Wet use chopped strand glass as reinforcement in extruded products
a technology of extruded products and glass, which is applied in the field of thermoplastic composites, can solve the problems of increasing the modulus or stiffness of the siding product, affecting the handling effect, and affecting the quality of the product, so as to improve the handling effect and improve the wind resistan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
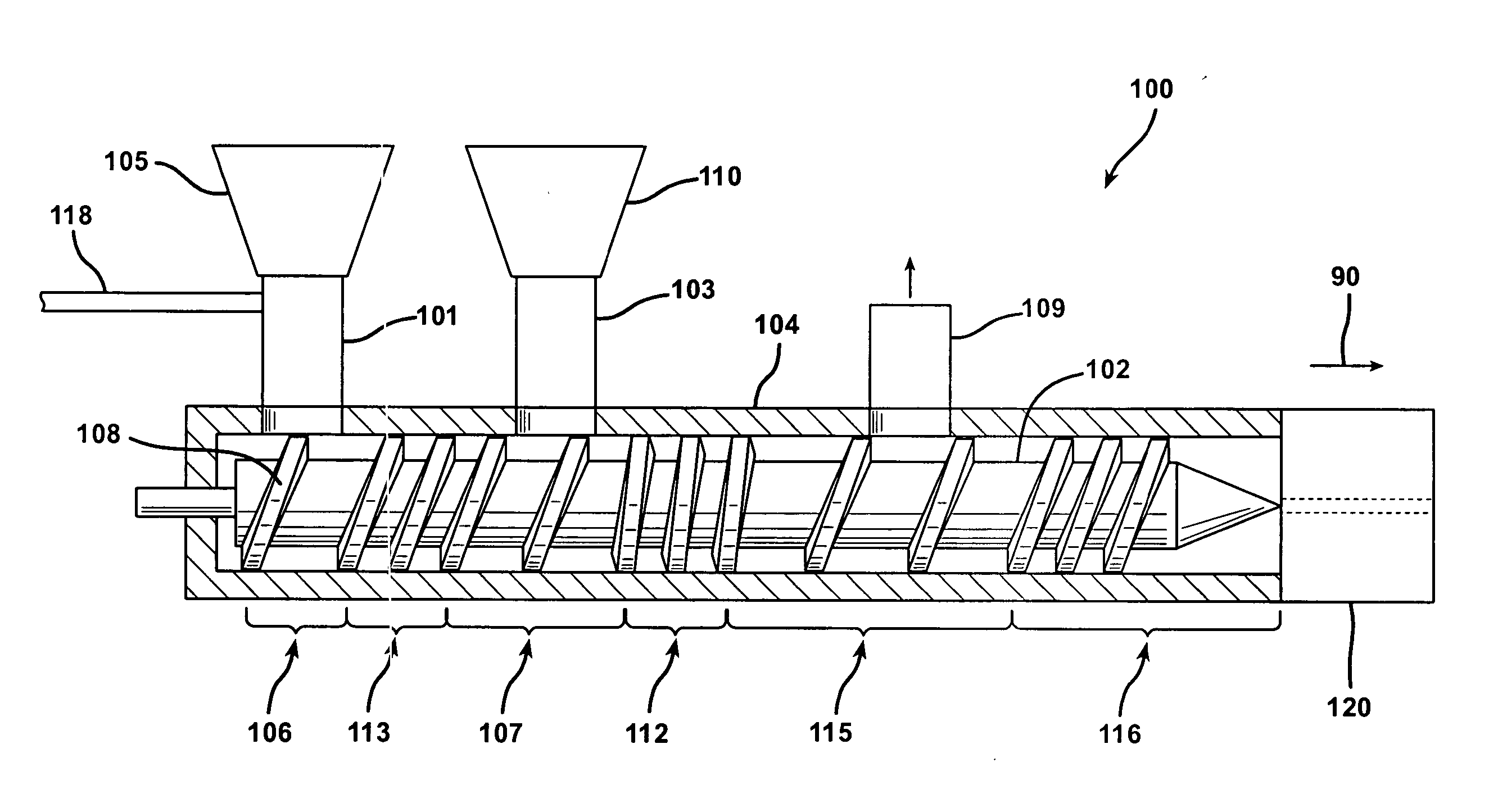
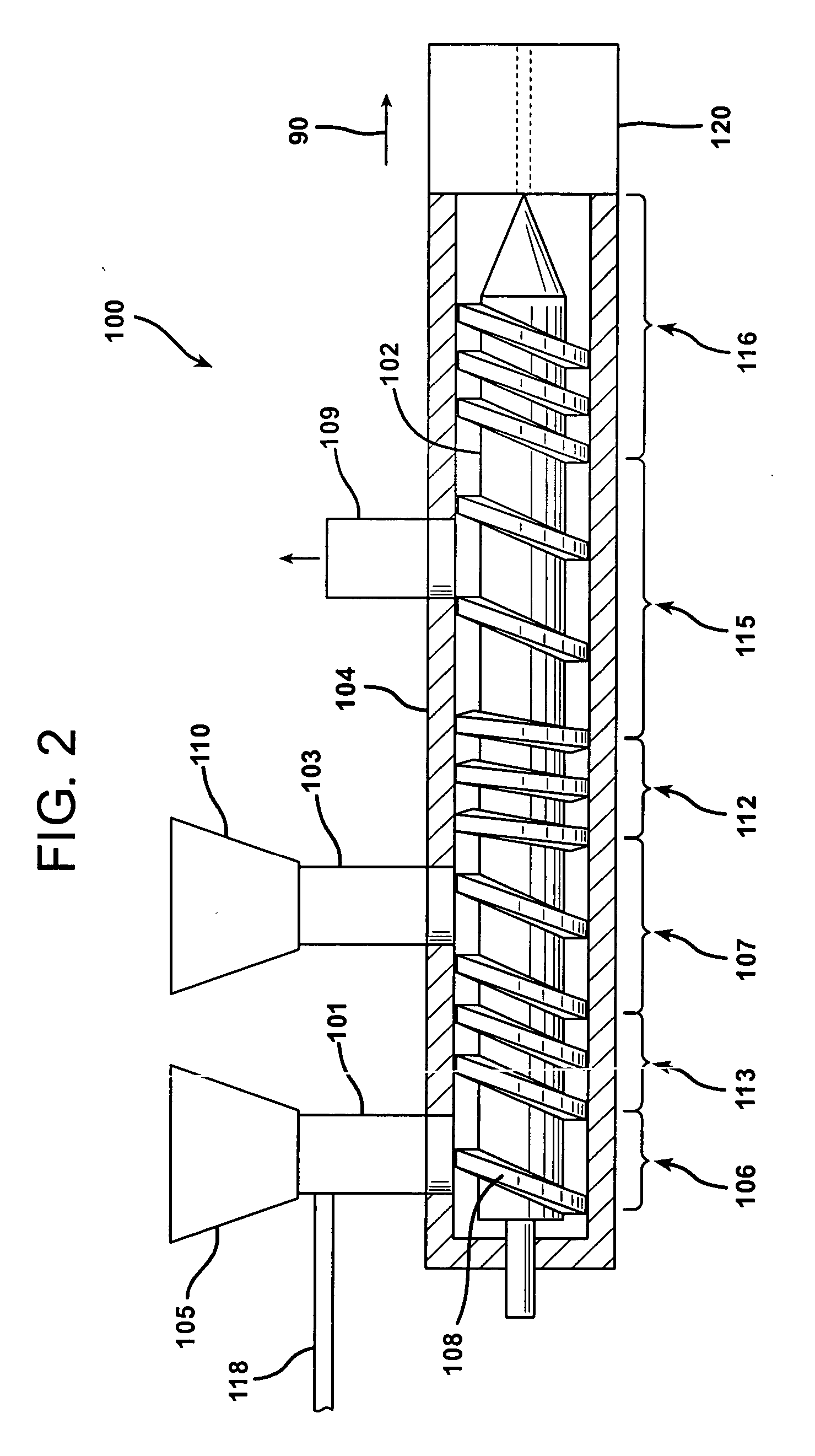
[0064] A PVC rigid extrusion compound was metered into the feedthroat of a 130 mm twin screw extruder at the rate of 2200 lb / hr. At the same time, WUCS glass fibers having a 12% moisture content were metered via a side mounted vibrator feeder into the feedthroat of the extruder at 33 lb / hr to give a 5% by weight glass composition. A low pressure zone located approximately 60% of the way down the barrel of the extruder was used to remove the moisture from the glass filled compound. The extruder was fitted with a sheet die to produce a 48 mils thick product. The product was produced on an extrusion line such as is depicted in FIG. 6. The product met the requirements of ASTM D3679 as tested.
example 2
[0065] A polypropylene blended with 2% of a maleic anhydride modified polypropylene was added to a feedthroat of a single screw 60 mm extruder. Approximately 16 inches downstream, wet use chopped strand glass fibers were added via a feedthroat in a high volume zone (e.g., a first low pressure zone). Located approximately another 16 inches down the barrel was a second low pressure zone fitted with a vacuum system set at 15 inches of mercury vacuum to remove moisture from the compound in the extruders. The extruder was fitted with a sheet die to extrude a 125 mils thick product.
[0066] Example 3
[0067] A compound formed of a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) resin, impact and process modifiers, a tin based stabilizer, a blowing agent, and an inorganic filler such as calcium carbonate was pre-blended with 15% of WUCS glass fibers having a 12% moisture content and fed into the feed throat of an 88 mm twinscrew extruder. The foamed extrudate was calibrated into a board.
example 4
[0068] The compound described above in Example 3 was fed into the feed throat of an 88 mm twinscrew extruder concurrently with WUCS glass fibers having a 12% moisture content at a rate sufficient to result in a foamed extrudate with 15% glass fiber content. The foamed extrudate was formed into a board.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com