Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
a semiconductor layer and semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, basic electric elements, electrical appliances, etc., can solve the problems of deterioration of high frequency characteristics or so-called frequency dispersion, insufficient suppression of frequency dispersion, and difficulty in forming a minute concave portion in the upper portion of the iii-v nitride semiconductor layer, etc., to reduce the influence of traps, suppress frequency dispersion, and the effect of gate length
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0068] A III-V nitride semiconductor device in the first embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. In the present specification, the III-V nitride semiconductor is a hybrid semiconductor including one of or two or more of boron nitride (BN), aluminum nitride (AlN), gallium nitride (GaN), and indium nitride (InN), and represented by a general formula of BxAlyGazIn1-x-yN (where 0≦x≦1, 0≦y≦1, and ≦0z≦z≦1).
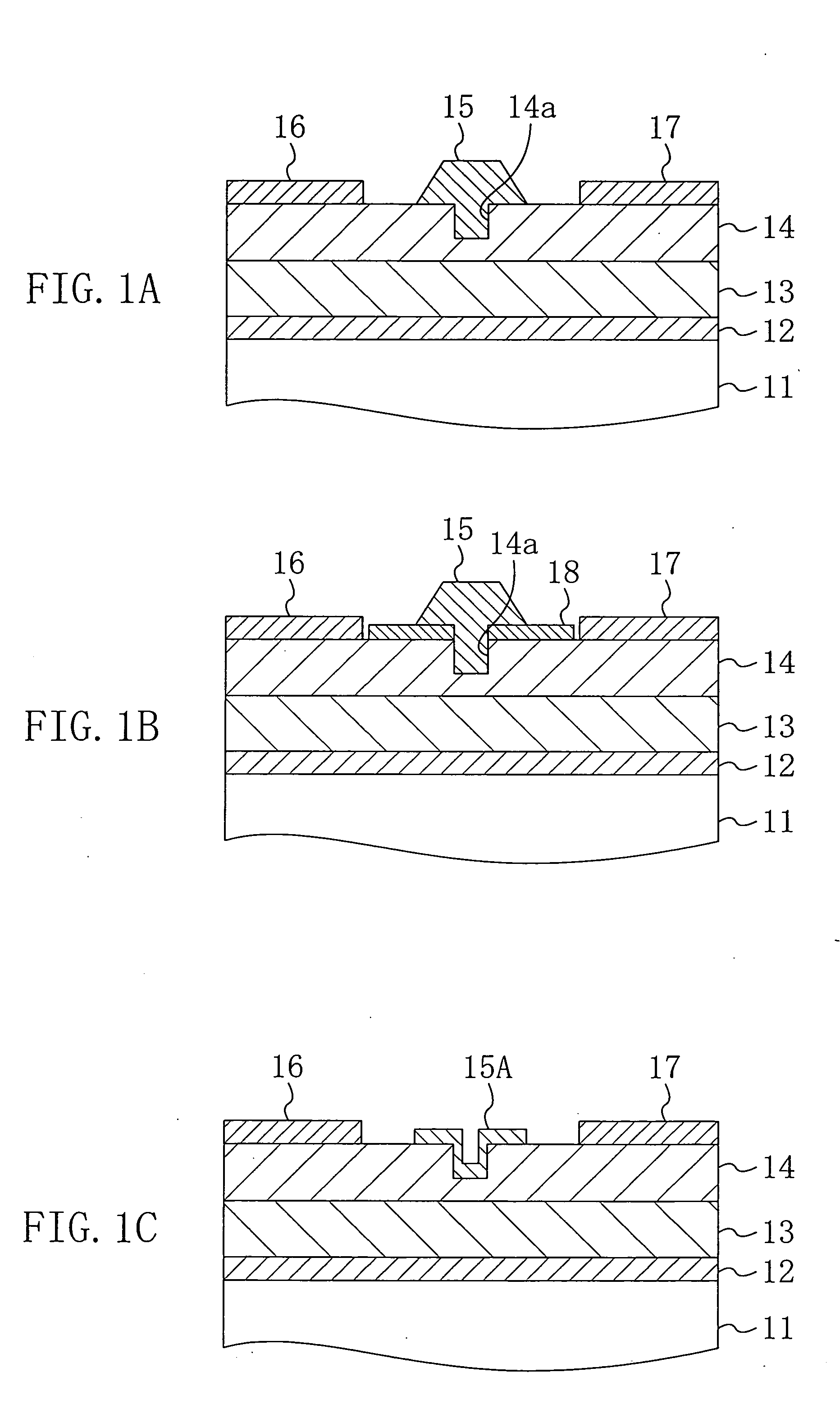
[0069]FIG. 1A is a cross-sectional block diagram of the III-V nitride semiconductor device in the first embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 1A, the III-V nitride semiconductor device is constituted so that, for example, a buffer layer 12 having a thickness of about 10 nm to 200 nm and consisting of aluminum nitride (AlN), a channel layer 13 having a thickness of about 2 μm to 3 μm and consisting of undoped gallium nitride (GaN), and a carrier supply layer 14 having a thickness of about 20 nm to 30 nm and consisting of n ty...
modification 1
of Embodiment 1
[0077]FIG. 1B is a cross-sectional block diagram of a III-V nitride semiconductor device in the first modification of the first embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 1B, the III-V nitride semiconductor device in the first modification is constituted so that a protection film 18 having a thickness of about 100 nm to 200 nm and consisting of silicon oxide or silicon nitride is provided in a region between the concave portion 14a and each of the source electrode 16 and the drain electrode 17 on the upper surface of the carrier supply layer 14.
[0078] According to the first modification of the first embodiment, since the protection film 18 is provided on the upper surface of the carrier supply layer 14, a trap density in both side portions of the gate electrode 15 on the upper surface of the carrier supply layer 14 can be reduced. It is, therefore, possible to further ensure suppressing the frequency dispersion resulting from the traps on the upper surface...
modification 2
of Embodiment 1
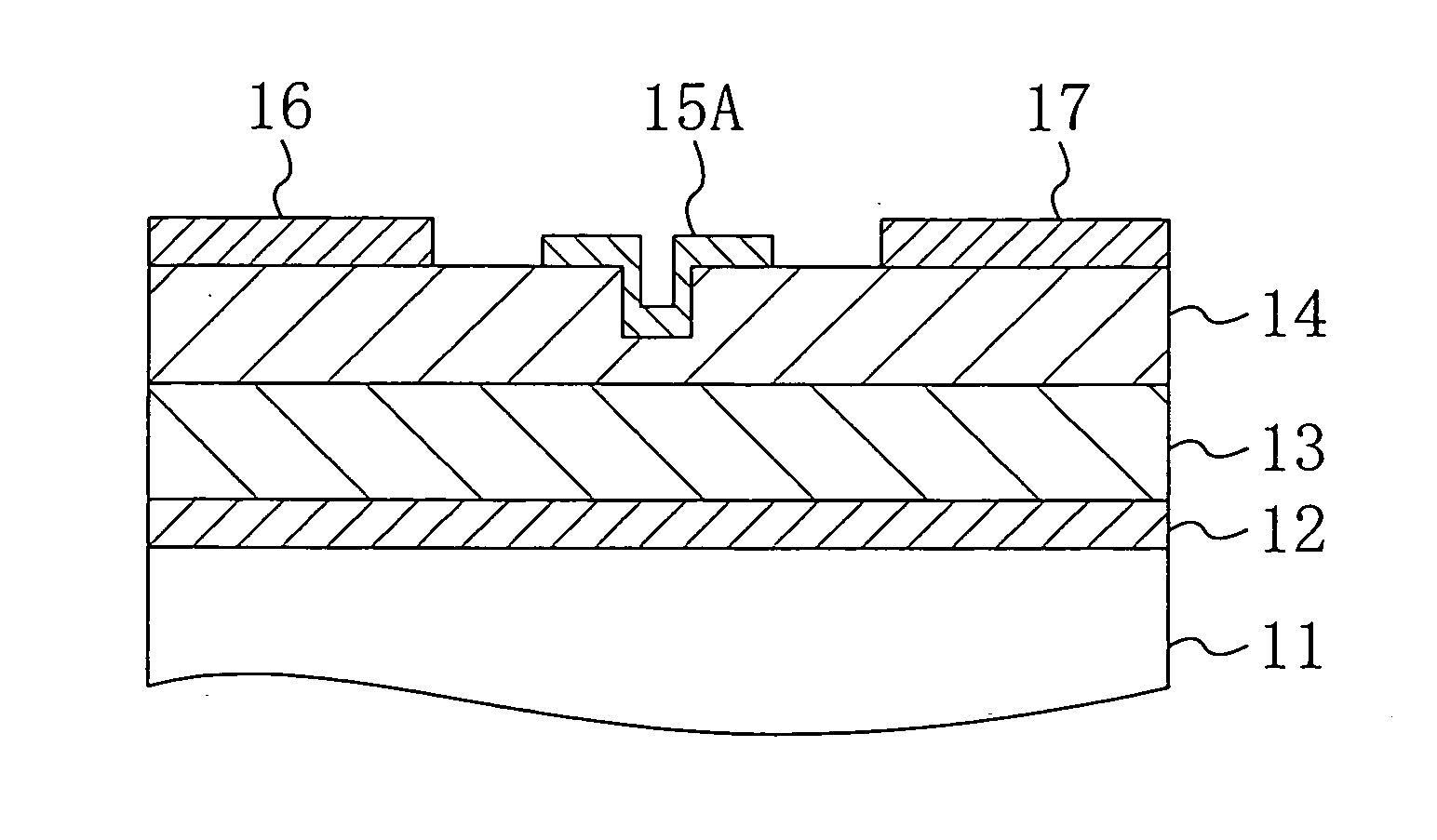
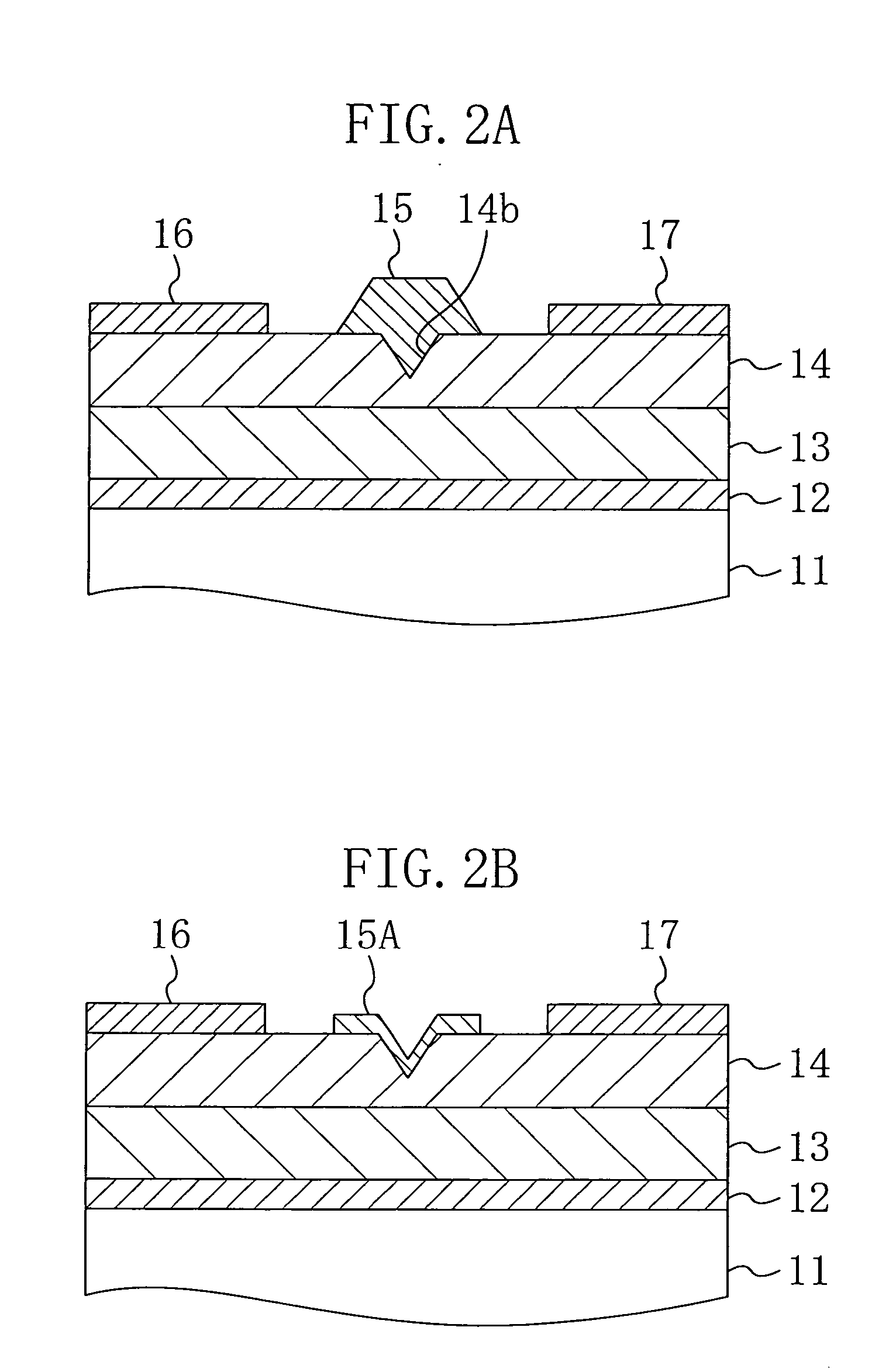
[0080]FIG. 1C is a cross-sectional block diagram of a III-V nitride semiconductor device in the second modification of the first embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 1C, the III-V nitride semiconductor device in the second modification is constituted so that a gate electrode 15A formed in the concave portion 14a, which is provided on the upper surface of the carrier supply layer 14, and serving as a Schottky electrode is provided not to be filled into the concave portion 14a but to extend along a bottom and a wall surface of the concave portion 14a and peripheral portions of the concave portion 14a. Since the gate electrode 15A is not filled into the concave portion 14a, an amount of a material used for the gate electrode 15A can be reduced and a throughput of a step of forming the gate electrode 15A can be improved.
Embodiment 2
[0081] A III-V nitride semiconductor device in the second embodiment of the present invention will be described hereinafter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com