Method of biomass processing
A biomass treatment and biomass technology, applied in the direction of biological sludge treatment, waste treatment, biological organic part treatment, etc., to achieve the effect of cost reduction and environmental protection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
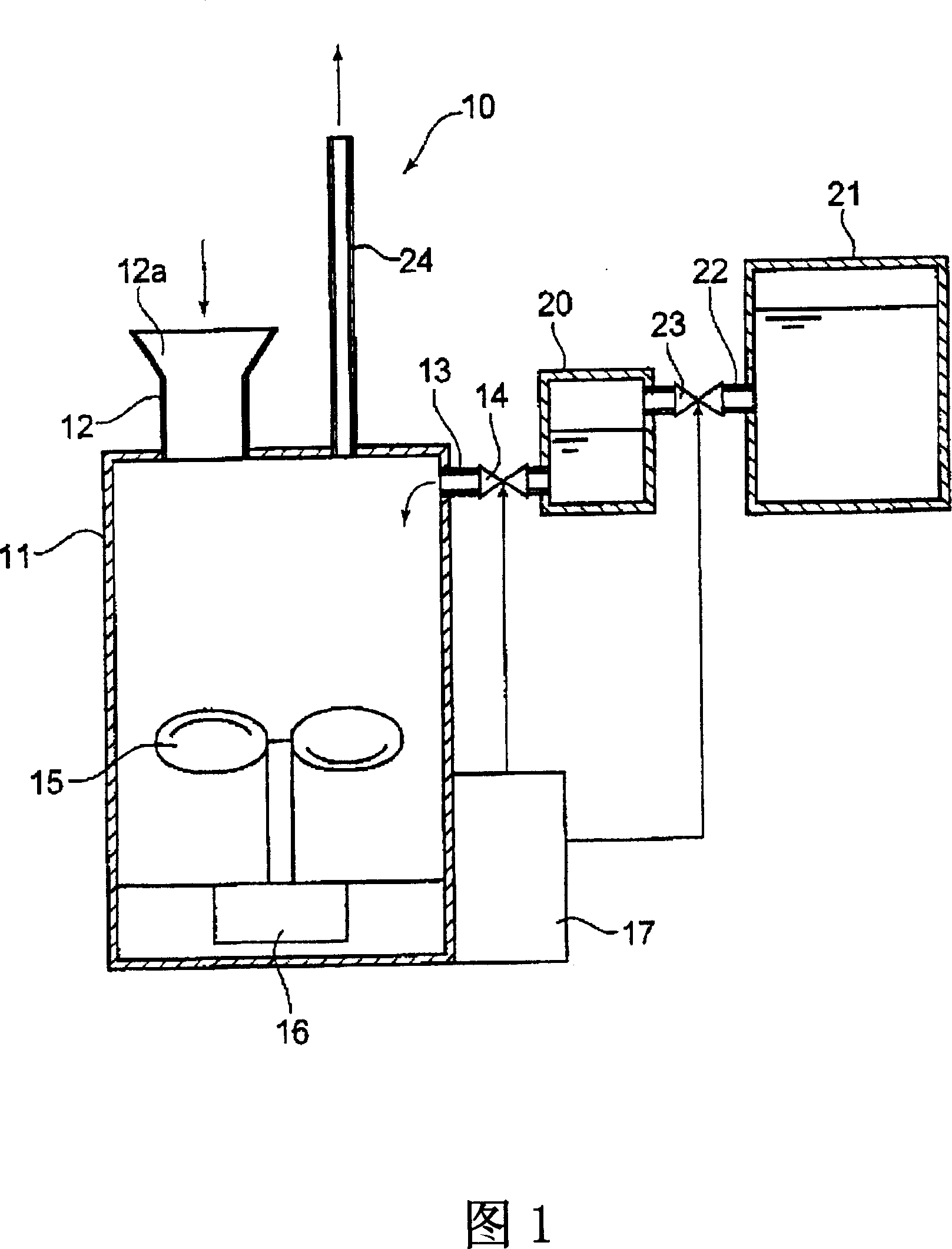
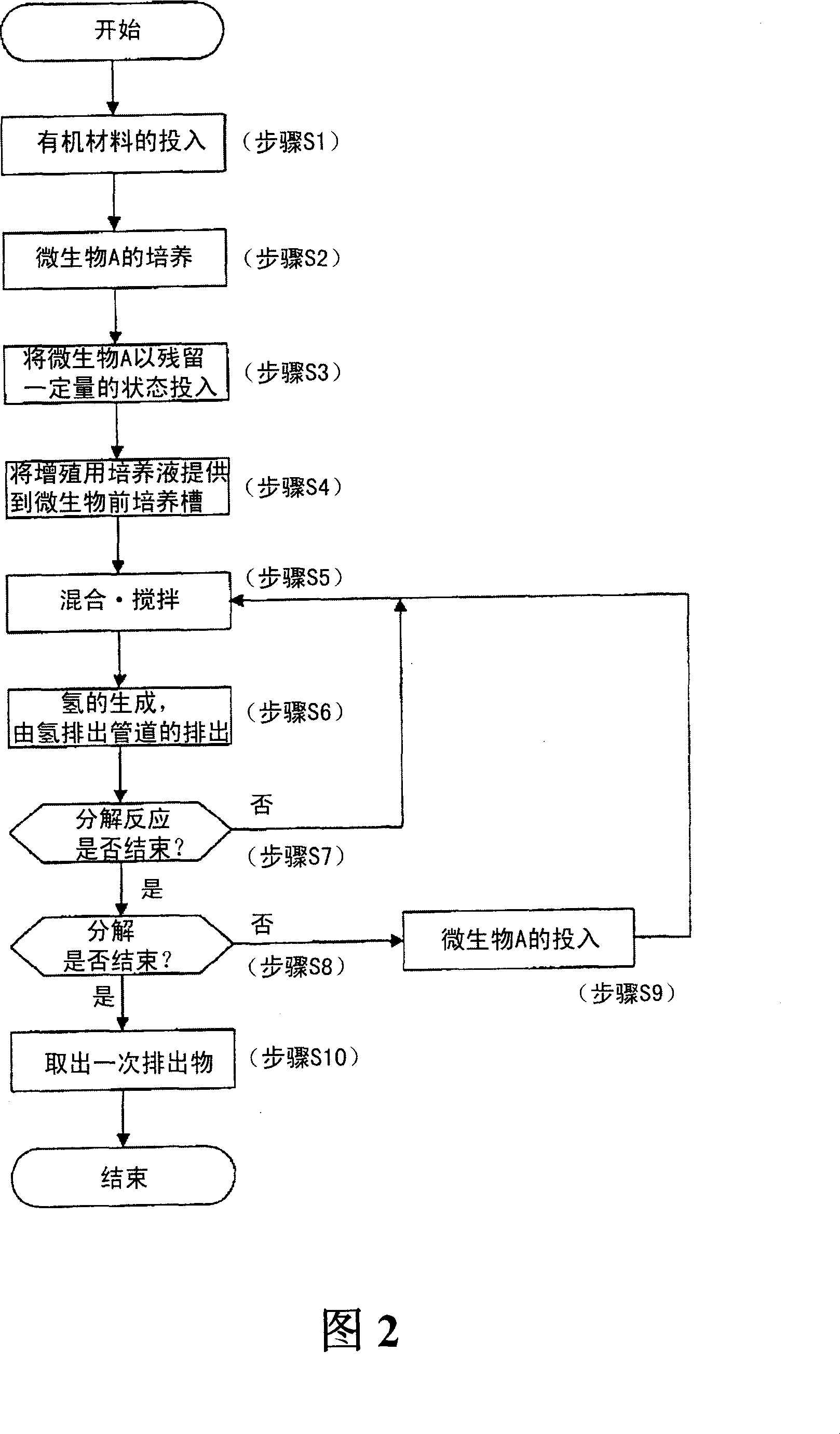
[0080] I. Hydrogen fermentation treatment
[0081] (1) Pre-cultivation of hydrogen-producing bacteria
[0082] A 300 ml Erlenmeyer flask was inoculated with 100 ml of PY medium supplemented with 0.1% glucose and hydrogen-producing bacteria, and cultured overnight in an anaerobic glove box (manufactured by BMW, USA, type 1024) at 37°C. In addition, the composition of PY medium is 10g peptone (peptone), 5g yeast (yeast extract), 500mg L-cysteine HCl, 8mg CaCl, 8mg MgSO in 1L of water 4 , 40mg KH 2 PO 4 , 400mg NaHCO 3 , and 80mg NaCl, no carbon source.
[0083] (2) Hydrogen fermentation method
[0084] In a 3000ml Erlenmeyer flask, add 1400ml of PY medium containing 7.5g of starch or glucose as a source of hydrogen generation and 100ml of a pre-culture solution of hydrogen-generating bacteria. The insertion port of FC-10) and the pH adjustment NaOH liquid inflow port were closed with rubber plugs, and placed outside the anaerobic glove box. Keep warm in a constant tempe...
Embodiment 1
[0097] Embodiment one: reclaim hydrogen and biogas from biomass (starch)
[0098] (1) Hydrogen fermentation treatment of starch (starch)
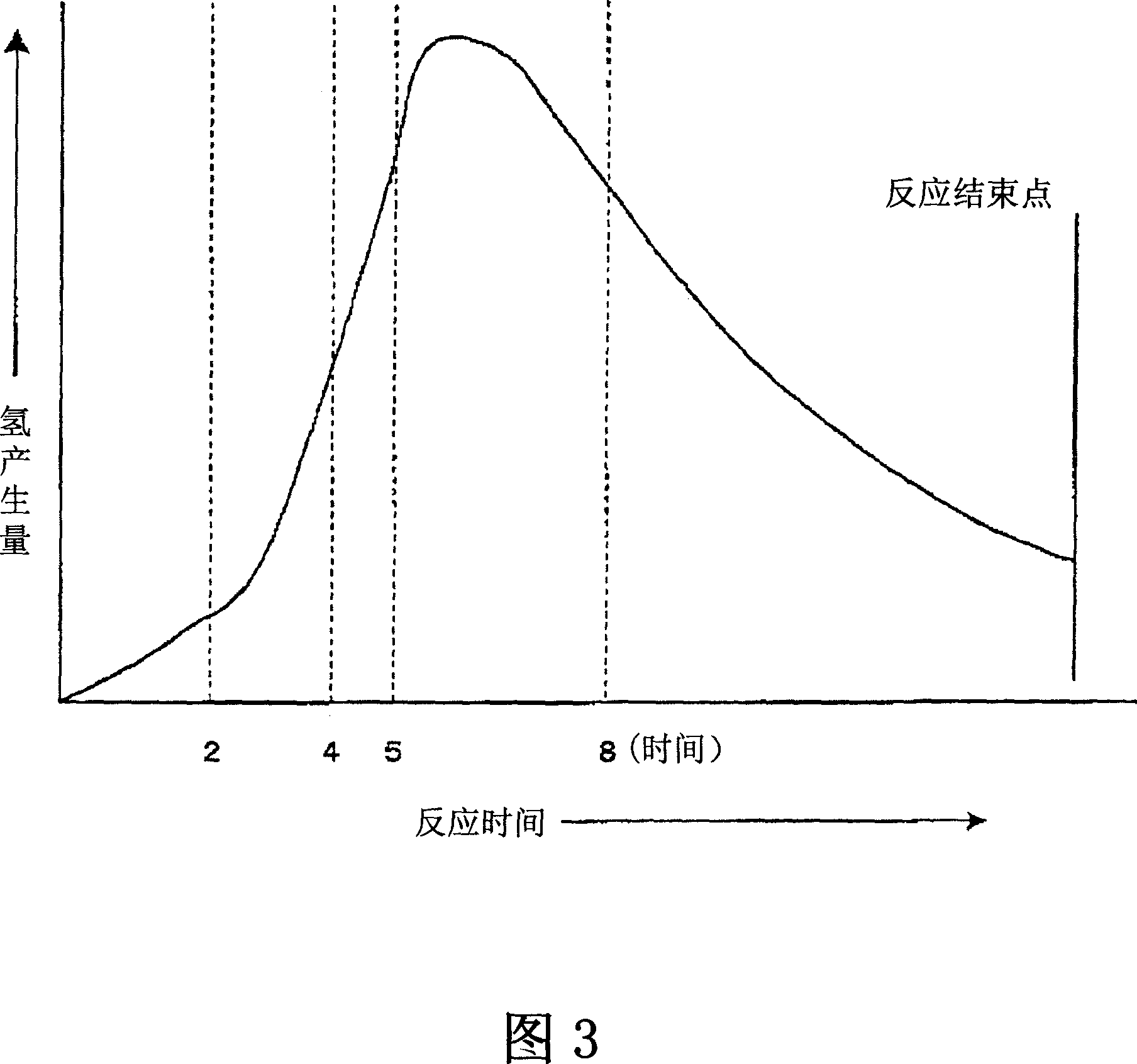
[0099] Add 1400 ml of PY medium containing 7.5 g of starch and 100 ml of pre-culture bacterial liquid of hydrogen-producing bacteria (Clostridium beijerinkii (Clostridium beijerinkii) AM21B strain) into a 3000 ml Erlenmeyer flask, and start culturing in a constant temperature water tank at 37°C. Foaming was observed after two to three hours from the start of the heat preservation, and the volume of gas generated reached the highest around seven to eight hours. It takes tens of hours for the generation of gas to end. A total of 3750ml of hydrogen was produced. Fermentation liquid (waste liquid) which is the culture liquid after hydrogen fermentation was poured into the biogas fermentation tank in the unprocessed state.
[0100] (2) Biogas fermentation treatment by starch fermentation liquid
[0101] The fermented liquid (waste liquid) af...
Embodiment 2
[0108] Embodiment two: reclaim hydrogen and biogas from biomass (glucose)
[0109] (1) Hydrogen fermentation treatment of glucose
[0110] Dilute the PY medium with ion-exchanged water to 5 times the diluted PY medium, 1400ml of the culture solution after dissolving 7.5g of glucose, and 100ml of the pre-culture solution of hydrogen-generating bacteria (Clostridium beijerinkii (Clostridium beijerinkii) AM21B strain) were added In a 3000ml Erlenmeyer flask, culture was started in a constant temperature water tank at 37°C. After about two hours from the start of heat preservation, bubbles are generated, the volume of gas generated reaches the highest in about seven hours, and the generation of gas ends in more than ten hours. The total amount of hydrogen produced was 5750ml. The fermented liquid (waste liquid) after the hydrogen fermentation was poured into the biogas fermentation tank in an untreated state.
[0111] (2) Biogas fermentation treatment by glucose fermented liqui...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com