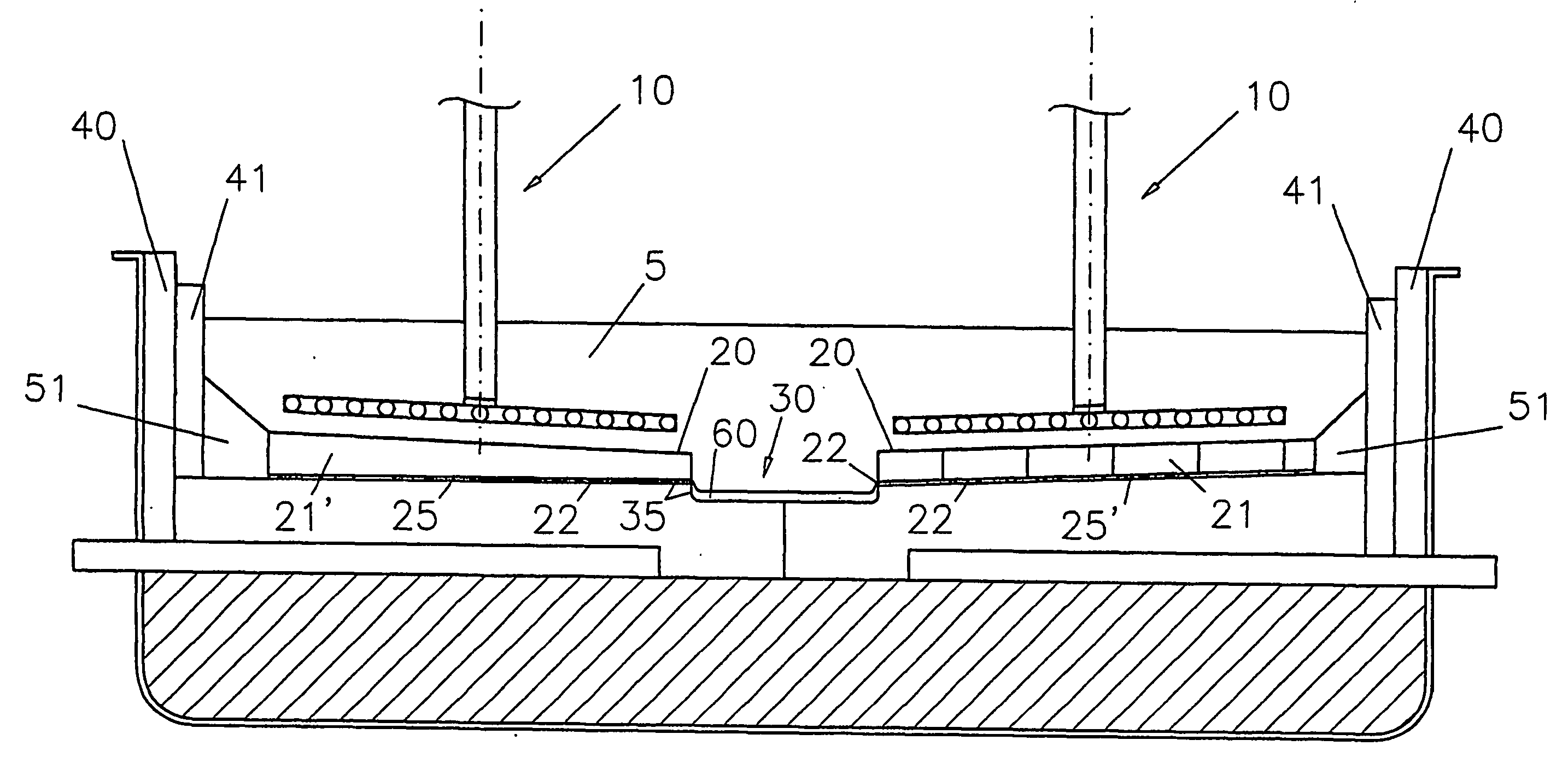
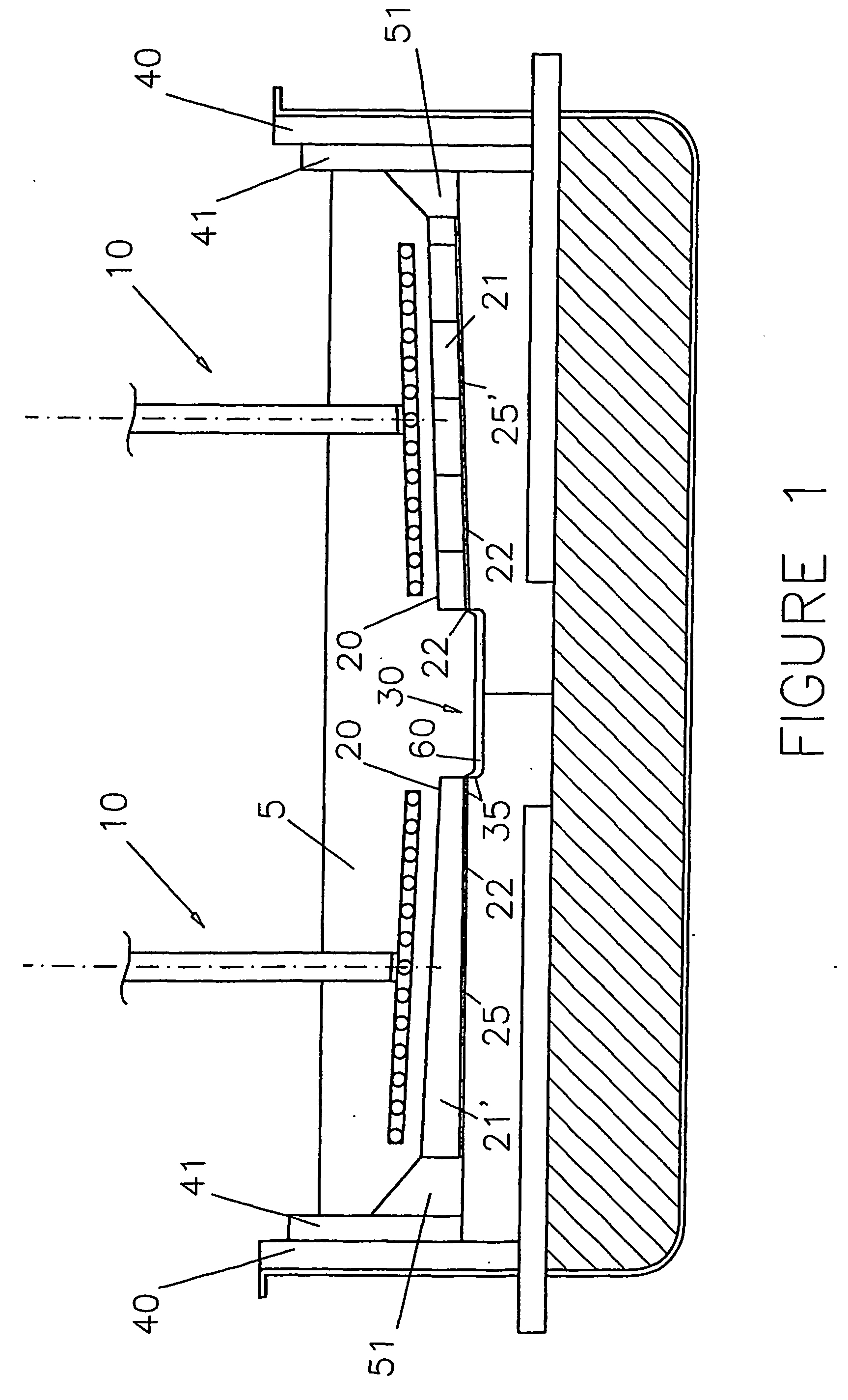
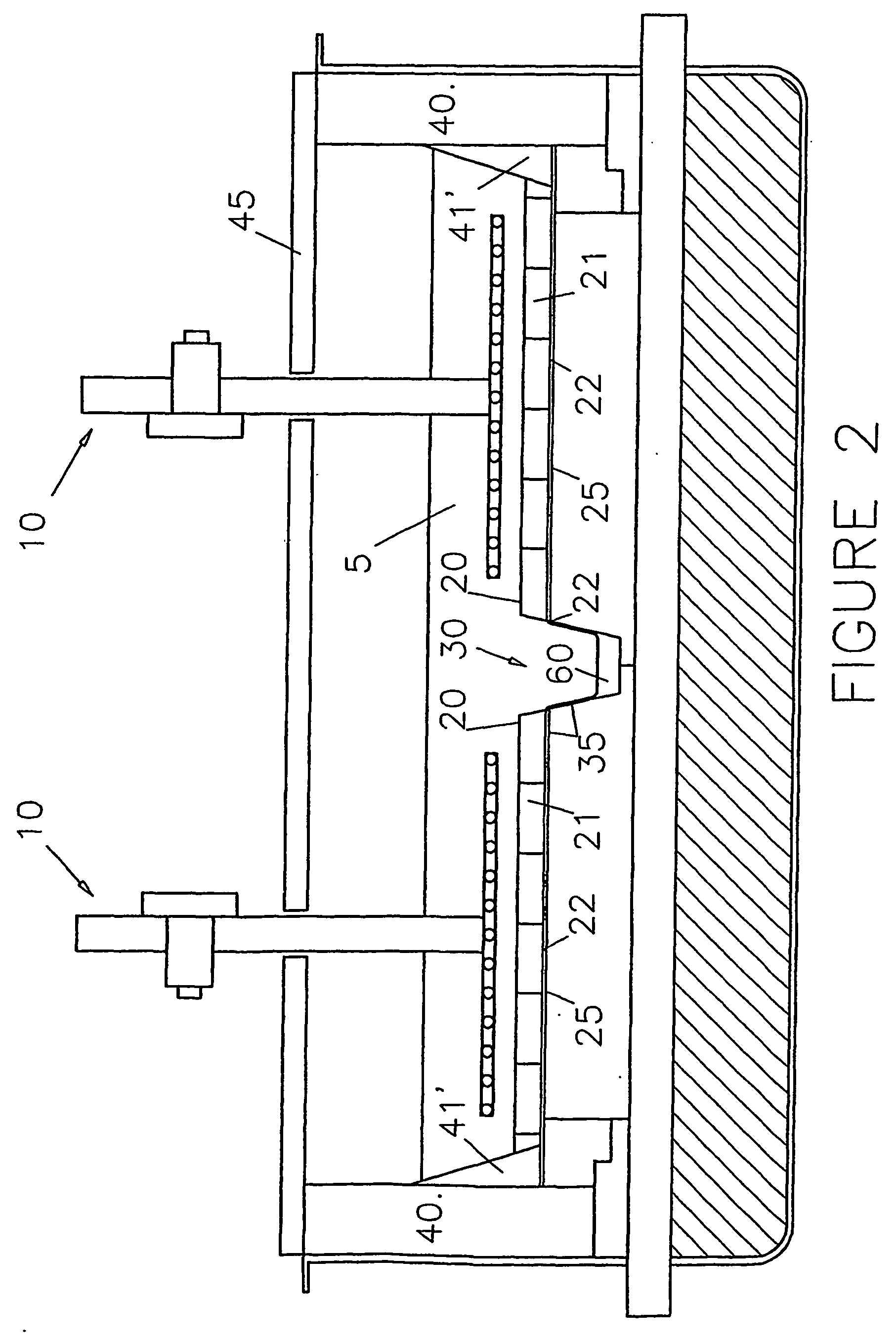
Aluminium-wettable porous ceramic material
a porous ceramic material and wettable technology, applied in the direction of isotope separation, dispersed particle separation, chemistry apparatus and processes, etc., can solve the problems of many difficulties encountered in the production of refractory boride coatings, and achieve energy saving, reduced cell voltage, and reduced cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
[0077] An aluminium-wettable ceramic structure was made of a mixture of material inert and resistant to molten aluminium, i.e. alumina and titania, and aluminium-wettable material, i.e. copper oxide. The ceramic structure was prepared by coating a polyurethane foam with a slurry of ceramic particles followed by a heat treatment.
[0078] The slurry of ceramic material consisted of a suspension of 40 g particulate Al.sub.2O.sub.3 with an average particle size of 10 to 20 micron, 2.5 g of particulate CuO with a particle size of less than about 45 micron, 2.5 g of particulate TiO.sub.2 with a particle size of less than about 45 micron in a colloidal alumina carrier consisting of 93 g deionised water and 6.6 g colloidal alumina particles with a colloidal particle size of about 10 to 30 nanometer.
[0079] A polyurethane foam having 10 to 20 pores per inch (equivalent to about 4 to 8 pores per centimetre) was dipped into the slurry and dried in air at 400 to 50.degree. C. for 20 to 30 minutes....
example 3
[0084] An aluminium-wettable openly porous ceramic structure as in Example 1 was tested as cathodic material for aluminium production.
[0085] The aluminium-wettable ceramic structure was placed on the bottom of a graphite receptacle having an inner diameter of 85 mm. The structure was covered with 120 g aluminium. The receptacle and its content was heated at a rate of 120.degree. C. / hour. At a temperature of 700.degree. C., the aluminium had formed an aluminium pool on which the ceramic structure was floating. The temperature was further increased to about 850.degree. C. and then maintained for 4 hours so that the molten aluminium completely aluminised and wet the ceramic structure.
[0086] After aluminisation, an amount of 1.5 kg electrolytic molten bath consisting of 68 weight % cryolite, 28 weight % aluminium fluoride and 4 weight % dissolved alumina was poured into the receptacle on top of the aluminium pool and aluminium-wetted ceramic structure. A carbon anode was dipped into the...
example 4
[0089] An openly porous silicon carbide structure (30 pores per inch which is equivalent to about 12 pores per centimetre) was rendered aluminium-wettable by coating it with a slurry-applied layer.
[0090] The slurry consisted of 75 g surface oxidised iron particles (-325 mesh), 75 g Silica sol Nyacol 830 (a milky aqueous liquid containing 32 weight % colloidal silicon hydroxide that is converted into silica upon heat treatment) and 0.35 g of an aqueous solution containing 15% PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) that was used to adjust the viscosity of the slurry.
[0091] The openly porous structure was dipped onto the slurry and then dried for 30 min. at 60.degree. C. The impregnated porous structure contained 0.278 g / cm.sup.3 of dried slurry including 0.214 g / cM.sup.3 surface oxidised iron particles.
[0092] The resulting structure was aluminium-wettable and suitable to be wetted by aluminium before use or in-situ when used for example as a cathode.
[0093] The aluminium-wettable porous structure was...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com