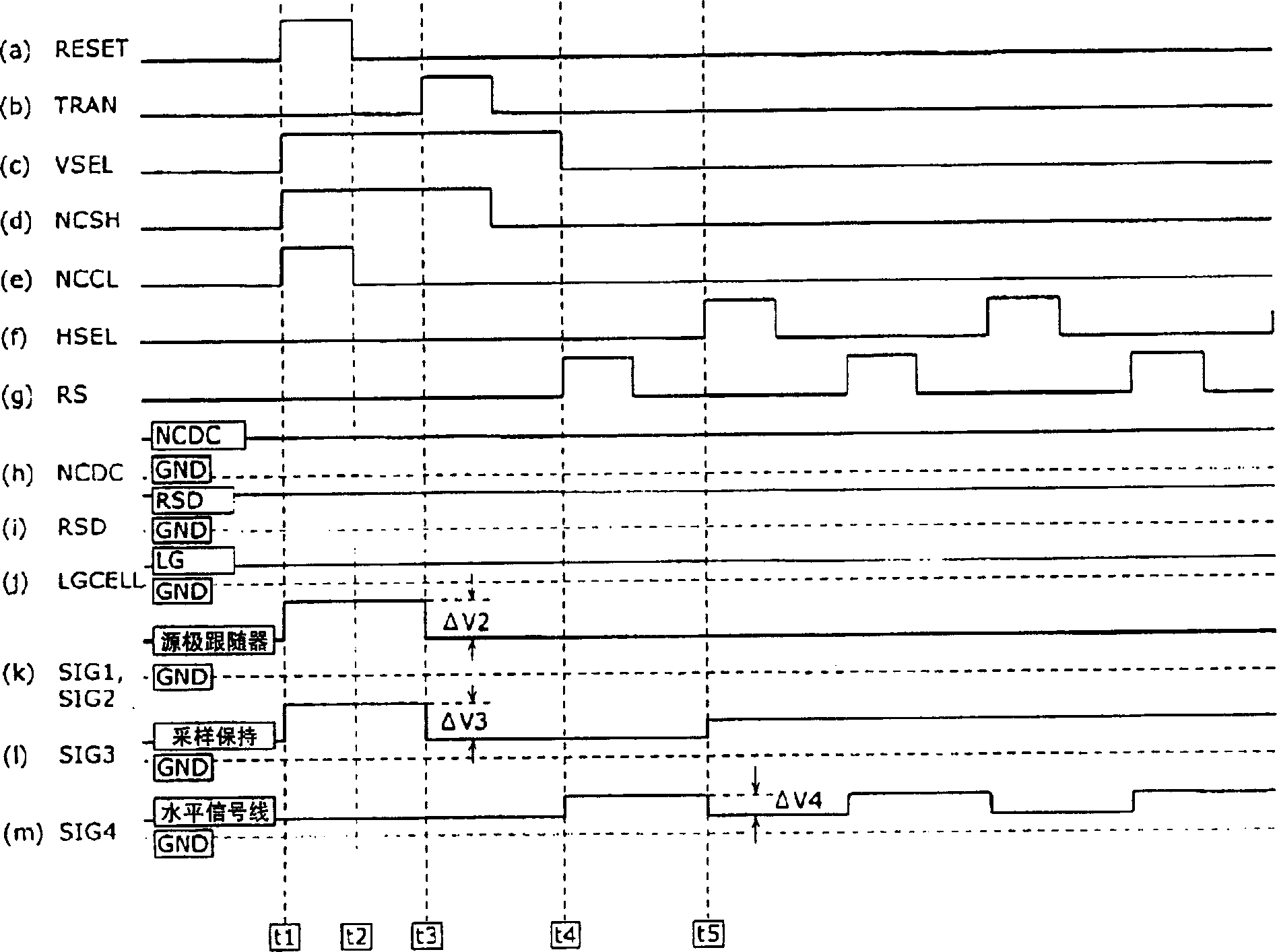
[0120] The solid-state imaging device 110 has a configuration in which a pixel signal amplifying section 60 (that is, a column amplifier 70 ) is inserted between the pixel section 10 and the noise canceling section 40 . Among them, its driving timing and figure 2 Same as shown.
[0121] That is, it becomes the following structure. At time t1, the RESET pulse is turned ON, and VDD is supplied to the floating propagation region FD. At this time, the VSEL pulse is turned ON, and the signal ( image 3 The node SIG11) is provid...
Embodiment approach 2
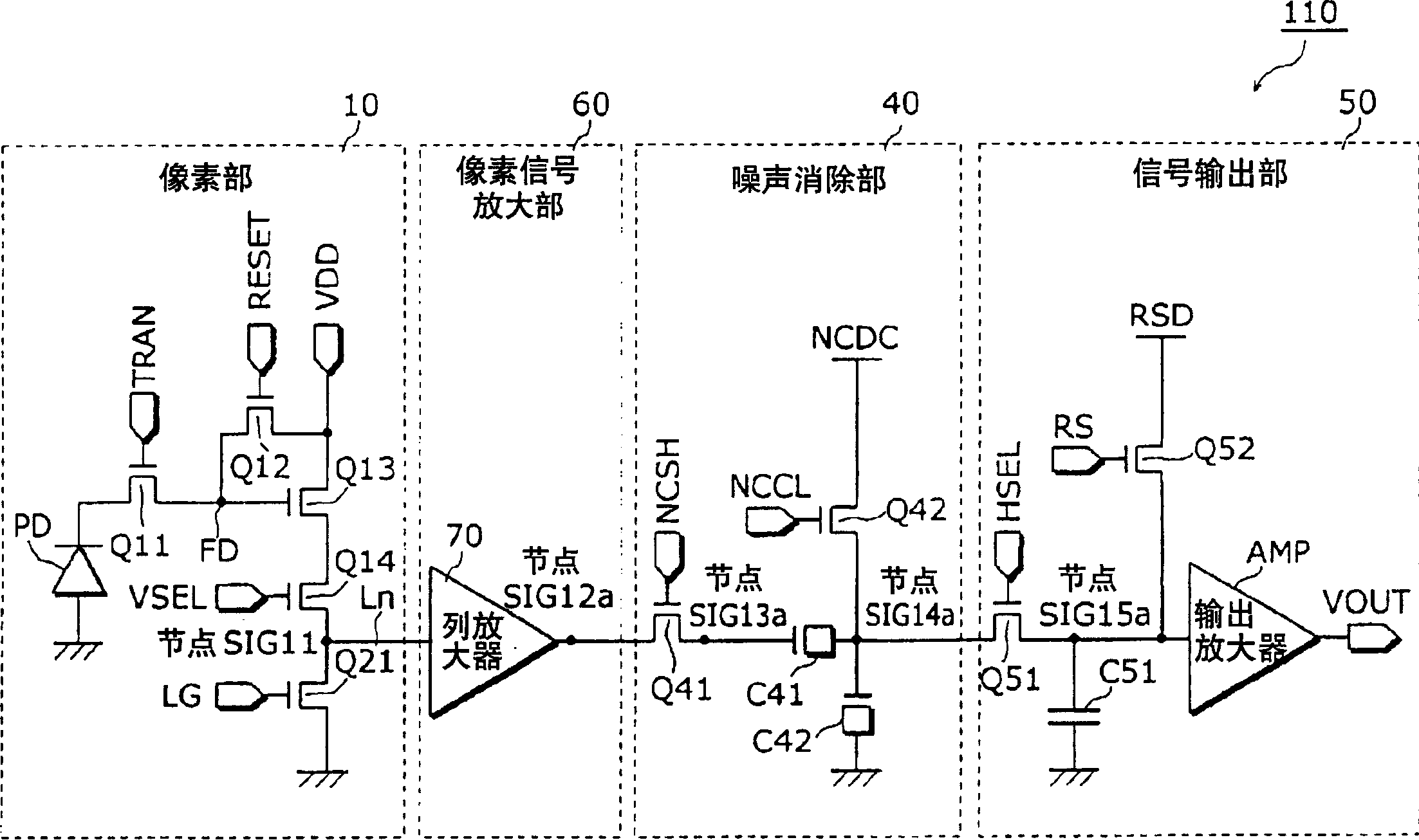
[0137] Figure 6 A circuit of an NMOS solid-state imaging device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention in which deterioration of pixel characteristics due to heat treatment in a P-type MOS formation process is prevented is shown. The solid-state imaging device 130 according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention differs from Embodiment 1 in that a source follower circuit for impedance conversion is added to the input portion of the signal output portion 50 a.
[0138] In Embodiment 2, in the circuit of Embodiment 1, the signal from the noise canceling unit 40 is transmitted to the horizontal signal line after first passing through the circuit for performing impedance conversion. Therefore, capacitance distribution due to parasitic capacitance of the horizontal signal line does not occur, and can be compared to The circuit of Embodiment 1 further improves sensitivity and reduces noise, and can also easily reduce the chip area.
[0139] Figure 7 is a driving ti...
Embodiment approach 3
[0147] Figure 8 It is a schematic circuit diagram of an NMOS solid-state imaging device that prevents deterioration of pixel characteristics due to heat treatment in a P-type MOS forming process according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0148] The solid-state imaging device 140 employs a configuration in which the pixel signal amplifier 60 b can change the amplification factor according to the level of the output voltage of the pixel unit 10 . In this configuration example, the pixel signal amplifying section 60b includes column amplifiers 70a and 70b with different amplification factors selected by the comparator COMP, and the column amplifiers are selected according to the level of the output voltage of the pixel section 10. One of 70a and 70b.
[0149] Comparing the potential of the node SIG61 and VREF in the pixel unit 10 with the comparator COMP, and controlling based on the output potential of the comparator COMP so that when the potential of the node SIG61...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com