Hydrolytically degradable alkylene oxide based polymers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
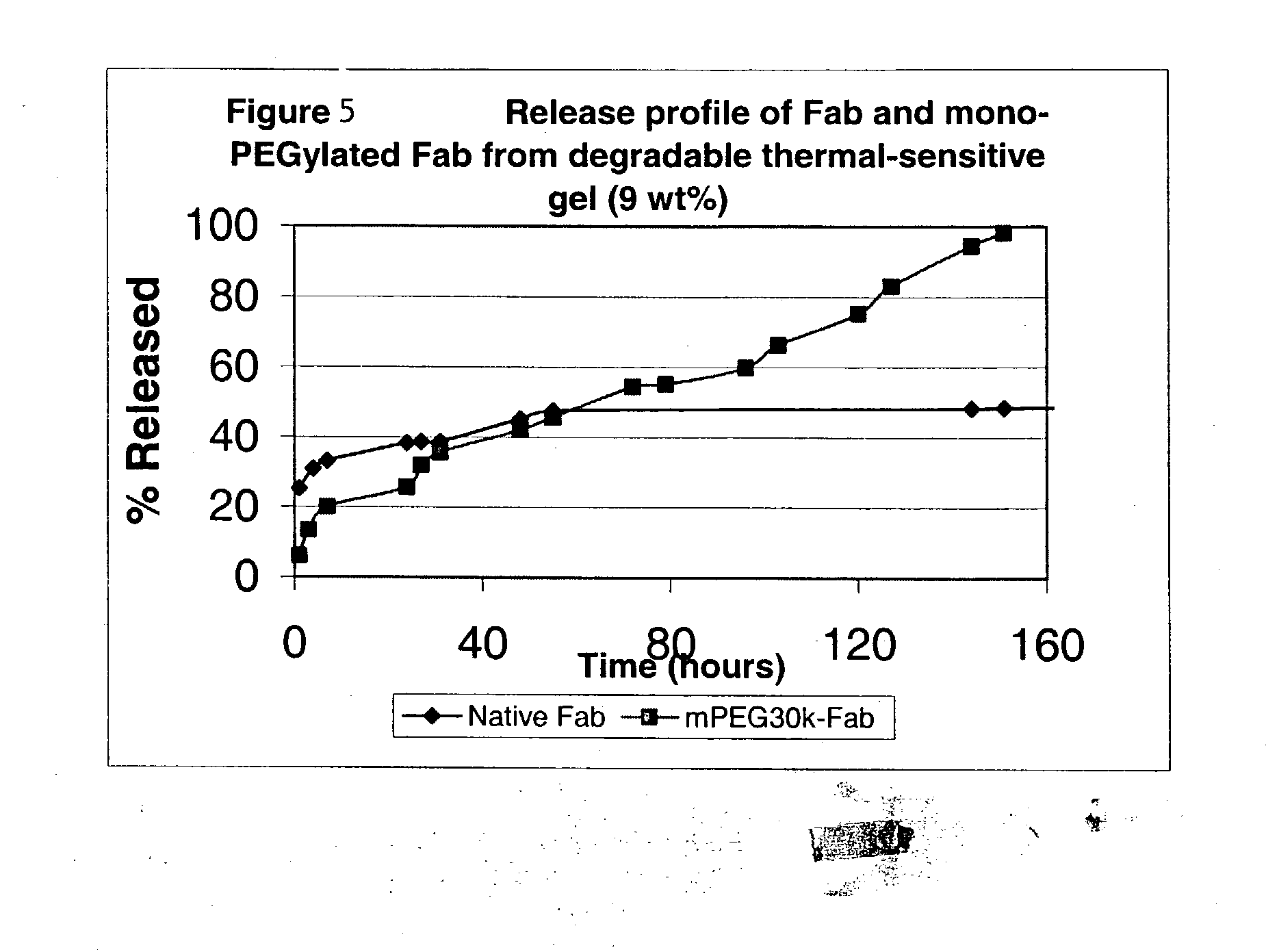
Examples
example 1
Synthesis of a Hydrolytically Degradable Oligomer Composed of Copolymer Subunits of Ethylene Oxide-Propylene Oxide-Ethylene Oxide Covalently Linked by Carbonate Bonds, (I)
[0117] An illustrative polymer of the invention was synthesized as follows by coupling to one another block copolymers each composed of a propylene oxide block (i.e., a series of propylene oxide monomers) sandwiched between two ethylene oxide blocks, where the block copolymers are covalently attached to one another by intervening carbonate bonds to form the resulting oligomer.
[0118] Poloxamer 407 (10.0 g, 0.78 mmole) was dissolved in 30 ml of CH3CN in a 50 ml round-bottom flask fitted with a Dean-Stark trap and a reflux condenser. The solution was heated to reflux and 20 ml of solvent was collected. After the Dean-Stark trap was removed, di-(N-succinimidyl) carbonate, DSC (1.1 equivalents, 0.22 g, 0.86 mmole), available from Fluka, and 4-dimethylaminopyridine, DMAP (2 equivalents, 0.19 g, 1.56 mmole) available fr...
example 2
Sol-Gel Characteristics of a Hydrolytically Degradable Oligomer Composed Of Triblock Copolymer Subunits of Ethylene Oxide-Propylene Oxide-Ethylene Oxide Covalently Linked by Carbonate Bonds, (I)
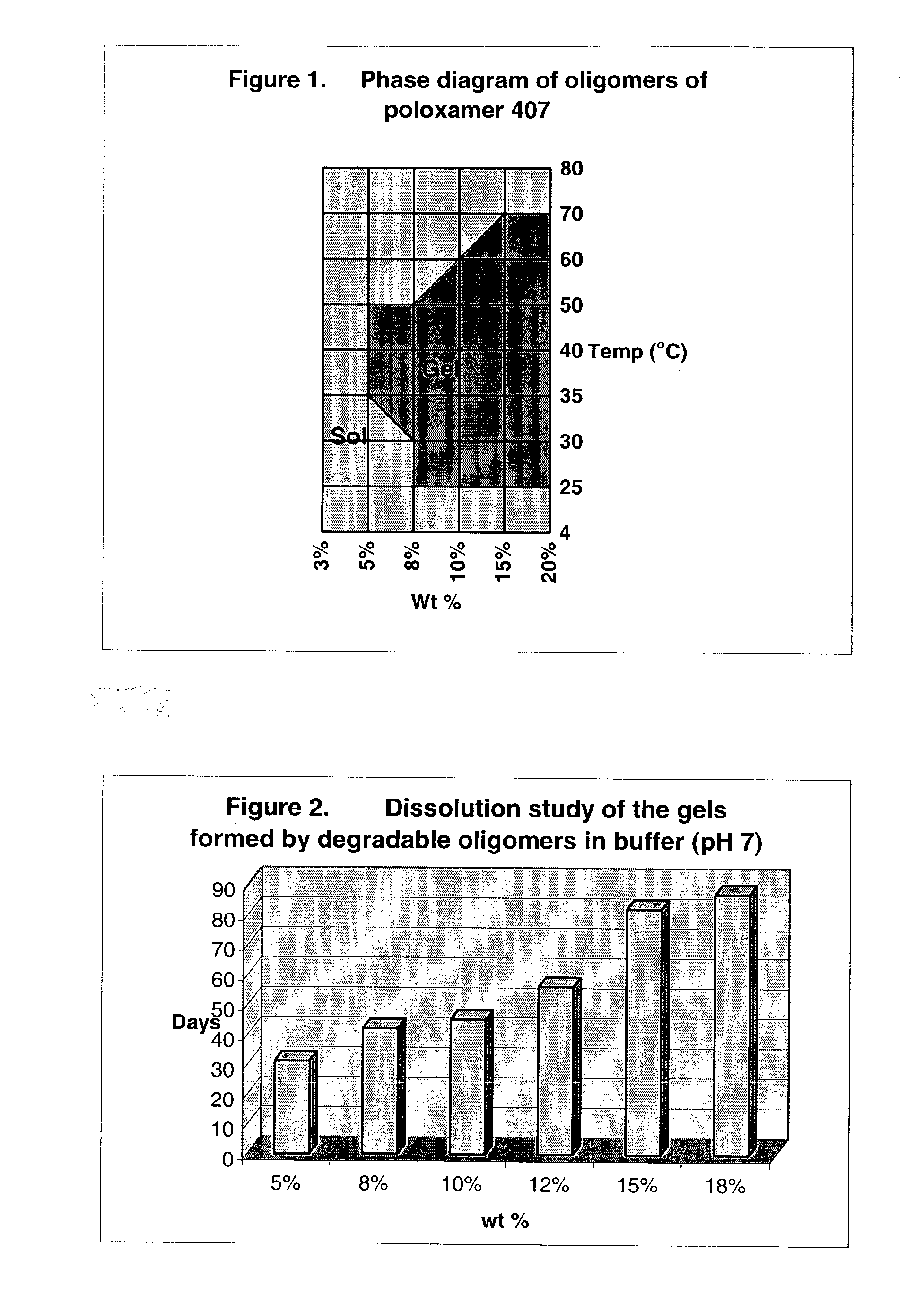
[0124] The oligomeric product, (I), from Example 1 above was dissolved in phosphate buffer (0.1 M, pH 7.0) at 4° C. at a number of different concentrations. The aqueous polymer-containing solutions were placed in a temperature-controlled water-bath. The temperature of the water bath was slowly increased, and the temperature at which each of the solutions became a solid gel (based upon visual inspection) was recorded. The sol-gel phase transition was then further refined by monitoring gel formation within two minutes after solutions of (I) at 4° C. were placed in a water bath at preset temperatures. The data was then used to generate a phase diagram demonstrating the sol-gel behavior of (I) at different concentrations and temperatures and is shown as FIG. 1.
[0125] In looking at FIG. 1, it ca...
example 3
Gel Formation and Degradation of (I)
[0128] The following illustrates another advantage of the polymers of the invention, i.e., their biodegradability.
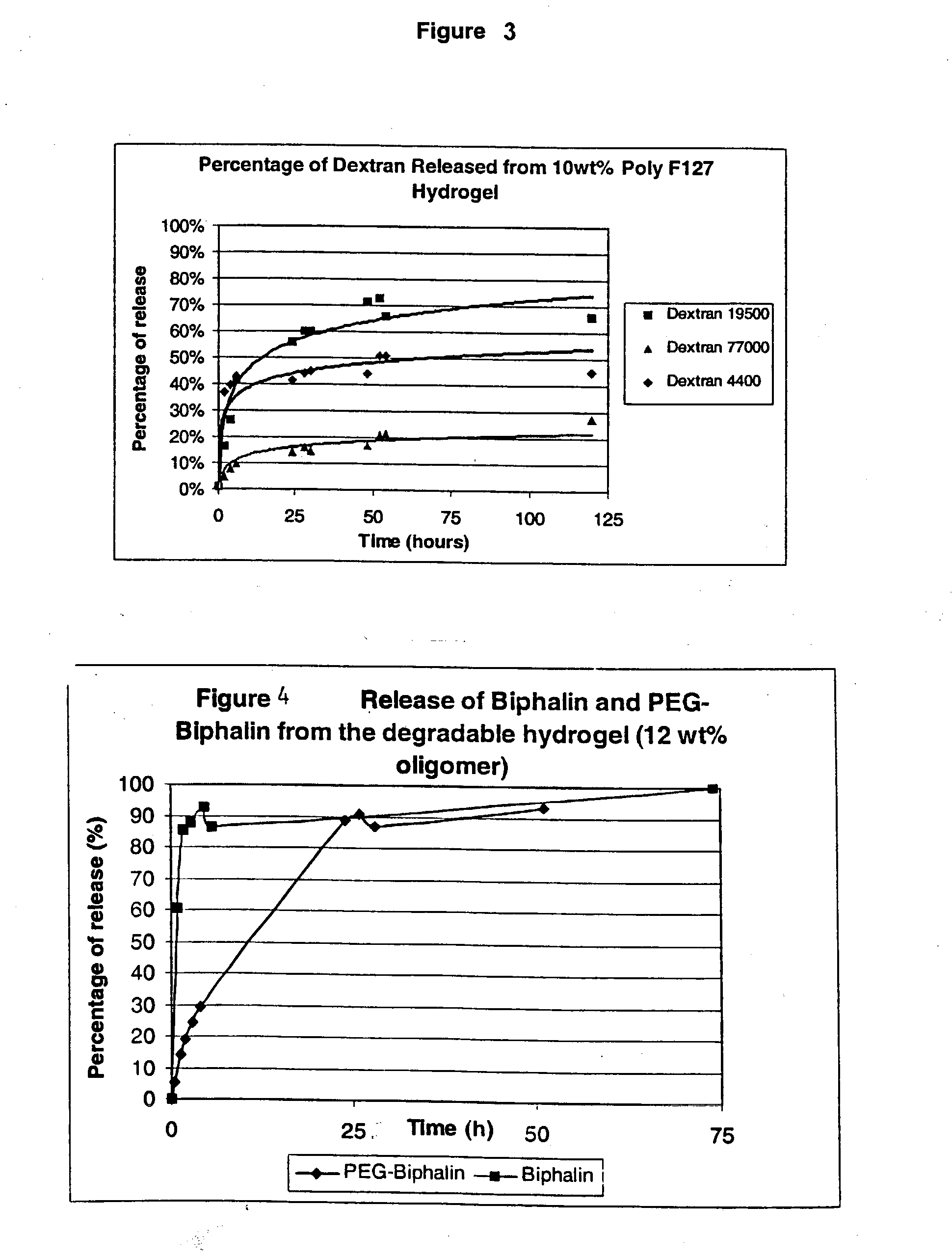
[0129] Polymer (I) was dissolved in phosphate buffer (0.1 M, pH 7.0) at 4° C. to final concentrations of 5%, 8%, 10%, 12% 15% and 18 wt %, respectively. The aqueous solutions (1 ml) were then each placed in an incubator at a temperature of 37° C. to form a gel. To the gel, 2 ml of phosphate buffer was added and the mixtures were then held at 37° C. until a solution formed. The dissolution of each of the gels at 37° C. was mainly due, not to a physical phase change, but due to their hydrolytic degradation over time (i.e., hydrolysis of the carbonate bonds). The dissolution of these representative gels over time is shown graphically as FIG. 2.
[0130] As can be seen from the dissolution data, dissolution times for each of the gel compositions increased with increasing polymer concentration of the gel. For example, the 5 wt % gel dissolv...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com