Integrated hydroponic and fixed-film wastewater treatment systems and associated methods
a wastewater treatment system and hydroponic technology, applied in biological water/sewage treatment, filtration separation, separation processes, etc., can solve the problems of large scale, large footprint, and frequent failure of systems, and achieve less land intensive, less impact, and reduced undesirable characteristics of influents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] A description of the preferred embodiments of the present invention will now be presented with reference to FIGS. 1-3.
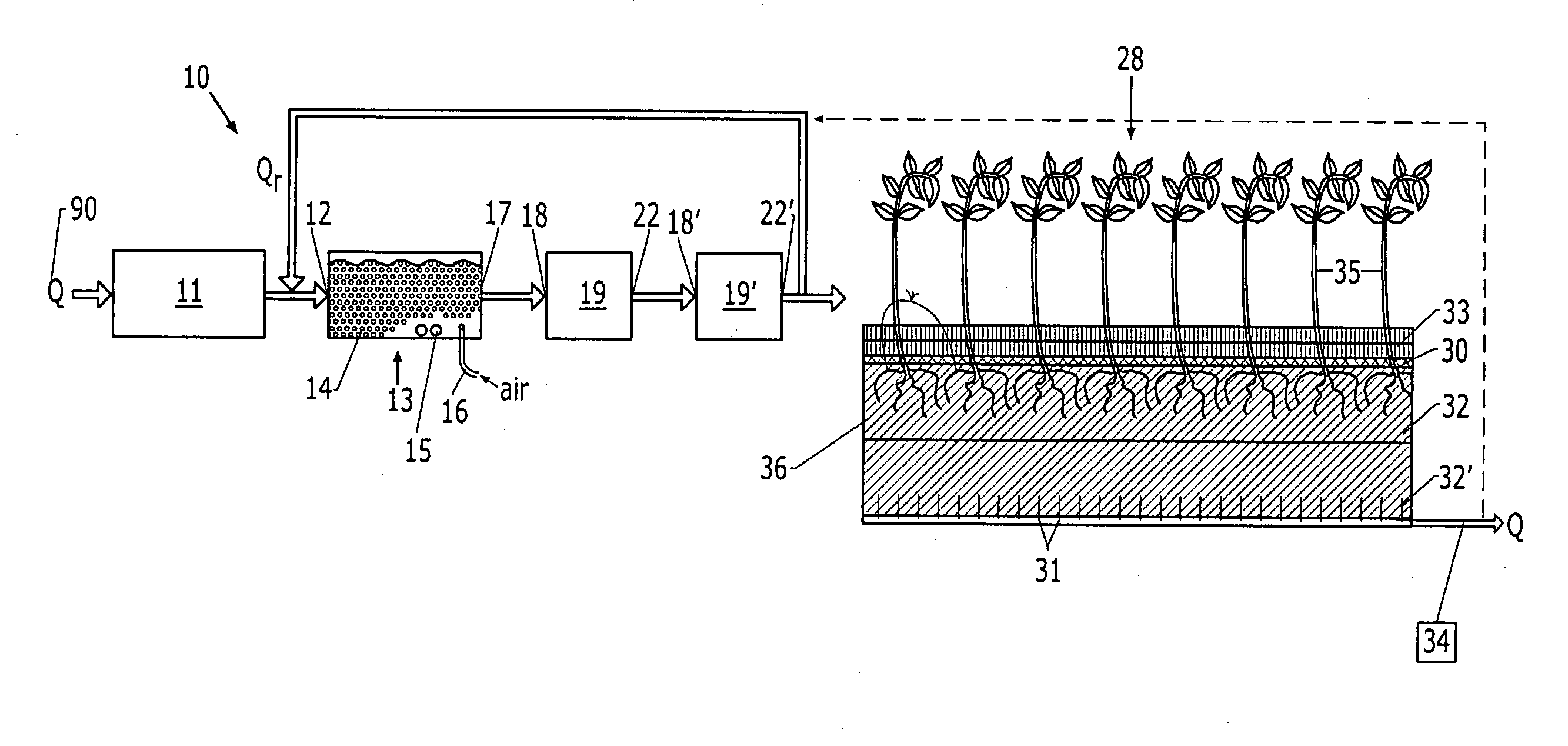
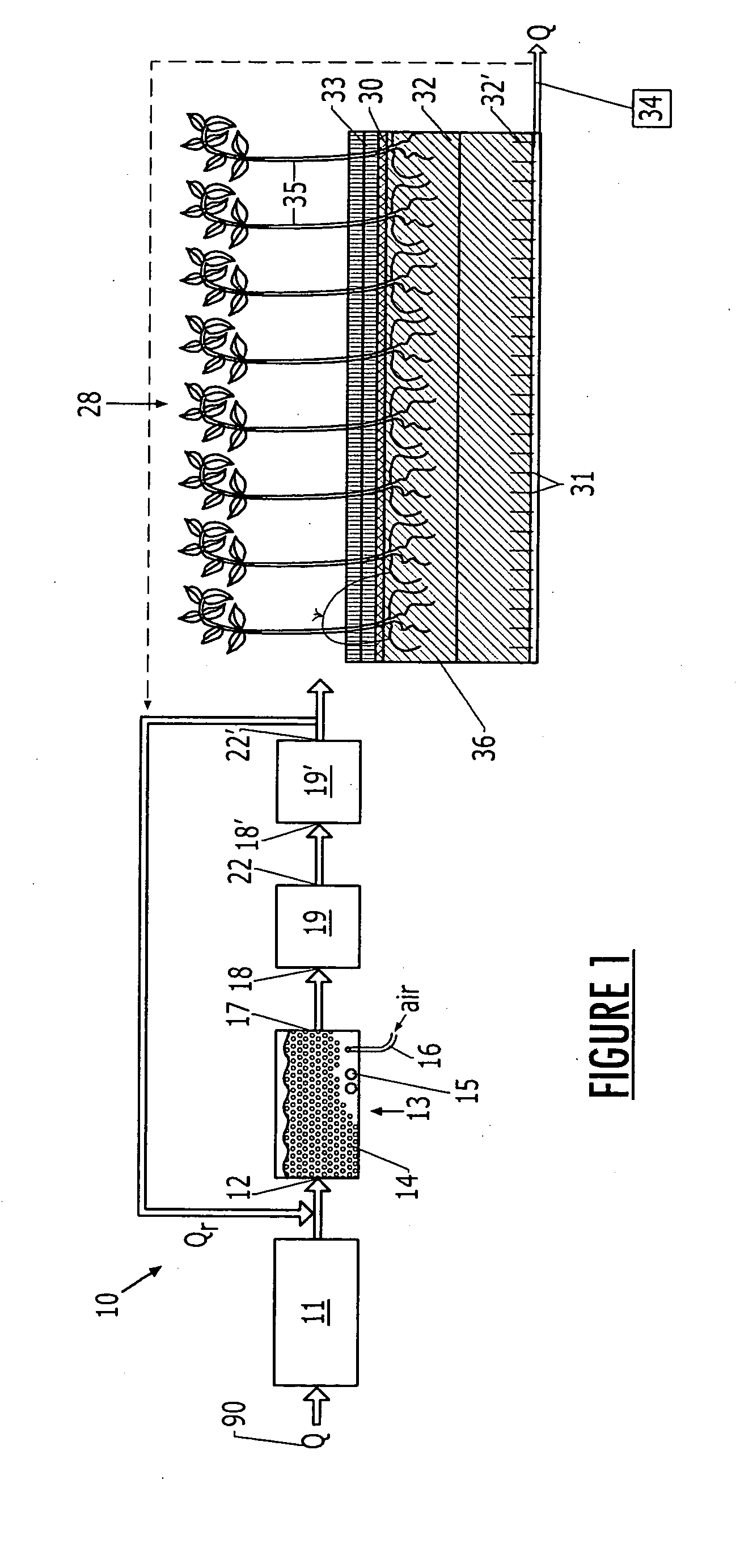
[0025] A schematic of a first embodiment 10 of the present invention (FIG. 1) illustrates the flow of wastewater through the system, entering a pretreatment module 11, into which influent 90 is channeled and permitted to reside for a predetermined period. The pretreatment module 11 may comprise, for example, a covered anaerobic reactor, which serves to perform an initial organic and solids removal. In this vessel 1 the solids from the influent settle, and anaerobic bacteria feed on the solids and wastes in the liquid. A means is provided for removing odors from gases or fumes that are produced herein.
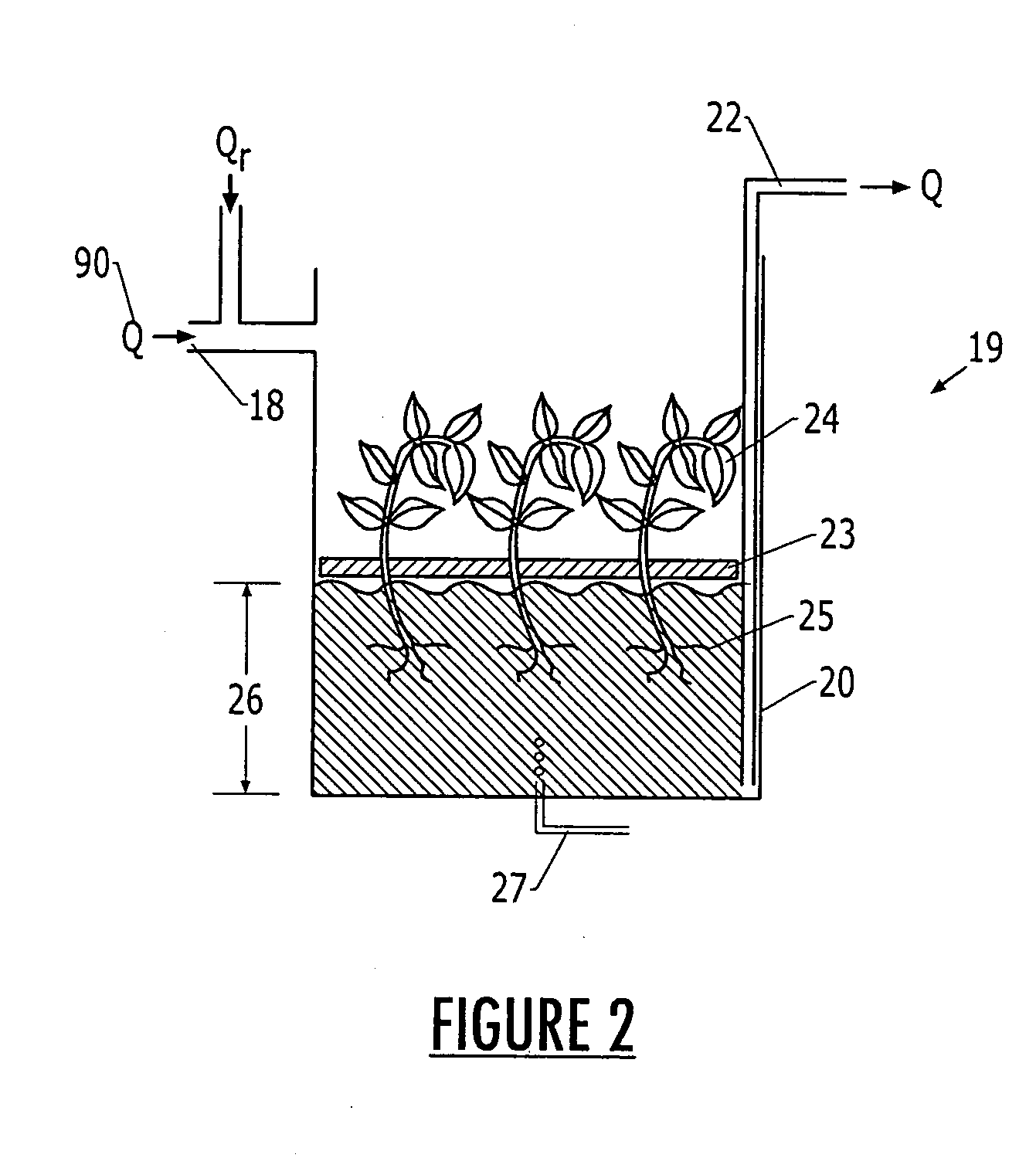
[0026] The wastewater 90 is then channeled to an inlet 12 of a fixed-film reactor, such as, but not intended to be limited to, a moving bed bioreactor (MBBR) 13, which as discussed previously achieves removal of organics and solids and denitrification. The fixed...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com