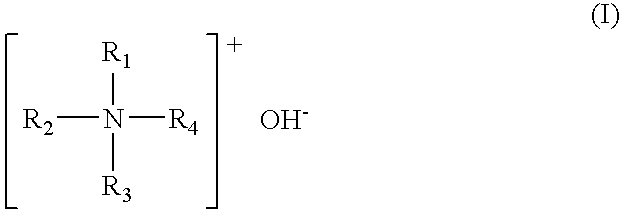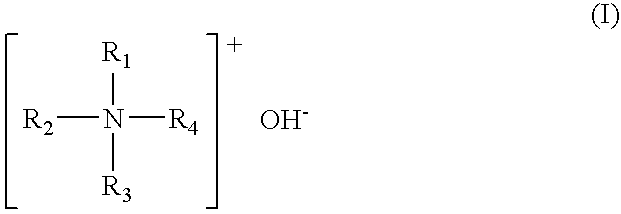Photoresist stripping solution and a method of stripping photoresists using the same
a technology of photoresist and stripping solution, which is applied in the direction of photomechanical equipment, instruments, photosensitive material processing, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the yield of semiconductor fabrication, affecting the performance of the substrate, and unable to provide adequate protection against corrosion of the substrate, so as to achieve the effect of protecting al
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
The following examples are provided for the purpose of further illustrating the present invention but are in no way to be taken as limiting. Unless otherwise noted, all compounding amounts are expressed by mass percent.
examples 13-19
[Substrate I]
Processed substrates were prepared by repeating the procedure employed in Examples 1-12.
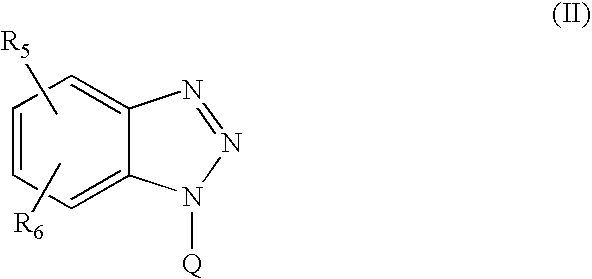
The processed substrates were stripped away of the post-ashing residues by dipping in photoresist stripping solutions (70° C.×30 min) consisting of 5 mass percent of tetrapropylammonium hydroxide (TPAH) as component (a), 20 mass percent of monoethanolamine (MEA) as component (b), 40 mass percent of component (c), and 30 mass percent of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) as component (e), plus 5 mass percent of component (d) (see Table 4 for the specific compound used), followed by rinsing with pure water. The strippability of the Al-based residue formed on the sidewall of each hole, the strippability of the Si-based residue formed around the opening of each hole, the state of corrosion of the Al wiring at the bottom of each hole, and the state of corrosion of Si in the reverse surface of the silicon wafer were evaluated by examination with an SEM (scanning electron microscope). The res...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com