Electrochemical machining method and apparatus
a technology of electrochemical machining and machining method, which is applied in the direction of machining electric circuits, manufacturing tools, power source circuits, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the conductivity of liquid electrolyte, affecting the performance, isostatic strength, and/or dimensional etc., to reduce the conductivity of liquid electrolyte and improve the quality of the honeycomb body. , the effect of reducing the conductivity of liquid electro
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019]The invention will now be described in detail with reference to a few preferred embodiments, as illustrated in the accompanying drawings. In describing the preferred embodiments, numerous specific details are set forth in order to provide a thorough description and understanding of the invention. However, it will be apparent to one skilled in the art that the invention may be practiced without some or all of these specific details. In other instances, well-known features and / or process steps have not been described in detail so as not to unnecessarily obscure the invention. In addition, like or identical reference numerals are used to identify common or similar elements.
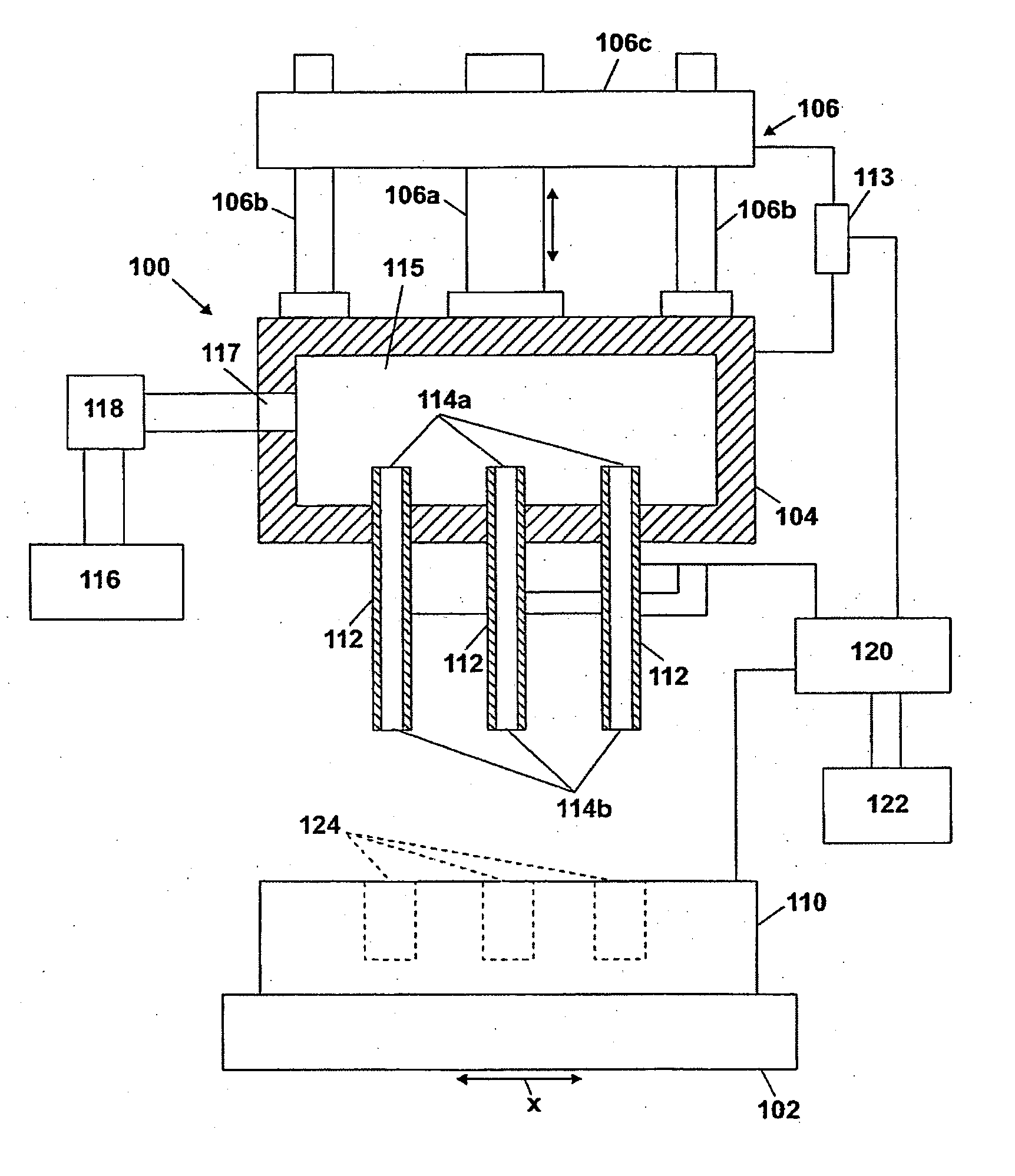
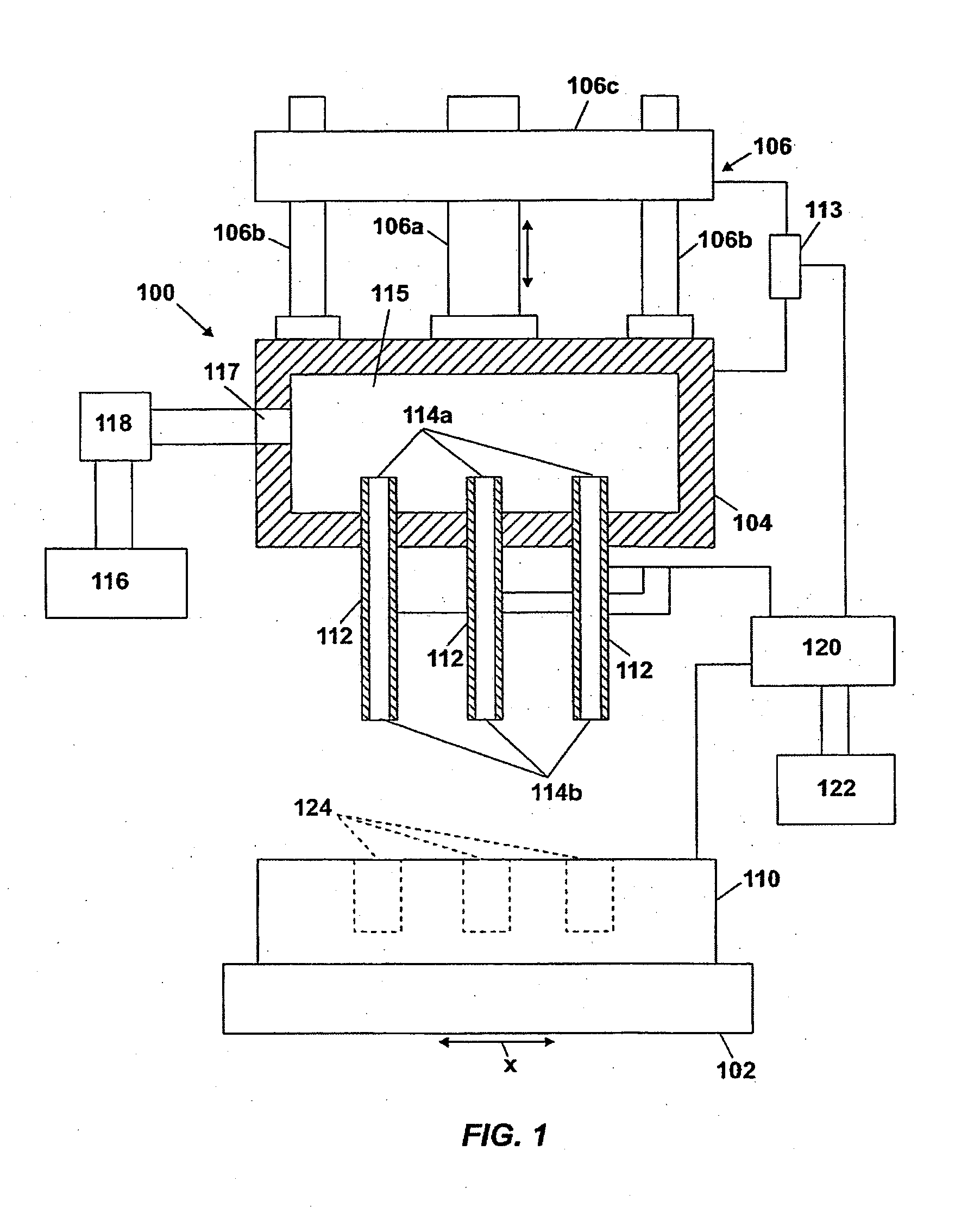
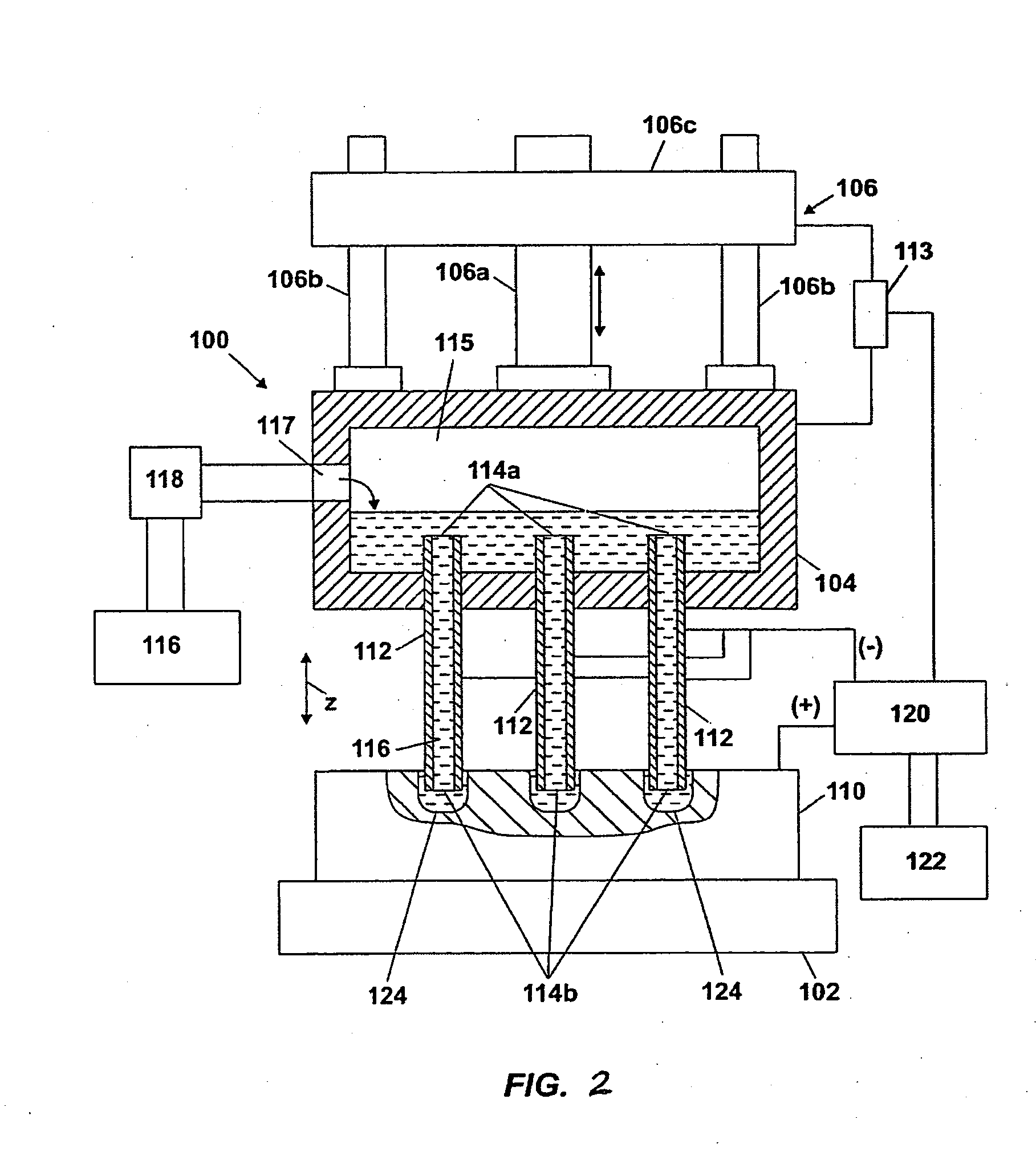
[0020]FIGS. 1 and 2 illustrate a simplified diagram of an electrochemical drilling system 100 of the invention. The system 100 includes a lower fixture 102 and an upper fixture 104 arranged in opposing relation thereto. The lower fixture 102 holds and supports a workpiece 110, such as a blank of hard, preferabl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| reverse voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| reverse voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com