Fluororesin composite compositions
a fluoropolymer and composite technology, applied in the field of heat-meltable fluoropolymer composite compositions, can solve the problems of low thermal conductivity, inability to say economic, and periodic replacement of tubes made of resins, and achieve excellent thermal conductivity, gas and chemical liquid barrier properties, and excellent thermal conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
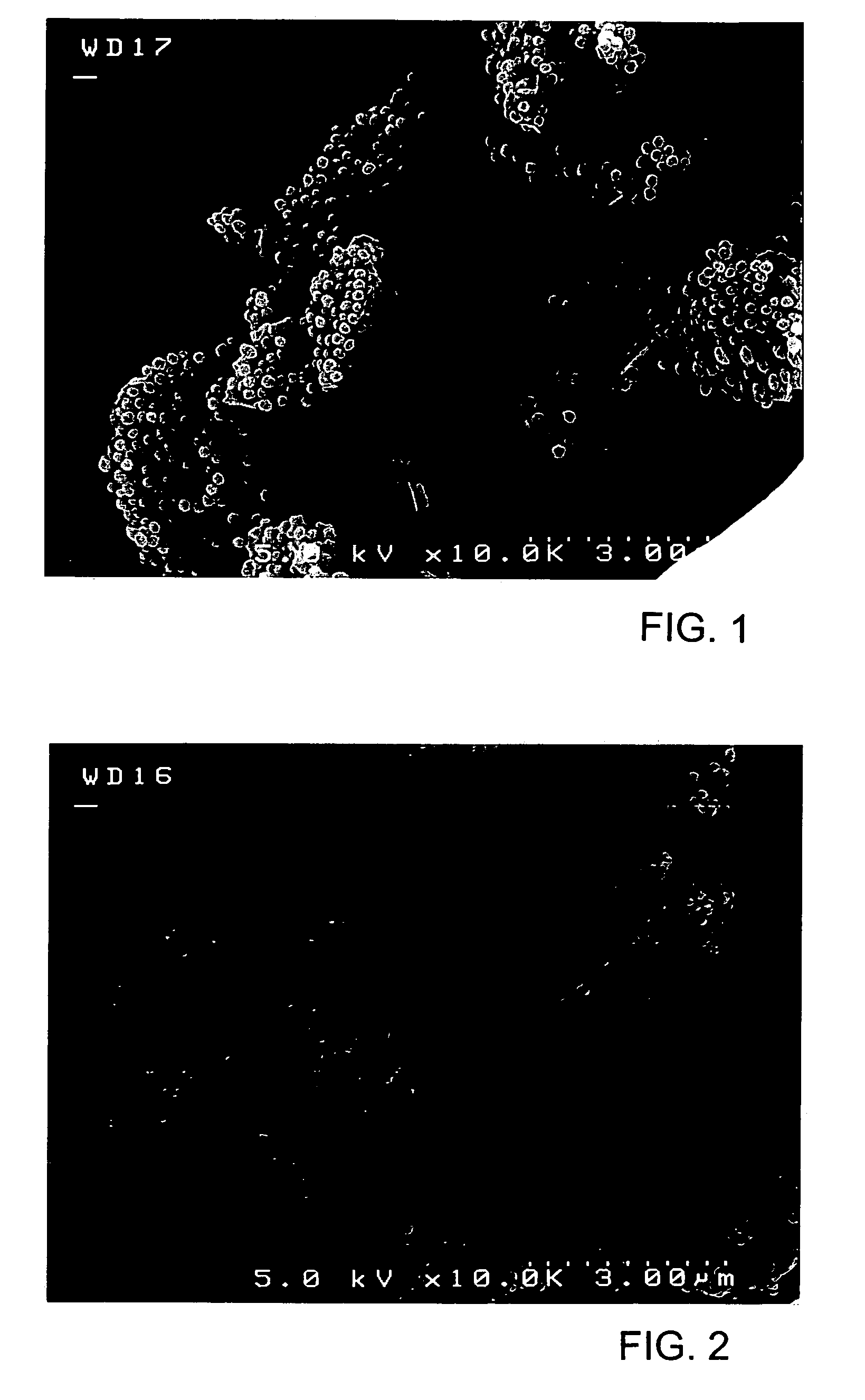
[0046] 60 kg of 30% by weight PFA aqueous dispersion (melting point: 307° C.; MFR: 1.9 g / 10 min) obtained by emulsion polymerization were put in an agitation tank (100-liter) of the down flow type having an agitation shaft with 6 vanes of the propeller type, and 500 g of 60% nitric acid were added with agitation at 300 rpm. In addition, agitation was conducted at 300 rpm for 10 min. After the aqueous dispersion was agglomerated, the agglomerated PFA particles were caused to come up and float on the aqueous polymerization medium by agitating the dispersion at 450 rpm for 20 min so that the PFA particles were separated from the aqueous polymerization medium. After that, the aqueous polymerization medium was discharged from the agitation tank, and water was put in the agitation tank to wash the PFA particles. After that, the PFA particles were dried at 160° C. for 24 hours, and as a result, PFA fine powder. The average particle size of the PFA fine powder thus obtained was 3 μm.
[0047]...
example 2
[0049] A heat-meltable fluoropolymer composite composition was obtained by the same method as described in Example 1 except that 80% by weight of PFA fine powder and 20% by weight of synthetic graphite were used. The nitrogen gas permeability and thermal conductivity of the heat-meltable fluoropolymer composite composition thus obtained were measured. Measurement results are shown in Table 1.
examples 3 to 6
[0050] Heat-meltable fluoropolymer composite compositions were obtained by the same method as described in Example 1 except that 90, 85 or 80% by weight of PFA fine powder and 10, 15 or 20% by weight of pure natural graphite (available from SEC Co., Ltd.; SNO-3; average particle size: 3 μm) as the layered-compound in place of synthetic graphite were used. The nitrogen gas permeability and thermal conductivity of the heat-meltable fluoropolymer composite compositions thus obtained were measured. Measurement results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| circumferential velocity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melt index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com