Drug delivery matrices to enhance wound healing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
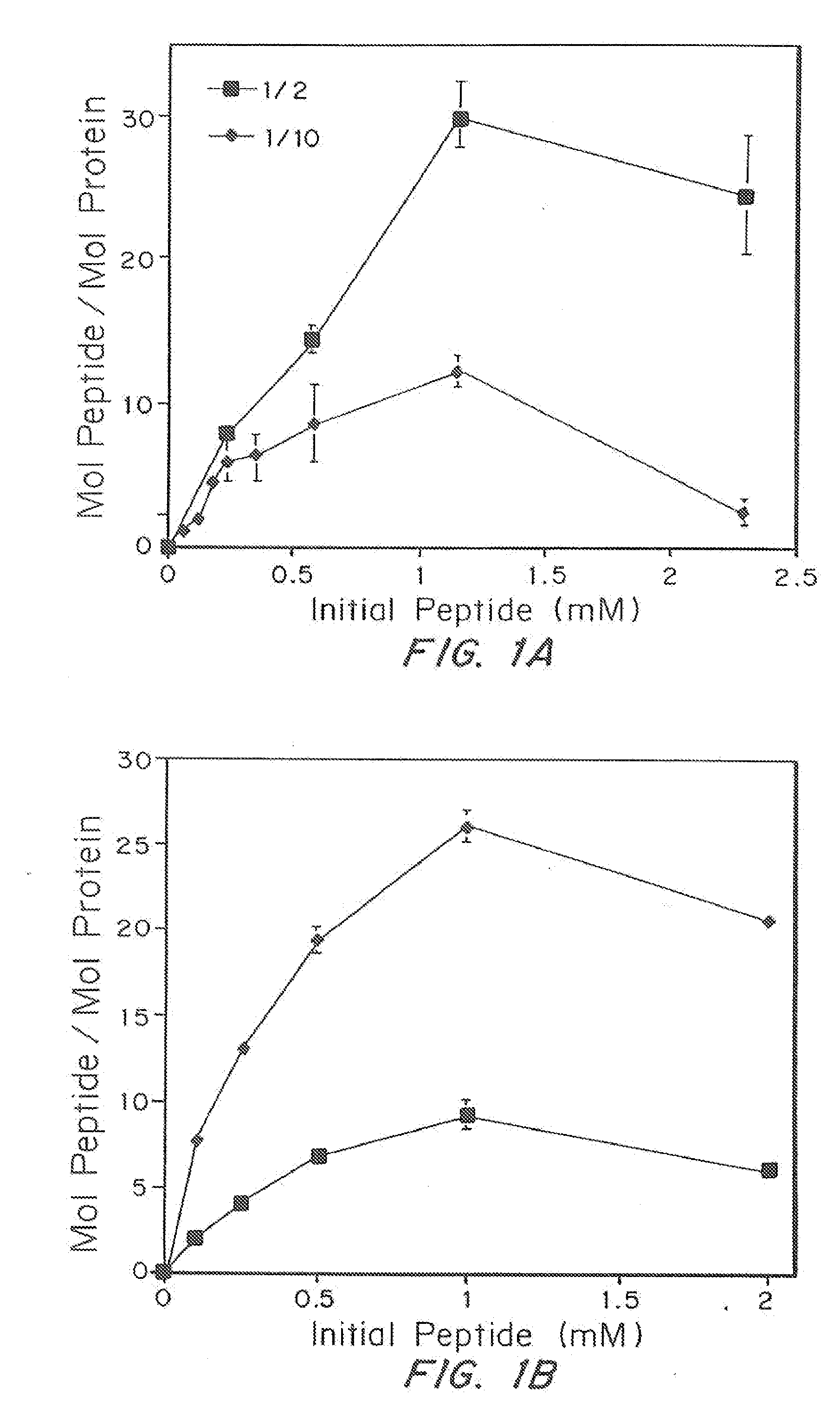
Determination of Incorporation into Fibrin Gels
[0078] A test measuring the native enzymatic activity of the coagulation enzyme, factor XIIIa, was performed. This test was performed by measuring the ability of fibrin gel from two different sources to covalently incorporate a synthetic substrate during the coagulation process. One source of the fibrin gel came from a fibrin glue kit, while the second source came from a purified fibrin gel. Peptides derived from α2-plasmin inhibitor can be covalently incorporated into fibrin gels through the action of factor XIIIa. Thus, one method for testing the enzymatic activity in a fibrin gel or dilution thereof involves testing the ability of different fibrin sources to incorporate this same peptide. The gels were synthesized with various amounts of fluorescently labeled peptide and washed with TBS (0.03 M, pH 7.4) to remove free peptide from the matrix. The gels were then degraded with the minimum amount of plasmin necessary and analyzed with ...
example 2
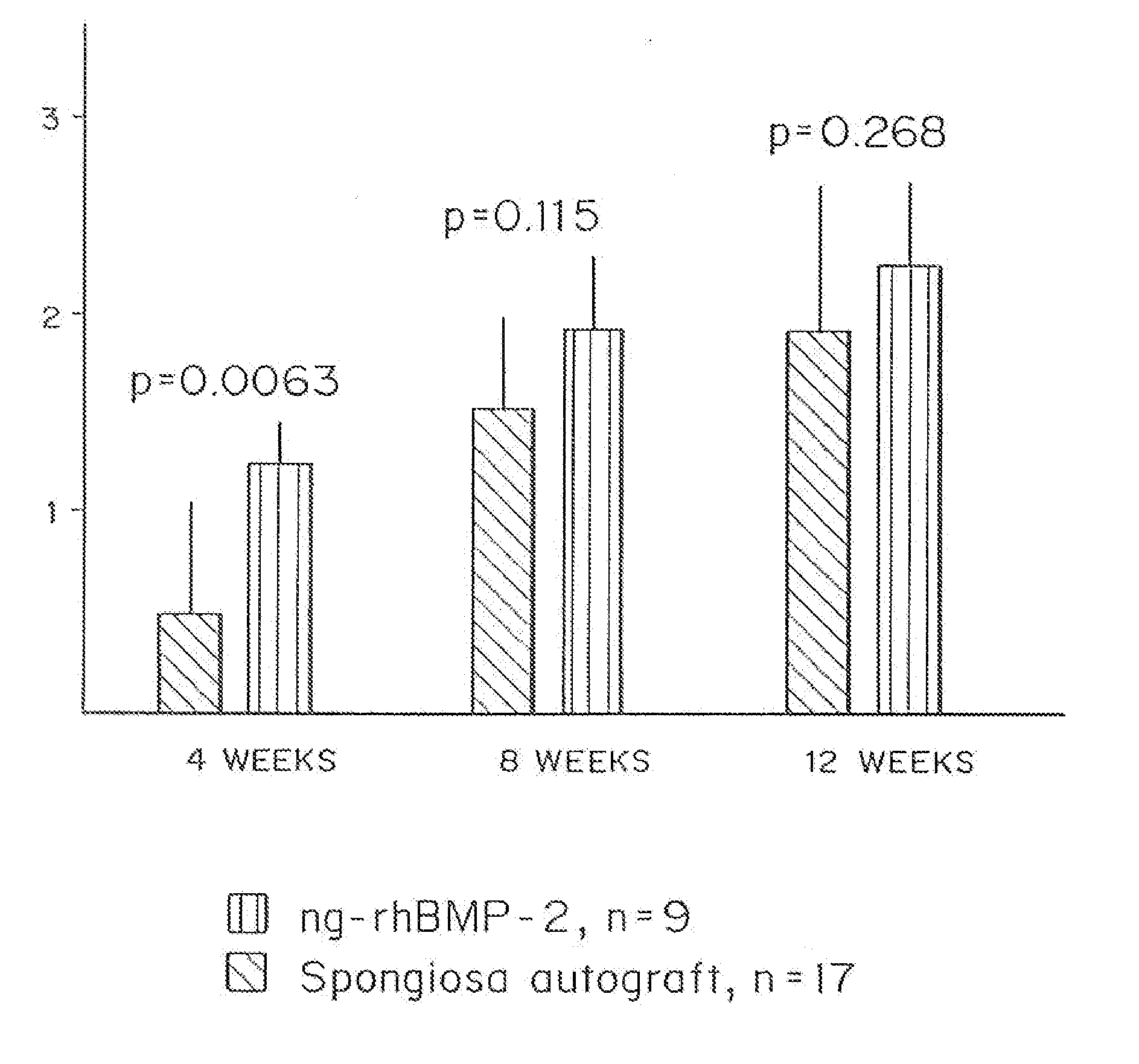
In Vivo Comparison of Fibrin Gels From Different Sources
[0080] A non-glycosylated recombinant form of a bone morphogenetic protein, which was prepared from prokaryotic (E. coli) (rh-BMP-2), was mixed in different fibrin gels, and the gels were tested in a rat femur defect. Because the protein was expressed in a prokaryotic system, it was not glycosylated. Fibrin gels were synthesized from a variety of sources. Purified fibrinogen from Sigma Chemical and a blood bank were employed, as well as fibrin glues (Baxter) at several dilutions. These gels were loaded with rh-BMP-2 and place in a critical size (5 mm full thickness) femur defect. It was observed that all of the fibrin glue dilutions employed and the Sigma fibrin gave a similar healing response, leading to bridging of every critical size defect. The fibrin from the blood bank gave a lower overall response, which was more likely due to cell infiltration properties than to retention of the rh-BMP-2. Therefore, while the healing r...
example 3
Comparison of Retention of Soluble and Insoluble Bioactive Molecules in a Fibrin Matrix
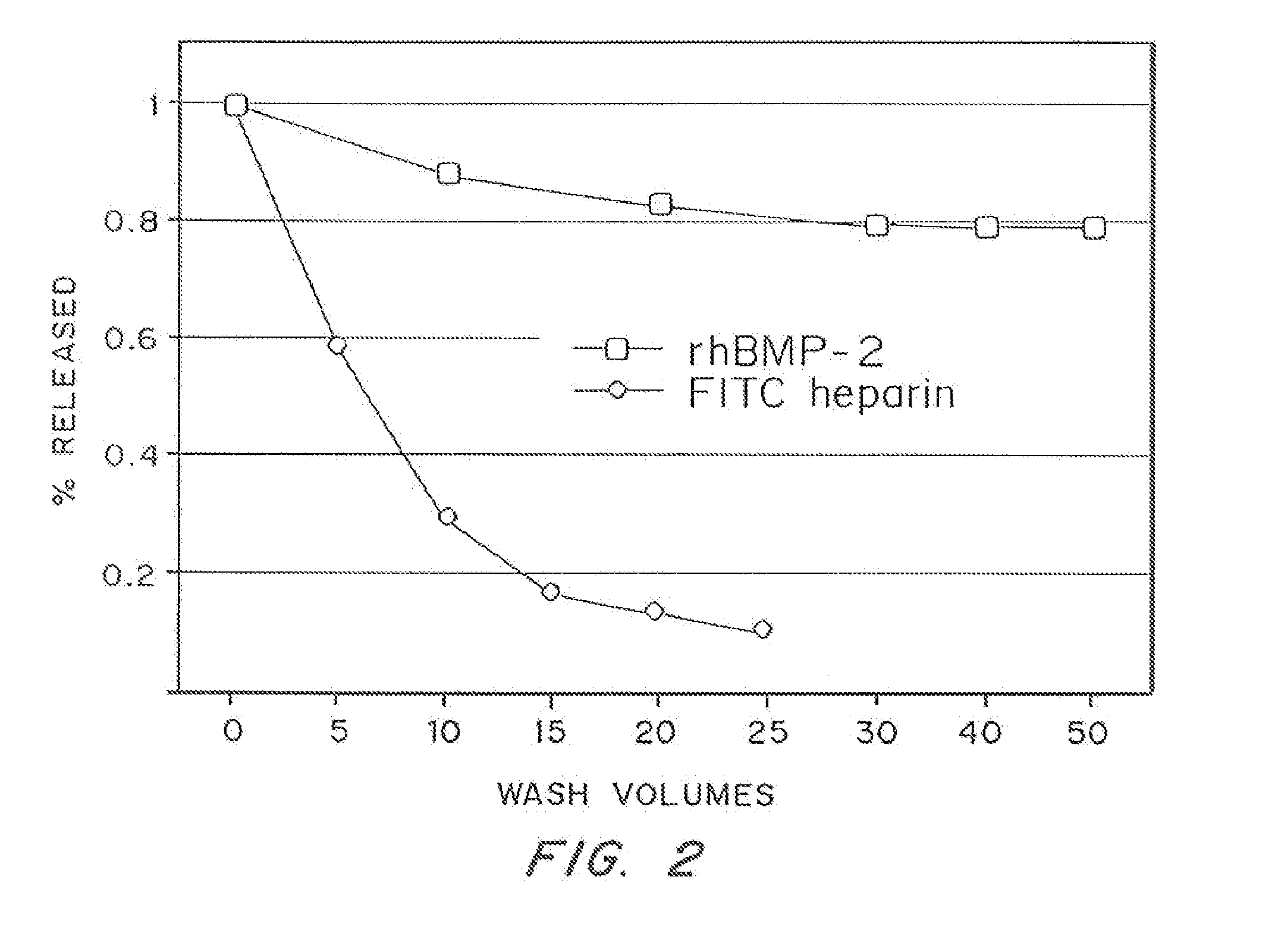
[0081] This invitro assay involved comparing the release kinetics of the entrapped non-glycosylated rh-BMP-2 to the release kinetics of a molecule that is known to have high solubility at physiological pH. Fibrin gels were polymerized using purified fibrinogen (Sigma) at 8 mg / mL and 2 U / mL thrombin at pH 7.4. Calcium was added so that the final concentration was 2.5 mM to increase the rate of gelation
[0082] These gels were synthesized with a bioactive molecule present during the coagulation process and the retention of the molecule inside the fibrin matrix was determined. Gels were washed and kept in phosphate buffered saline (PBS 0.01 M, pH 7.4) at 37° C. and the wash was changed every 12 hours. After thorough washing, the gels were degraded with 0.05 Units of plasmin. The amount of each bioactive molecule present in the washes and in the degraded matrix was determined.
[0083] In the first test...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com