Composite of support matrix and collagen, and process for producing support substrate and composite
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
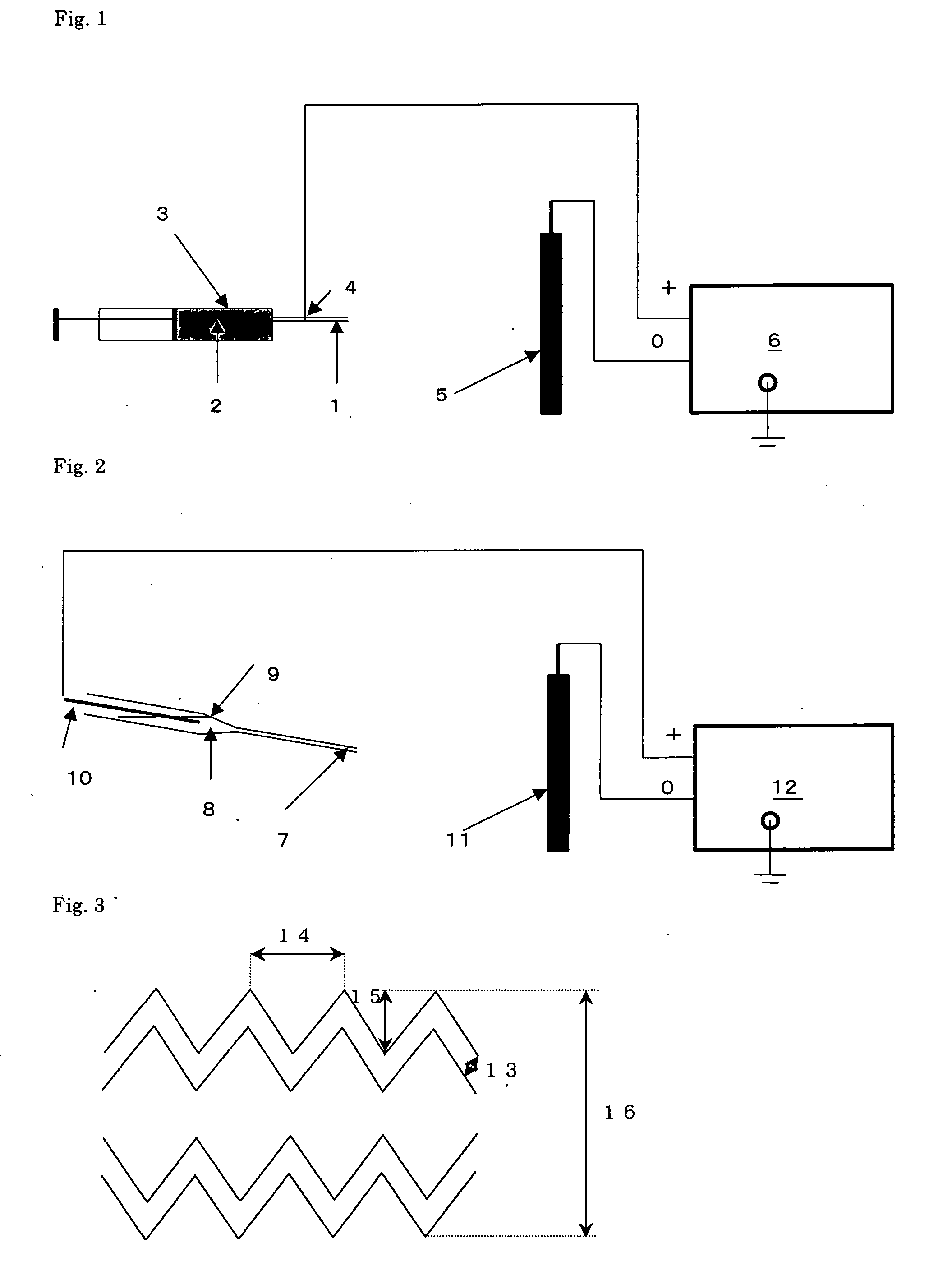
[0091] A dope was prepared by mixing 1 g of polylactic acid and 8 g of methylene chloride at room temperature (25° C.). An apparatus such as shown in FIG. 2 was used for 5 minutes of discharge of the solution to a fiber substance collecting electrode 5 (2 mm diameter, 200 mm length, 70-S surface roughness), causing rotation at 60 rpm. During this time, the collecting electrode 5 was rotated 150 rpm in the circumferential direction. The inner diameter of the ejection nozzle 1 was 0.8 mm, the voltage was 12 kV, and the distance from the ejection nozzle 1 to the fiber substance collecting electrode 5 was 10 cm. The end of the fiber structure collected at the fiber substance collecting electrode 5 was held fixed against a finger while the fiber substance collecting electrode 5 was pulled out toward the end fixed against the finger, to obtain a polylactic acid tube. The obtained polylactic acid tube had a diameter of 2 mm, a length of 20 mm, a basis weight of 20 g / m2, a bellows-shaped se...
example 2
[0092] The same treatment was carried out as in Example 1, except that the basis weight was 40 g / m2.
example 3
[0093] A 2 mm-diameter rod was reinserted into the polylactic acid tube obtained in Example 1, and this was fixed at the center of a 3 mm diameter tube. A 1.5 unit volume of a buffer solution containing 260 mM sodium bicarbonate, 200 mM HEPES and 50 mM sodium hydroxide was mixed with a 10 unit volume of 0.3% aqueous (type II) collagen solution by Koken Co., Ltd., while cooling on ice, and the mixture was placed in the holding tube in which the polylactic acid tube was fixed. A procedure in which the external atmosphere pressure was reduced and restored to ordinary pressure was repeated three times, and then the tube was kept at 37° C. for gelling. After gelling, the 2 mm diameter rod was pulled out and lyophilization was carried out to obtain a collagen cylindrical body.
[0094] The yield elongation of the obtained molded article was measured using a Tensilon device (INSTRON) with reference to DIN53507, 53504, giving a yield elongation value of 38%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com