Succinic acid - producing bacterium and process for producing succinic acid
A technology for the production of succinic acid and bacteria, applied in the field of fermentation industry, can solve the problems of unknown contribution of succinic acid-biosynthetic system, lack of gene expression analysis of pyruvate oxidase, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
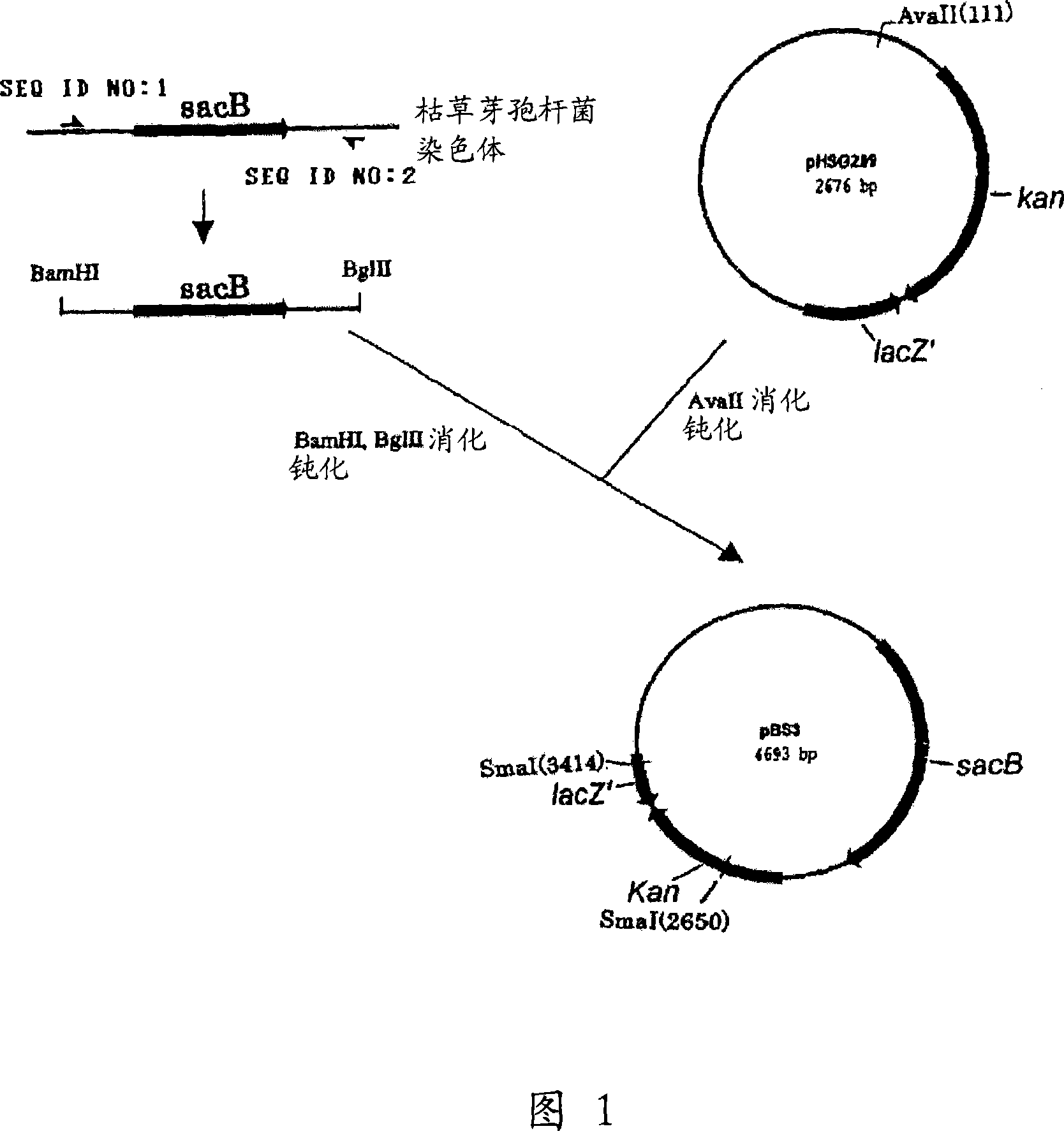
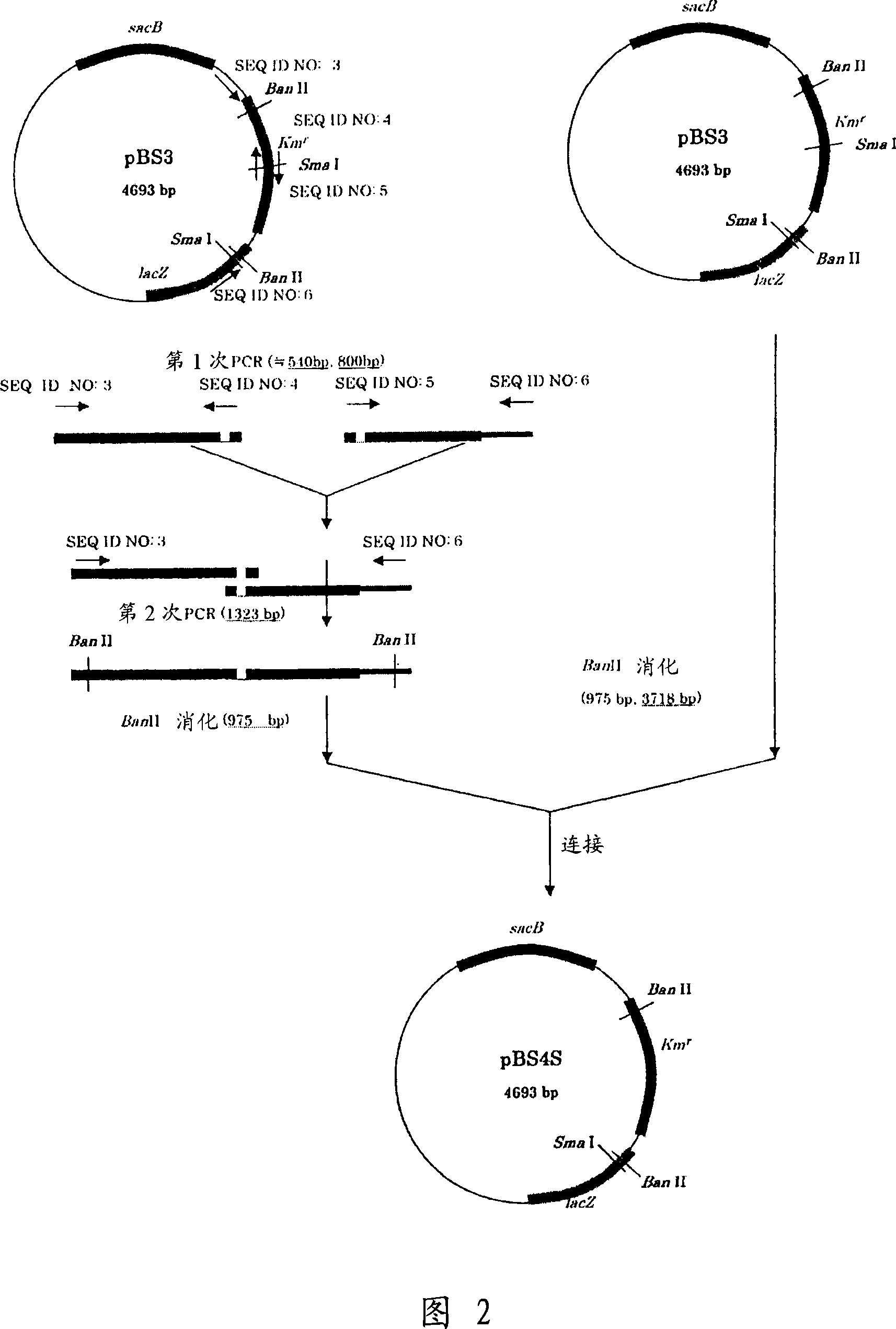
[0149] Construction of a destruction vector carrying the sacB gene
[0150] (A) Construction of pBS3
[0151] The sacB gene was obtained by PCR using chromosomal DNA of Bacillus subtilis as a template and SEQ ID NOS: 1 and 2 as primers. PCR was performed using LA Taq (Takara Bio Inc.) in such a manner that one cycle of incubation at 94°C for 5 minutes, followed by a cycle of denaturation at 94°C for 30 seconds, annealing at 49°C for 30 seconds and extension at 72°C for 2 minutes was repeated 25 times. The PCR product thus obtained was purified by a conventional method, then digested with BglII and BamHI, and blunt-ended. The fragment was inserted into the site of pHSG299 which had been digested with AvaII and made blunt-ended. Competent cells of Escherichia coli JM109 (Takara Bio Inc.) were used for transformation with this DNA, and the transformed cells were plated on LB medium containing 25 μg / ml kanamycin (hereinafter, abbreviated as Km) , and incubated overnight. Then...
Embodiment 2
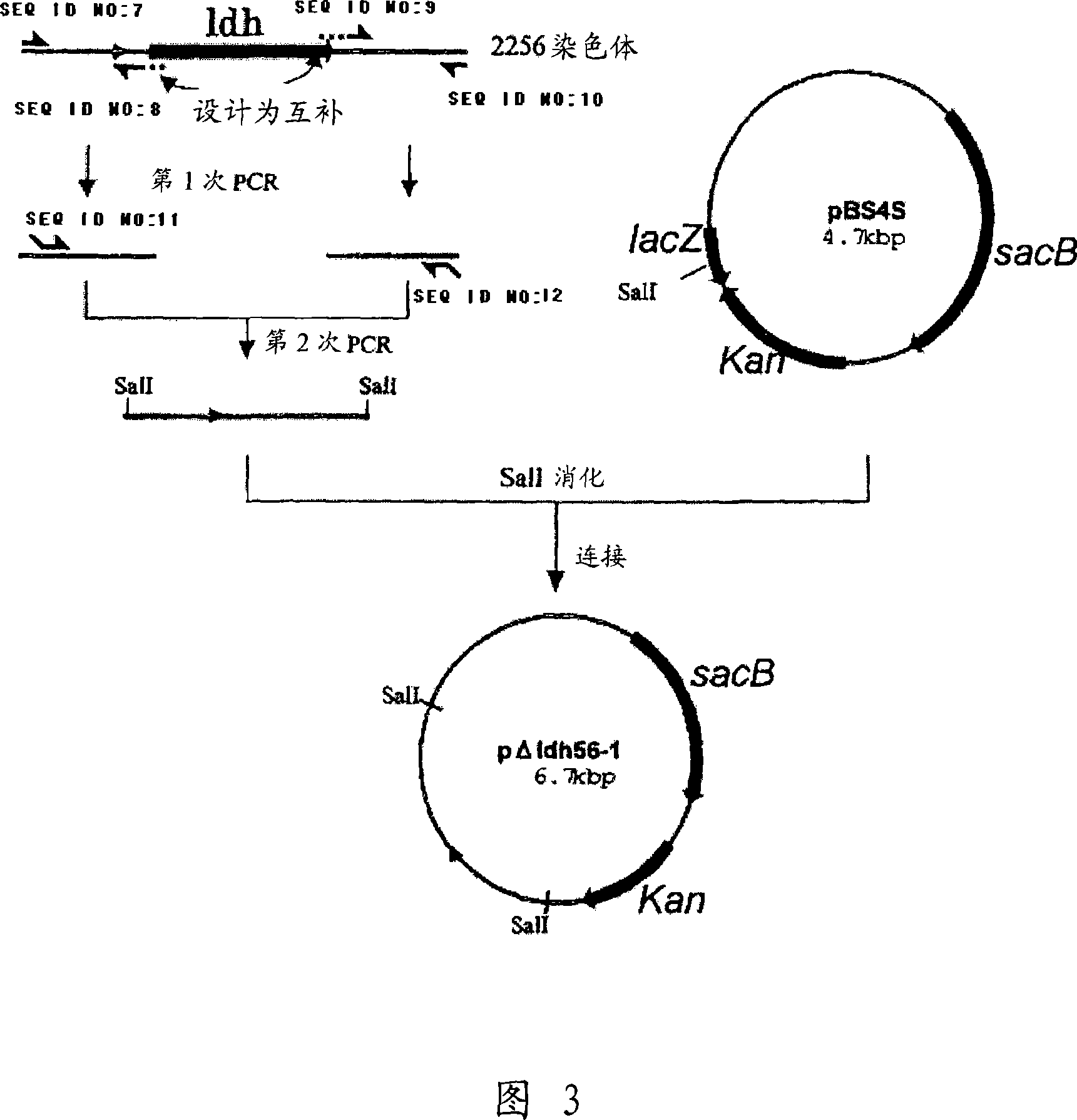
[0156]
[0157] (A) Cloning of the fragment used to disrupt the lactate dehydrogenase gene
[0158]Using synthetic DNAs designed according to the nucleotide sequence (Ncgl2810 of GenBank Database accession number NC_003450) of the gene of Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032 (GenBank Database accession number NC_003450) that has been disclosed as primers, obtained from its ORF by exchange PCR A fragment of the lactate dehydrogenase gene (hereinafter, abbreviated as ldh gene) of the Brevibacterium lactofermentum 2256 strain which was deleted. That is, PCR was performed by a conventional method using chromosomal DNA of Brevibacterium lactofermentum 2256 strain as a template and synthetic DNAs SEQ ID NOS: 7 and 8 as primers, thereby obtaining an amplified product of the N-terminal region of the ldh gene. On the other hand, in order to obtain the amplification product of the C-terminal region of the ldh gene, PCR was performed by a conventional method using the genomic DNA of th...
Embodiment 3
[0166]
[0167] (A) Cloning of a fragment disrupting the pyruvate oxidase gene
[0168] Using synthetic DNAs designed according to the nucleotide sequence (NCgl2521 of GenBank Database accession number NC_003450) of the gene of Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032 that has been published as primers, the Brevibacterium lactofermentum 2256 bacterial strain that its ORF has been deleted is obtained by exchange PCR Fragment of pyruvate oxidase gene (hereinafter, simply referred to as poxB gene). That is, PCR was performed using the genomic DNA of the Brevibacterium lactofermentum 2256 strain as a template and the synthesized DNAs of SEQ ID NOS: 29 and 30 as primers, thereby obtaining an amplified product of the N-terminal region of the poxB gene.
[0169] On the other hand, in order to obtain the amplification product of the C-terminal region of the poxB gene, PCR was performed using the genomic DNA of Brevibacterium lactofermentum 2256 as a template and the synthetic DNAs SEQ I...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com