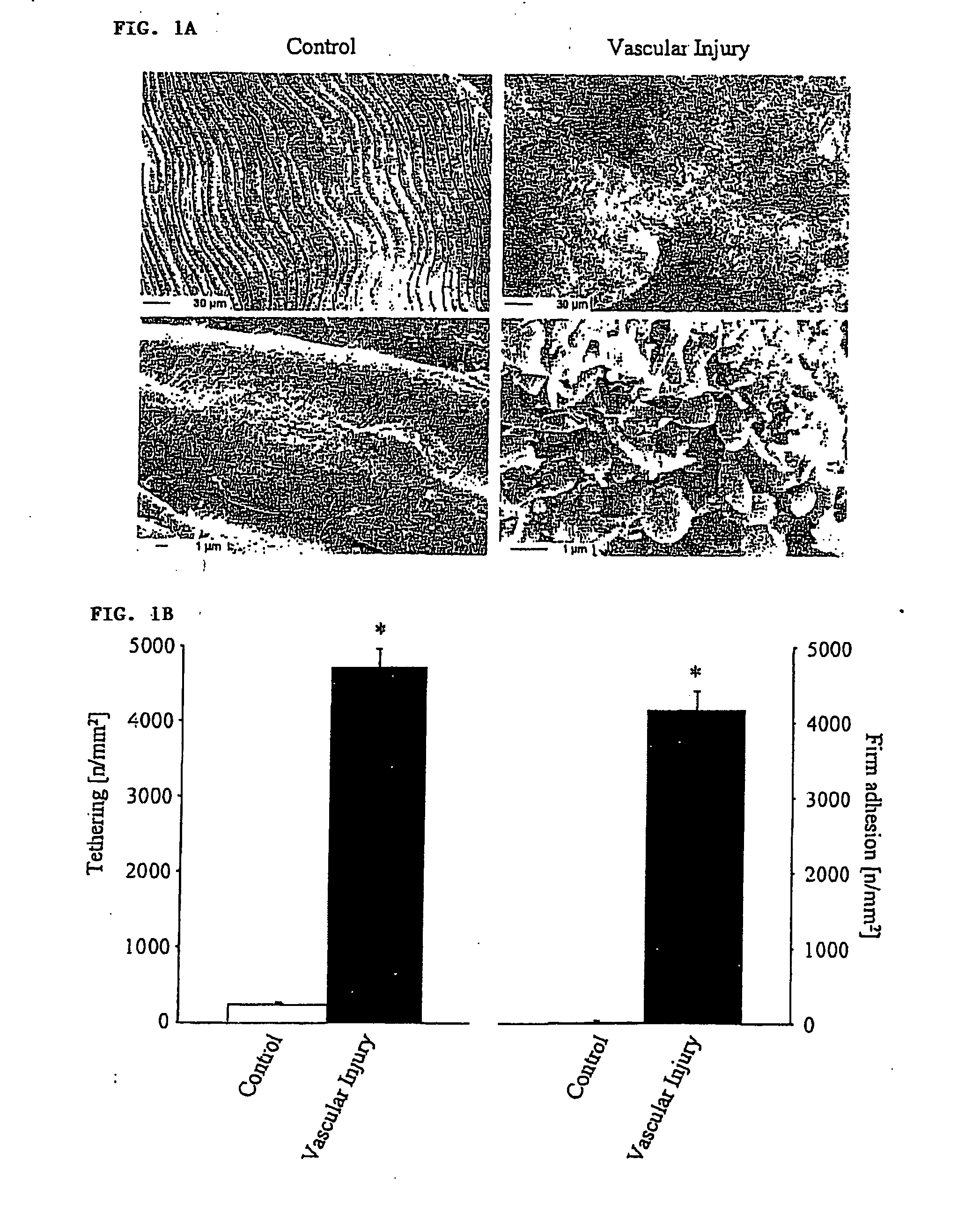
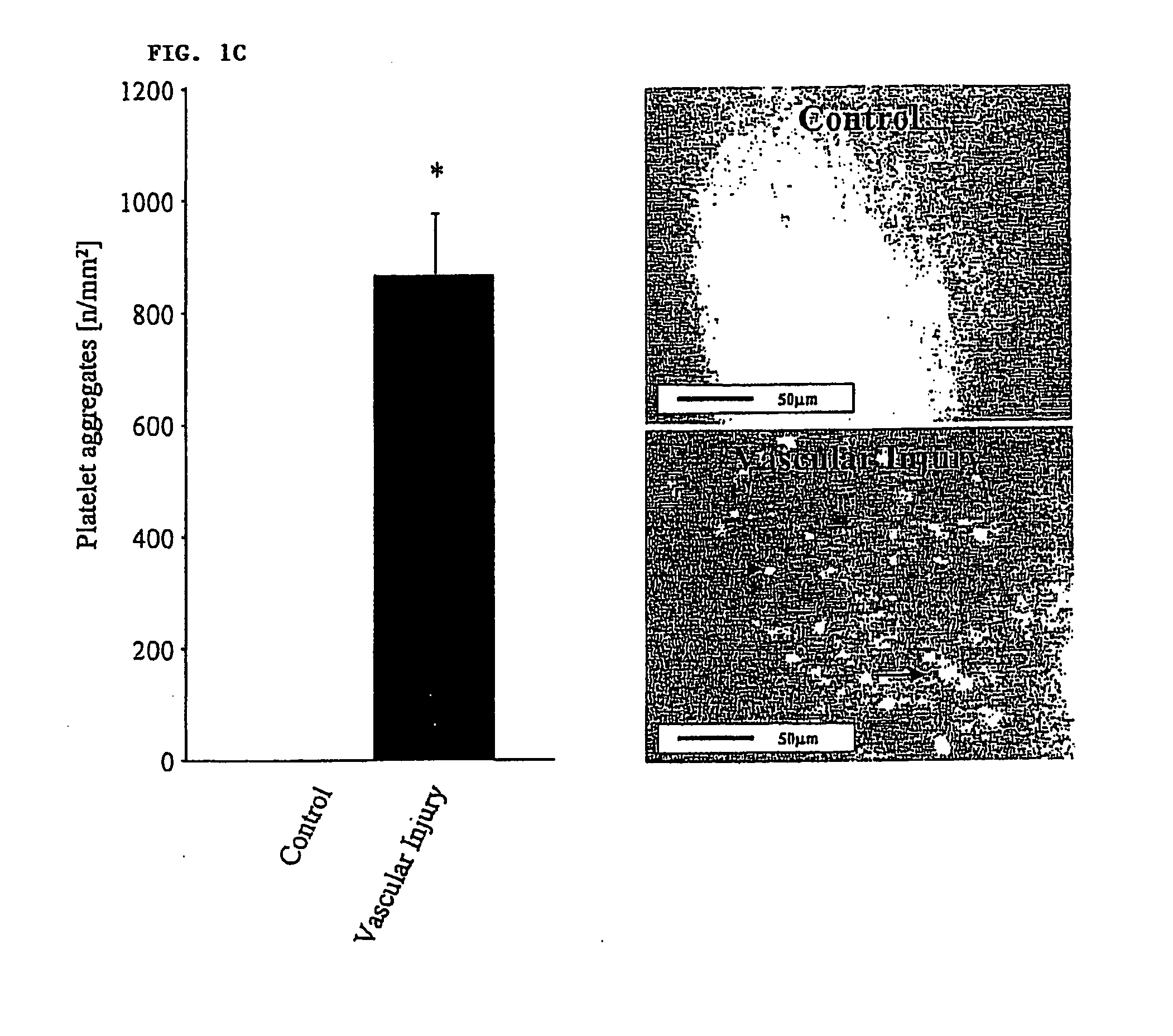
Agents which bind to epitopes of glycoprotein VI
a glycoprotein and epitope technology, applied in the field of agents binding to glycoprotein epitopes, can solve the problems of reducing the number of compounds to be screened using platelets, affecting the ability of platelets to aggregate, and the risk of death or myocardial infarction, etc., and reducing the likelihood of finding inhibitors functional with platelets. , the effect of increasing the likelihood of finding inhibitors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Cloning of the Immunoadhesin of GP VI (Fc-GPVI-nt)
[0697] We generated an immunoadhesin of the GP VI receptor by generating a recombinant fusion protein of the n-terminal part of GP VI—which encodes the extracellular domain of GPVI—together with the Fc part of an IgG. The Fc was amplified from a human heart cDNA library (Clonetech, Palo Alto, Calif.) by PCR using the forward primer 5′-cgcggggcggccgcgagt-ccaaatcttgtgacaaaac-3′ and the reverse primer 5′-gcgggaagctttcatttacccggagacagggag-3′. The PCR reaction was performed at 58° C. annealing temperature and 20 cycles with the Expand High Fidelity PCR Sytem (Roche Molecular Biochemicals, Mannheim, Germany). The PCR fragment was cloned in the plasmid pADTrack CMV with NotI / HindIII and the sequence was checked by sequencing (MediGenomix, Martinsried, Germany).
[0698] For cloning of the extracellular domain of the human GPVI RNA from cultured megakaryocytes was isolated (RNeasy Mini Kit; Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacter...
example 2
Generation of the Adenovirus for Fc-GPVI-nt (Ad-Fc-GPVI-nt)
[0700] The plasmid pADTrack CMV Fc-GPVI-nt was linearized with PmeI (New England Biolabs, Beverly, Mass.) overnight, dephosphorylated and purified (GFX DNA and Gel Purification Kit; Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Uppsala, Sweden). For recombination electrocompetent E. coli BJ5183 (Stratagene, La Jolla, Calif.) were cotransformed with 1 μg of the linearized plasmid and 0.1 μg pAdeasy1 at 2500 V, 200 □ and 25 μFD (E. coli-pulser; Biorad, Heidelberg, Germany), plated and incubated overnight at 37° C. The colonies were checked after minipreparation of the plasmid-DNA with PacI and the positive clones were retransformed in E. coli DH5_.
[0701] For transfection (Effectene Transfection reagent; Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) of 293 cells plasmid-DNA was digested with PacI. The cells were cultured for 7 days and harvested by scraping and centrifugation. The pellet was resuspended in Dulbecco's PBS and the cells were lysed by four repetitive...
example 3
Fc-GPVI-nt Protein and Fc Control Immunoadhesin Purification
[0704] The culture supernatant of Ad-Fc-GPVI-nt-infected Hela cells was collected 2 days after infection, centrifugated (3800 g, 30 min, 4° C.) and filtrated (0.45 μm). The immunoadhesin was precipitated by addition of 1 vol. ammonium sulfate (761 g / l) and stirred overnight at 4° C. The proteins were pelleted by centrifugation (3000 g, 30 min, 4° C.), dissolved in 0.1 Vol PBS and dialysed in PBS overnight at 4° C. The protein solution was clarified by centrifugation (3000 g, 30 min, 4° C.) and loaded on a protein A column (HiTrap™ protein A HP, Amersham Pharmacia Biotech AB, Uppsala, Sweden). The column was washed with binding buffer (20 mM sodium phosphate buffer pH 7.0, 0.02% NaN3) until OD280□0.01 and eluted with elution buffer (100 mM glycine pH 2.7). The eluted fractions were neutralized with neutralisation buffer (1 M Tris / HCl pH 9.0, 0.02% NaN3), pooled, dialysed in PBS overnight at 4° C., aliquotated and frozen at ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com