Patents
Literature
37results about How to "Improve S/N" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
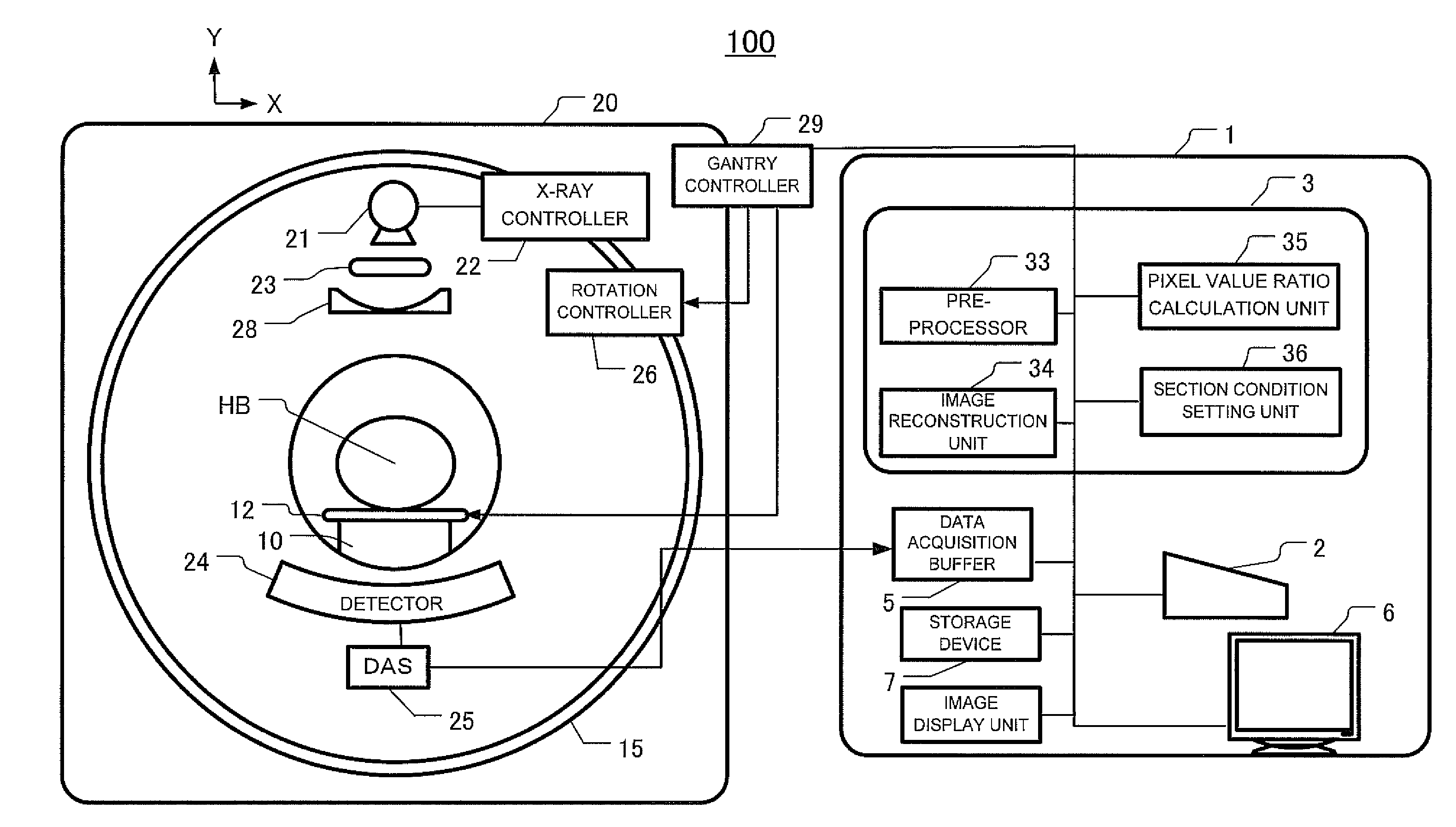
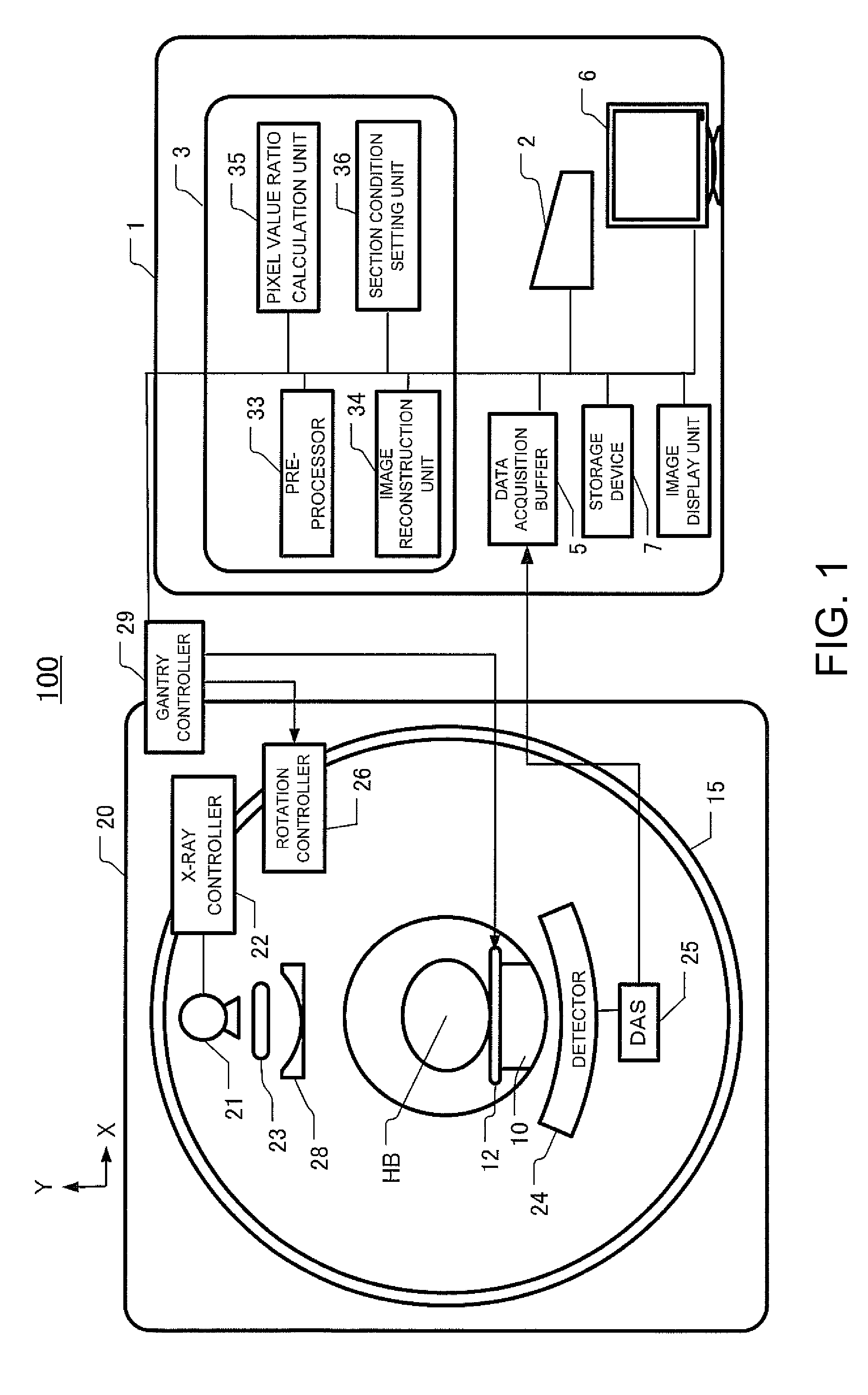
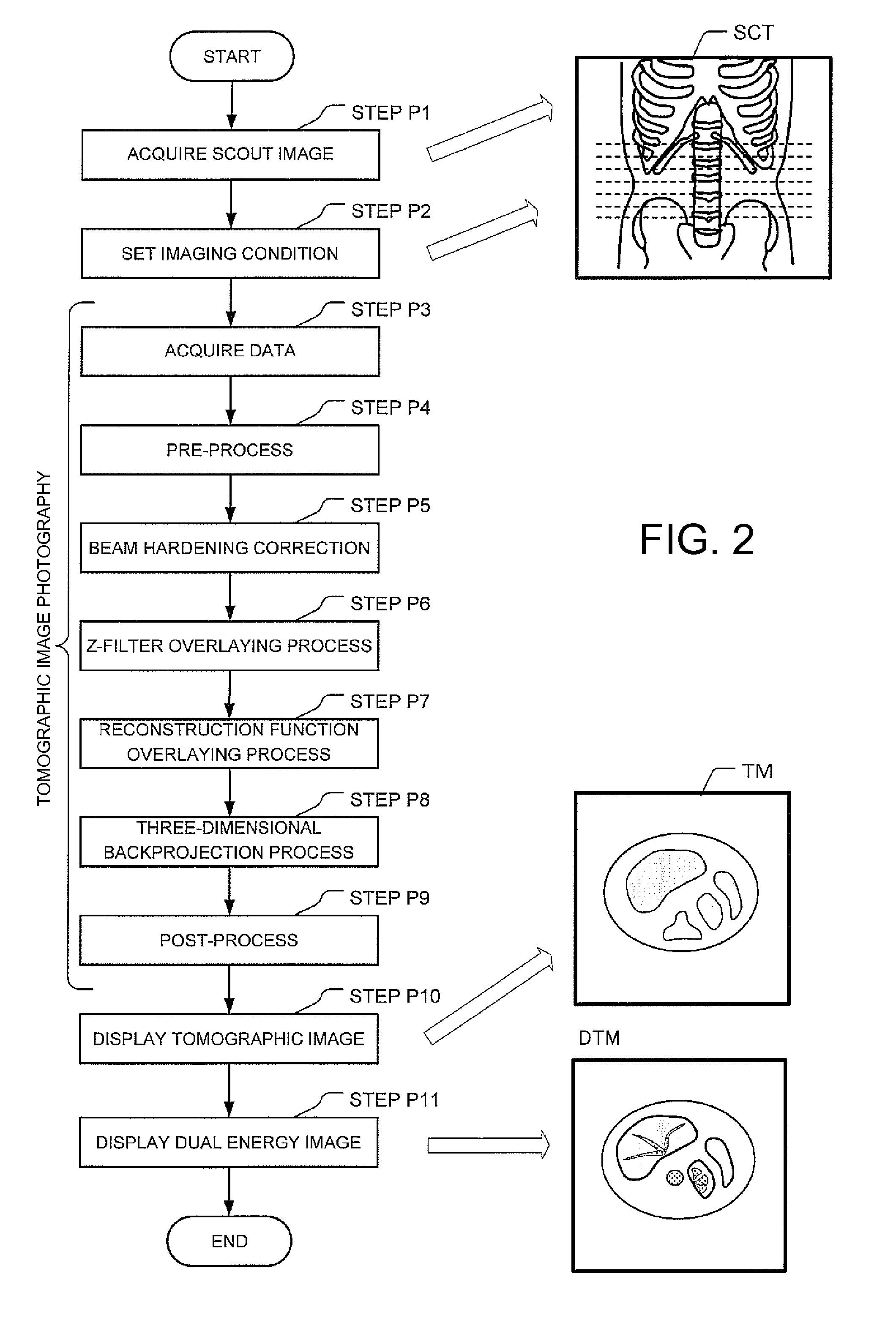
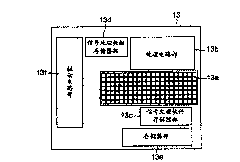
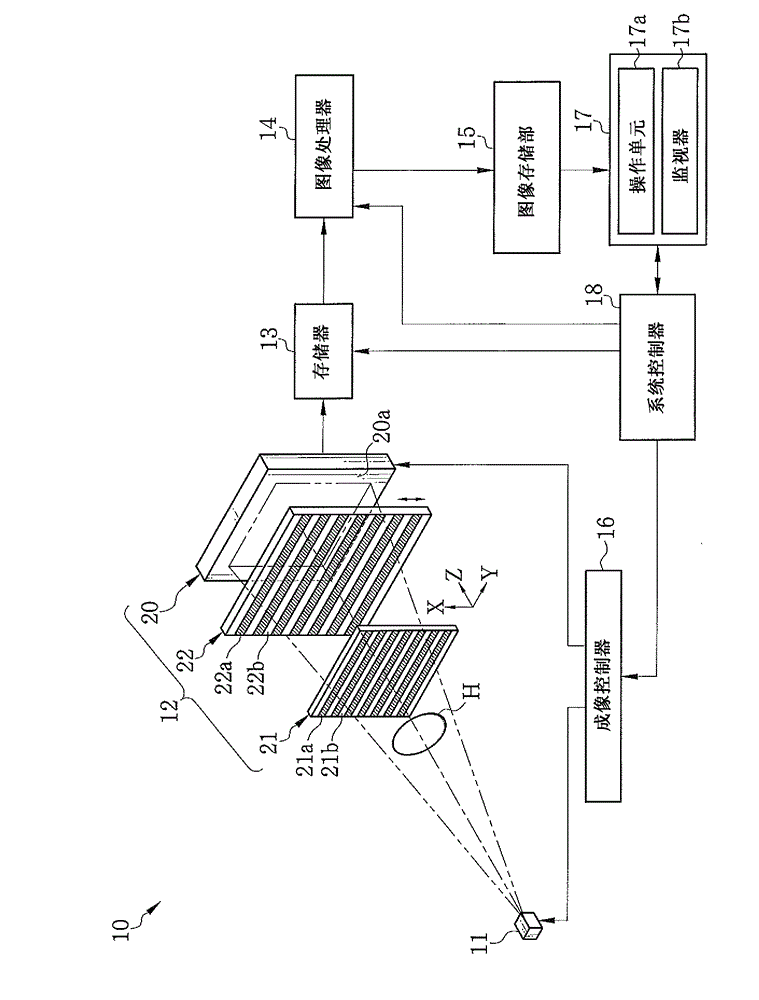
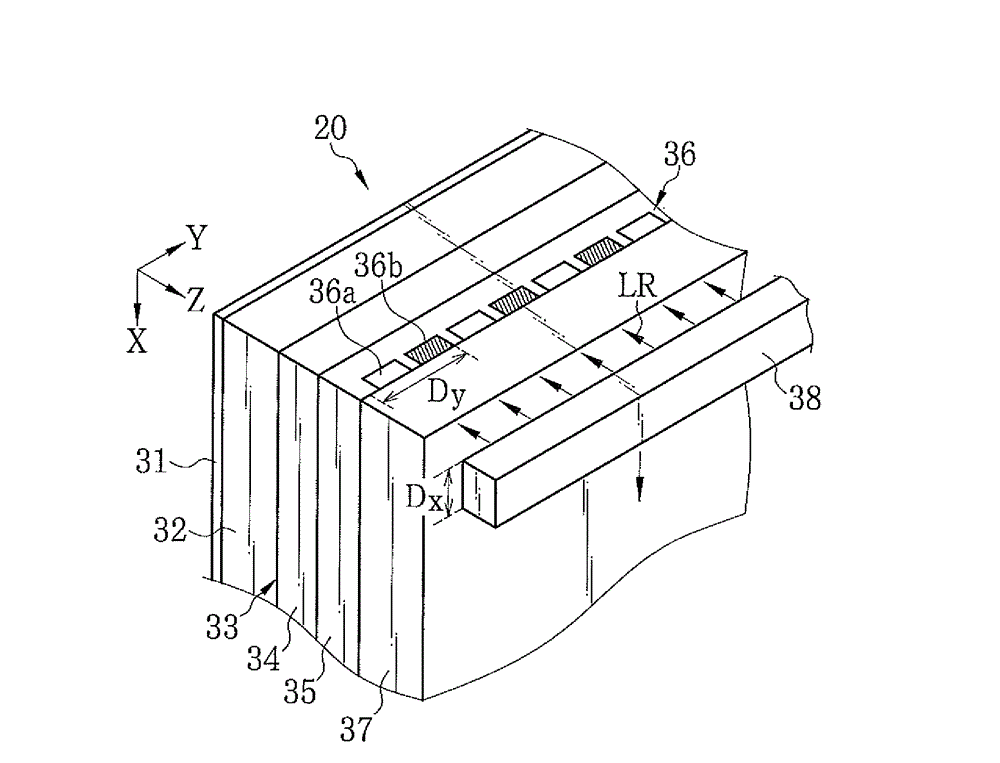
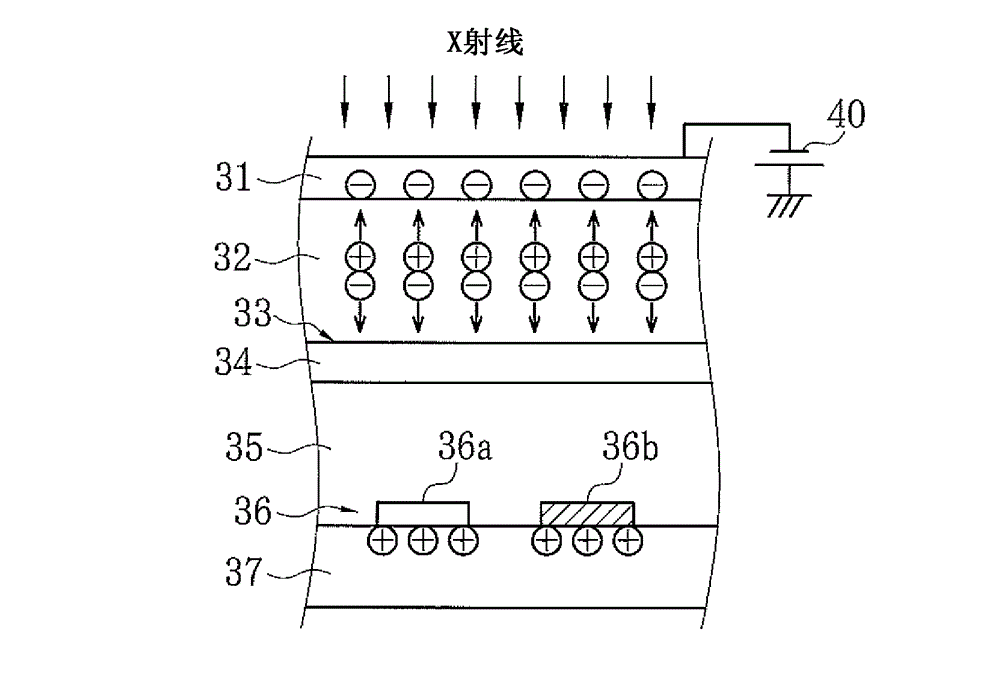
X-ray ct apparatus and image processing apparatus
ActiveUS20090122953A1Improve S/NHigh contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhysicsImage segmentation
An X-ray CT apparatus includes an X-ray radiation unit which applies a first X-ray having a first energy spectrum and a second X-ray having a second energy spectrum different from the first energy spectrum to a subject, an X-ray data acquisition unit which acquires first X-ray projection data of the subject based on the first X-ray and second X-ray projection data of the subject based on the second X-ray, and an image reconstruction unit which determines information about a difference between the first X-ray and the second X-ray with respect to an image of the subject, segments the image into at least two pixel areas based on the difference information, and sets part of the segmented pixel areas to a dual energy image obtained by a weighted subtraction process based on X-ray projection data having a plurality of energy spectrums.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Living body observing device
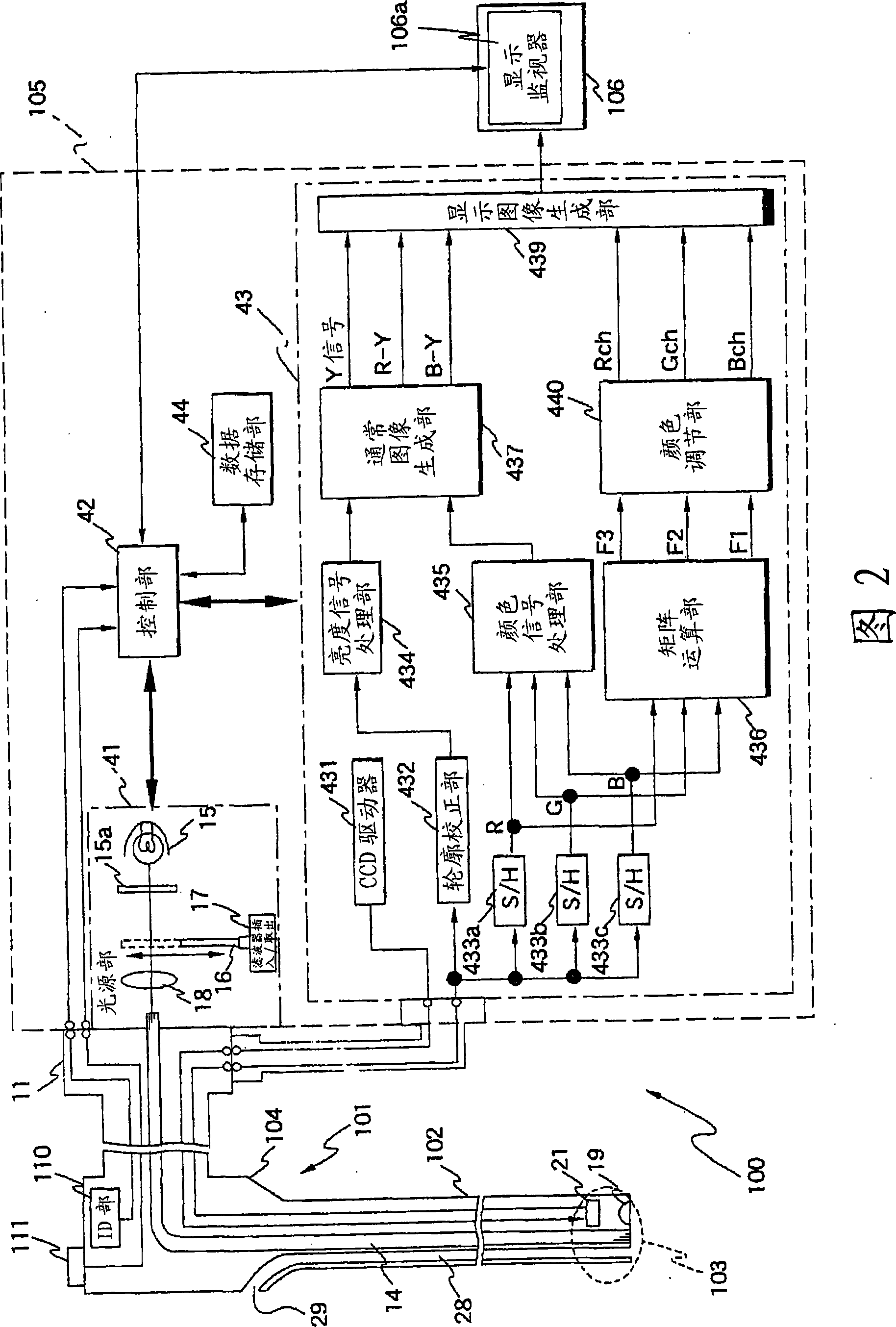
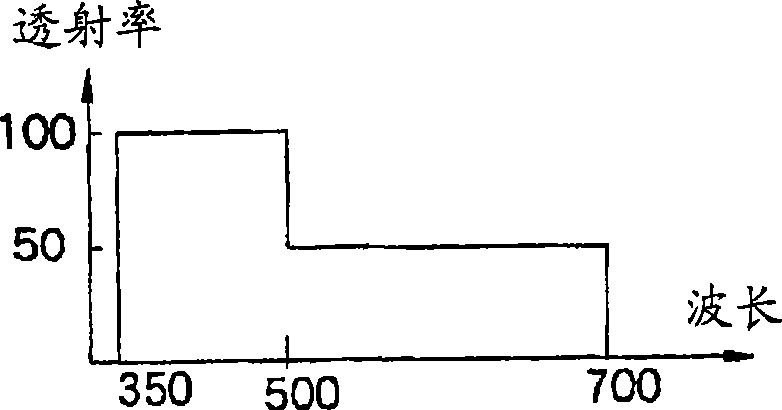
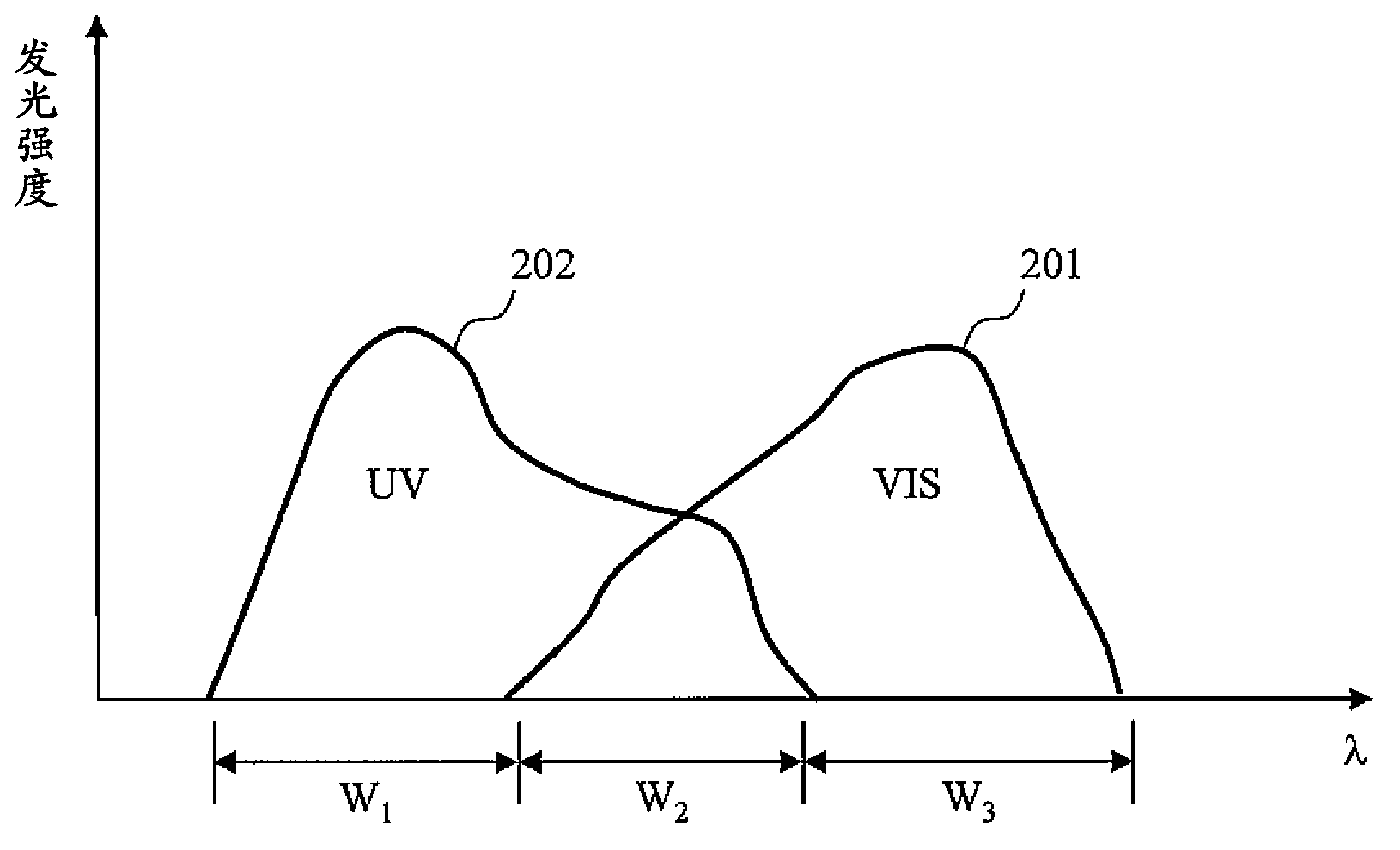
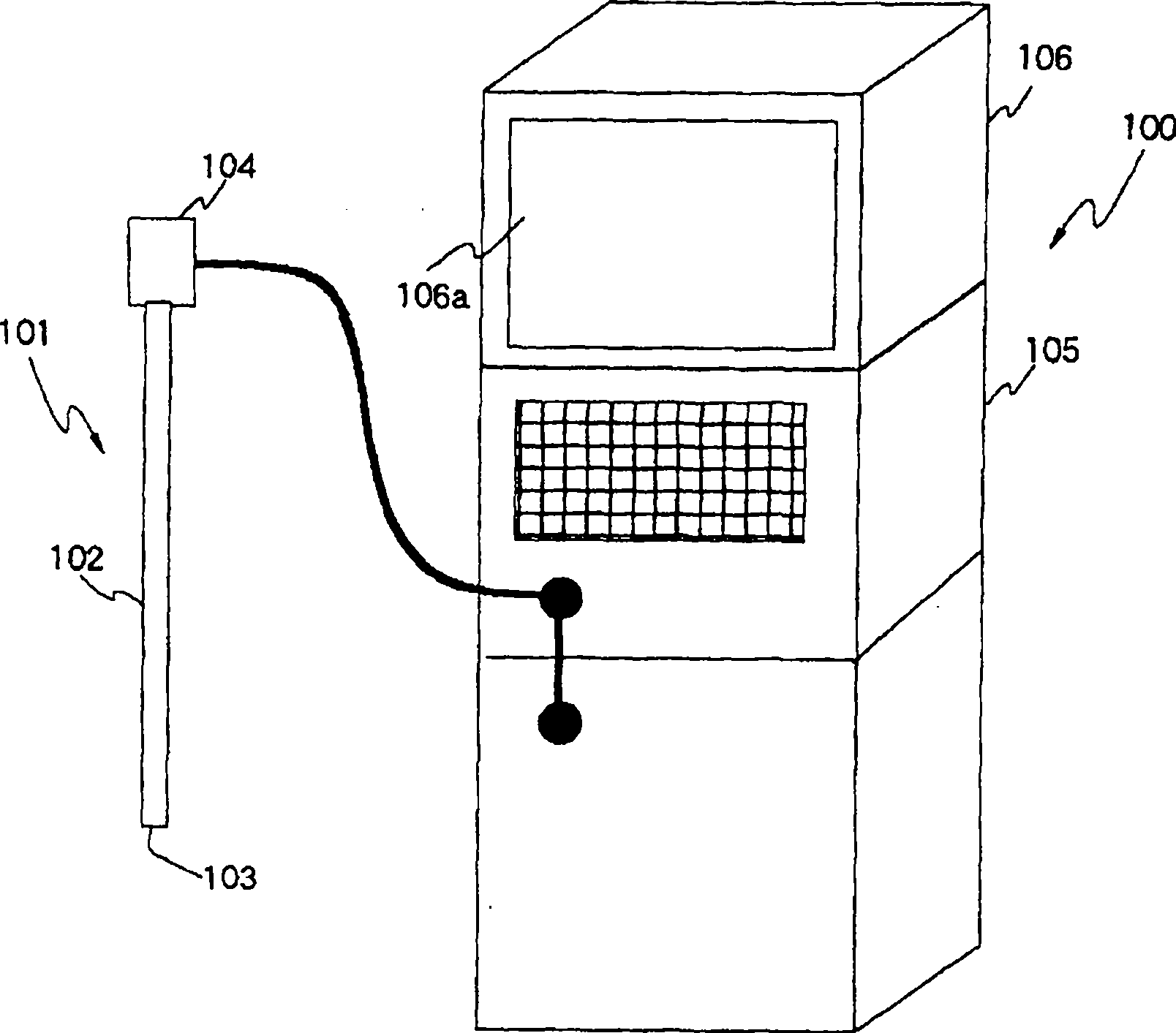
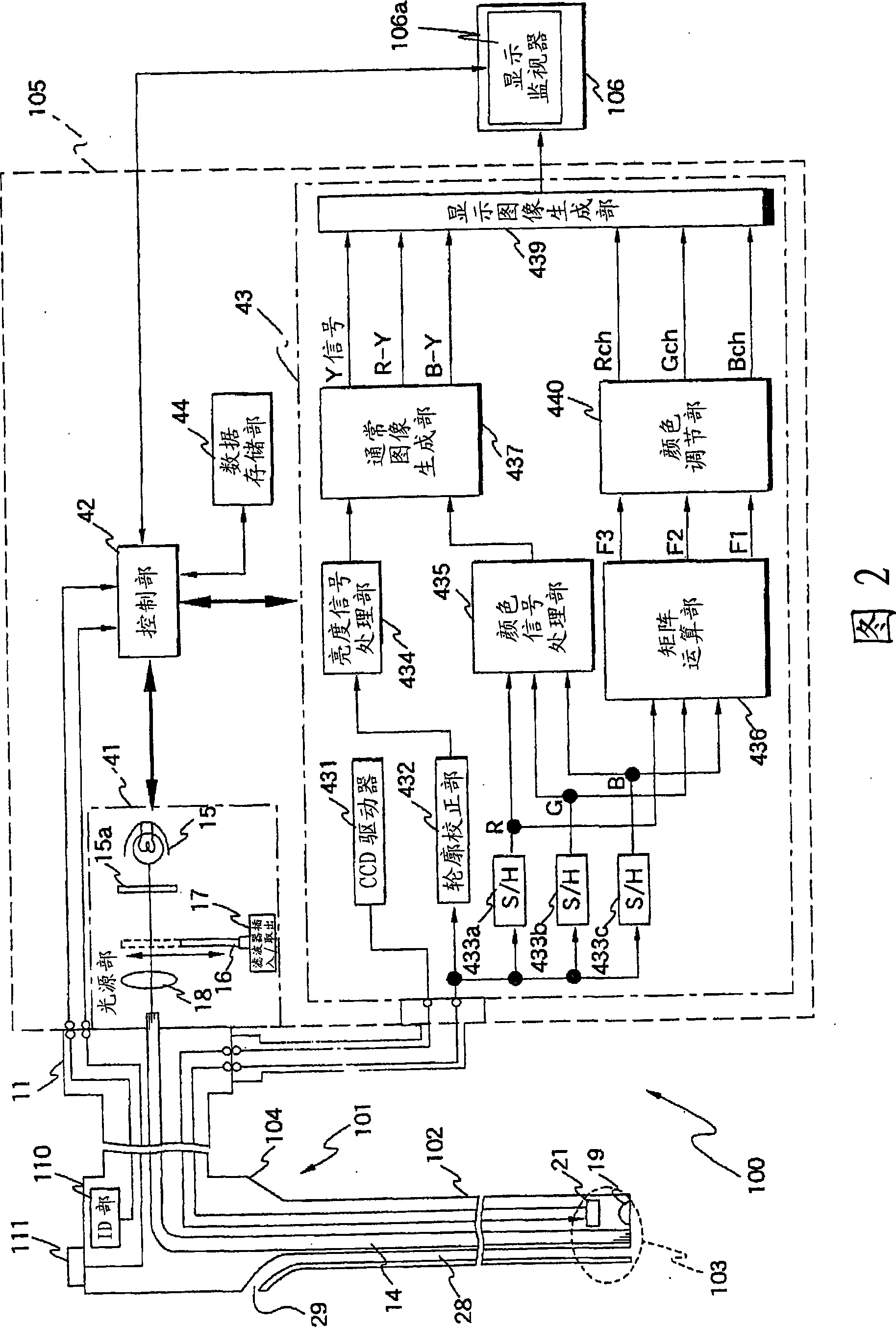
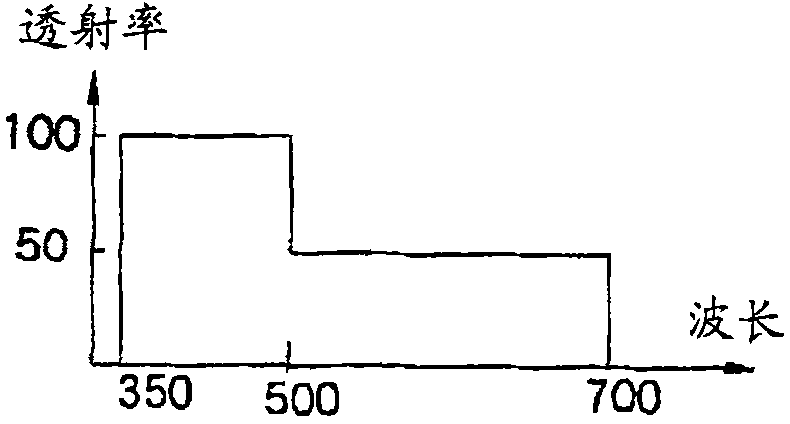
A light source unit (41) connected with a control unit (42) and an endoscope (101) emits whit light with a specified light quantity based on a signal from the control unit (42). The light source unit (41) comprises a lamp (15) as a white light source, an infrared cutting filter (15a), a light quantity limiting filter (16) inserted / removed into / from a light path to limit a light quantity in a specified wavelength region of white light, a filter inserting / removing drive unit (17) for inserting / removing the light quantity limiting filter (16) into / from the light path, and a condenser lens (18) for emitting white light. For example, the light quantity limiting filter (16) limits, when transmittance in a blue band is 100%, transmittance in the other bands to 50%. Accordingly, an S / N in a visible light region in generating a discrete spectral image by a lighting light is improved.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Signal processing device, radar apparatus, target object method
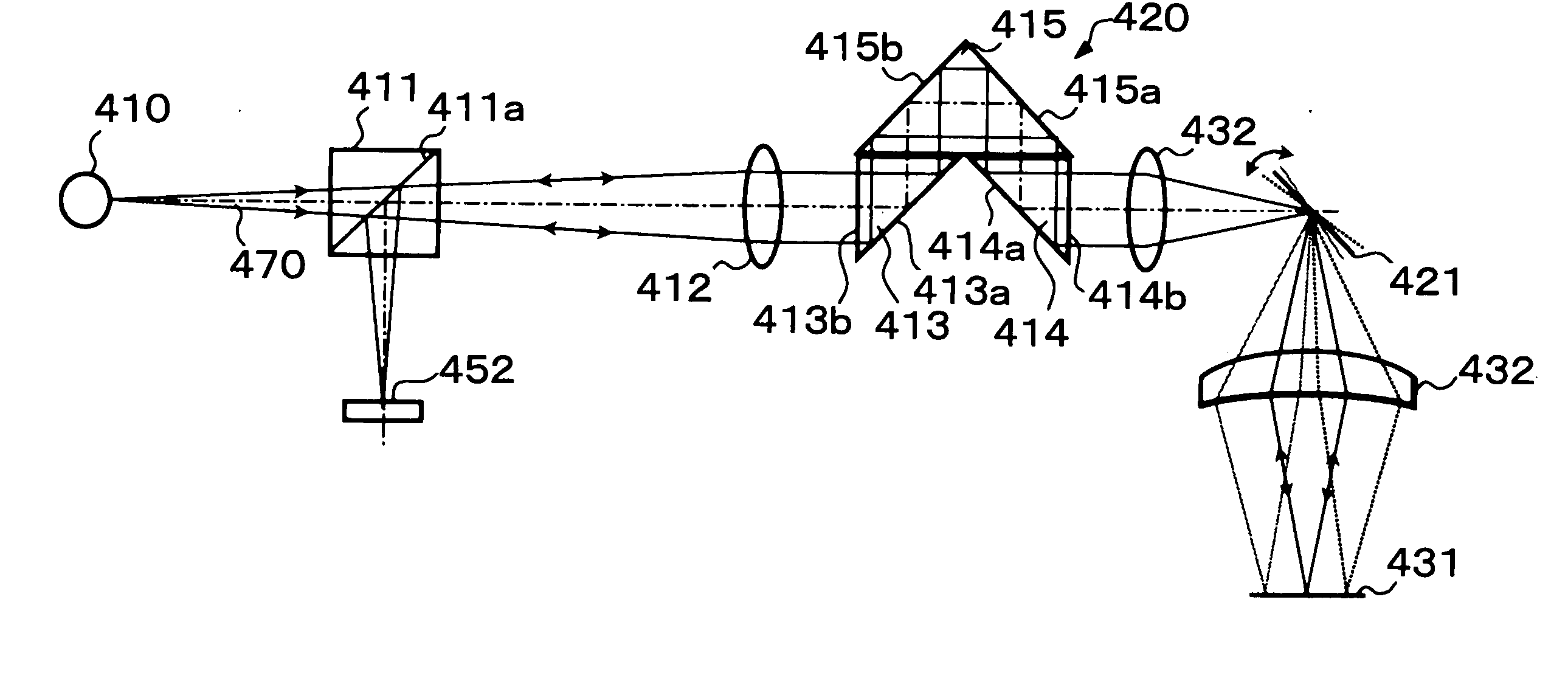
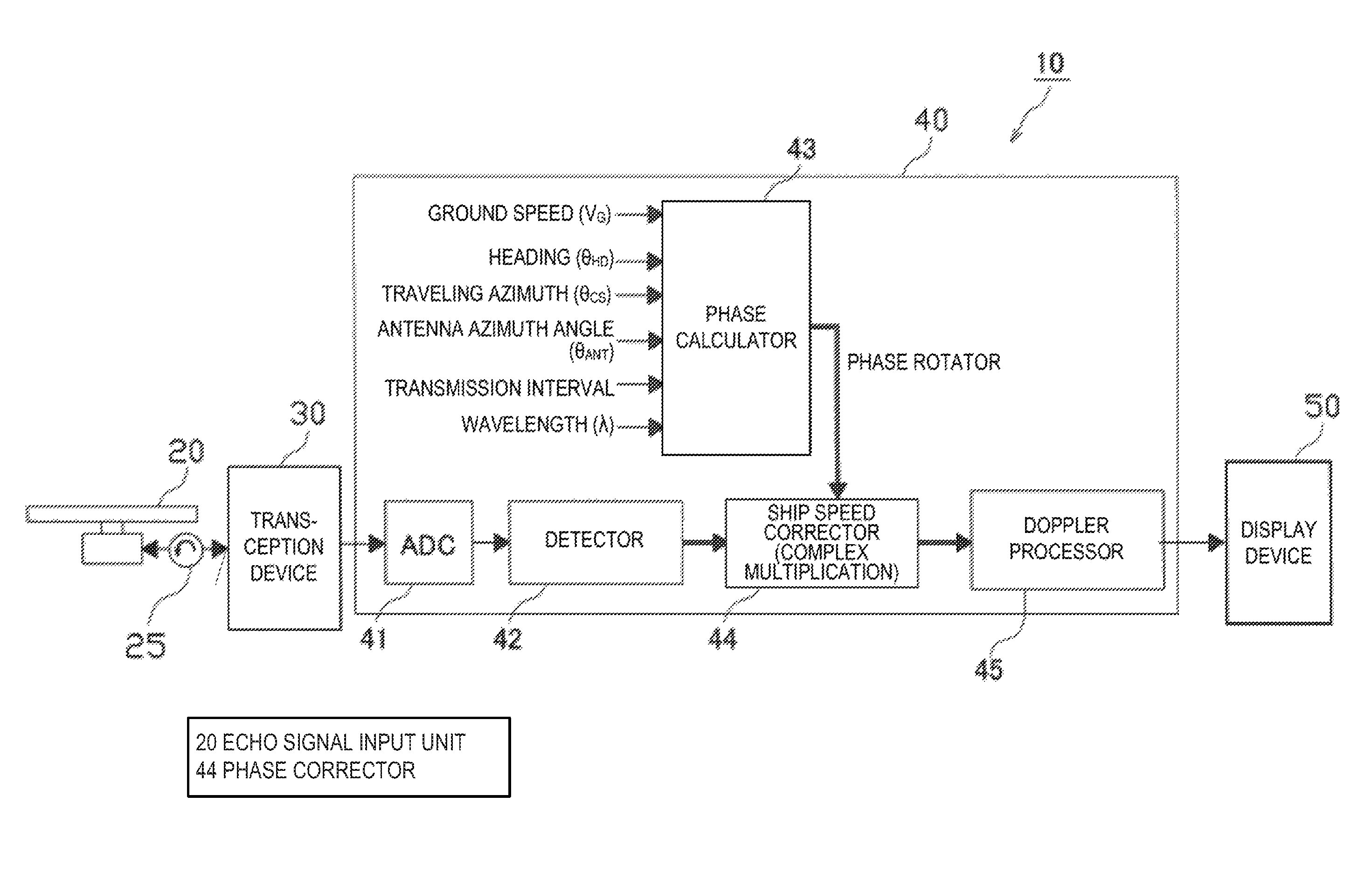
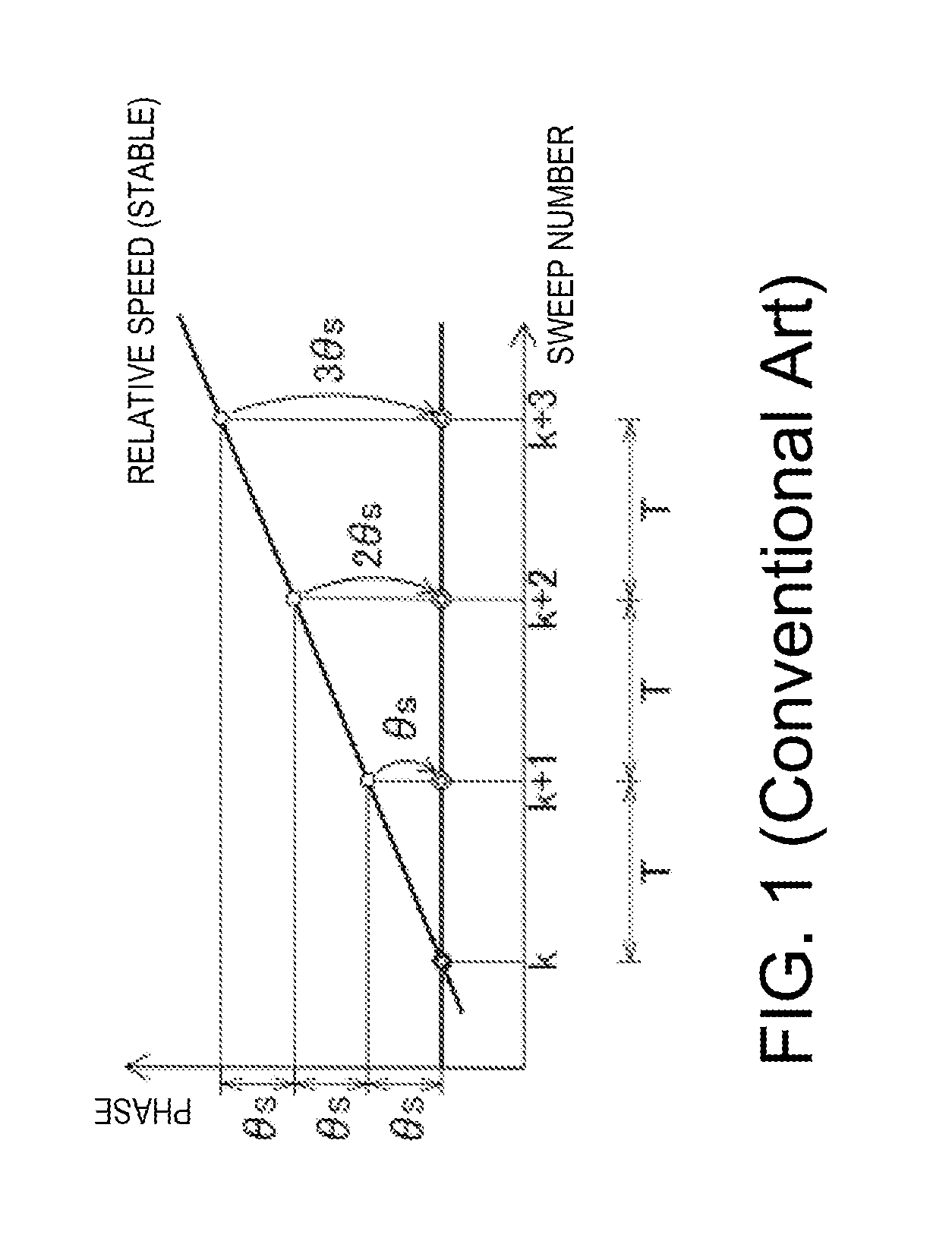
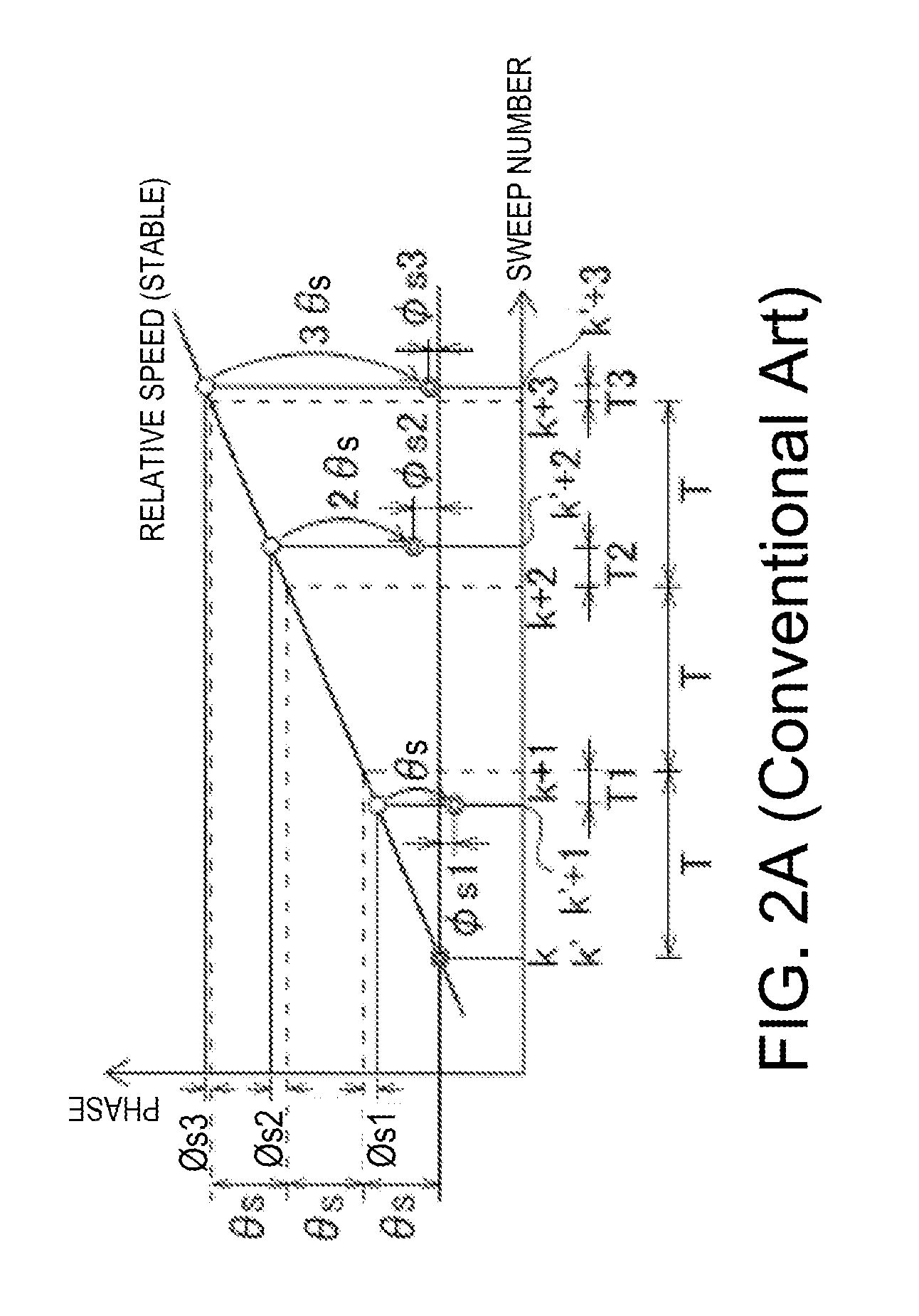
ActiveUS20140062760A1Eliminate errorsReduce distractionsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase correctionSignal generator
A signal processing device is provided. The device includes an echo signal input unit for receiving echo signals resulted from transmission signals reflected on an object. The transmission signals are transmitted from a transmission source at transmission timings at predetermined time intervals, at least one of the transmission timings shifted from the other timings in time. The device includes a complex reception signal generator for generating complex reception signals, a phase calculator for calculating a phase change amount of the complex reception signals with respect to a reference phase, a phase corrector for phase-correcting the complex reception signals and outputting the corrected signals, and a Doppler processor for performing Doppler processing on the corrected signals and outputting the Doppler-processed signals as Doppler echo signals of the object.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
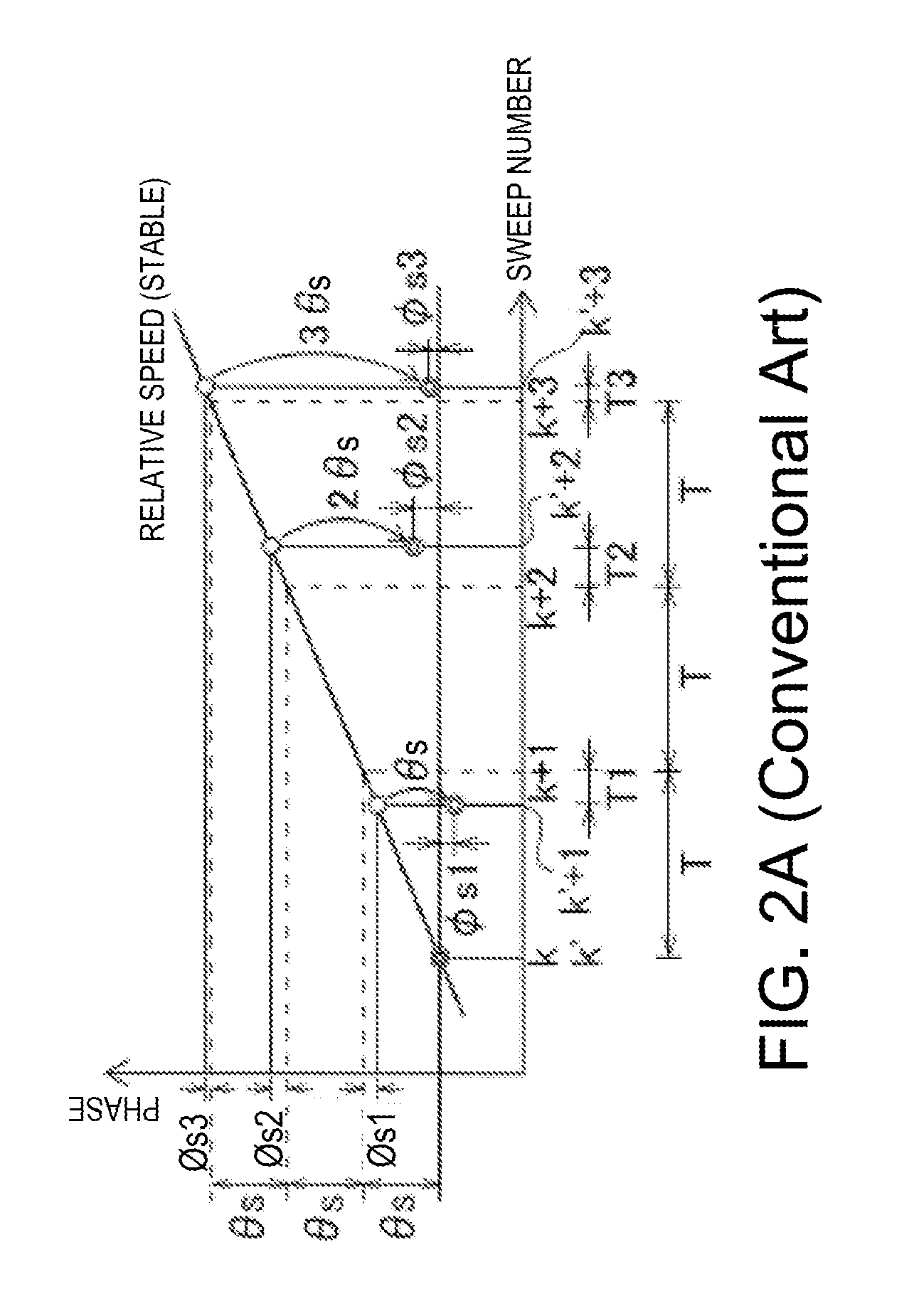
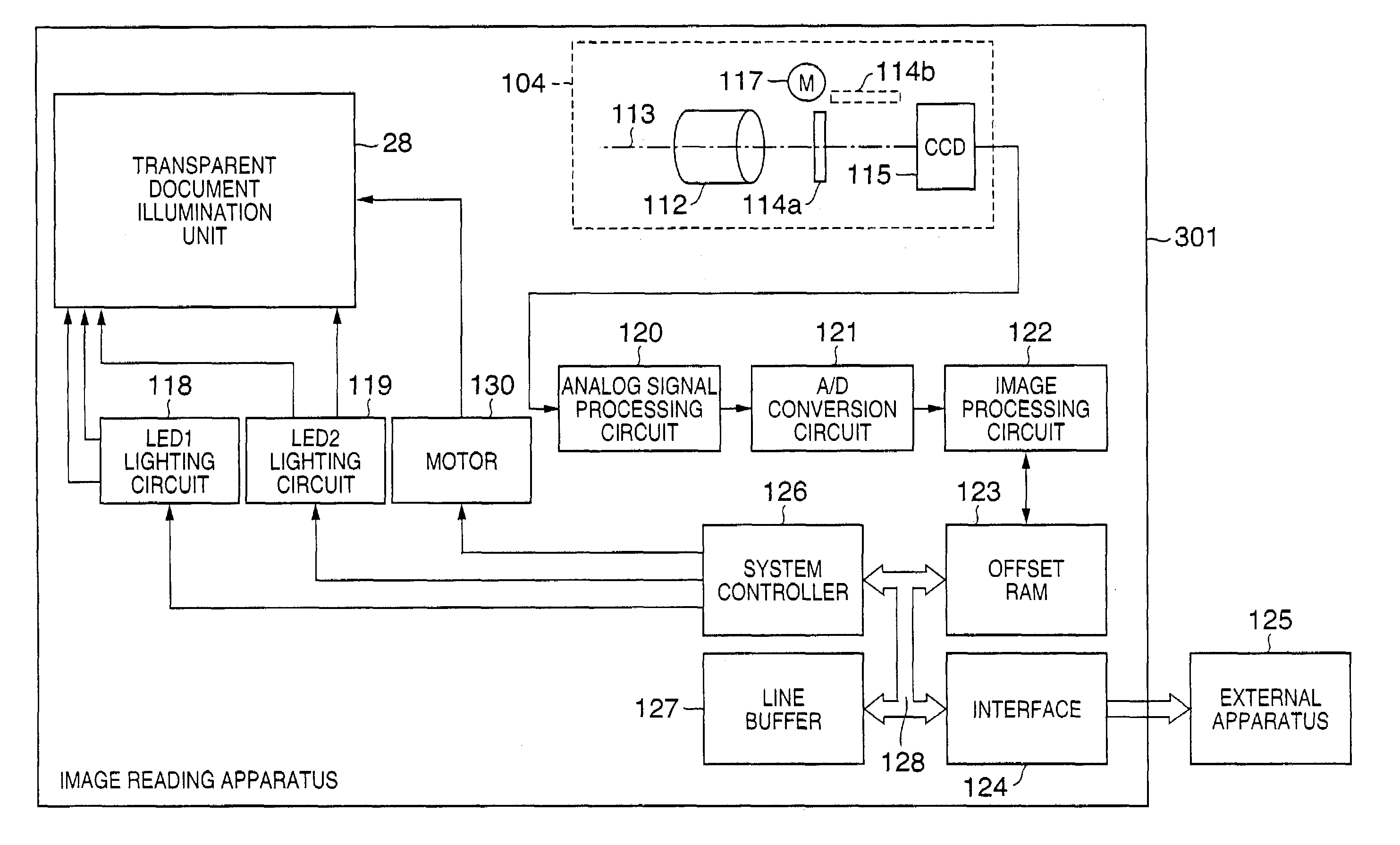
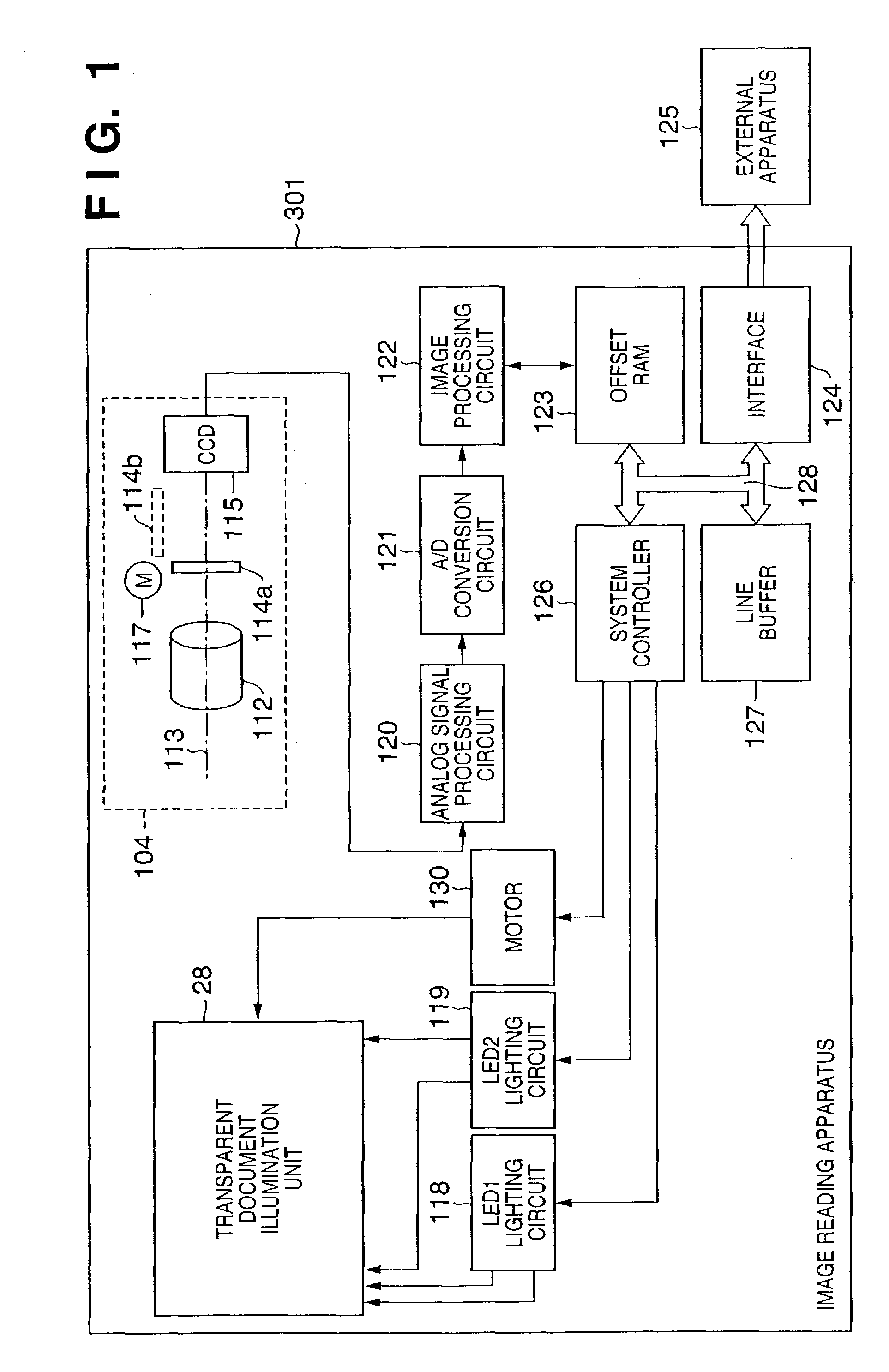
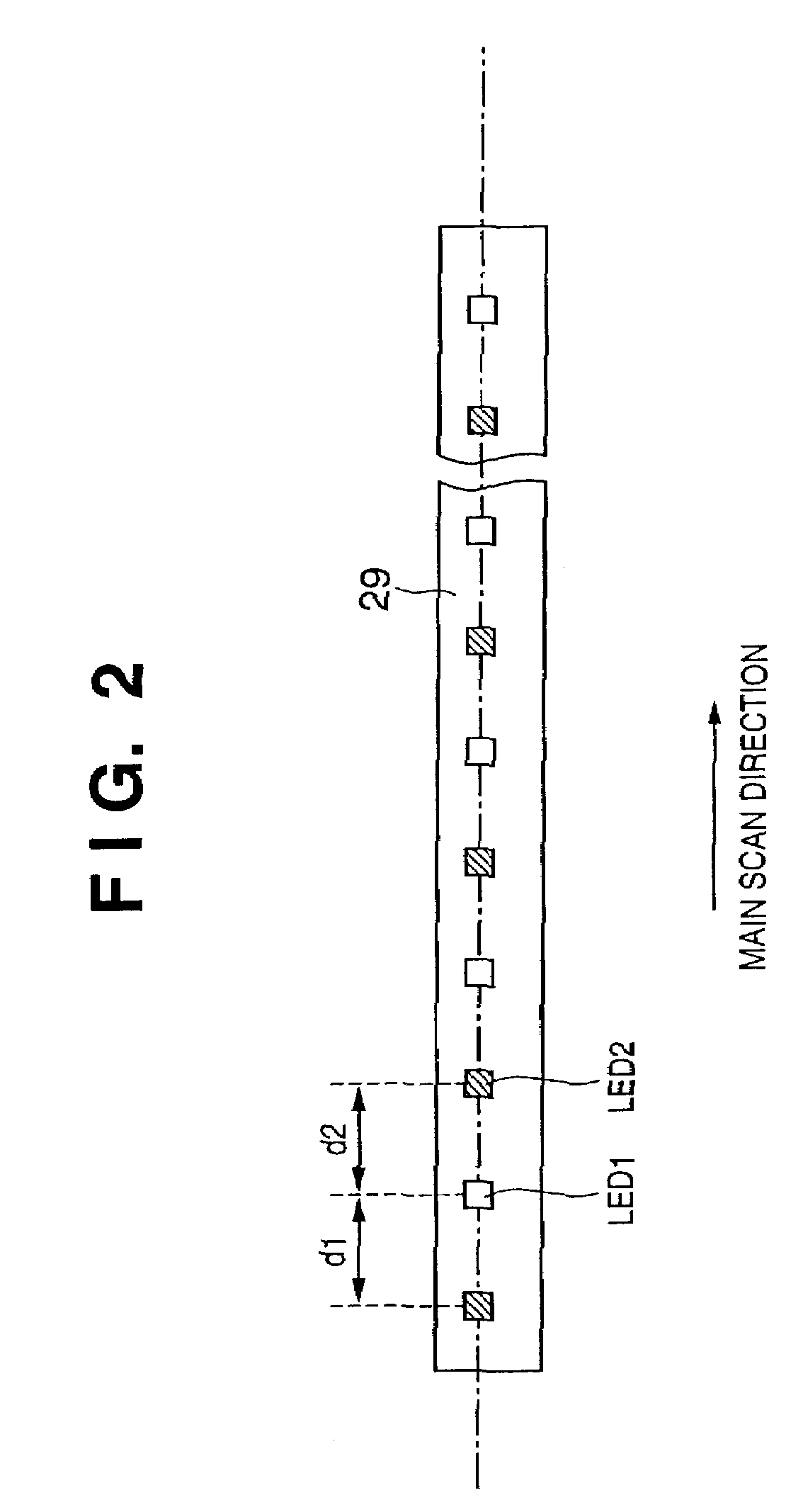
Image signal correction light source that can cope with dust and scratch on transparent document, and its control
InactiveUS7224483B2Suppress position deviationImprove S/NDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsSignal correctionLight source
In a method of controlling an image reading apparatus, which has an illumination unit adapted to irradiate an object with first and second light rays in different frequency ranges, and a light-receiving unit adapted to receive light coming from the object, and to output a signal, and reads an image of the object by moving the illumination unit and light-receiving unit relative to the object, the light-receiving unit outputs a first signal in response to irradiation with the first light ray, and outputs a second signal in response to irradiation with the second light ray. Upon reading image information for one line by the image reading apparatus, the second light ray is controlled to be sequentially turned on at a plurality of timings to sandwich the ON timing of the first light ray, and image signals for one line corresponding to the first and second light rays are obtained by averaging or adding respective pieces of image information obtained at the plurality of timings for each of the first and second signals.
Owner:CANON KK
Solid state image pickup device and camera using the same
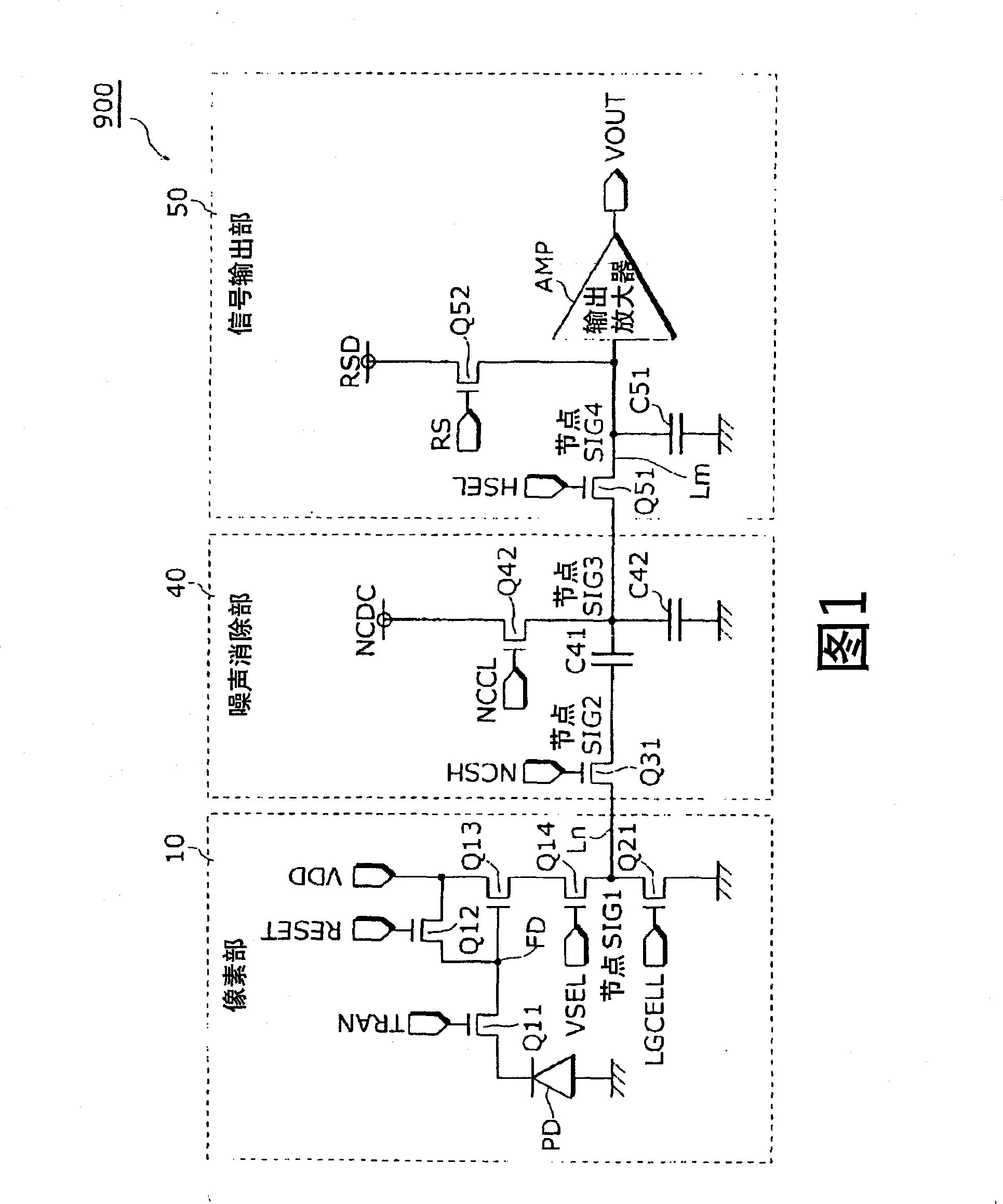
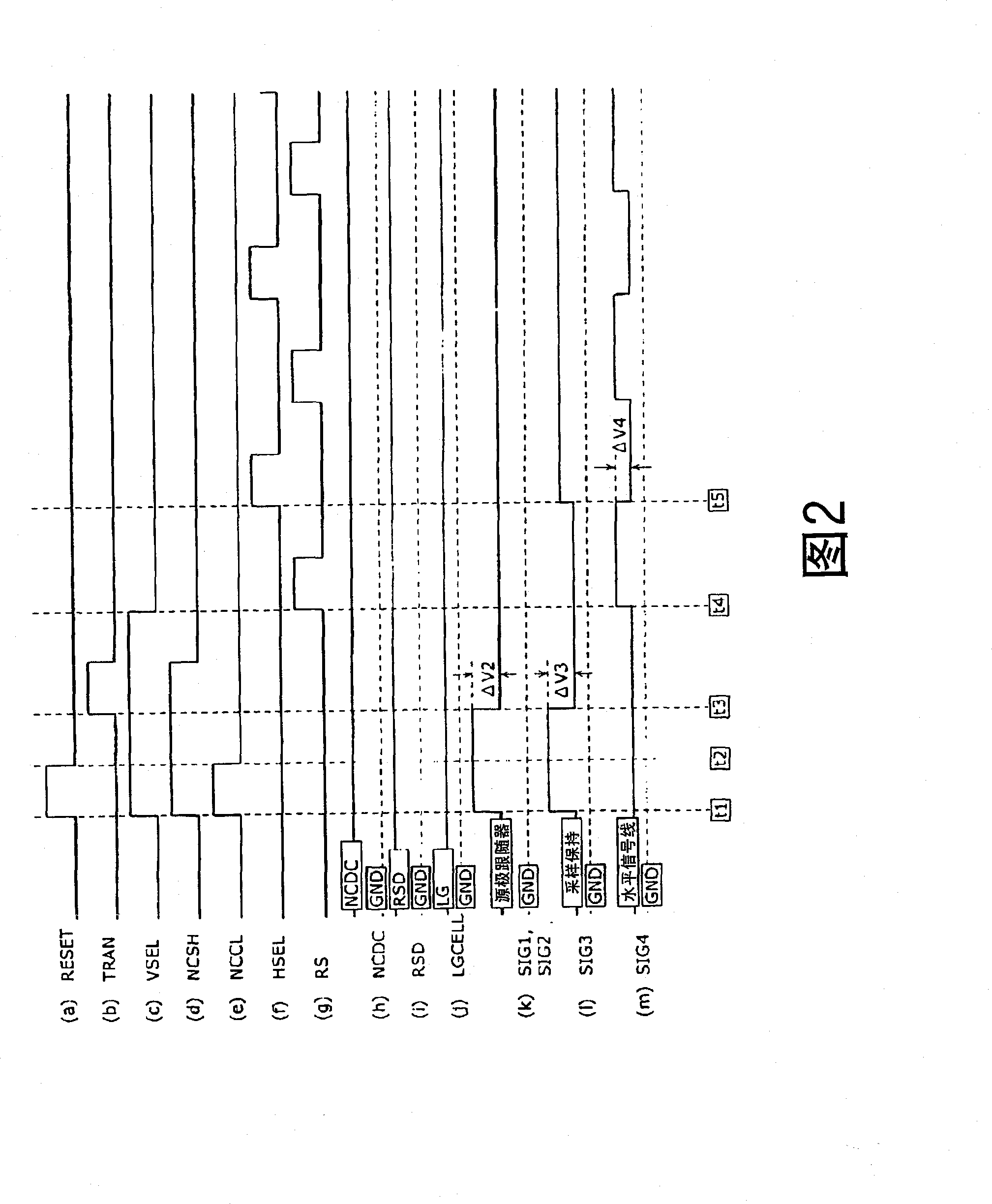
ActiveCN1910910AImprove linearityImprove S/NTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAudio power amplifierPhotoelectric conversion
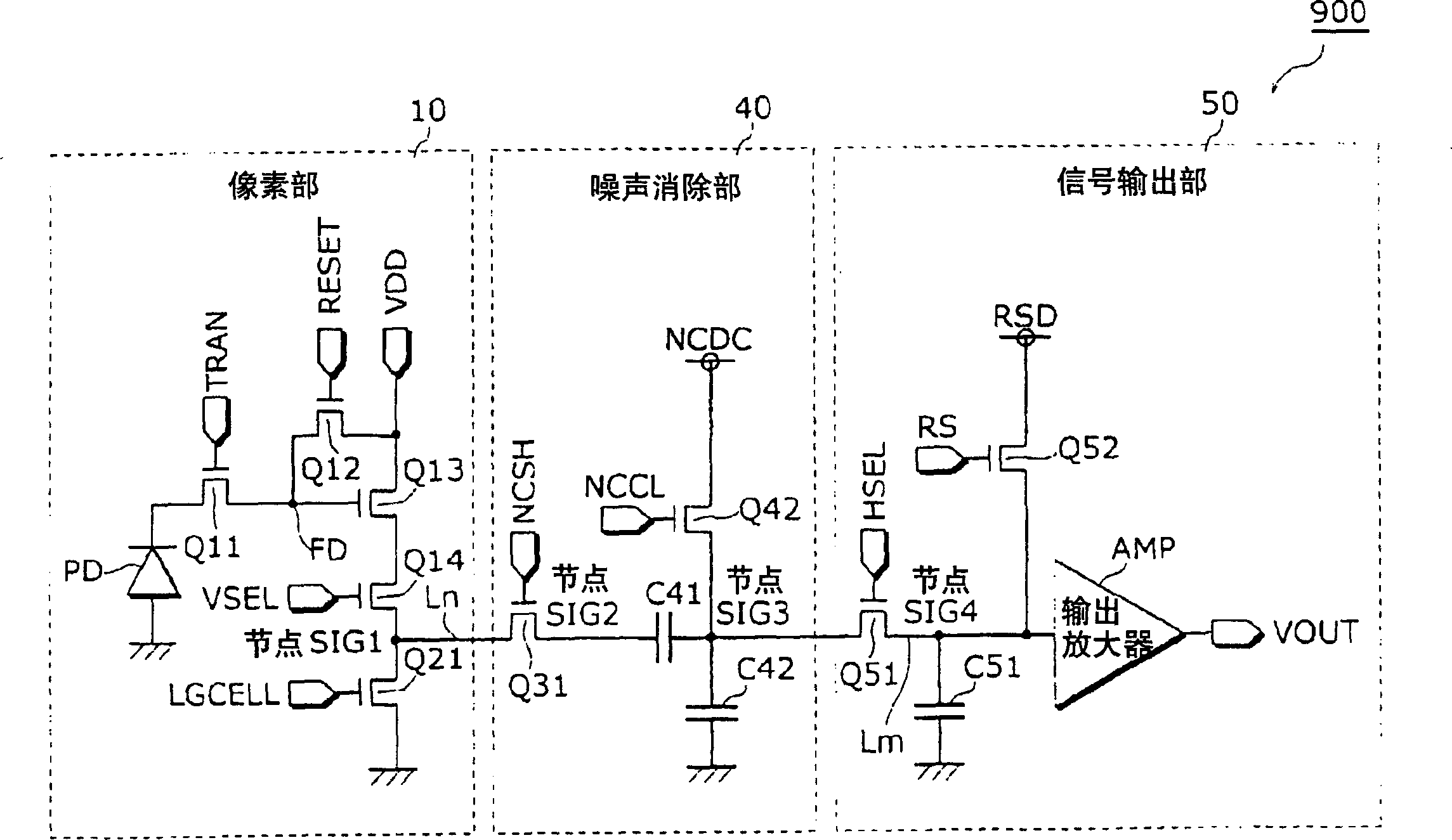
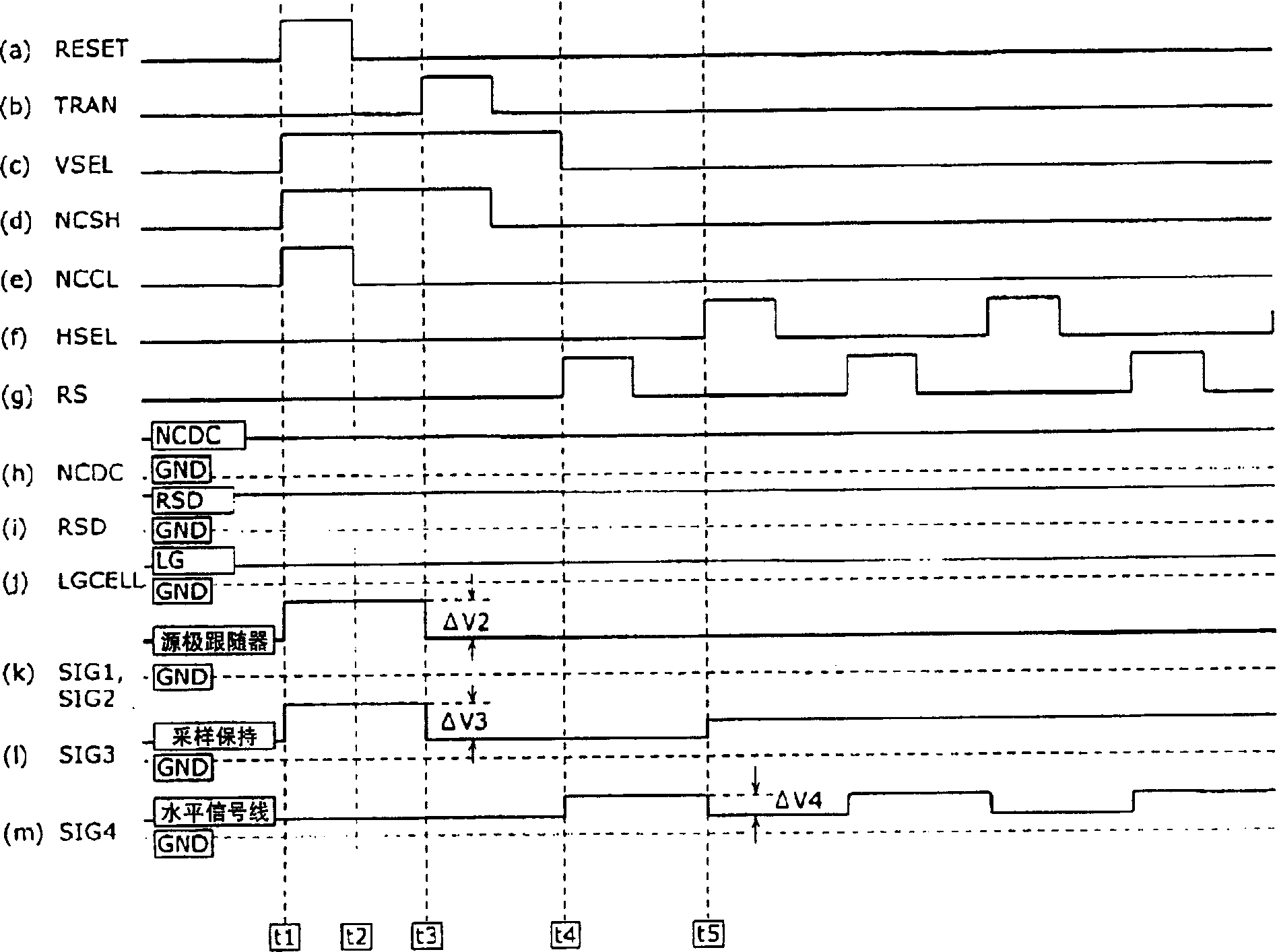
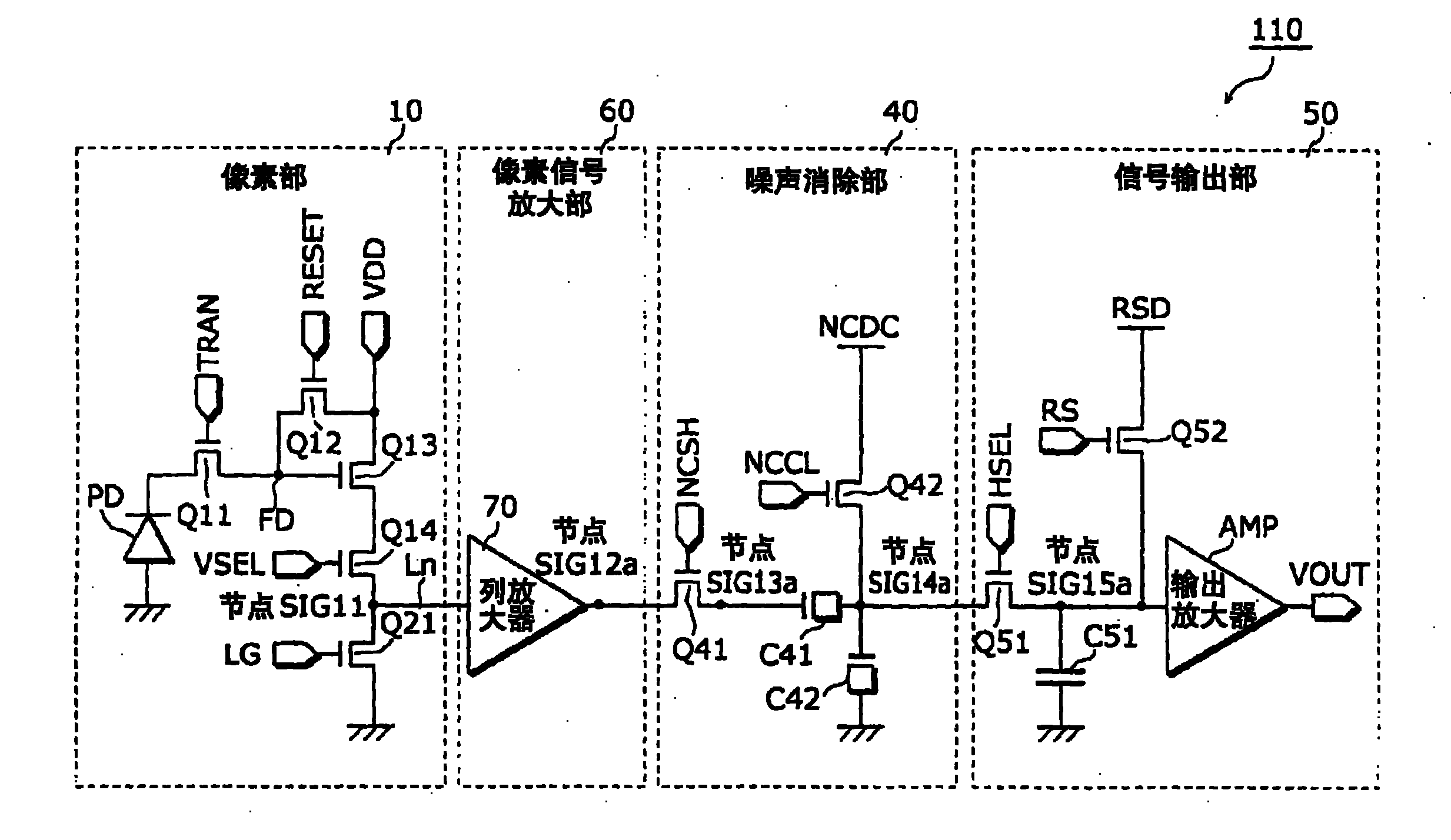
A solid state image pickup device 110 is provided with: a plurality of pixel units 10 that are arranged two-dimensionally and include a photoelectric conversion unit (photodiode PD) that converts light into a charge and an amplification unit (amplifier Q13) that converts the charge into a voltage and outputs it; a plurality of noise signal removal units (noise cancellation units 40) that are provided one for each column and remove noises contained in the voltage outputted from the amplifier Q31 of the pixel unit 10 belonging to the column; and a plurality of column amplification units (column amplifiers 70) that amplify the voltage outputted from the amplifier Q13 of the pixel unit 10 and output the amplified voltage to the noise cancellation unit 40, and enables increase in sensitivity and reduction in noise with low power consumption.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Spectrophotometer
InactiveCN103221802AImprove S/NRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyLight beamLength wave
The present invention is capable of obtaining highly stabilized transmission and absorption spectra with high S / N and drift suppressed over a long time even when the amount of light of a light source temporally changes in a single-beam spectrophotometer. A spectrophotometer comprises: a light source; a sample cell; a polychromator which generates the transmission spectrum of a sample in the sample cell by dispersing light transmitted through the sample out of light from the light source into a plurality of wavelength components; an image sensor which detects the transmission spectrum of the sample; a light source monitor light detector which detects light not transmitted through the sample out of the light from the light source; and a calculation unit which corrects the transmission spectrum of the sample using an output signal of the light source monitor light detector.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Optical ranging sensor and electronic equipment
An optical ranging sensor includes a light emitting unit for projecting a light beam on an object to be measured, a light receiving unit on which a light spot of reflected light of the light beam from the object is formed, and a processing circuit unit for processing output signals from the light receiving unit and detecting a distance to the object. The light receiving unit includes an effective light receiving part having light receiving cells arranged in matrix form in a first direction in which a position of the light spot moves as the object moves along a direction of an optical axis of the light emitting unit, and in a second direction orthogonal to the first direction. A size of the effective light receiving part in the second direction is not smaller than a radius of the light spot but not larger than a diameter thereof.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
Radiation imaging apparatus
The invention refers to a radiation imaging apparatus, and specifically an X-ray imaging apparatus has first and second gratings, an X-ray image detector, and a differential phase image production section. The first grating passes X-rays emitted from an X-ray source to produce a first periodic pattern (G1 image). The second grating is disposed in a rotated state while being kept in parallel with the first grating. The second grating partly shields the G1 image to produce a second periodic pattern image (G2 image) with moire fringes. The X-ray image detector detects the G2 image to produce image data. The differential phase image production section produces a differential phase image based on the image data. The X-ray image detector has a difference in sharpness between two orthogonal directions within its detection surface, and is disposed such that one of the directions with the high sharpness crosses the moire fringes.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Piezoelectric microphone chip and piezoelectric microphone
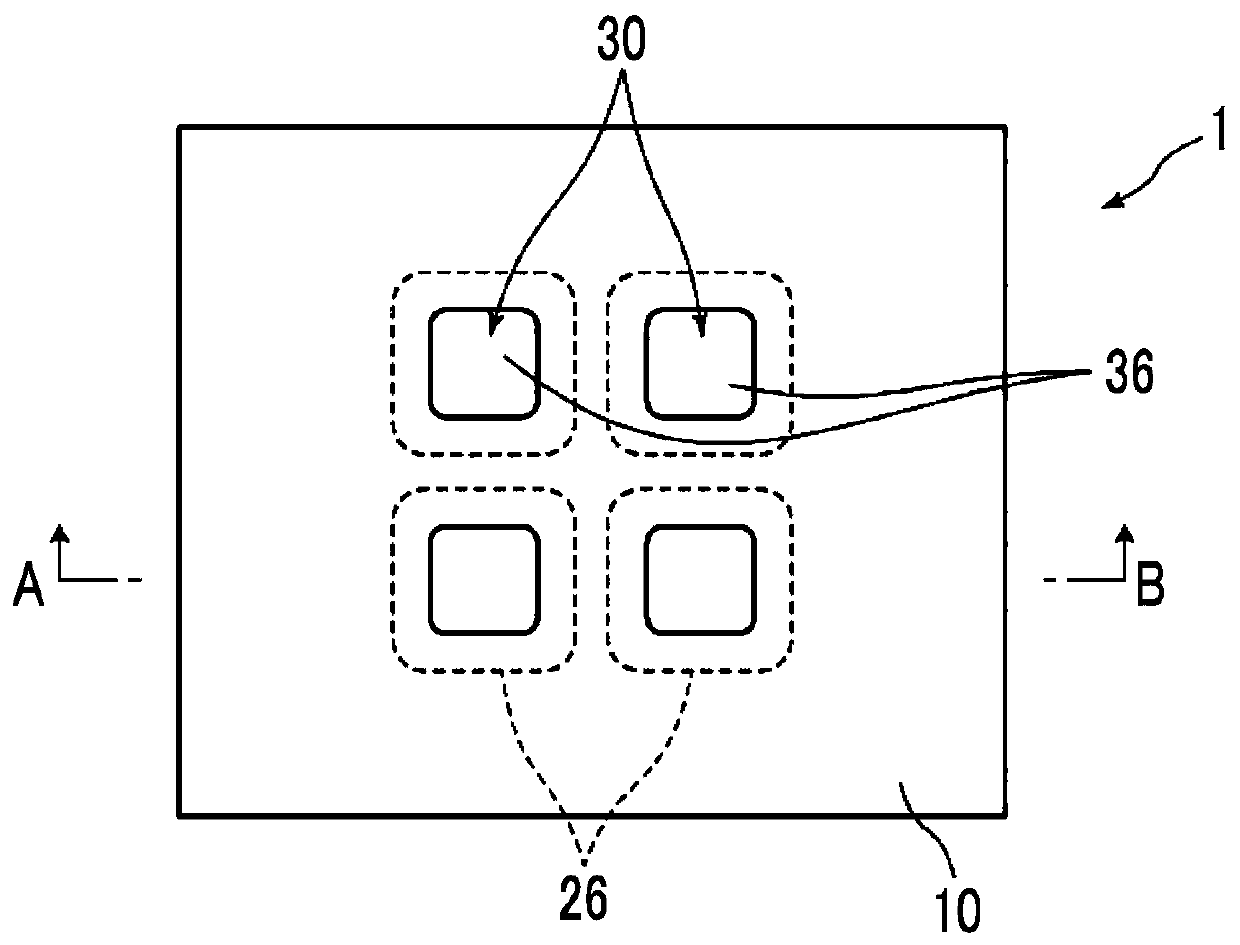
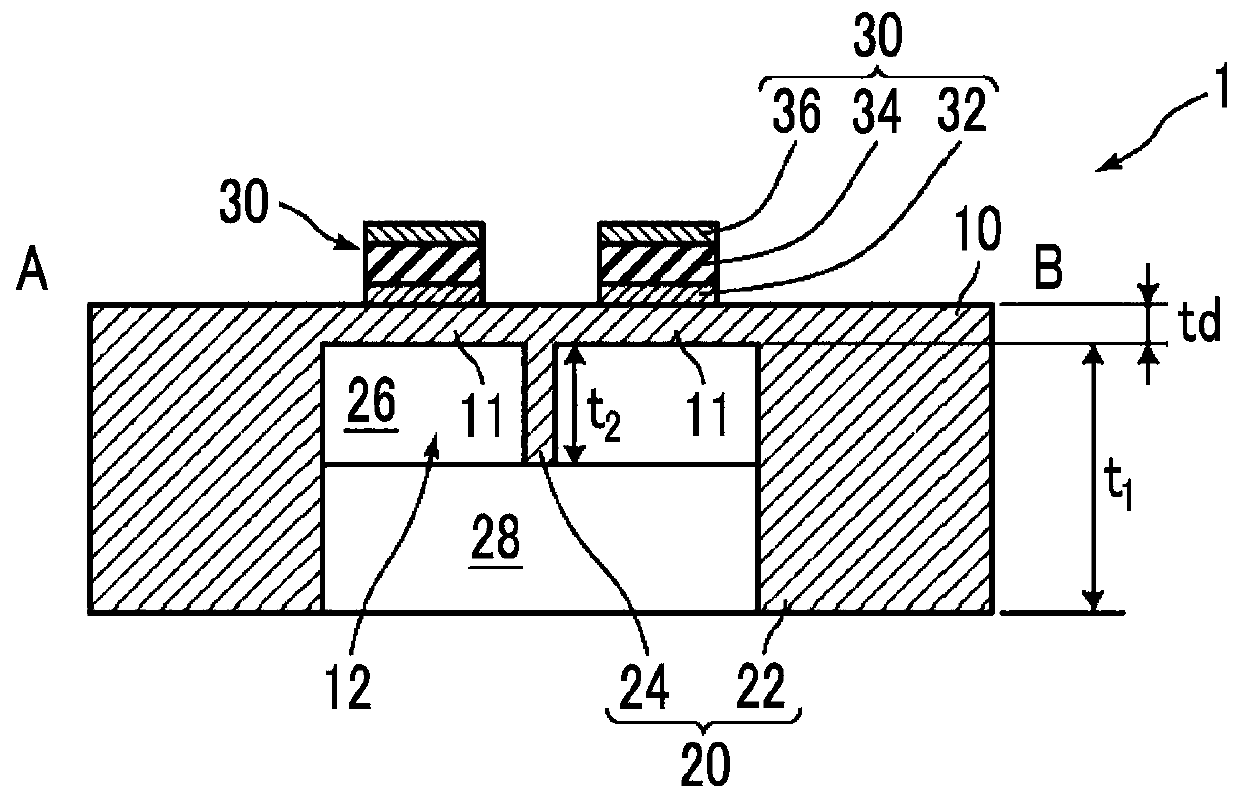
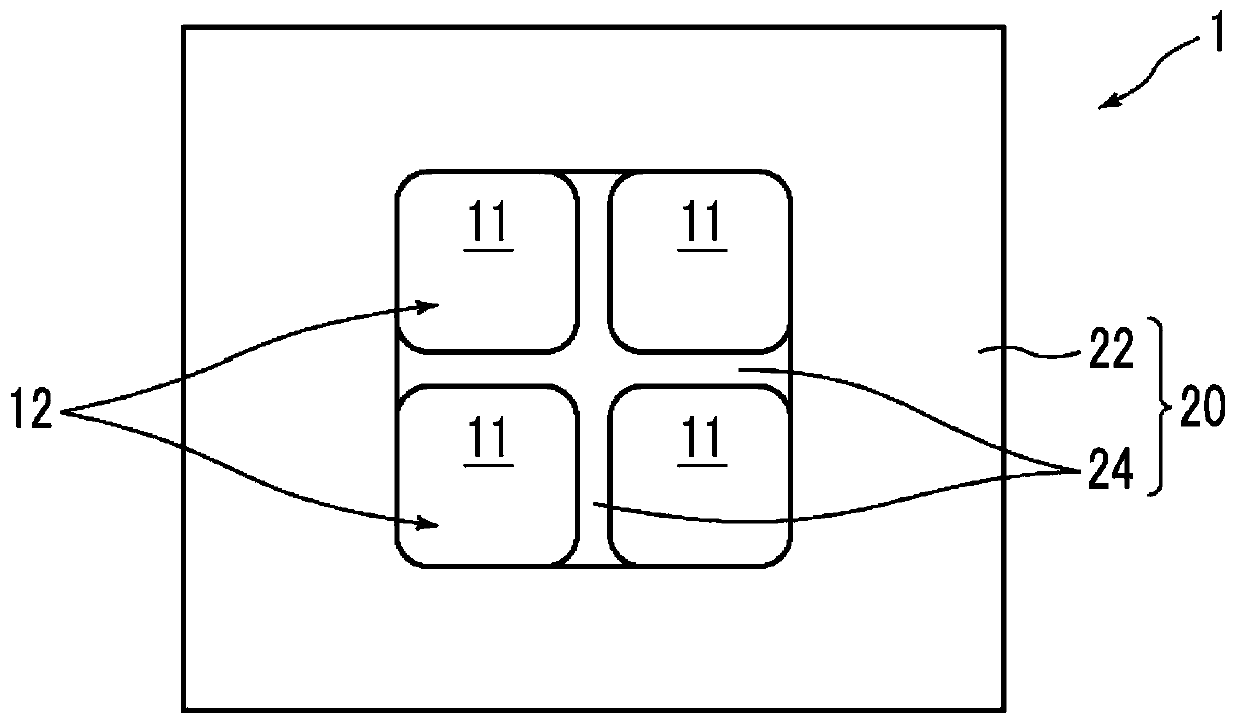
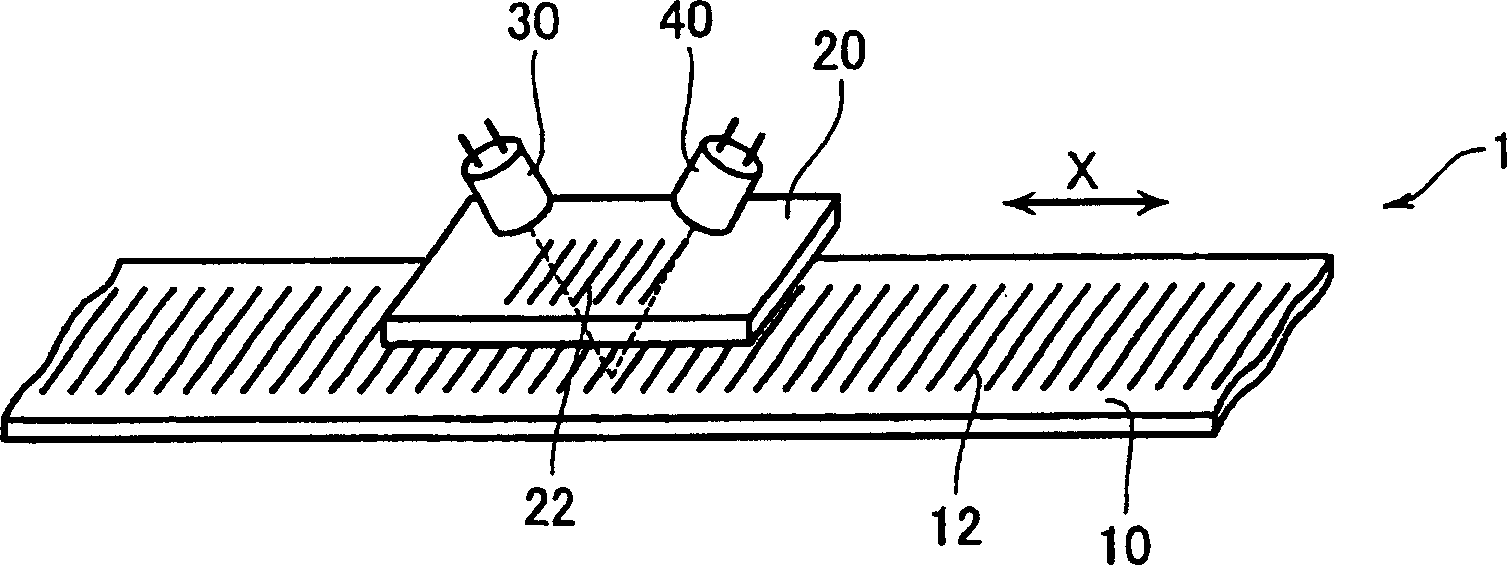
ActiveCN110603817AThere will be no problems such as cloggingImprove S/NPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesMicrophonesHemt circuitsEngineering
The present invention provides a piezoelectric microphone chip and a piezoelectric microphone, the piezoelectric microphone chip having high sensitivity to a sound pressure detection signal and beingsuitable for mounting to a package. The piezoelectric microphone is provided with: one thin plate; a diaphragm support structure that is provided on one surface of the thin plate, and comprises an outer edge support part for supporting the outer edge of the thin plate and a separating support part for dividing the thin plate into a plurality of diaphragms in cooperation with the outer edge supportpart; one or more piezoelectric conversion parts each formed by stacking, on each of the diaphragms, a first electrode, a piezoelectric film and a second electrode in order from the side of each of the diaphragms; and a signal detection circuit for detecting outputs from the piezoelectric conversion parts provided on the plurality of diaphragms, wherein the relationship among the thickness t1 ofthe outer edge support part, the thickness t2 of the separating support part, and the thickness td of the thin plate 10 is 13.3*td < t2 < t1-20 [mu]m.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Photoelectric encoder, scale therefor and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveCN1786671AImprove machining accuracyIncrease the amount of lightConverting sensor output opticallyGratingThin membrane
The main scale (10) has a convex grating (12), for example a chrome film, formed on a base element (11). The base member (11) and the chrome thin film constitute a reflective surface, which is set to provide a sufficient amount of received light on the light receiving surface. The convex grating (12) can be precisely shaped by photoetching the film.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
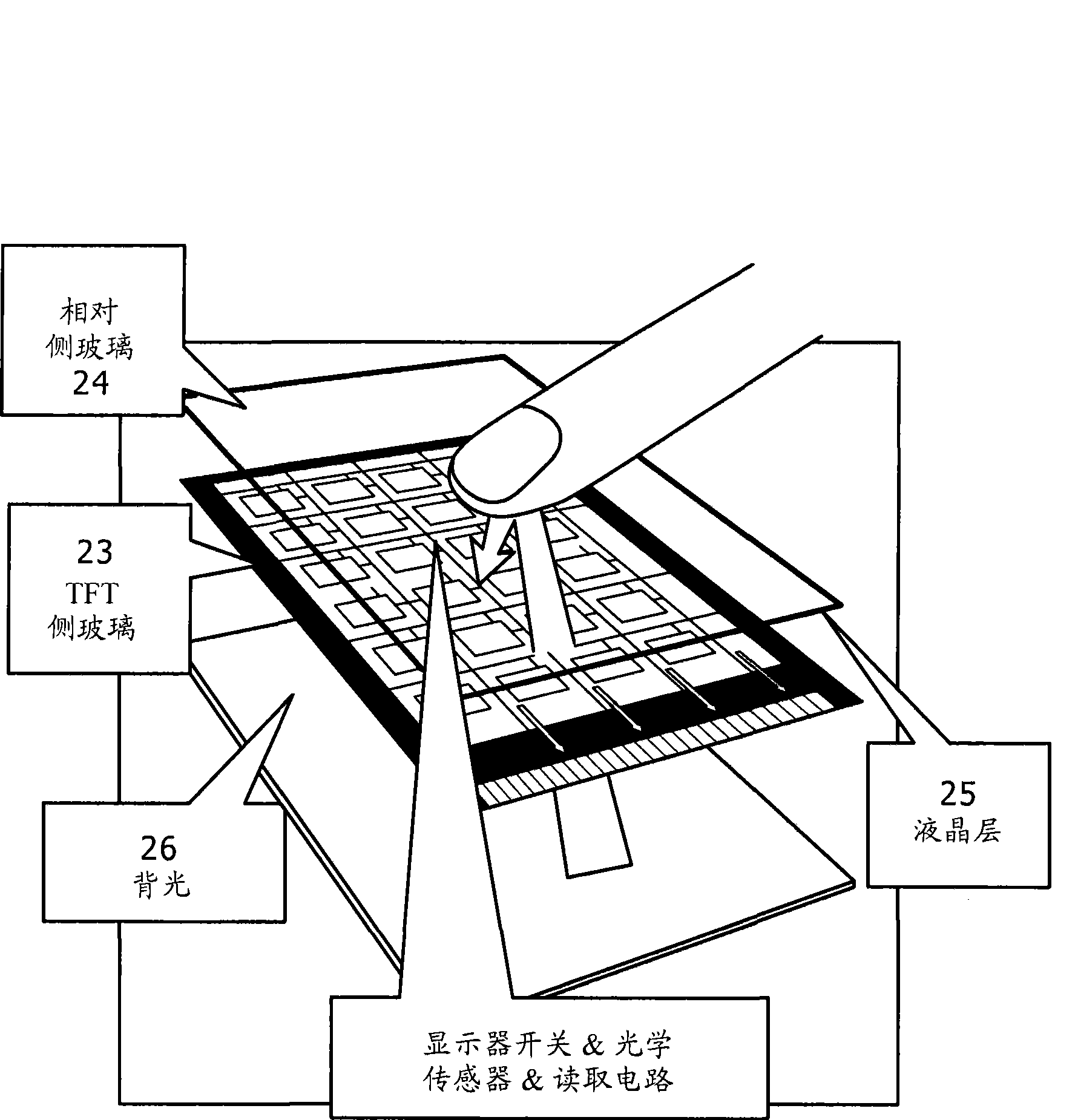
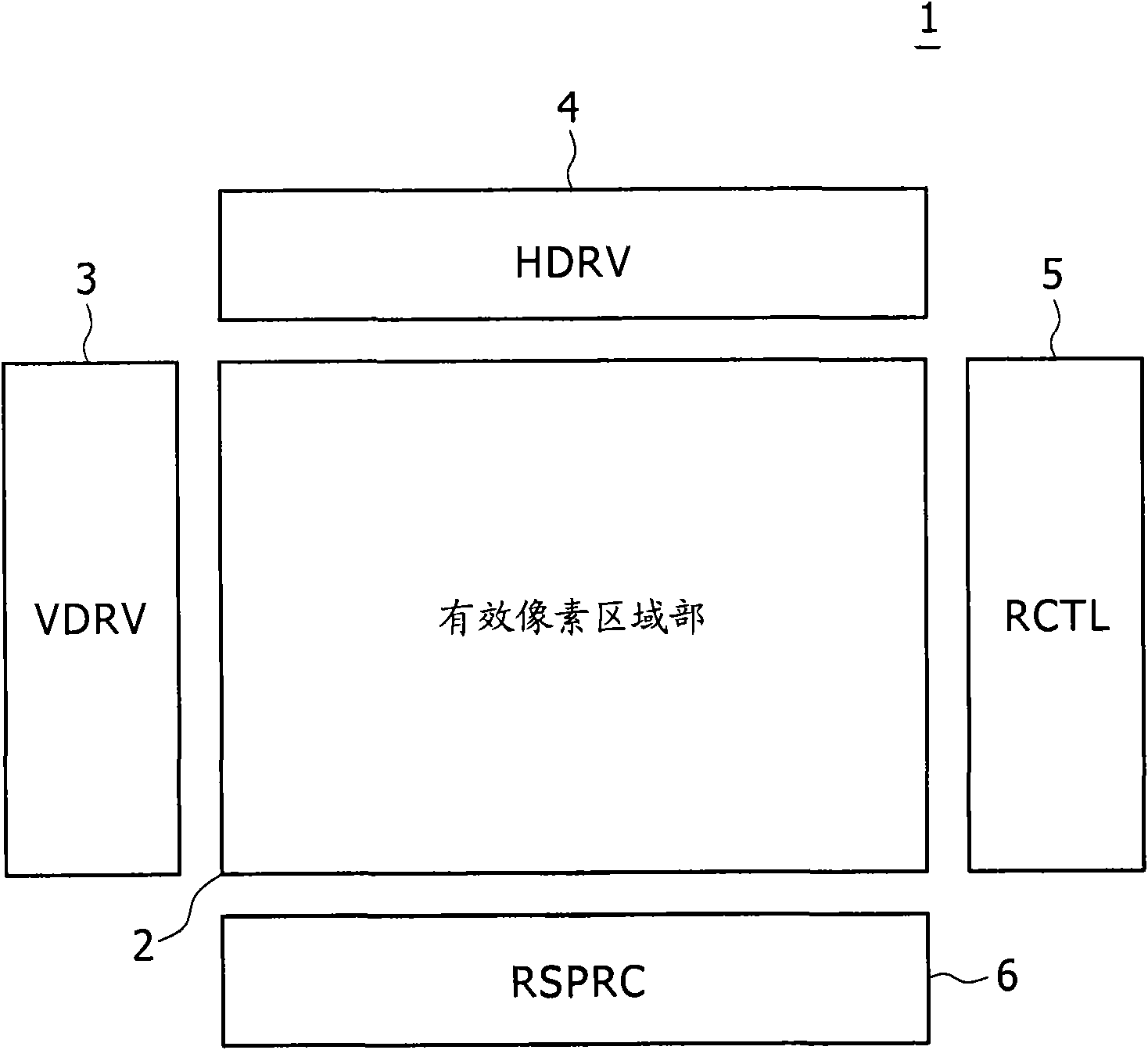
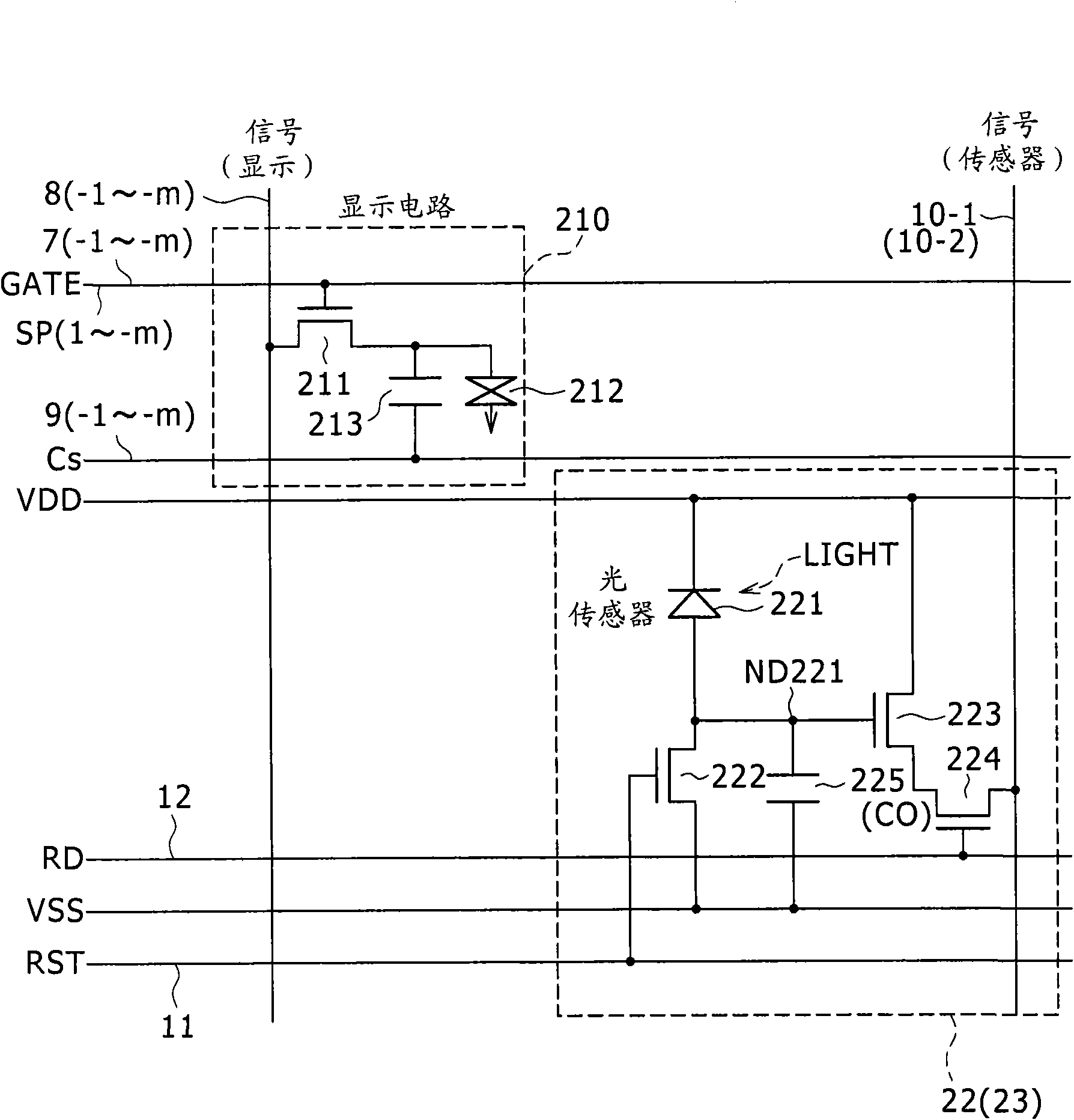
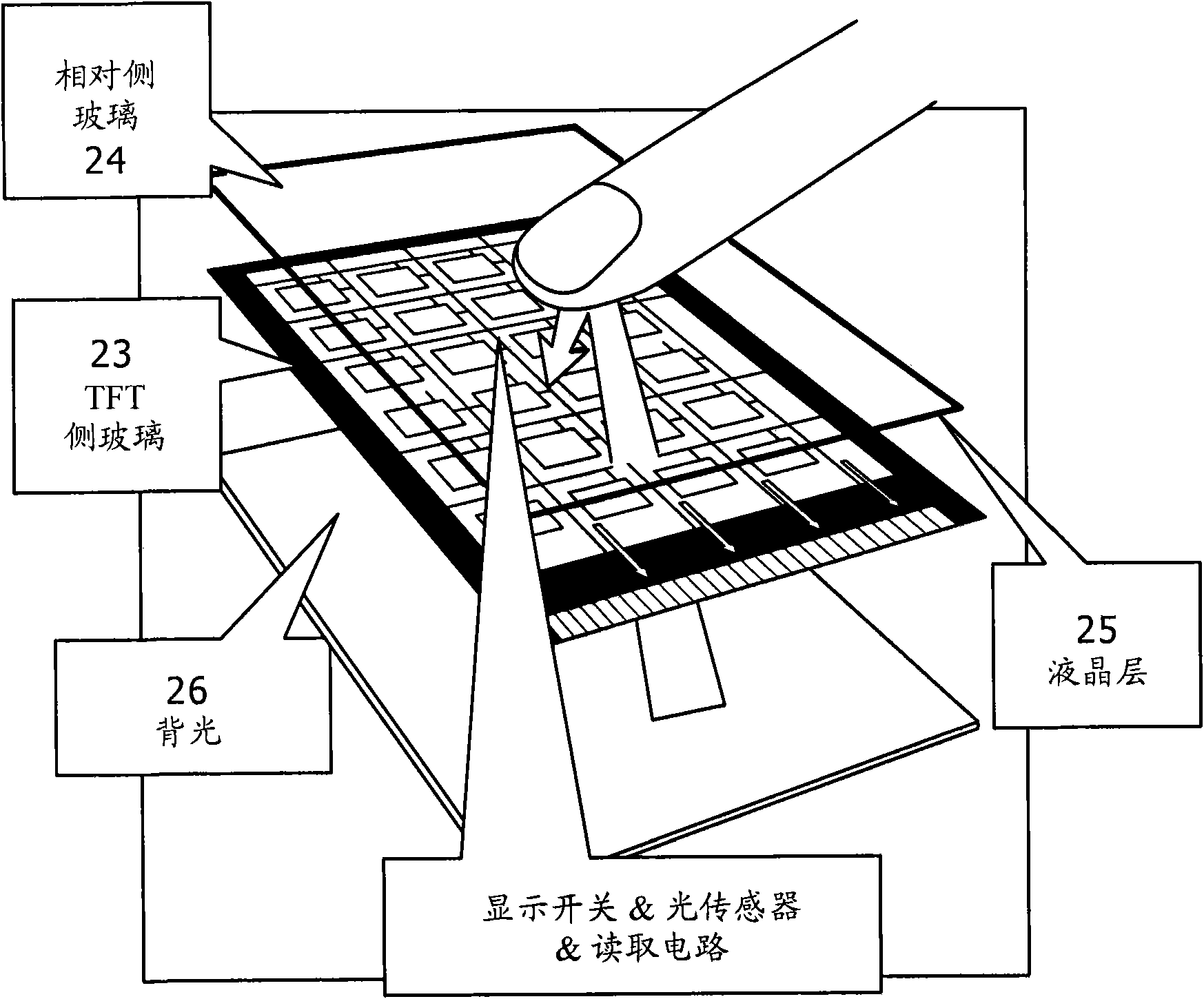
Display and electronic apparatus
InactiveCN101464588AEliminate reflected lightImprove S/NStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsPhase differenceDisplay device
A display is provided. The display includes at least one display cell having a display circuit; at least one light receiving cell including a light receiving element; a light emitting section operative to radiate light to the side of a display surface; and a polarizing plate disposed on the front side in the display relative to a region in which the light emitting section is disposed and regions in which the display cell and the light receiving cell are formed, wherein a phase difference plate is disposed at a position which is on the front side relative to the light receiving cell and in either of an emitting optical path of the light emitting section and a reflecting optical path toward the light receiving cell.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC
Peak suppressing method and data transmission device
InactiveCN1392670AAvoid saturationImprove S/NPower distribution line transmissionFrequency-division multiplexEngineeringPeak value
A peak suppression method detects a peak value exceeding a threshold value of a transmitting signal, forms a peak value prediction signal which is limited to a noise cancelling frequency band of a receiving end, based on the detected peak value of the transmitting signal, and subtracts the peak value prediction signal from the transmitting signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Display and electronic apparatus
InactiveCN101685582AReduce the impactImprove S/NStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsOptoelectronicsPhysics
A display is provided. The display includes at least one display cell having a display circuit; at least one light receiving cell including a light receiving element; a light emitting section operative to radiate light to the side of a display surface; and at least one transparent plate disposed on the front side in the display relative to a region in which the light emitting section is disposed and regions in which the display cell and the light receiving cell are formed, wherein an antireflection layer is formed on a most face-side surface of the display.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC
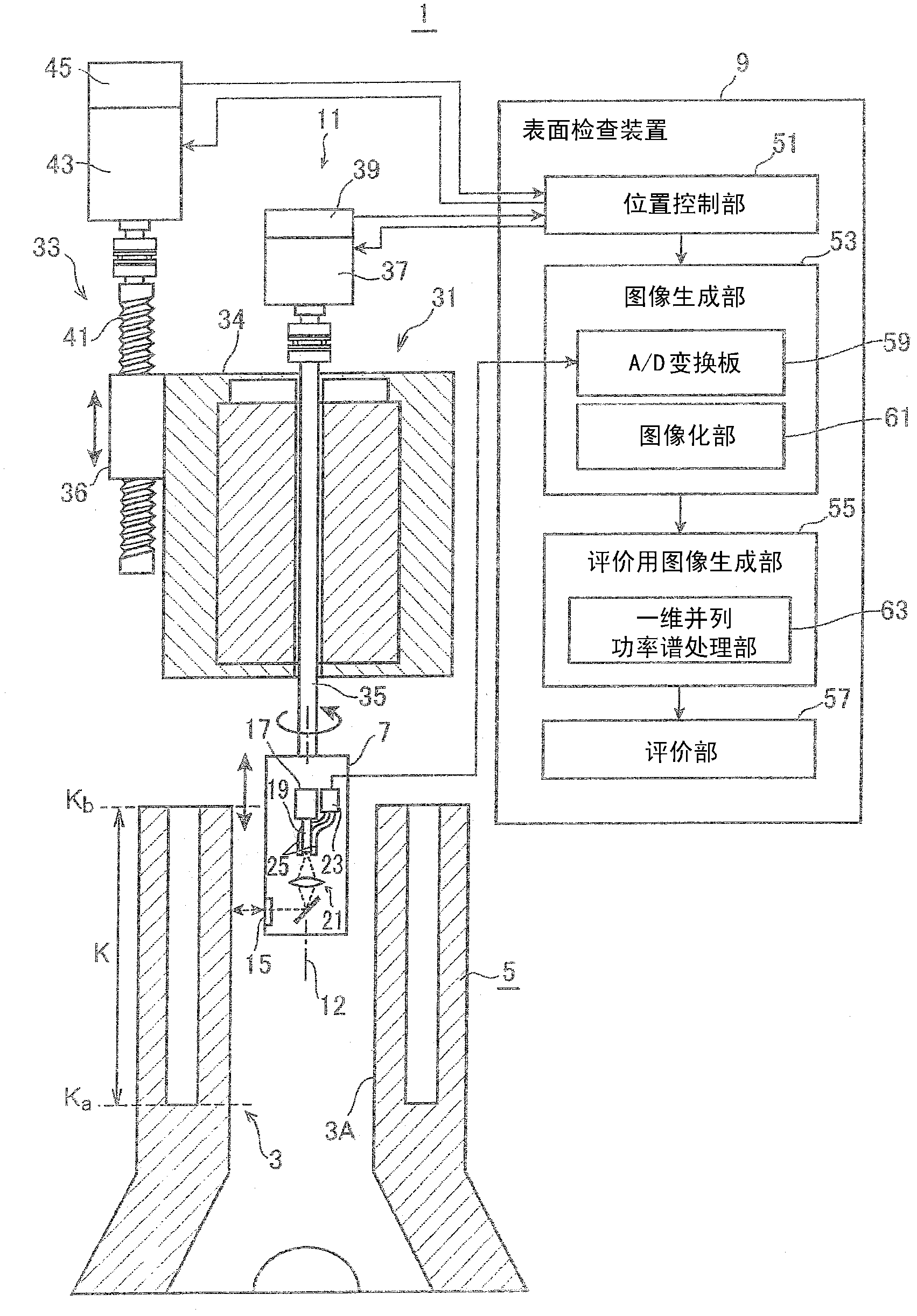
Surface examination device
InactiveCN102428361AShorten inspection timeEffective judgmentImage enhancementImage analysisEngineeringCylinder block
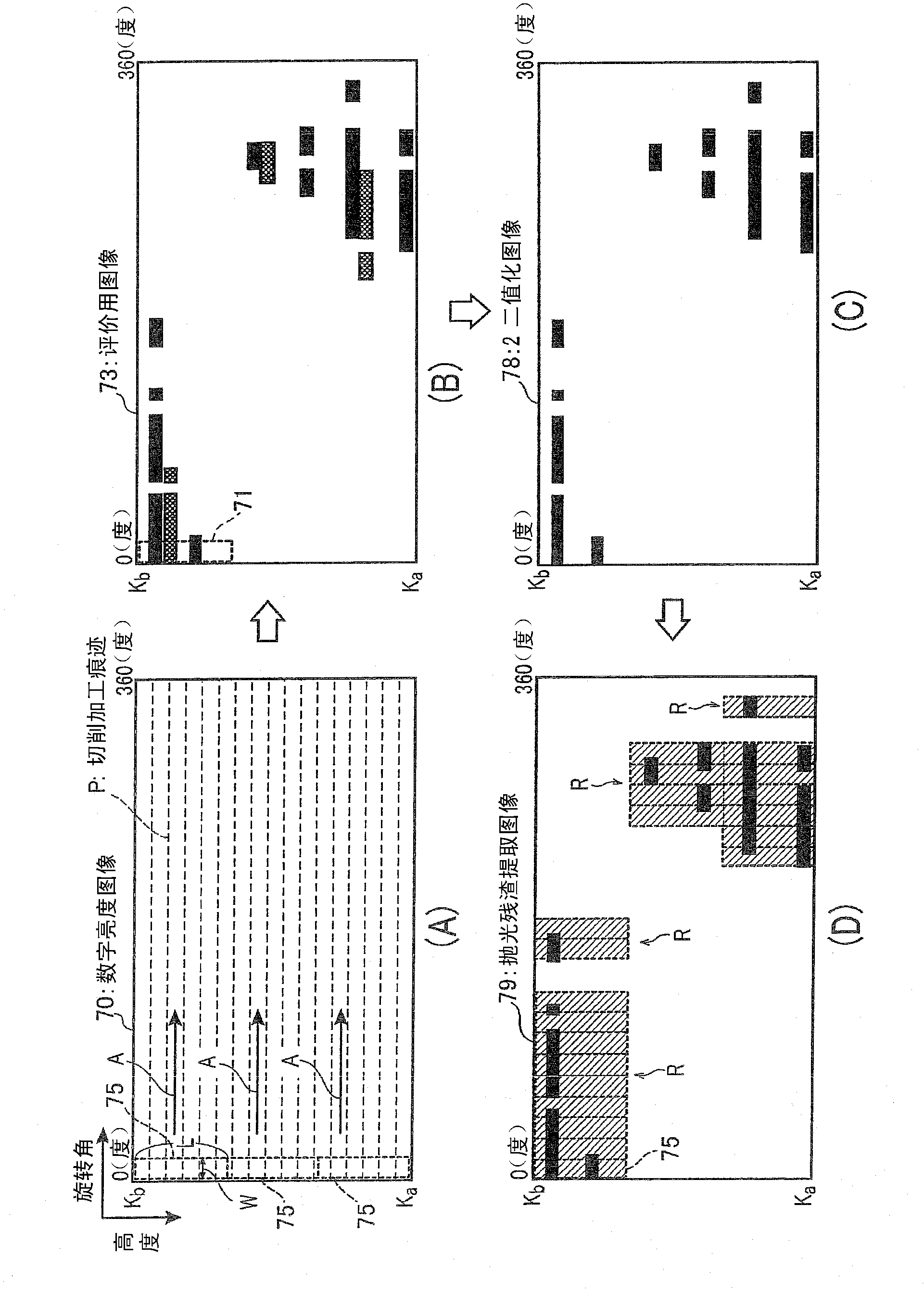
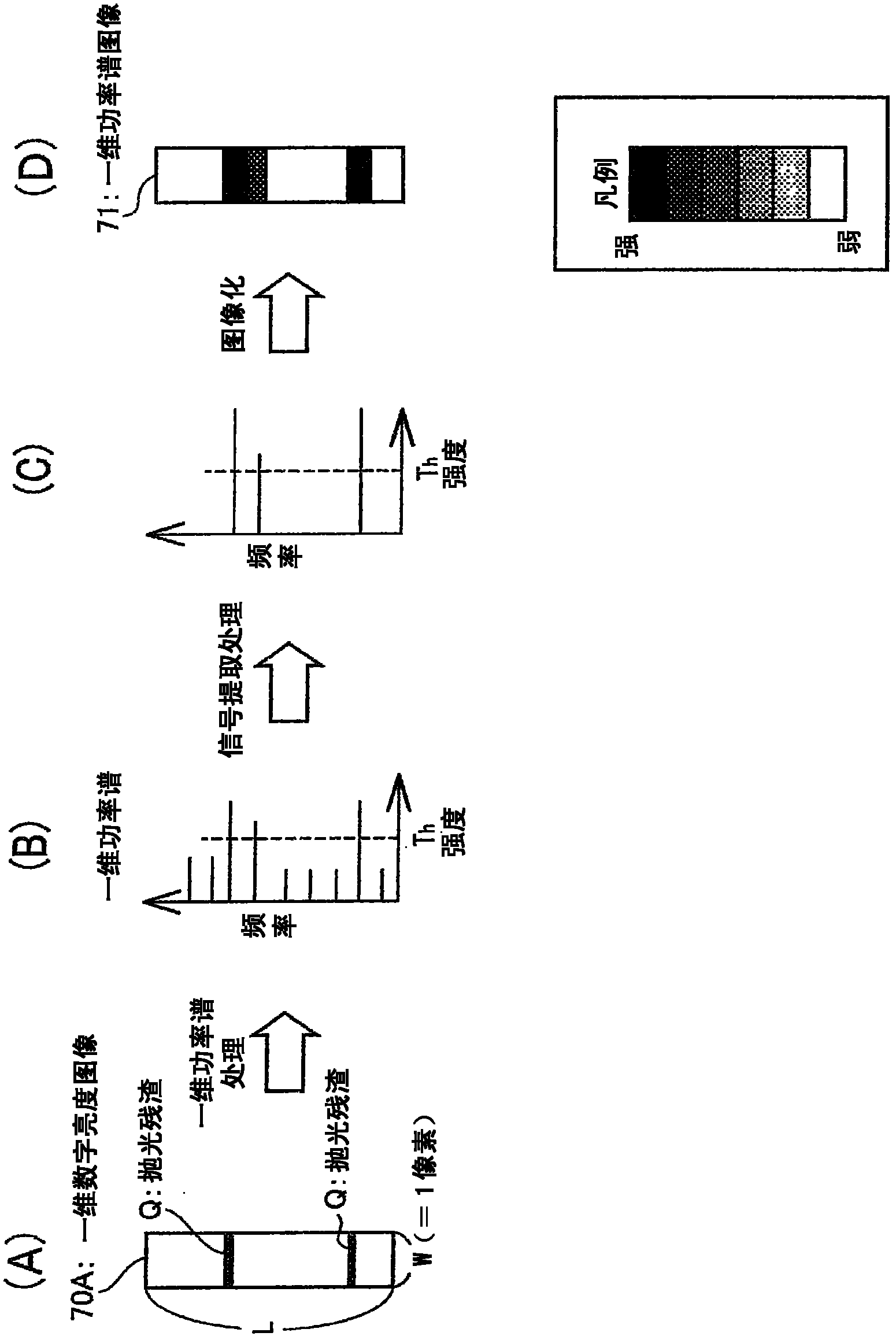
A deep machining scratch is detected, if any, the position and size can be inferred, and thereby the examination time can be shortened. A surface examination device (9 )for examining the inner surface (3A) of a bore (3) formed in a cylinder block (5) by boring and honed on the basis of a digital brightness image (70) of the inner surface (3A) is provided with an evaluation image creating unit (55) for creating linear power spectrum images (71) in a direction perpendicular to the direction of the cutting scratch (P) along the direction of the cutting scratch (P) from the digital brightness image (70), arranging the linear power spectrum images (71) parallel, and thus creating an evaluation image (73) and evaluating unit (57) for evaluating the presence / absence of an unhoned region (Q) of the inner surface (3A) of the bore (3); on the basis of the pixel values of the pixels of the evaluating image (73).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Signal Extraction Method of Electromagnetic Flowmeter
InactiveCN106066196ALittle changeReduce electricityVolume/mass flow by electromagnetic flowmetersElectrode potentialExcitation current
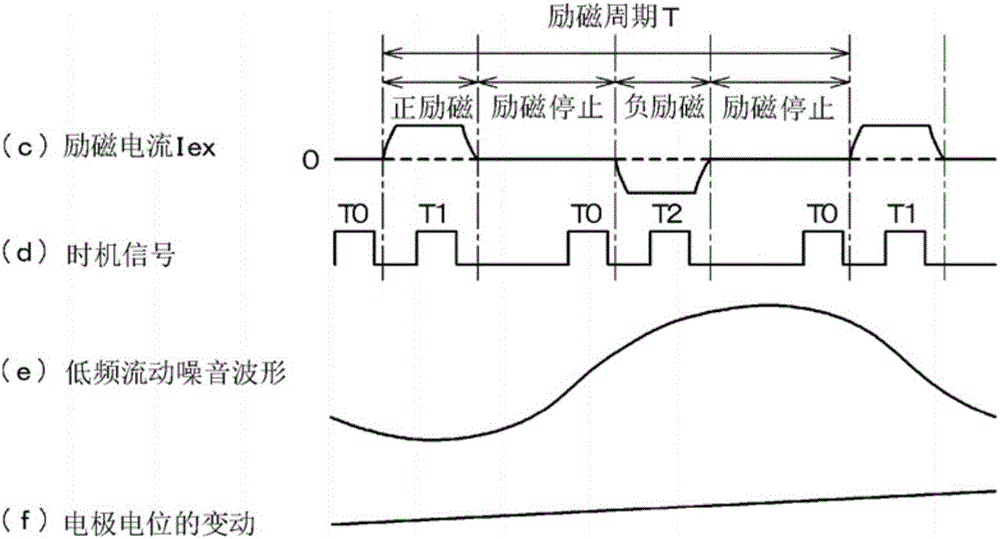
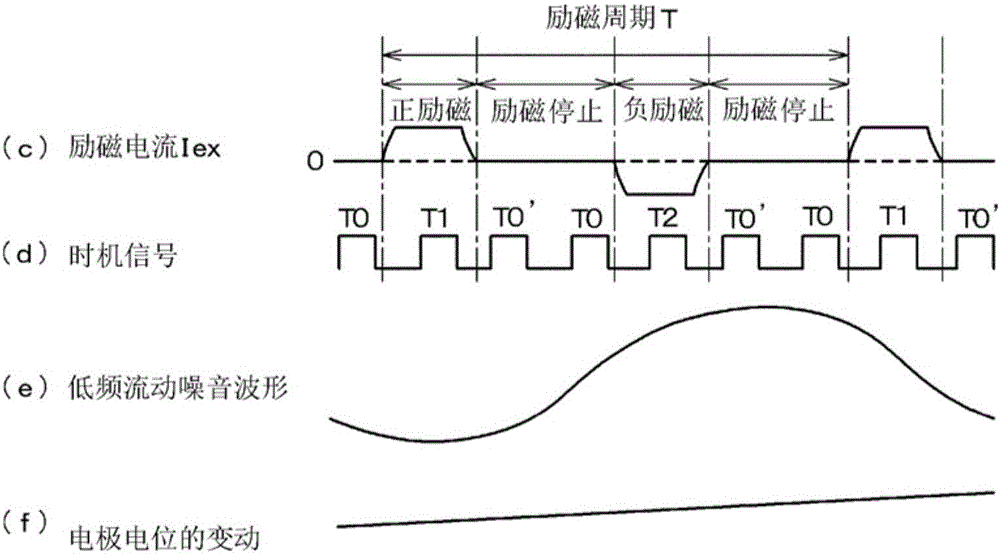
The invention provides a signal extraction method of an electromagnetic flowmeter, in order to improve S / N according to an excitation method with low powder consumption and perform signal processing with less output fluctuation. In an exciting current waveform (c), an excitation stop period is arranged between a positive excitation interval and a negative excitation interval. Sampling times T1 and T2 of the positive and negative excitation intervals and sampling time T0 of the excitation stop period are determined according to a timing signal (d), and the flow velocity and the flow rate are obtained from the times T1 and T2 and the difference between the electrode potentials extracted at the time T0. In addition to the electromotive force which is used as a flow rate signal, the electrode potentials sampled at times T0, T1, T2 include flow noise (e) superimposed on the electrode, and the electrode potential (f) which fluctuates slowly are also sampled. By obtaining the difference between the electrode potentials at the time T1, T2 and the preceding time T0 and obtaining the flow rate with a short sampling period, correct flow velocity and flow rate are obtained, and flow noise (e) and electrode potential fluctuation (f) cancel each other and can be effectively removed.
Owner:TOKYO KEISO
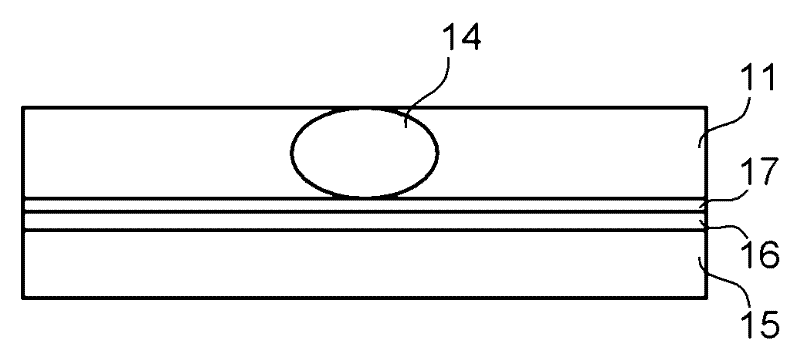
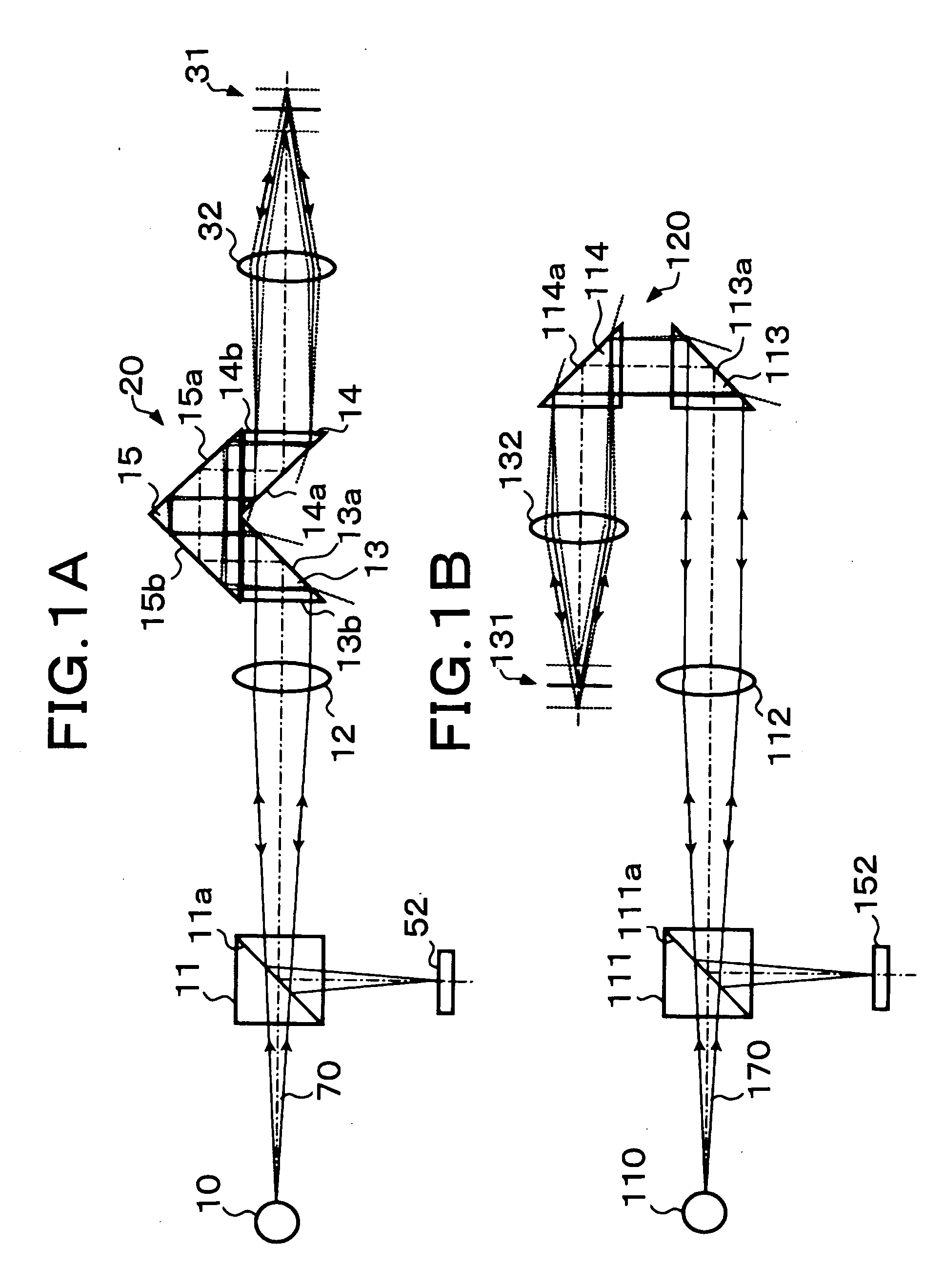
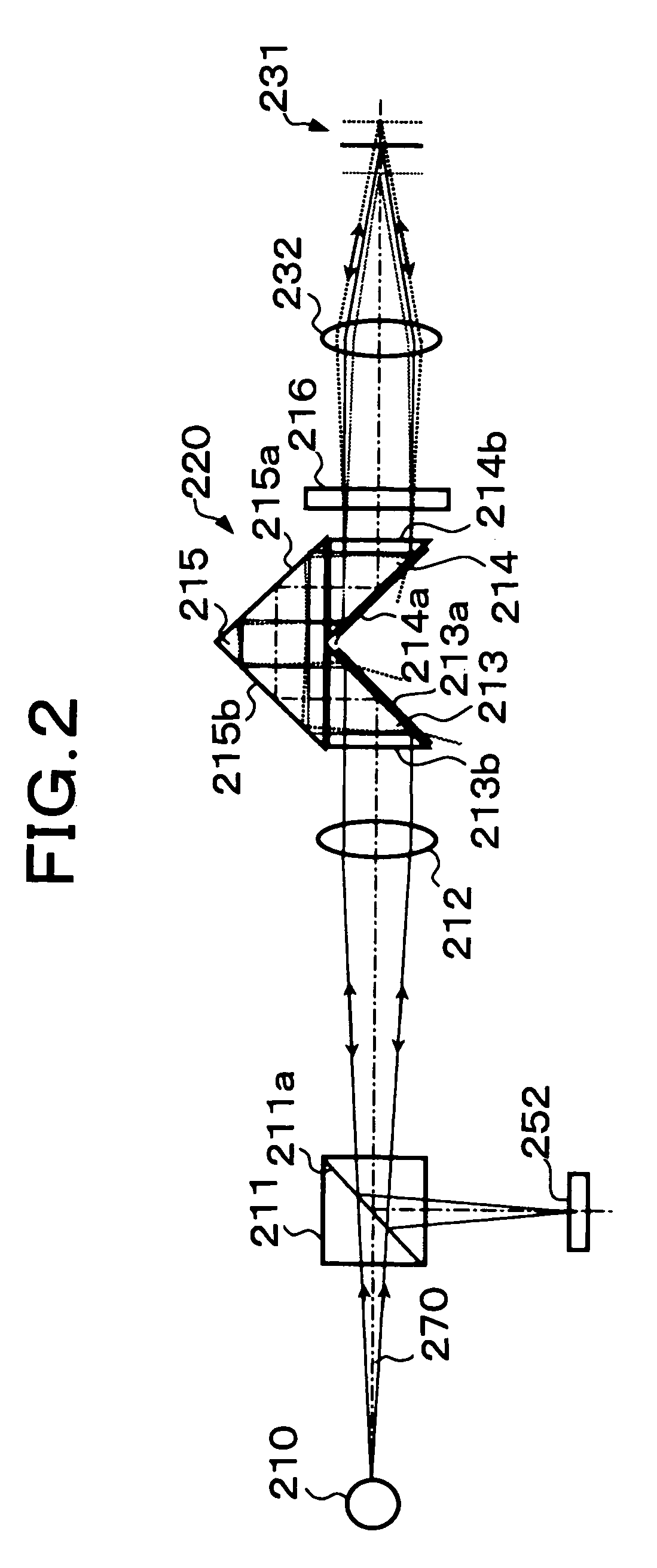
Microscope device
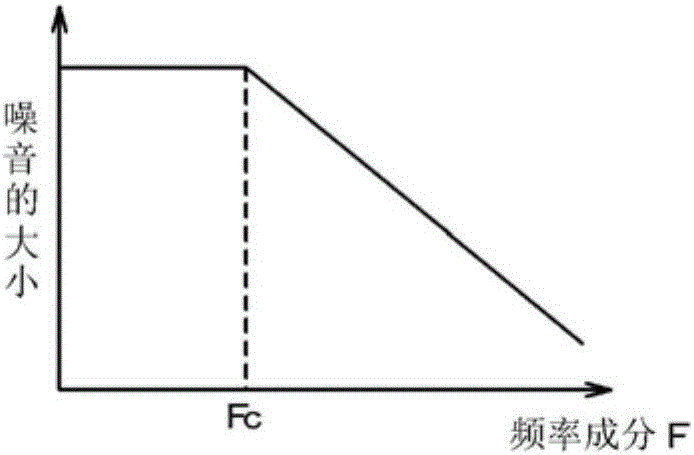
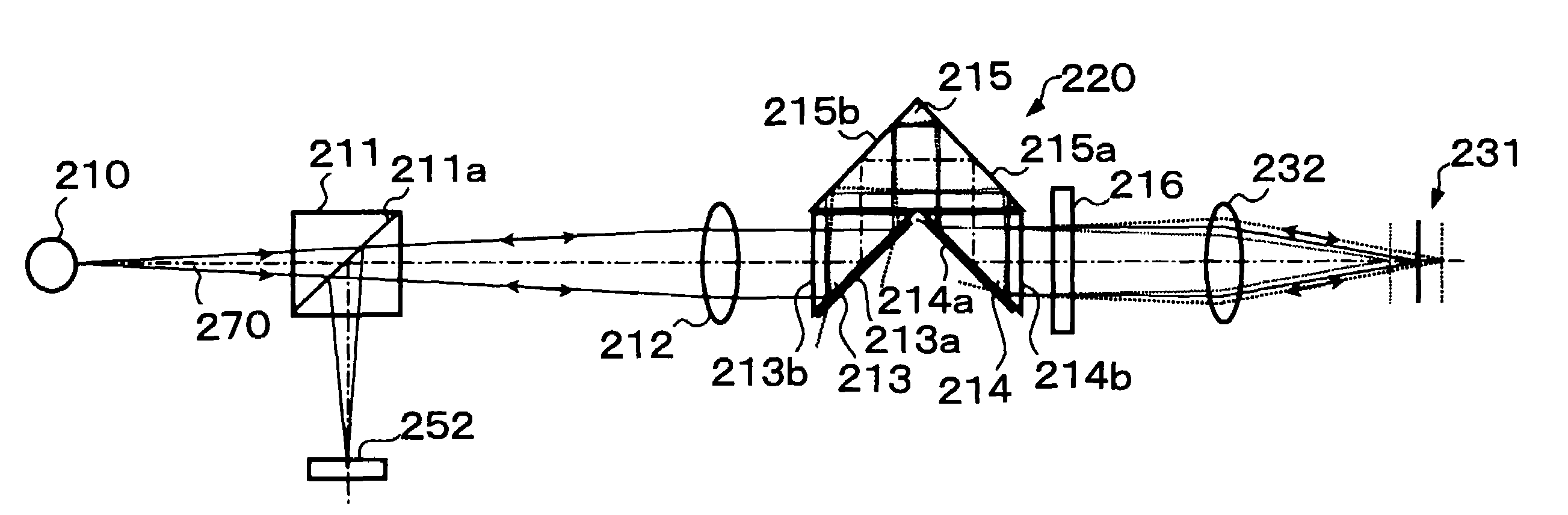
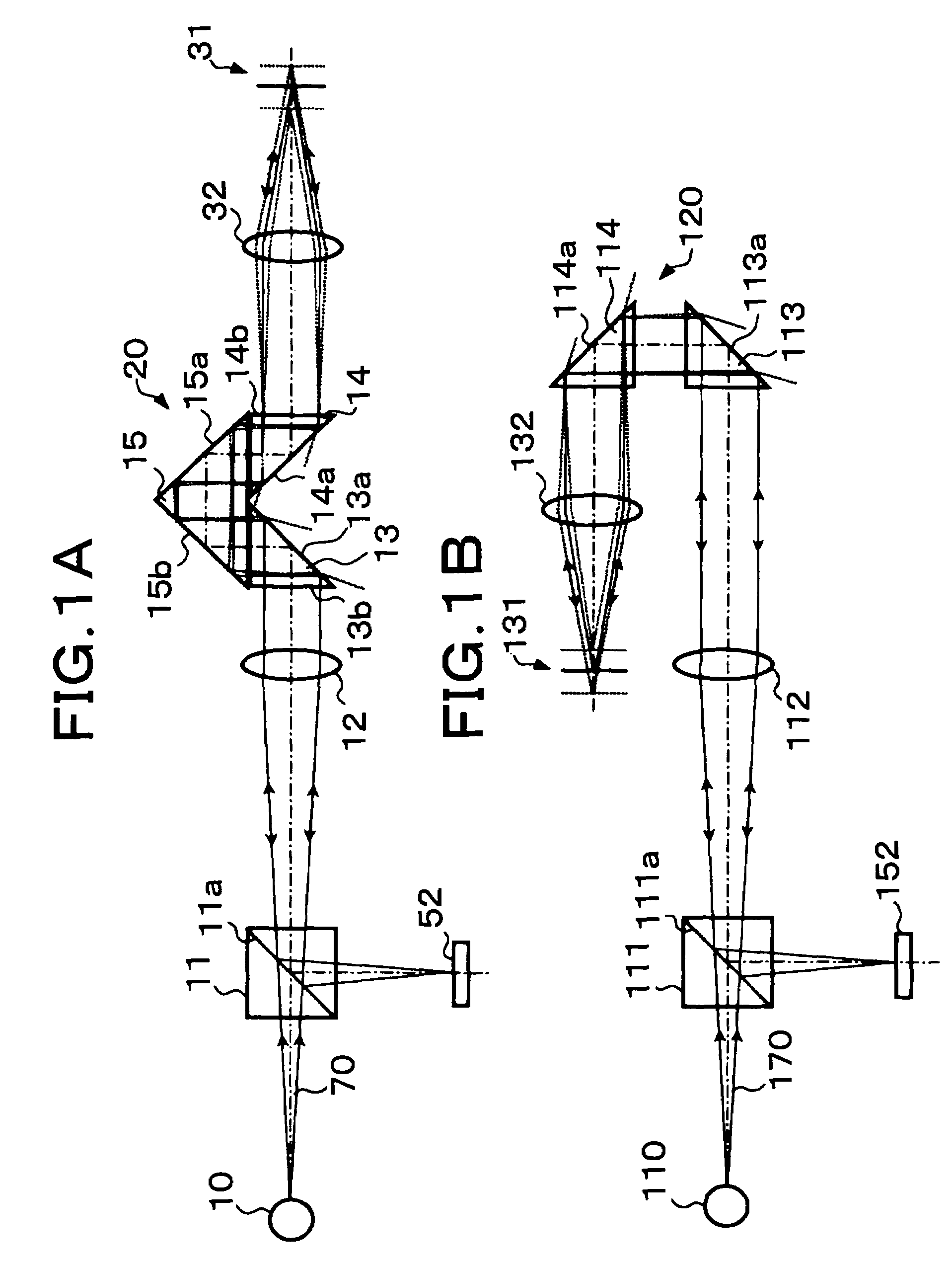
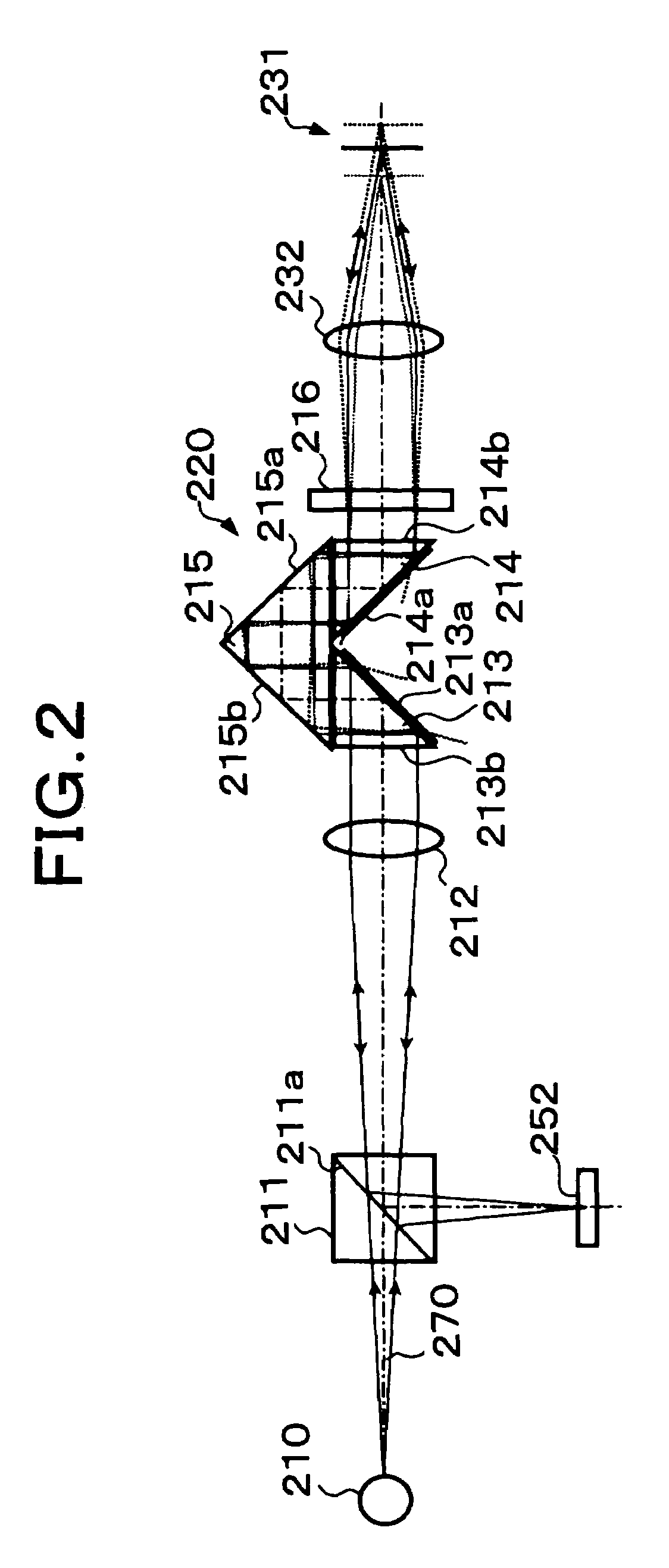
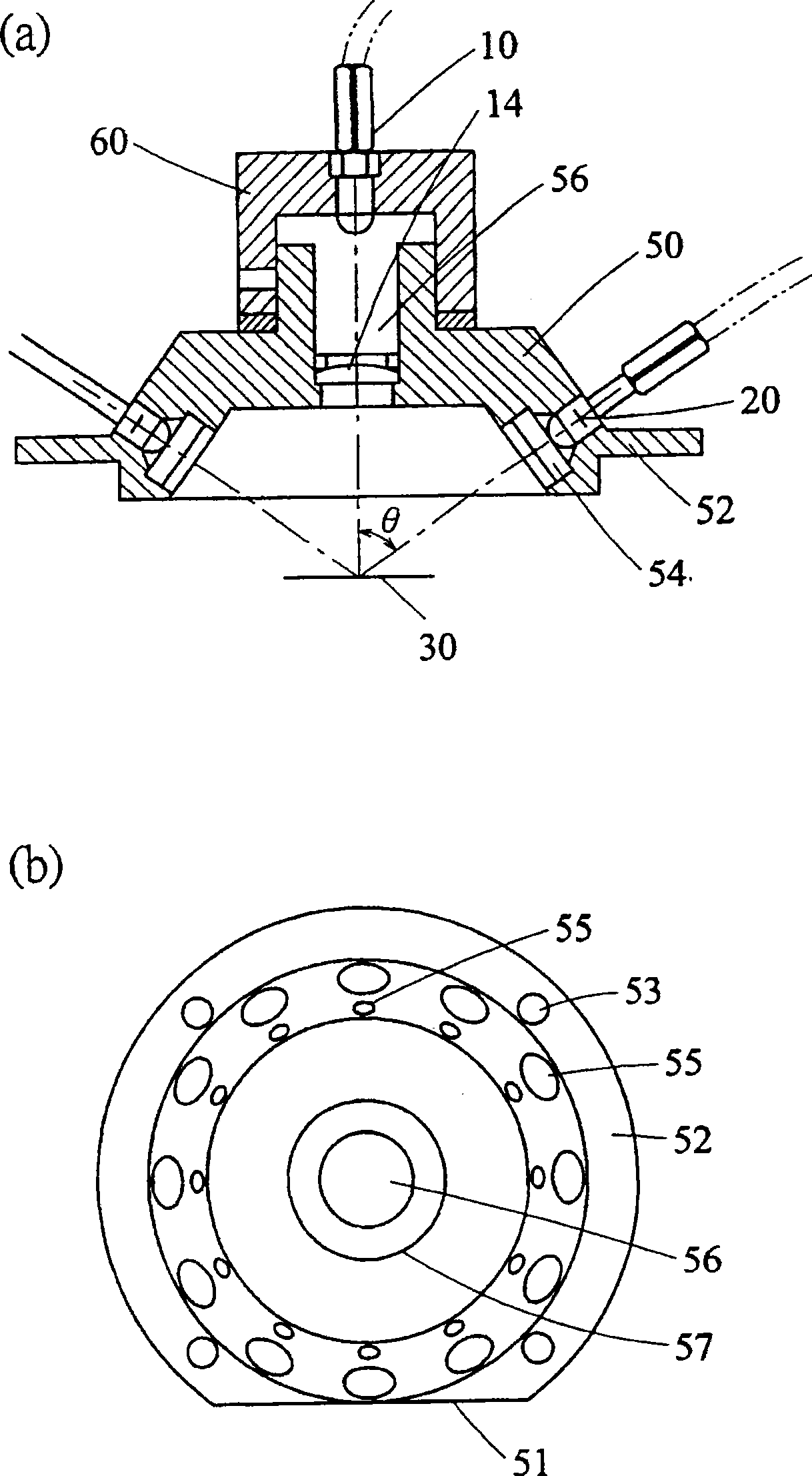
Specularly reflected light from a convergence position on an object surface 31 enters a second critical-angle prism 14, another prism 15, and a first critical-angle prism 13 of a parallel beam selection optical system 20 in this order as a parallel beam traveling along the optical axis. The critical-angle prisms 13, 14 have critical angles of 45 degrees with respect to the wavelength of the light beam. Light beams other than the parallel light beam are removed at oblique surfaces 13a, 14a of the critical-angle prisms 13, 14, thereby allowing only the parallel light beam to exit as a regular light beam. This parallel beam is formed into a convergent light by a collimator lens 12, reflected by a half prism 11 and converged on an image pickup surface of an image pickup device 52. In this way, unnecessary noise light can be removed without placing a pin hole plate such as that placed before the image pickup plane in a confocal microscope.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
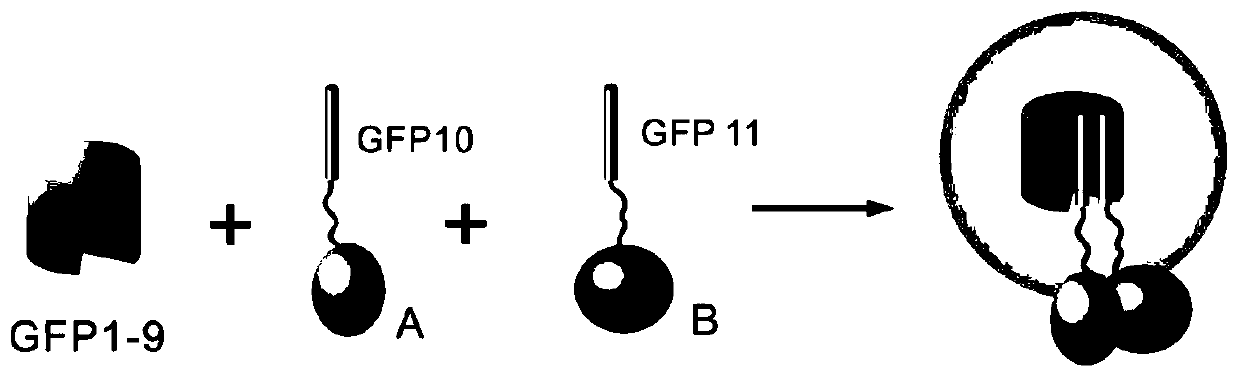
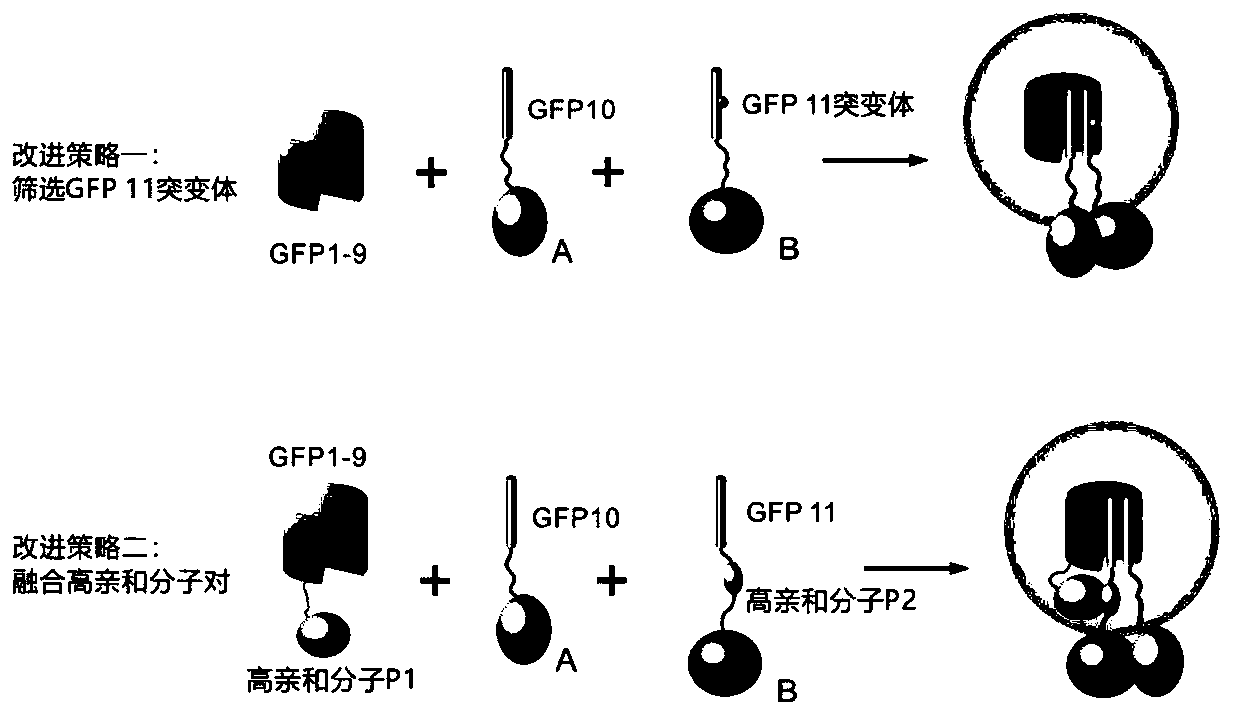
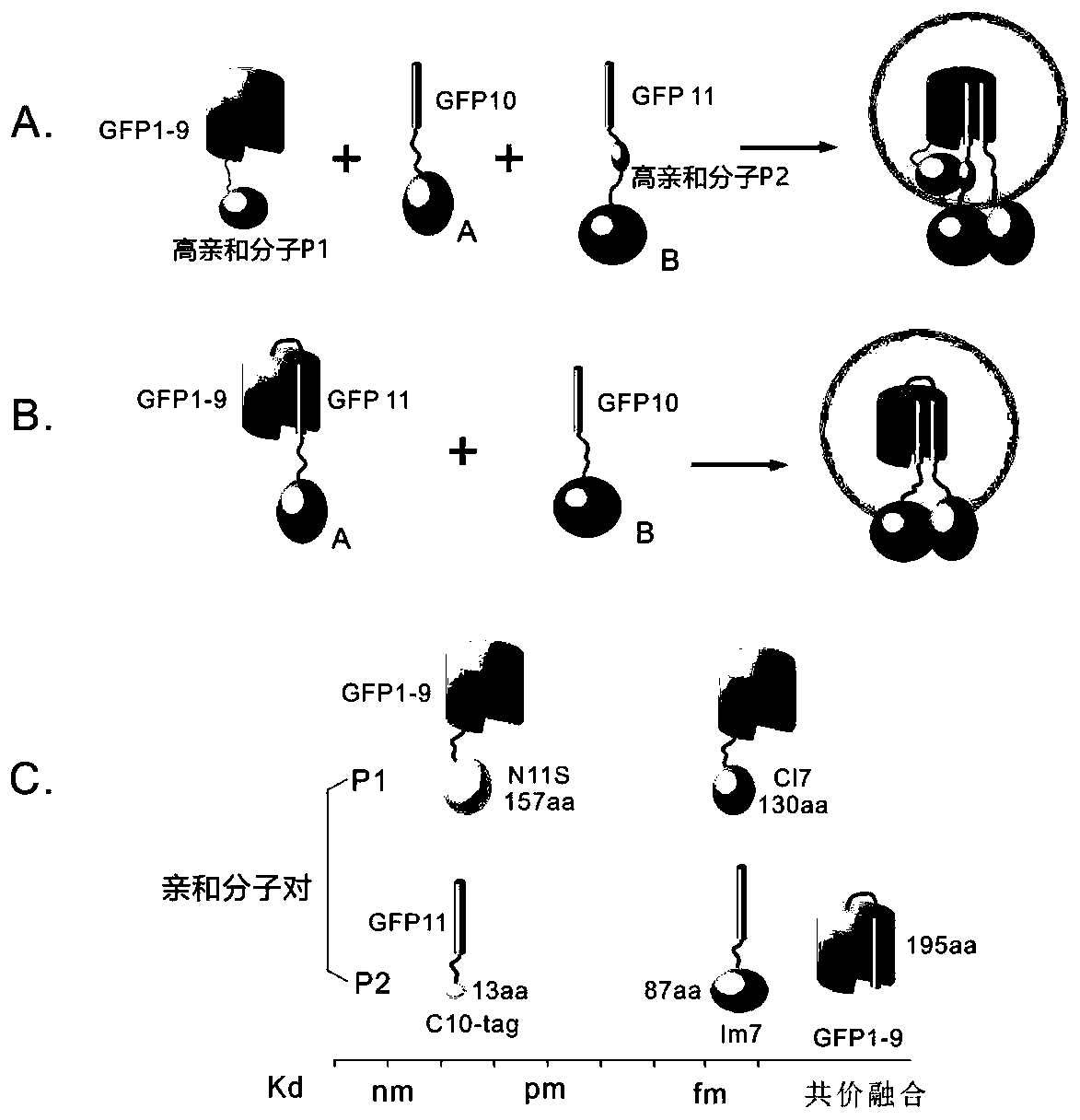
Segmented green fluorescent protein system for protein interaction detection
ActiveCN110283244AImprove S/NAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceNucleic acid sequencing
The invention discloses a protein fragment. Nucleic acid sequences encoding the protein fragment is shown in SEQ ID No: 56 or SEQ ID No: 57 or SEQ ID No: 58. The invention further discloses a segmented green fluorescent protein system for protein interaction detection, which comprises GFP10 in a three-part sfGFP system, and further comprises a protein encoded by the nucleic acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 58, or further comprises proteins encoded by the nucleic acid sequences shown in SEQ ID No: 56 and SEQ ID No: 57. The invention further discloses recombinant vectors, recombinant bacteria, transgenic cell lines or expression cassettes comprising the aforementioned nucleic acid sequences, and also discloses the application of the protein fragment to detection of the interaction among proteins, or the application of the nucleic acid sequences to detection of the interaction among proteins. A fluorescent signal of the improved segmented sfGFP system is significantly improved.
Owner:重庆明道捷测生物科技有限公司
Crystal oscillator piece and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveCN101657965AImprove S/NStable temperature characteristicsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksEtchingCrystal oscillator
A crystal oscillator piece in which generation of leakage oscillation is suppressed, and its manufacturing method. The method for manufacturing a crystal oscillator piece comprises a step for forming a first etching mask on the surface of a crystal wafer and forming a second etching mask on the backside thereof, dipping the crystal wafer in etching solution, and dissolving the crystal at a part not covered with the first etching mask and the second etching mask to form an oscillation leg, and characterized in that the length of a first projection projecting from a position corresponding to the first end of the first etching mask is set, in the second etching mask, such that the first residue formed on the first side face side becomes constant regardless of positional shift of the first and second etching masks, and the first and second etching masks regulate the second residue formed on the second side face side such that one of two main axes passing the centroid and intersecting a cross-section orthogonal to the longitudinal direction of the oscillation leg dynamically and perpendicularly is formed substantially in parallel with the surface or the backside of the crystal wafer.
Owner:CITIZEN WATCH CO LTD
Recording/reproducing method in read-only holographic recording medium, and read-only holographic recording medium
InactiveCN102099752AAvoid formingAvoid exposureRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing using optical interference patternsSignal beamHolographic recording
A recording signal beam and a recording reference beam are applied on a first surface of a holographic recording medium, information as an interference pattern is recorded in the holographic recording medium, and a reflecting layer is adhered on a second surface which faces the first surface in the holographic recording medium. Then, a reproduction reference beam is applied on the first surface of the holographic recoding medium and is reflected by the reflecting layer, and a reproduction signal beam from the holographic recording medium is read out on the side of the first surface of the holographic recording medium.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CHEM & MATERIAL CO LTD
Microscope device
InactiveUS20050141080A1Improve contrast and resolutionDesign freedom be reduceMicroscopesMicroscopePrism
Specularly reflected light from a convergence position on an object surface 31 enters a second critical-angle prism 14, another prism 15, and a first critical-angle prism 13 of a parallel beam selection means 20 in this order as a parallel beam traveling along the optical axis. The critical-angle prisms 13, 14 have critical angles of 45 degrees with respect to the wavelength of the light beam. Light beams other than the parallel light beam are removed at oblique surfaces 13a, 14a of the critical-angle prisms 13, 14, thereby allowing only the parallel light beam to exit as a regular light beam. This parallel beam is formed into a convergent light by a collimator lens 12, reflected by a half prism 11 and converged on an image pickup surface of an image pickup device 52. In this way, unnecessary noise light can be removed without placing a pin hole plate such as that placed before the image pickup plane in a confocal microscope.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Thermal conductivity detector and gas chromatograph
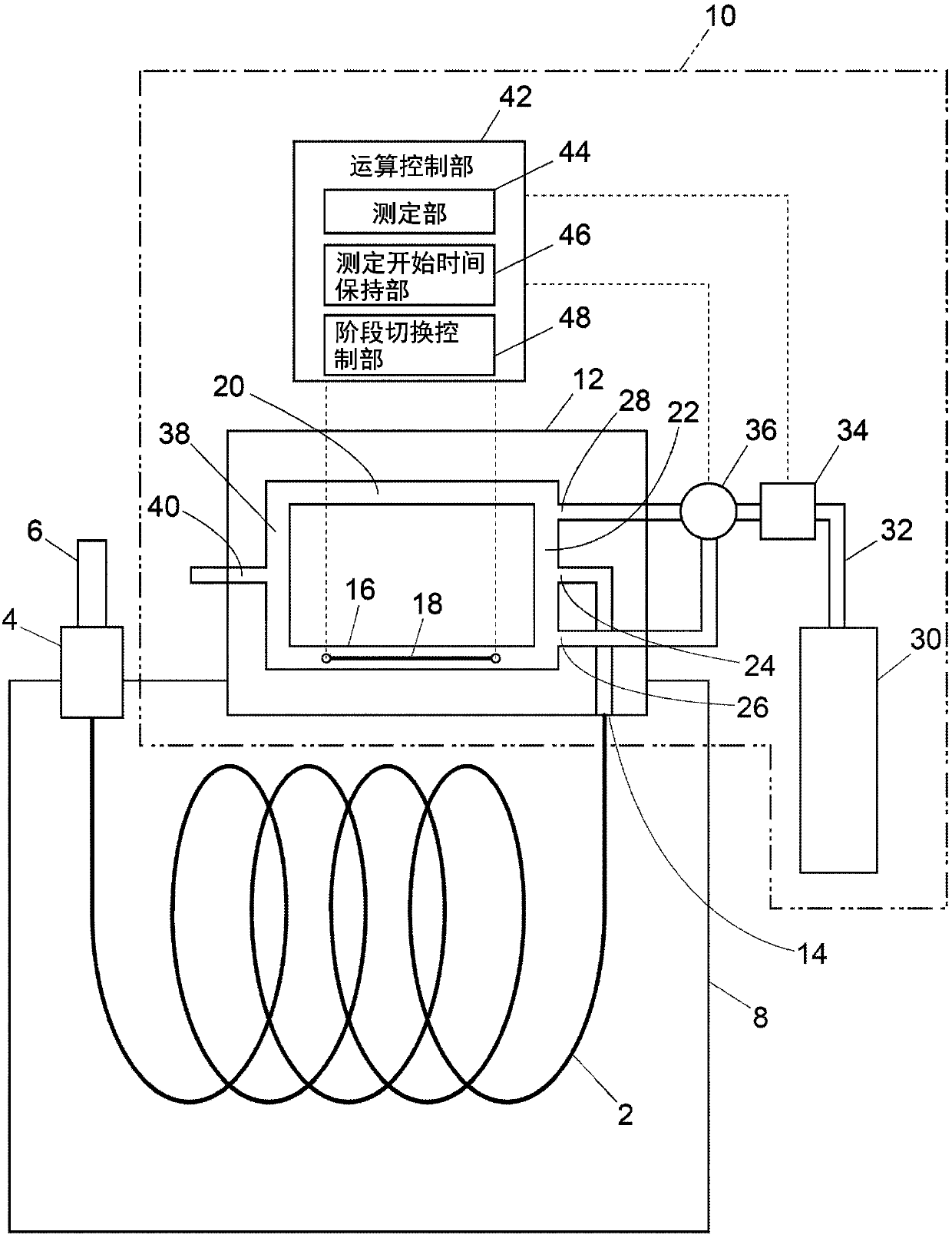
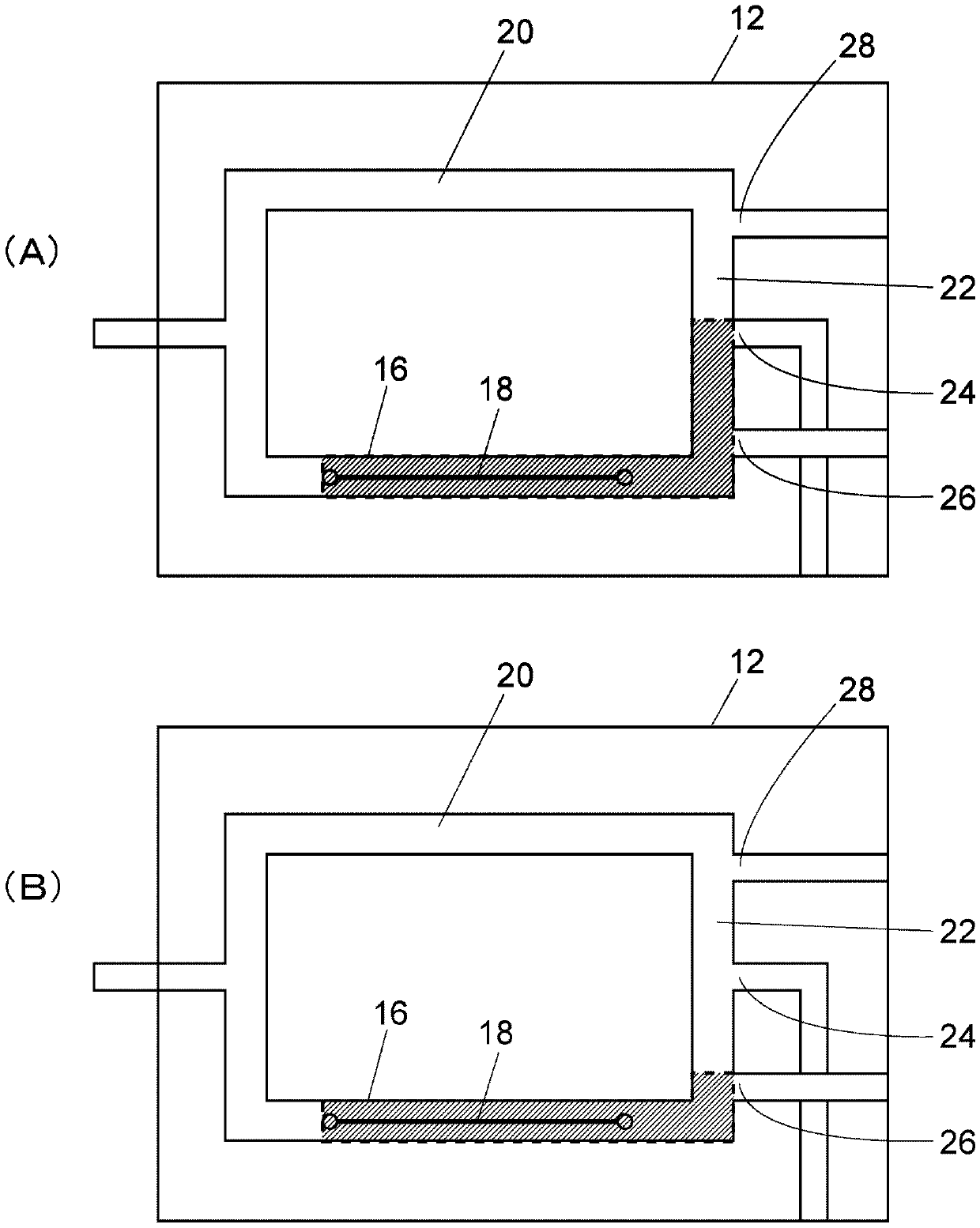
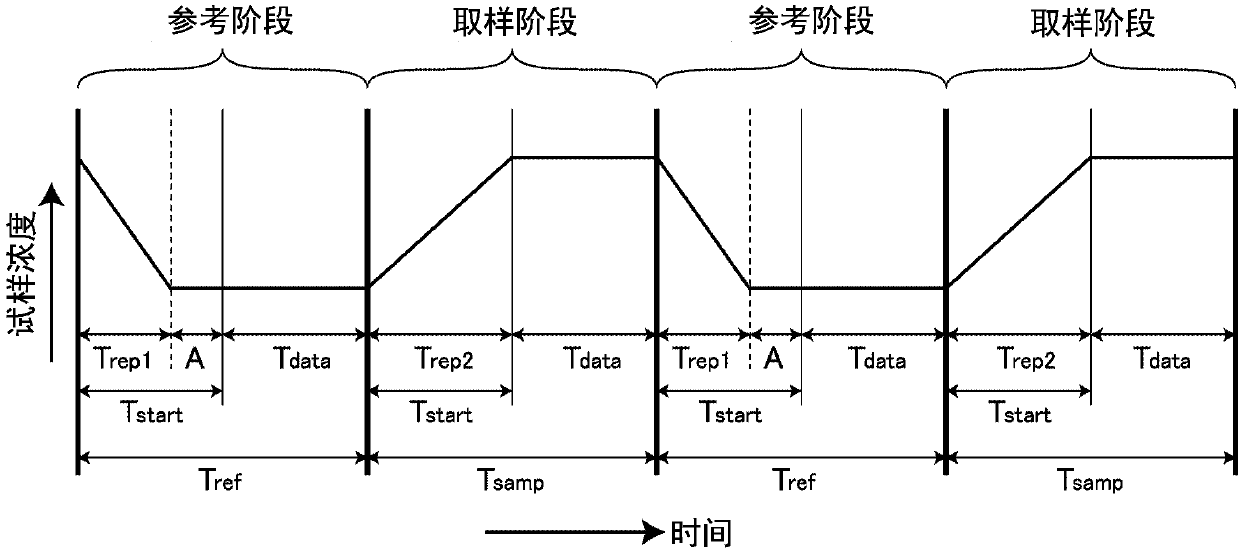
ActiveCN107807197AIncrease the lengthGrowth acquisition timeMaterial thermal conductivityComponent separationStart timeThermal conductivity
The invention provides a thermal conductivity detector and a gas chromatograph. Detection sensitivity of a single-filament thermal conductivity detector is to be increased. A thermal conductivity detector is a single-filament thermal conductivity detector, and includes a measurement cell, a phase switching mechanism, and a measurement section. The measurement section starts measurement of thermalconductivity of a sample gas after a lapse of a sample gas measurement start time that is set in advance, after a reference phase is switched to a sample phase by the phase switching mechanism, and starts measurement of thermal conductivity of a reference gas after a lapse of a reference gas measurement start time that is set in advance as a length of time different from the sample gas measurementstart time, after the sample phase is switched to the reference phase by the phase switching mechanism.
Owner:SHIMADZU SEISAKUSHO LTD
Signal processing device, radar apparatus, target object method
ActiveUS9354303B2Improve S/NReduce distractionsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase correctionSignal generator
A signal processing device is provided. The device includes an echo signal input unit for receiving echo signals resulted from transmission signals reflected on an object. The transmission signals are transmitted from a transmission source at transmission timings at predetermined time intervals, at least one of the transmission timings shifted from the other timings in time. The device includes a complex reception signal generator for generating complex reception signals, a phase calculator for calculating a phase change amount of the complex reception signals with respect to a reference phase, a phase corrector for phase-correcting the complex reception signals and outputting the corrected signals, and a Doppler processor for performing Doppler processing on the corrected signals and outputting the Doppler-processed signals as Doppler echo signals of the object.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Angular velocity detection circuit, angular velocity detection device, electronic apparatus, and moving object
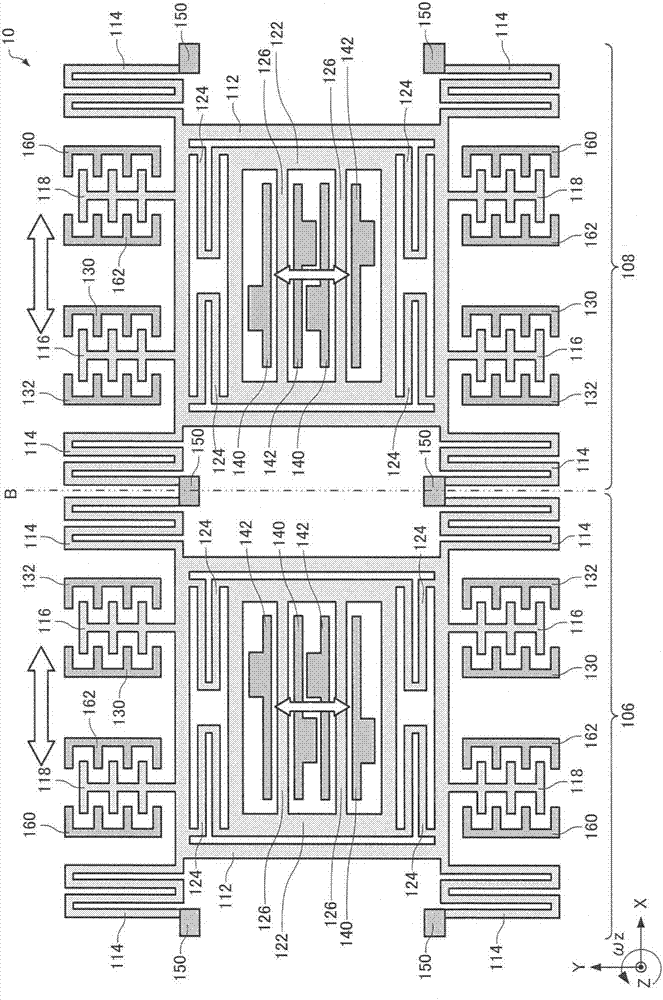
InactiveCN107152928AImprove S/NHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSignal onAngular velocity
The invention provides an angular velocity detection circuit, an angular velocity detection device, an electronic apparatus, and a moving object. The angular velocity detection circuit includes: a first conversion unit that includes a first operational amplifier, and converts a first detection signal, which is output from a first detection electrode and is input to a first input terminal of the first operational amplifier, into a voltage; an angular velocity signal generation unit that generates an angular velocity signal on the basis of an output signal of the first conversion unit; and a first correction signal generation unit that generates a first correction signal for reducing an offset of the angular velocity signal which occurs due to a leakage signal included in the first detection signal on the basis of a signal based on drive oscillation of the angular velocity detection element. The first correction signal is input to the first input terminal or a second input terminal of the first operational amplifier directly or through a resistor.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Device and method for radiometric measurement of plurality of samples
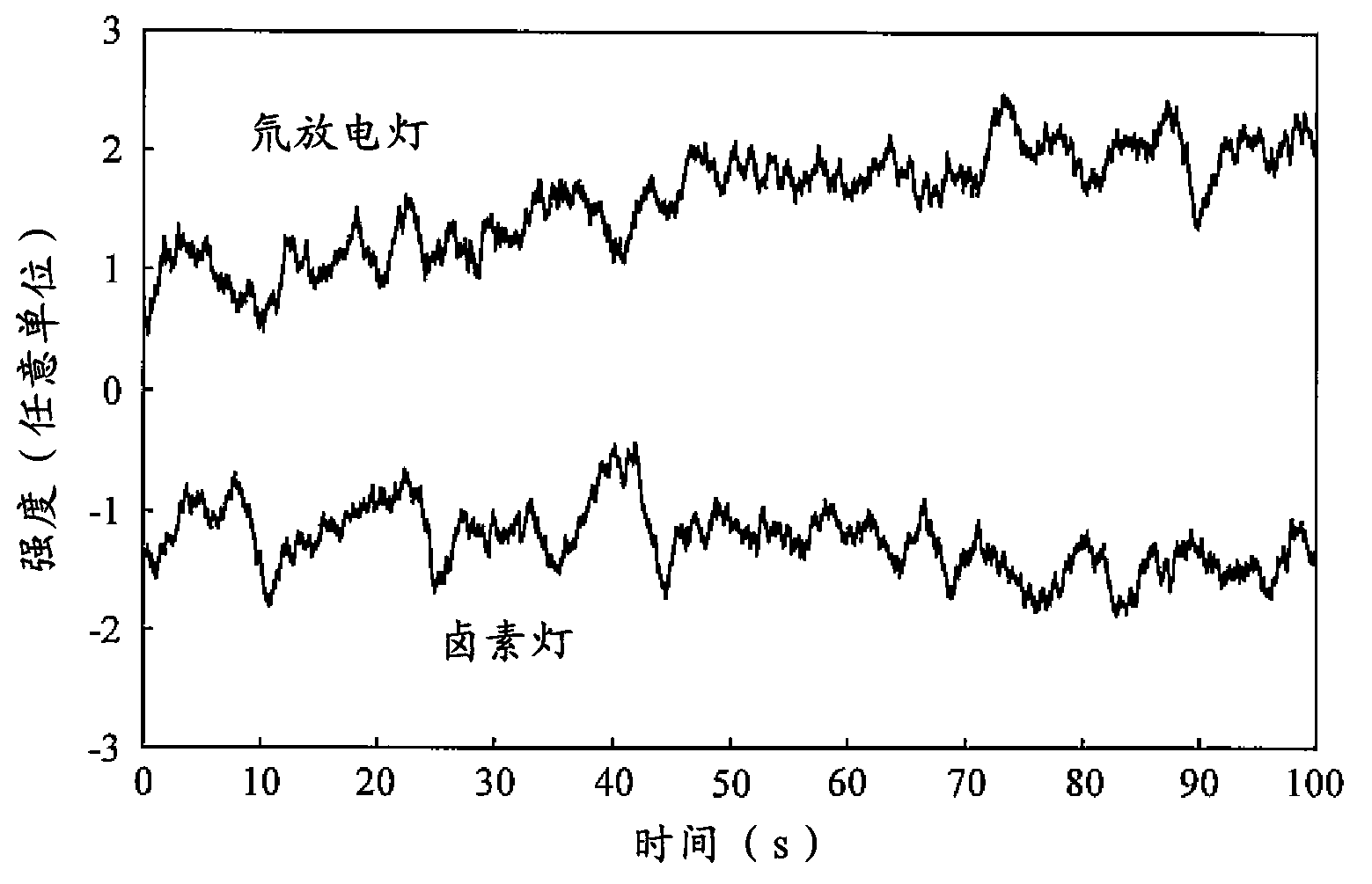
InactiveCN101821609ADifferent time characteristicsImprove S/NFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluenceRadiation frequency
The invention relates to an apparatus for radiometrically investigating a plurality of samples, with: a radiation device providing a plurality of radiation elements, a radiation element comprising at least one emitter element, wherein the radiation device preferably provides at least two emitter elements which provide radiation with different radiation spectra, wherein at least two of said emitter elements are adapted to emit radiation during time periods which at least partially overlap, and a control device, controlling said radiation elements, a sample holder member providing a plurality of sample positions for supporting a plurality of samples, wherein preferably at least a part of the radiation device and the sample holder member are adapted to be moved against each other during the investigation procedure and wherein at least one radiation element is adapted to irradiate a sample with radiation via a first optical path which causes the sample to emit sample radiation with at least one sample radiation frequency via a second optical path towards at least one detection device, said at least one detection device being adapted to detect the sample radiation of at least two samples as a sum signal during time periods which at least partially overlap; and an evaluation device which is adapted to evaluate the sample radiation of at least one individual sample from said sum signal. The invention relates further to a method for photometrically investigating sample radiations of at least one sample, which are caused by the radiation of N emitter elements of at least one radiation element wherein said N emitter elements are emitting radiation during time periods which at least partially overlap, to detect the sample radiation of at least two samples as a sum signal during time periods which at least partially overlap and to evaluate the sample radiation of at least one individual sample from said sum signal.
Owner:EPPENDORF AG
Living body observing device
A light source unit (41) connected with a control unit (42) and an endoscope (101) emits whit light with a specified light quantity based on a signal from the control unit (42). The light source unit (41) comprises a lamp (15) as a white light source, an infrared cutting filter (15a), a light quantity limiting filter (16) inserted / removed into / from a light path to limit a light quantity in a specified wavelength region of white light, a filter inserting / removing drive unit (17) for inserting / removing the light quantity limiting filter (16) into / from the light path, and a condenser lens (18) for emitting white light. For example, the light quantity limiting filter (16) limits, when transmittance in a blue band is 100%, transmittance in the other bands to 50%. Accordingly, an S / N in a visible light region in generating a discrete spectral image by a lighting light is improved.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Solid state image pickup device and camera using the same
ActiveCN1910910BImprove linearityImprove S/NTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAudio power amplifierEngineering
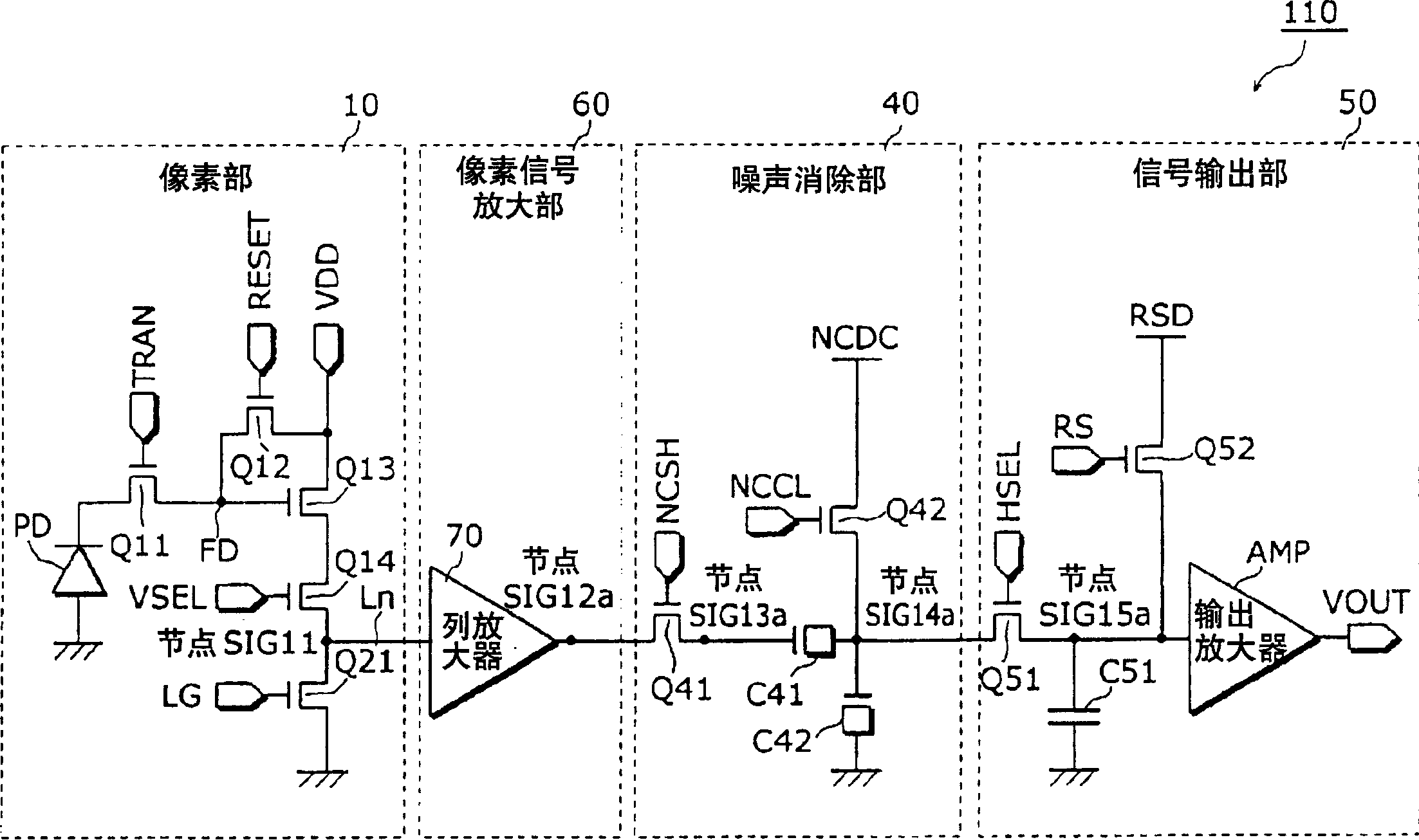
A solid state image pickup device 110 is provided with: a plurality of pixel units 10 that are arranged two-dimensionally and include a photoelectric conversion unit (photodiode PD) that converts light into a charge and an amplification unit (amplifier Q13) that converts the charge into a voltage and outputs it; a plurality of noise signal removal units (noise cancellation units 40) that are provided one for each column and remove noises contained in the voltage outputted from the amplifier Q31 of the pixel unit 10 belonging to the column; and a plurality of column amplification units (columnamplifiers 70) that amplify the voltage outputted from the amplifier Q13 of the pixel unit 10 and output the amplified voltage to the noise cancellation unit 40, and enables increase in sensitivity and reduction in noise with low power consumption.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Triple quadrupole mass analyzer
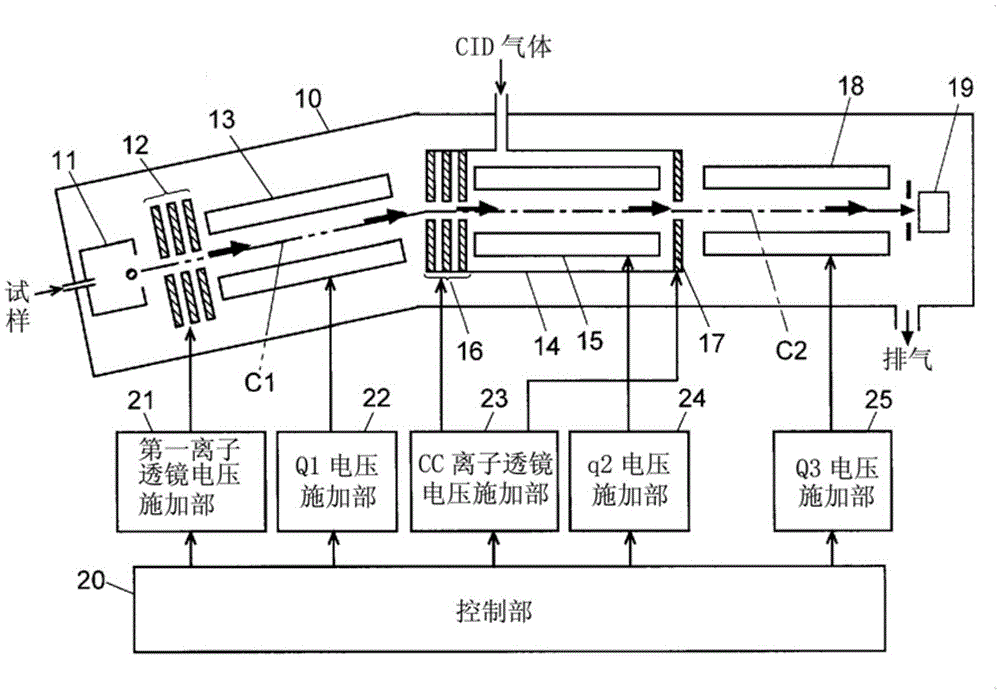
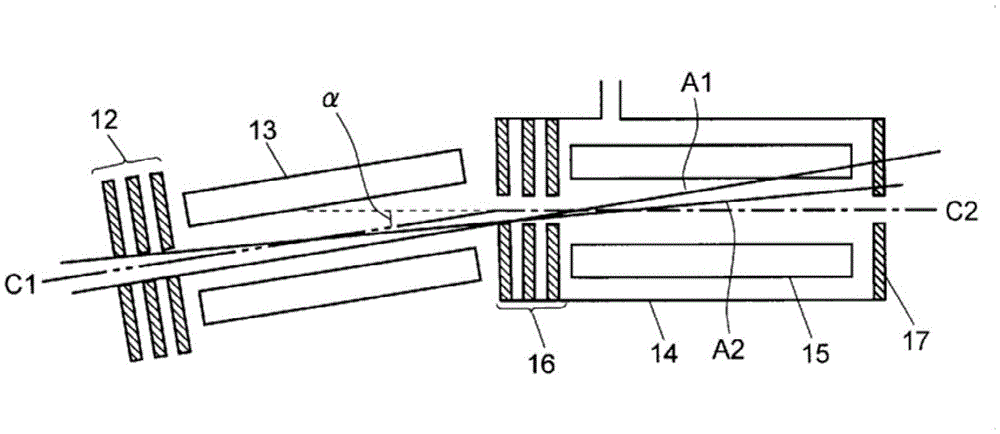
ActiveCN103650101BAvoid incidenceReduce noiseStability-of-path spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsStable stateOptical axis
Each element is configured such that the linear ion optical axis (C1) of the ion source (11), the first ion lens (12), and the front-stage quadrupole mass filter (13) are in contact with the ions in the collision unit (14) The linear ion beam axis (C2) of the guide (15) and the rear-stage quadrupole mass filter (18) obliquely intersects at a predetermined angle in the space between the front-stage quadrupole mass filter and the collision cell. The metastable He molecules (He*) generated by the ion source cannot reach the exit of the collision cell and are removed even if they pass through the front-stage quadrupole mass filter. On the other hand, the precursor ions passing through the front-stage quadrupole mass filter are bent along the zigzag ion optical axis under the action of the DC electric field formed by the ion lens (16) on the entrance side, and are efficiently introduced into the collision cell . He*, which causes noise, can be reliably removed without using an ion optical element with a special shape or structure.
Owner:SHIMADZU SEISAKUSHO CO LTD
Growth state measuring device for crop in cultivation
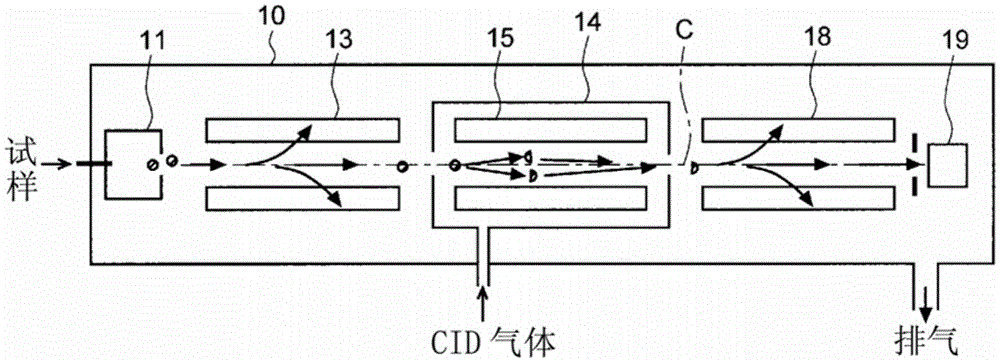
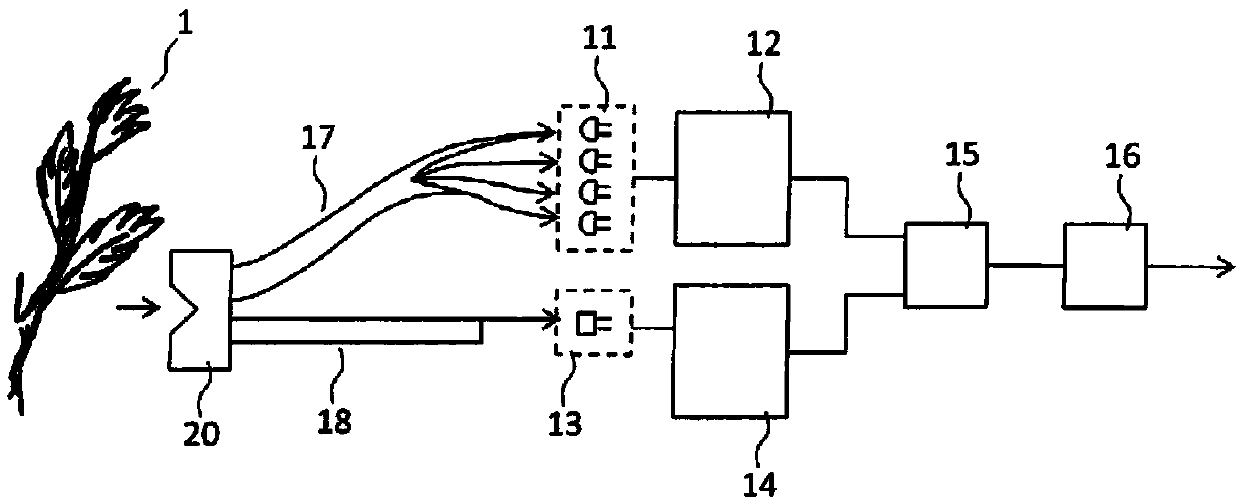
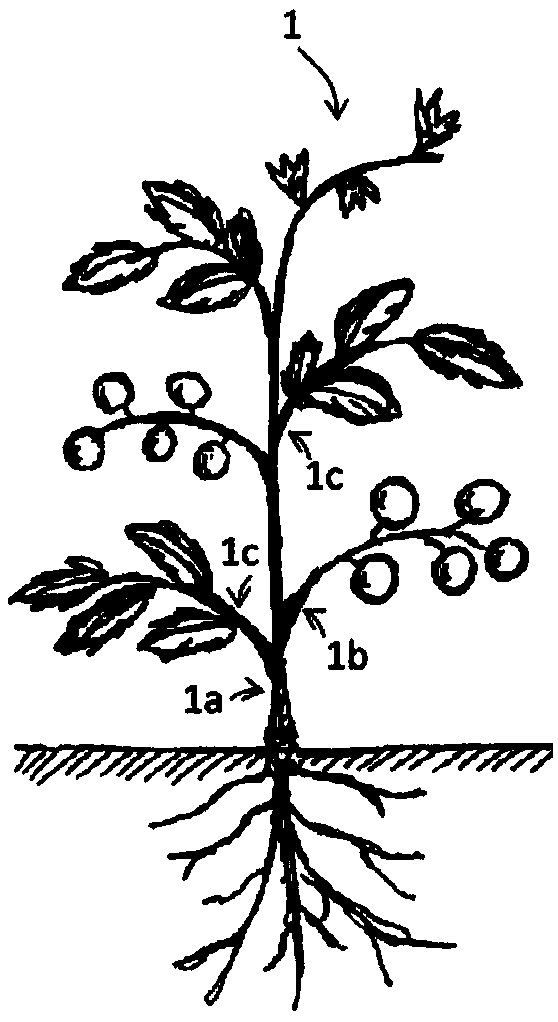
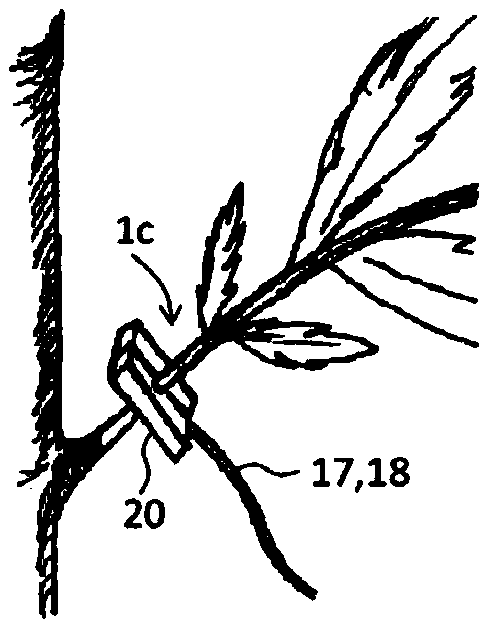
ActiveCN109932366AEliminate the effects ofImprove S/NMaterial analysis by optical meansPhysicsMeasurement site
A growth state measuring device for a crop in cultivation is provided, which can continuously measuring the nutritional state of the plant in a non-contact, non-destructive manner at a cultivation site such as open air or indoors with respect to the cultivated crop at the growth stage before harvesting. The growth state measuring device for the crop in the cultivation according to the present invention includes a light source (11), a light projection control unit (12), a light receiving unit (13), a light receiving control unit (14), and a calculation unit (15). The plant (1) is a crop in thecultivation stage before the harvesting. Measurement sites (1a), (1b), (1c) are any one of a stem, a fruit handle, and a petiole, and the living body holding structure is attached to a stem, a fruit handle or a petiole. In the calculation unit (15), the arithmetic processing is performed using the difference between a light-receiving signal, at the time of light projection, obtained by the detection light at the time of irradiation by the light source (11) and a light-receiving signal, while the light projection is not performed, obtained by the detection light before or after irradiation timing.
Owner:ORGANIC NICO
Information reproduction method and information reproduction device adopting same method
InactiveCN1540658ASuppress nonlinear componentsImprove S/NModification of read/write signalsCode conversionTarget signalBit array
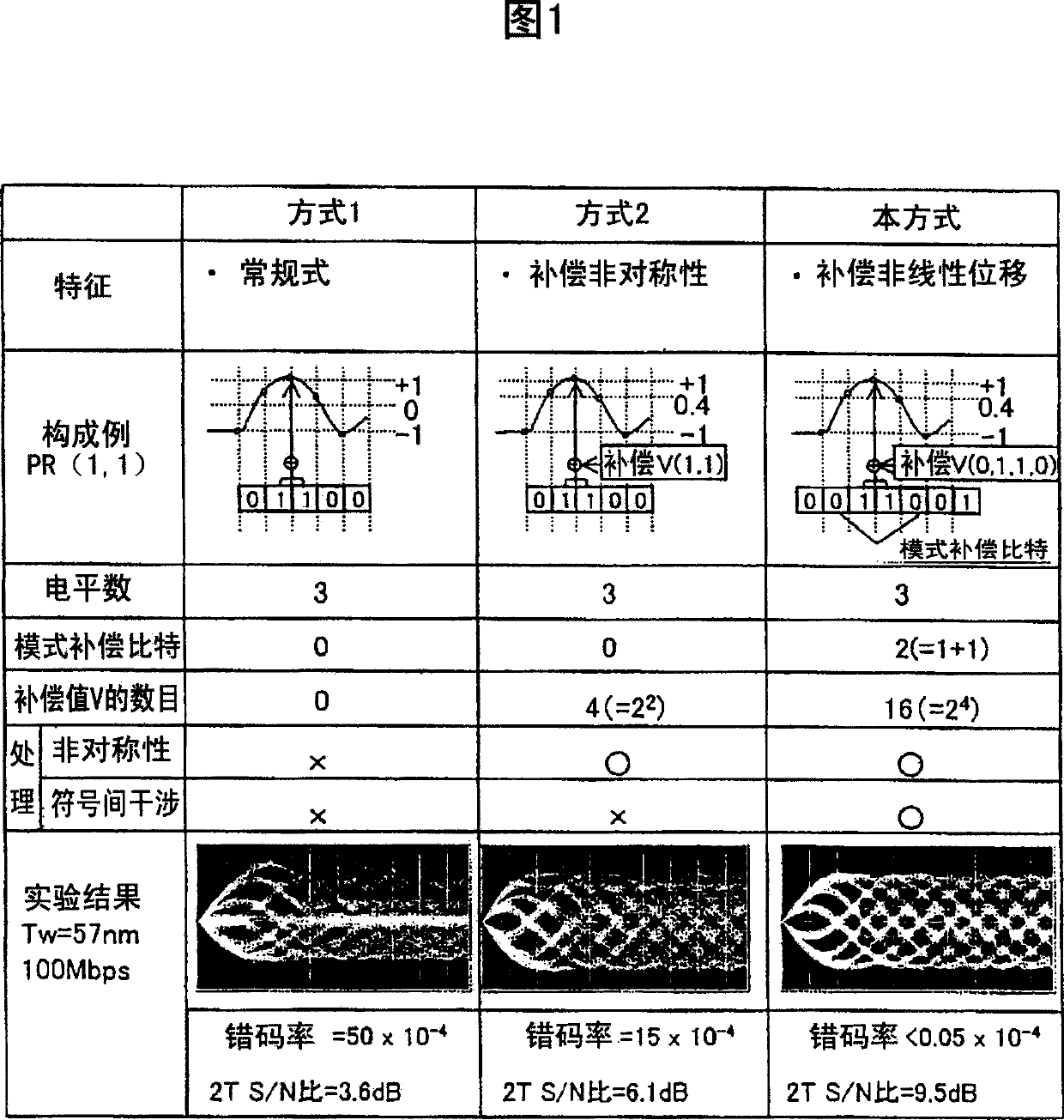
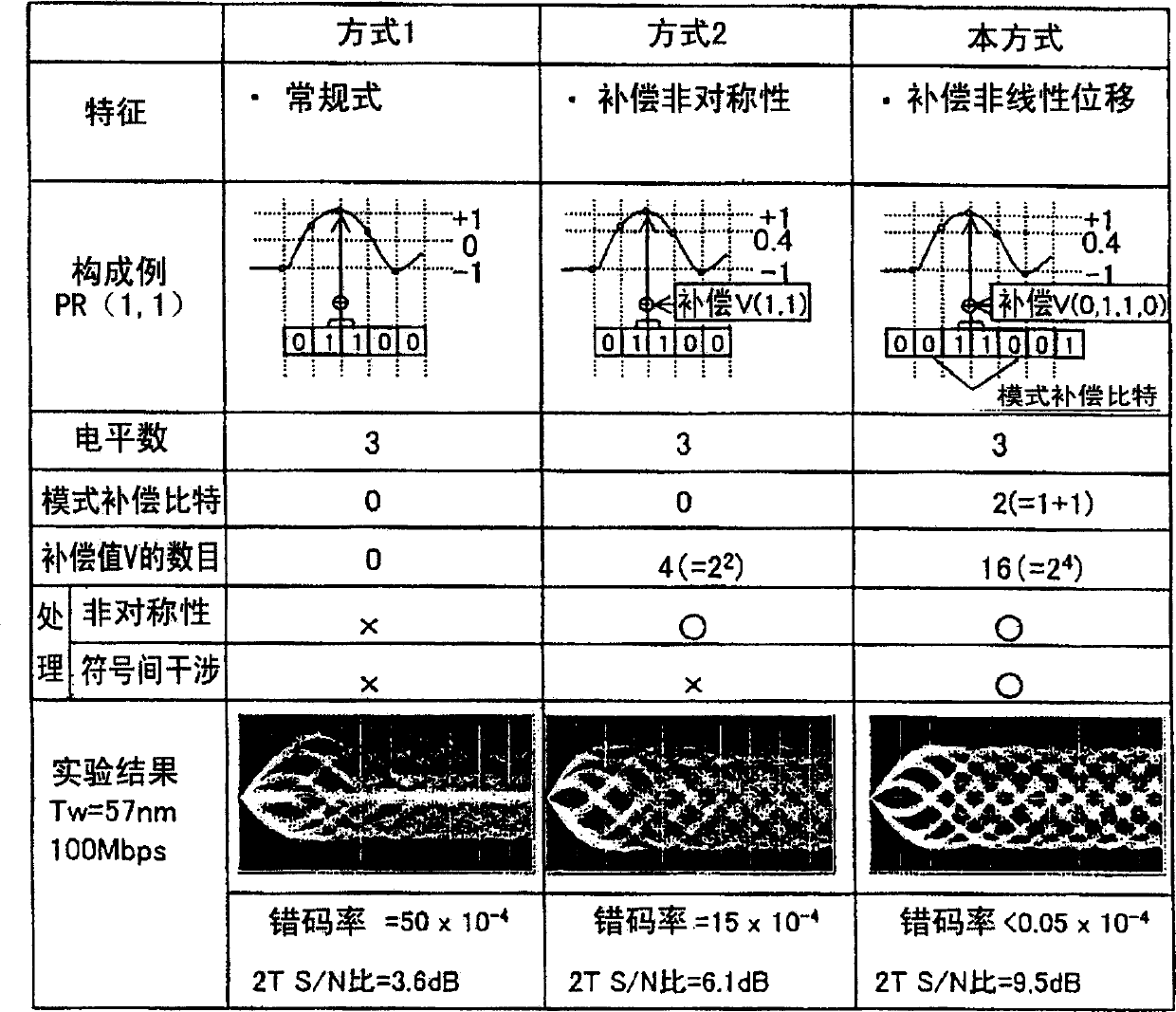
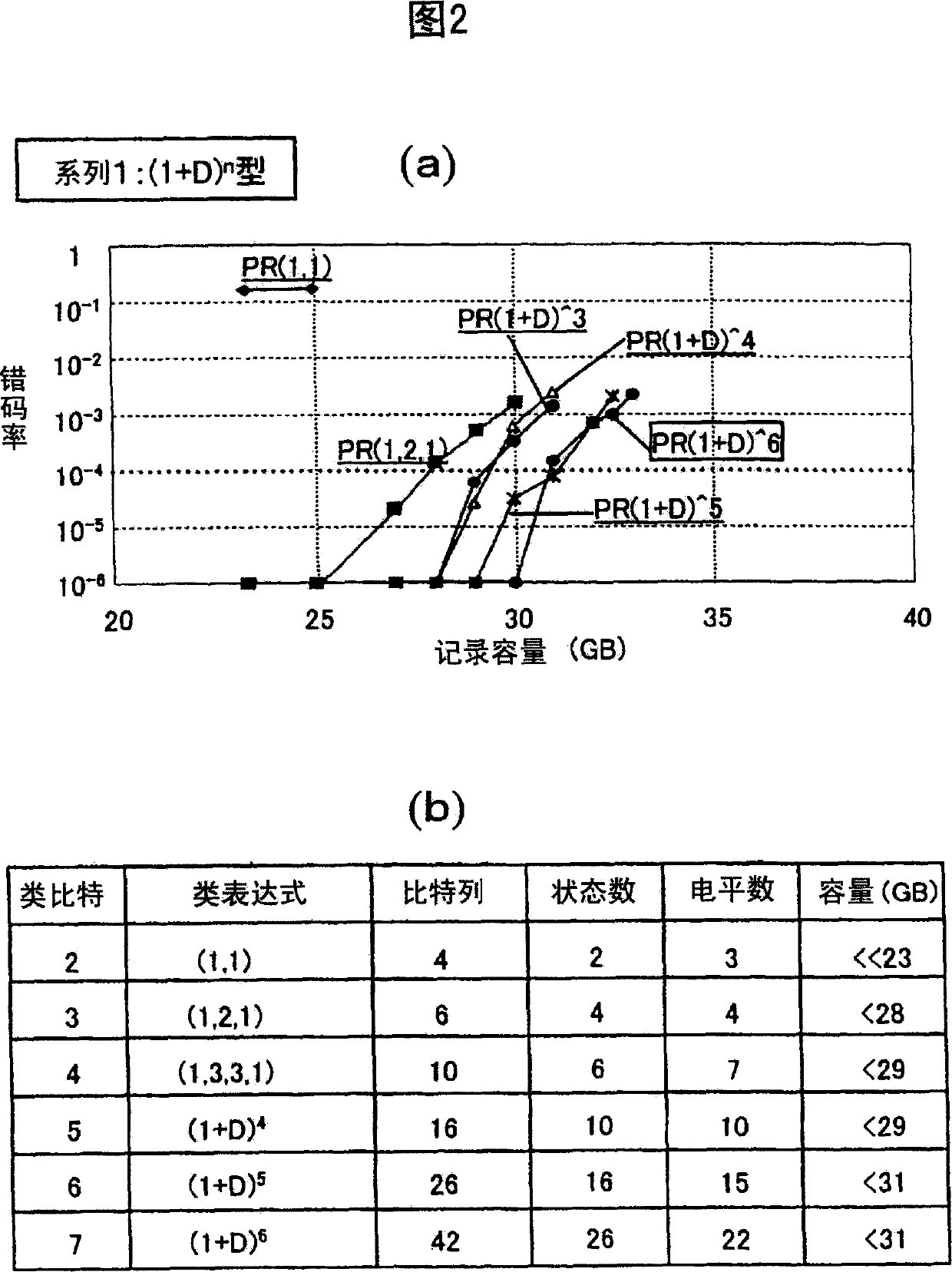
Disclosed herewith is an information reproducing method for realizing significant expansion of disk capacity and processing signals having different minimum run lengths, as well as an optical disk drive that uses the method. To achieve the above objects, a PRML method is used. According to the method, a compensation value is added to an initial target value decided by a convolution operation of NN bits according to a bit array consisting of N bits (N>NN) to obtain a new target value, which is then compared with each of reproduced signals sequentially to select a bit array in which the error between the reproduced signal and the target signal is minimized most likely, then the selected bit array is binarized.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
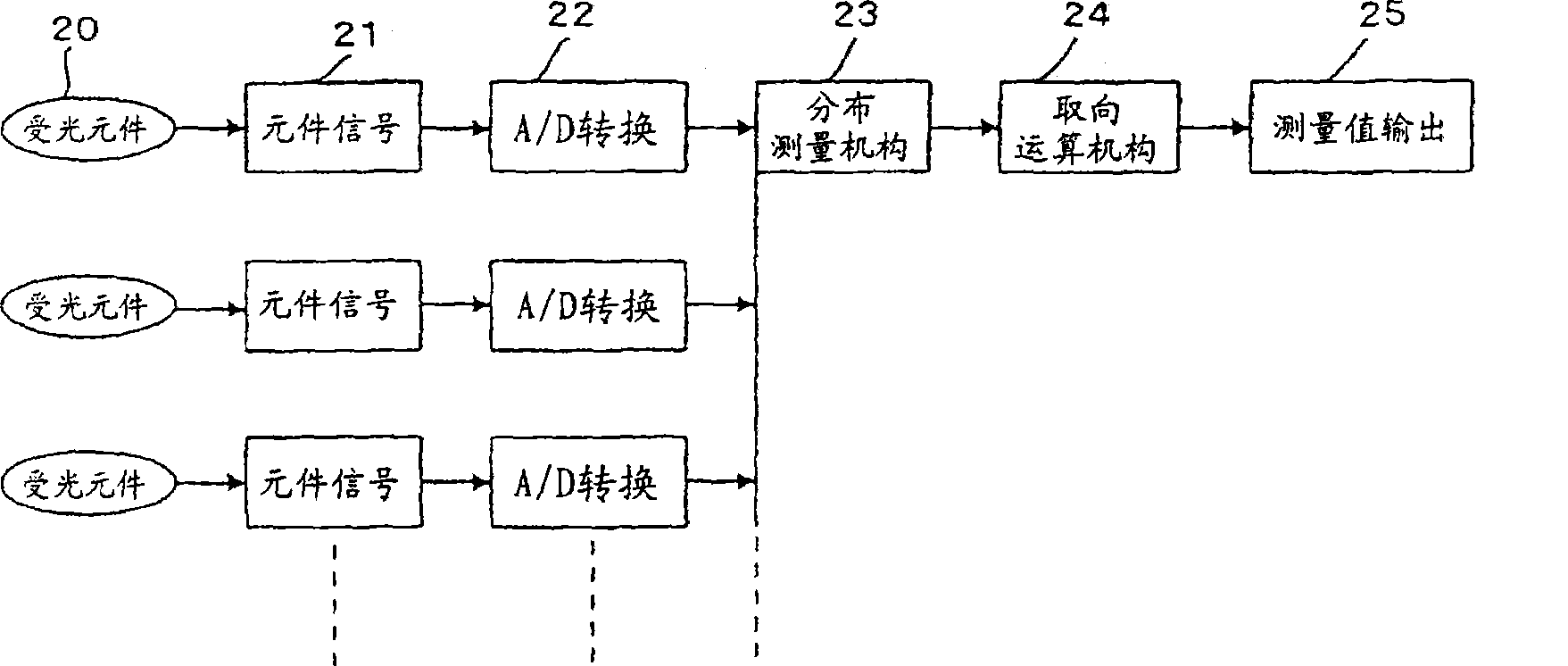
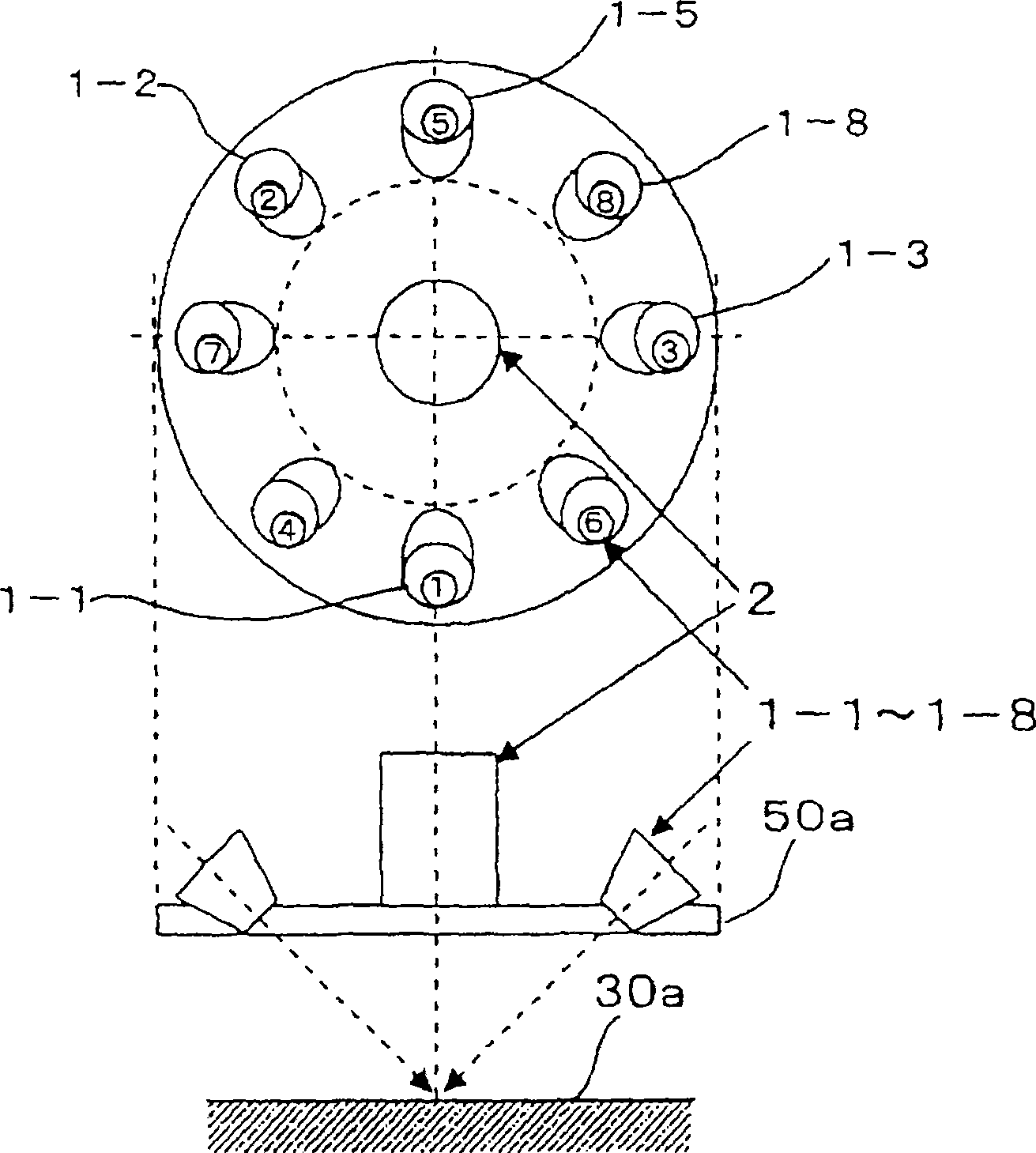
Orientation analysis meter
ActiveCN100507520CGood orientationQuick measurementScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansOrientation analysisPlastic film
An orientation analyzer, which can quickly measure the fiber orientation of paper, the molecular orientation of film, or the orientation of fillers in plastics, reducing the cost and volume of parts. The orientation analyzer of the present invention measures the object to be measured based on a light-emitting assembly that irradiates light to the object to be measured, a light-receiving assembly that receives reflected light reflected by the object to be measured, and a signal from the light-receiving assembly. Orientation of objects, wherein multiple light emitting components are arranged around the light receiving component.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com