Long-acting veterinary polypeptides and methods of producing and administering same
a polypeptide, long-acting technology, applied in the field of polypeptides and polynucleotides encoding same, can solve the problems of preventing the development of many otherwise promising drug candidates, affecting the clinical value of the drug, so as to improve the biological half life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
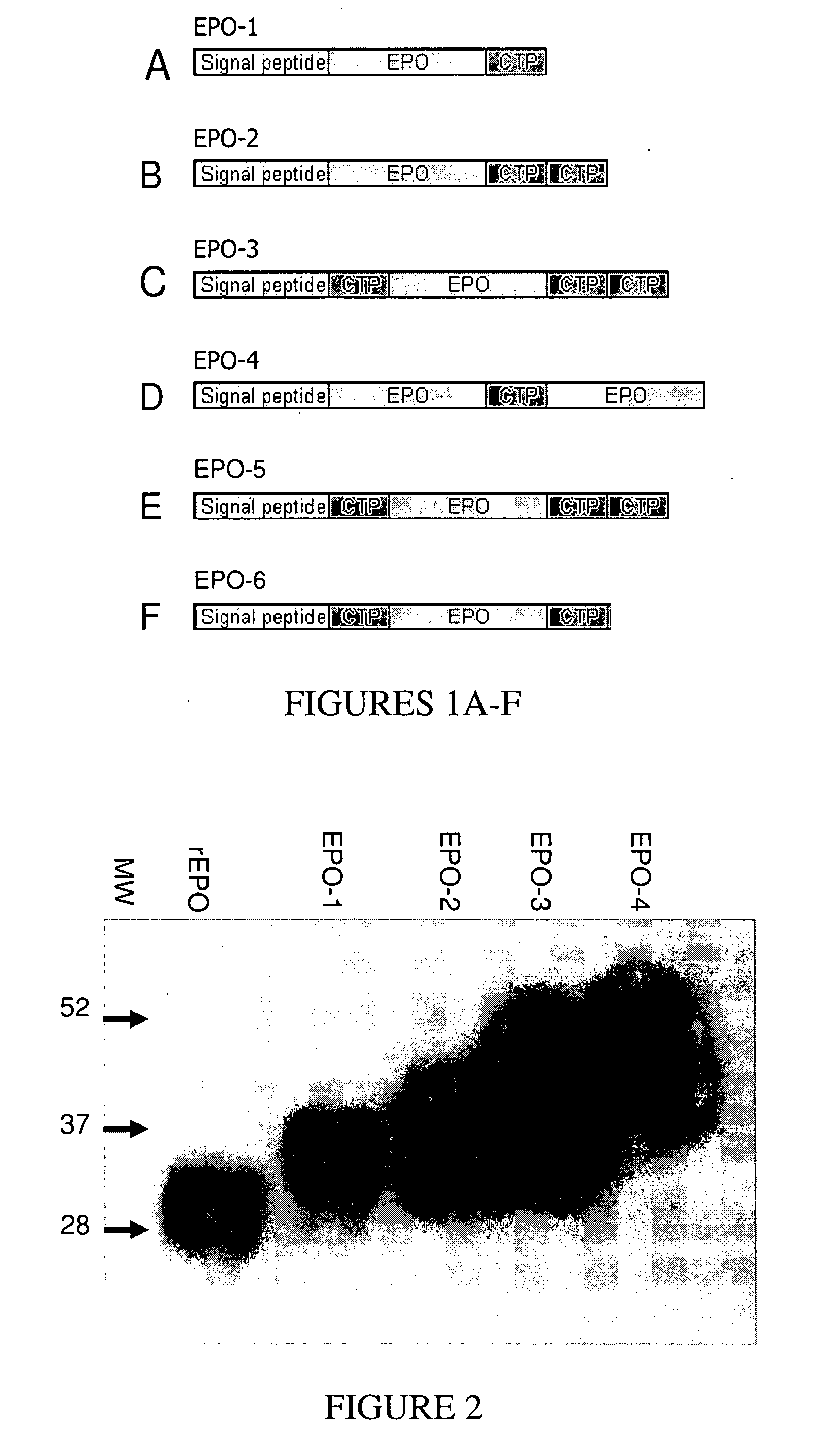
Generation of EPO Constructs
Materials and Methods:
[0278] Construction of expression vector pCI-dhfr: pCI-neo mammalian expression vector was purchased from Promega (catalog no. E1841). The vector contains a CMV IE enhancer / promoter and neomycin phosphotransferase gene. The pSV2-dhfr clone was purchased from ATCC (Catalog No. 37146). The plasmid contains the murine dhfr gene. The construction of pCI-dhfr vector was performed as follows: [0279] a. The pSV2-dhfr plasmid was digested with restriction enzyme BglII (3′ end of the dhfr gene). DNA polymerase I, Large (Klenow) Fragment was used to fill-in the 5′ overhangs to form blunt ends. The DNA was then digested with restriction enzyme AvrII (5′ end of the dhfr gene). The dhfr gene (AvrII-blunt end) fragment was isolated. [0280] b. The pCI-neo vector was digested with restriction enzyme BstXI (3′ end of the neo gene). DNA polymerase I, Large (Klenow) Fragment was used to remove the 3′ overhangs to form blunt ends. The DNA was then di...
example 2
Expression and Isolation of EPO-CTP Polypeptides
Materials and Methods
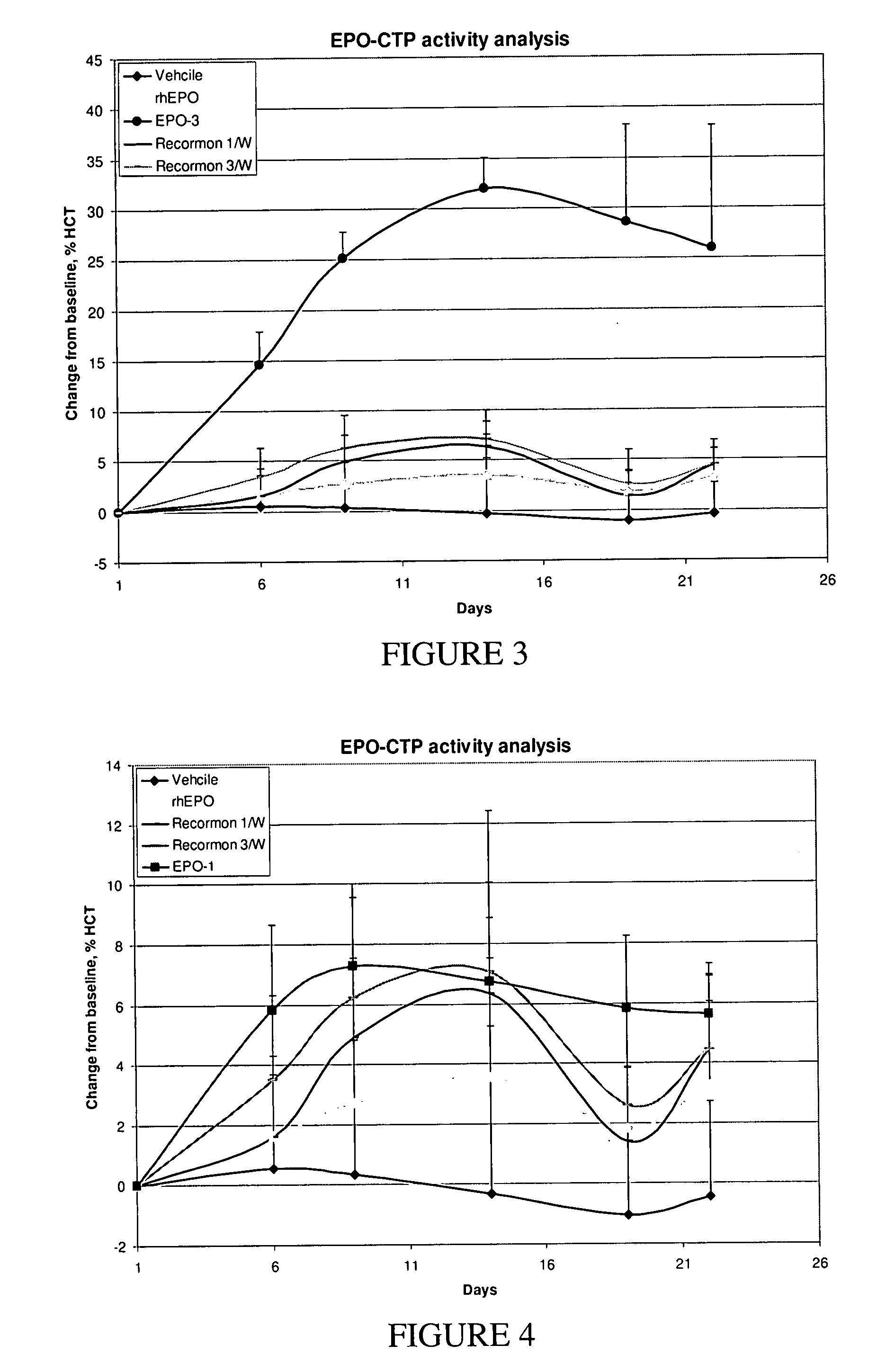
[0298] DNA transfection and clone selection: DG44 cells were transfected with pCI-DHFR expression vectors containing EPO-CTP variants using FuGENE6 Reagent (FUGENE Transfection Reagent—Roche Cat. 11 815 091 001). 48 hr following transfection, cells were diluted and seeded at 50-200 cells per well in a selective medium (CD DG44 Medium w / o HT (Gibco: Scotland part: #07990111A) Sku num.: ME060027 supplemented with 8 mM L-Glutamine Biological Industries: Cat: 03-020-1A) and 18 mL / L of 10% Pluronic F-68 solution (Gibco: Cat: 240040-032). Selected clones were screened for highest protein production using commercial ELISA. 3-5 producing clones per each variant were frozen for a backup cell bank. A selected clone for each variant was adapted to growth in larger scale cultures up to 1 L flasks on an orbital shaker platform. Supernatants were collected and analyzed by ELISA, SDS-PAGE and western blot. Following the withdr...
example 3
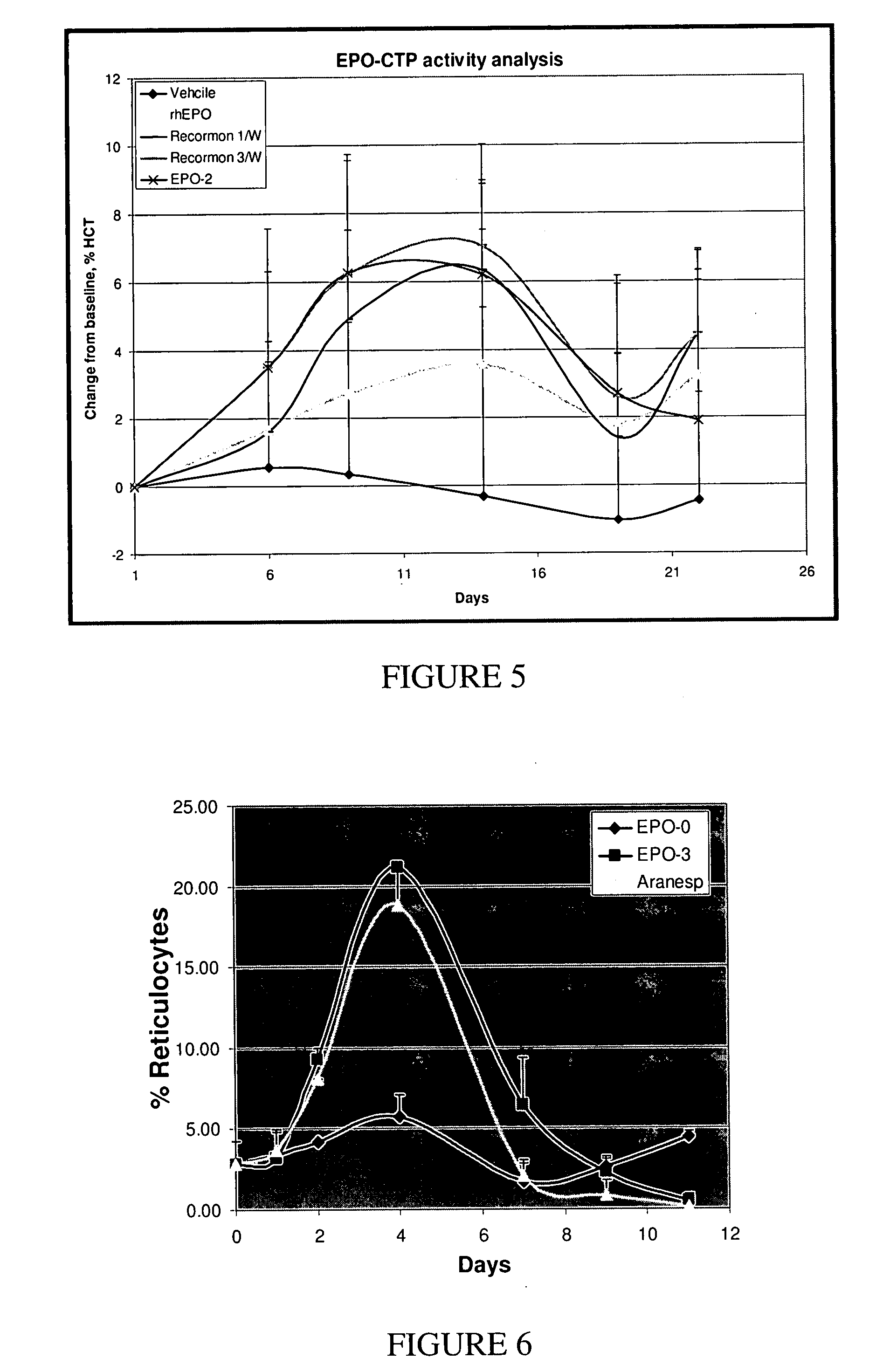
Biological Activity of the EPO-CTP Polypeptides of the Present Invention
[0304] The TF-1 bioactivity test represents the ability of the EPO-CTP variants to bind its receptor and then stimulate activity which results in cell proliferation. Therefore, this test was used as a first step in evaluating the biological potency of the EPO-CTP polypeptides of the present invention.
Materials and Methods
[0305] Cell Proliferation Analysis: Proliferation assay was performed with the cell line TF-1, measuring levels of MTT cellular stain as a function of EPO activity (Kitamura et al., Kitamura, T. et al. (1989) Establishment and characterization of a unique human cell line that proliferates; Hammerling U. et al. In vitro bioassay for human erythropoietin based on proliferative stimulation of an erythroid cell line and analysis of carbohydrate-dependent microheterogeneity. Journal of Pharm. Biomed. Analysis 14(11): 1455-1469 (1996). Exponentially growing TF-1 cells were washed twice, plated at ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com