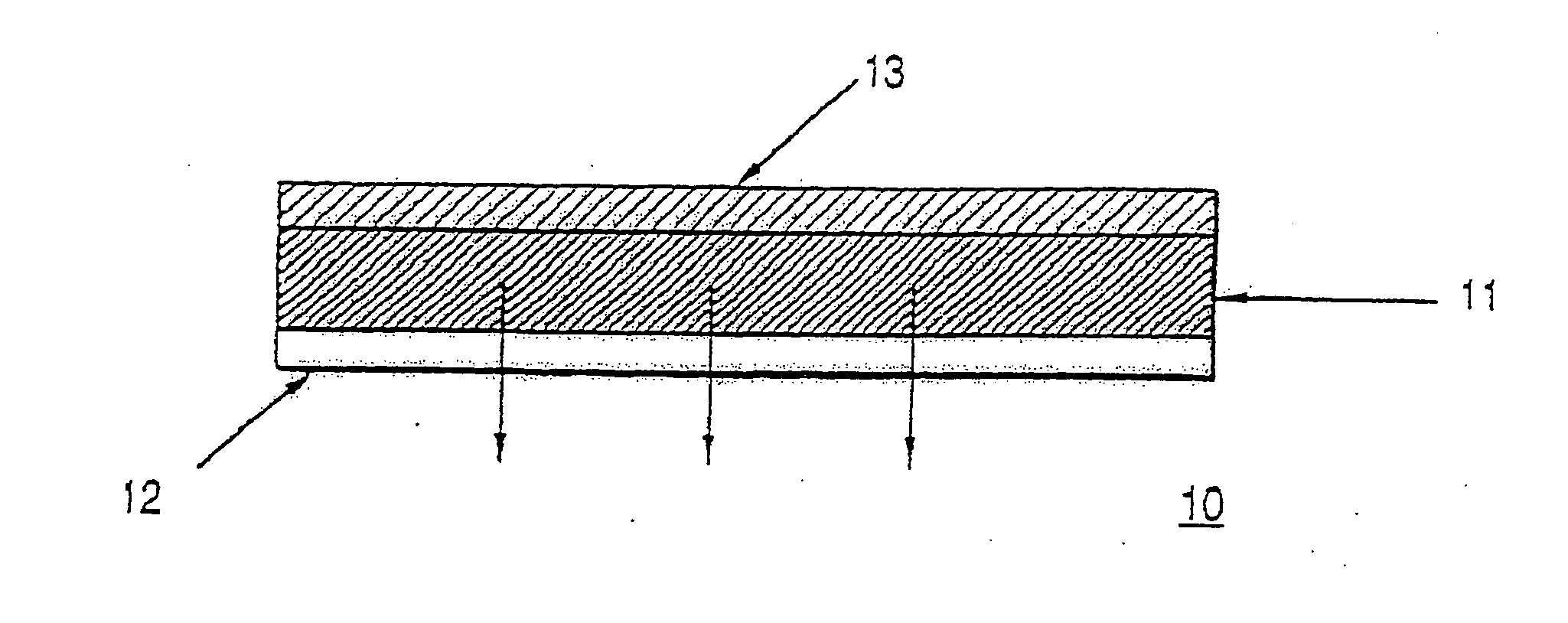
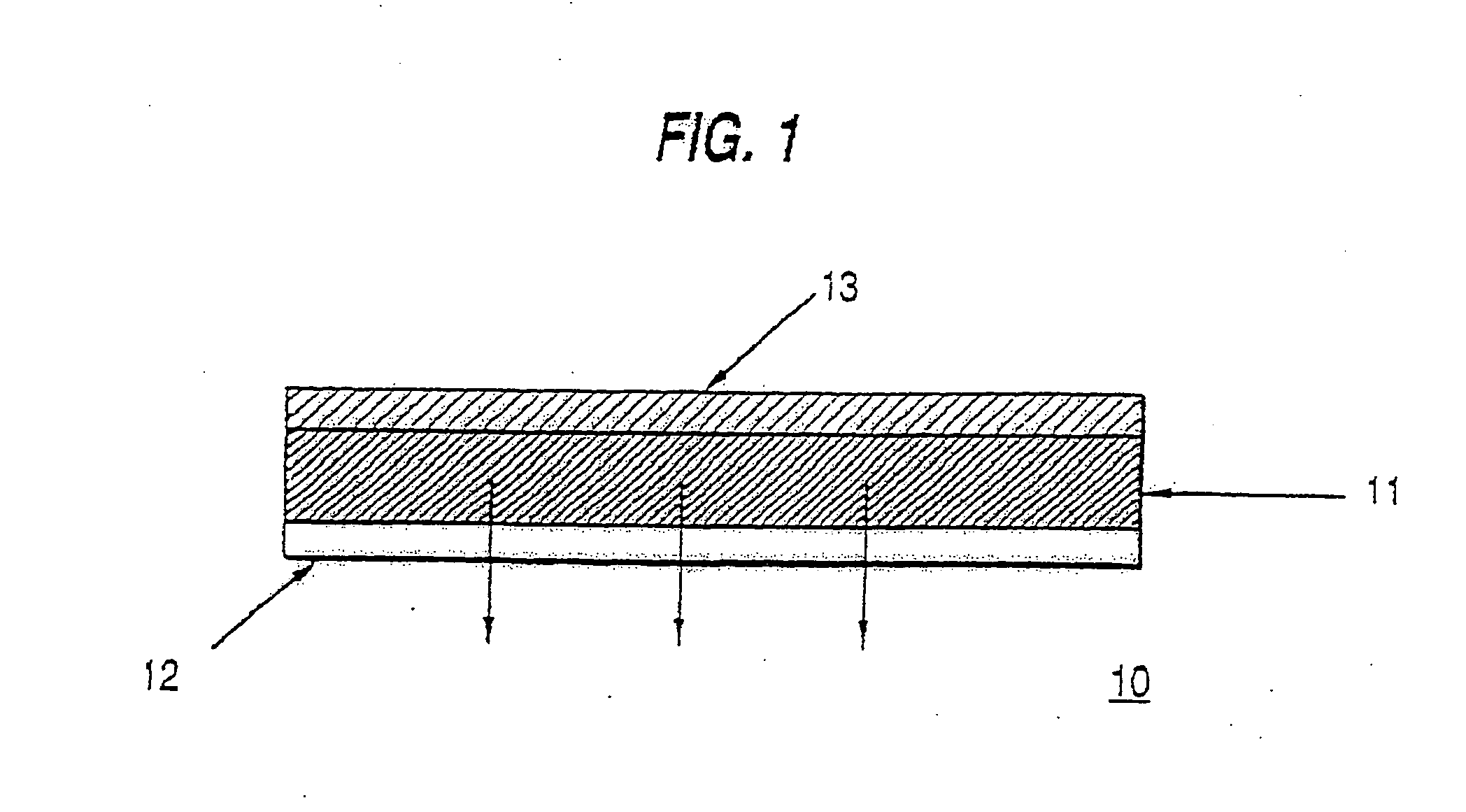
Composition and method for controlling drug delivery from silicone adhesive blends
a technology of silicone adhesive and blend, which is applied in the direction of pharmaceutical delivery mechanism, bandage, sheet delivery, etc., can solve the problems of increased shear of pressure-sensitive adhesive materials, limited commercial application of transdermal drug delivery systems, and loss of cohesivity and adhesion,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
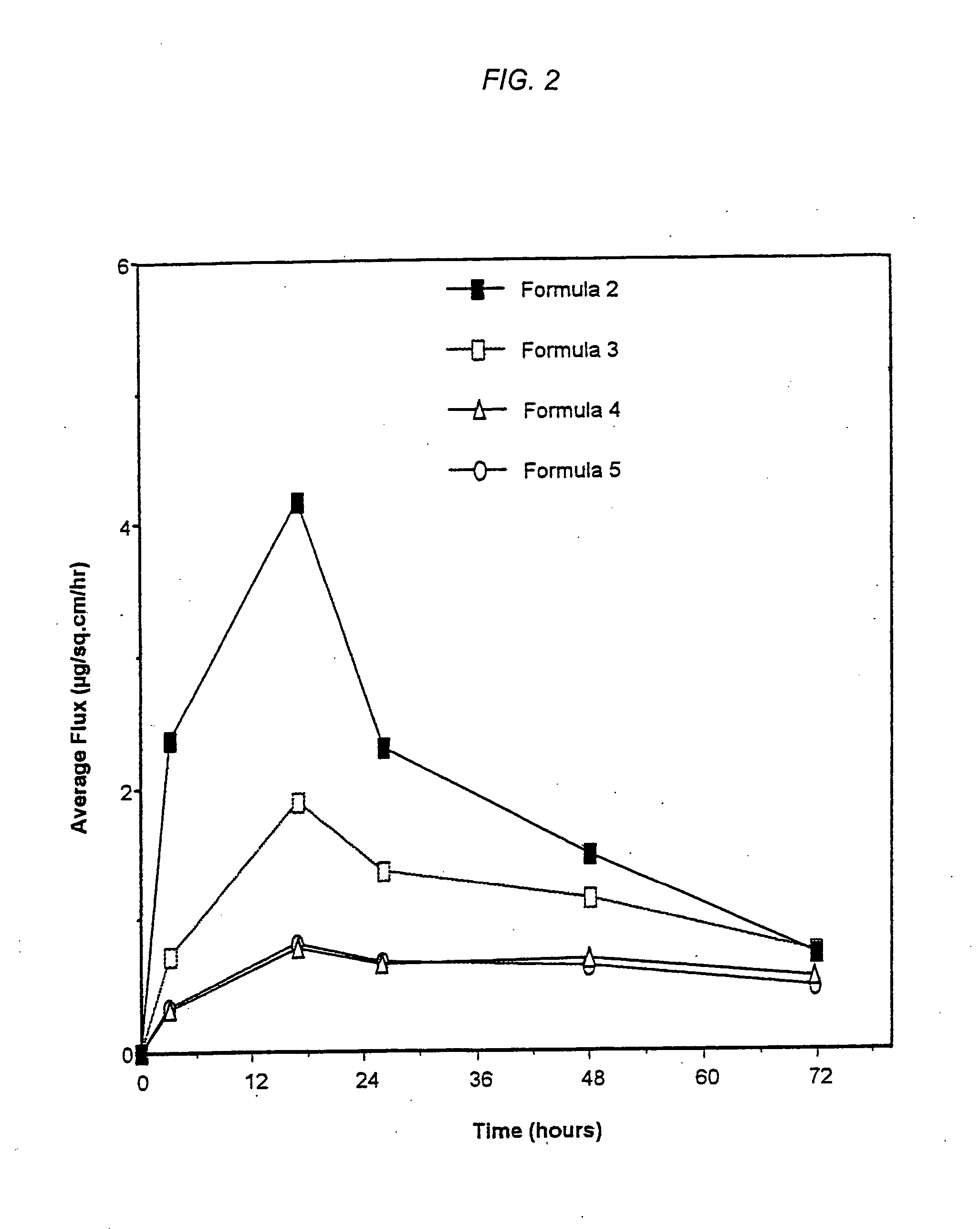
[0033] The following specific examples are included as illustrative of topical systems and compositions within the contemplation of the invention. These examples are in no way intended to be limiting of the scope of the invention. Other aspects of the invention will be apparent to those skilled in the art to which the invention pertains. The weight percentages in the examples are based on dry weight of the total transdermal composition, unless otherwise noted.
[0034] As used herein, the term, “flux” is defined as the absorption of the drug through the skin or mucosa, and is described by Fick's first law of diffusion:
J=−D(dCm / dx), [0035] where J is the flux in g / cm2 / sec, D is the diffusion coefficient of the drug through the skin or mucosa in cm2 / sec and Dcm / dx is the concentration gradient of the drug across the skin or mucosa.
[0036] The following commercially available products were used in the example: “BIO-PSA 7-4202 and 7-4502 are trademarks of Dow Corning Corporation, Medical...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com