Patents
Literature
123results about "Power source circuits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
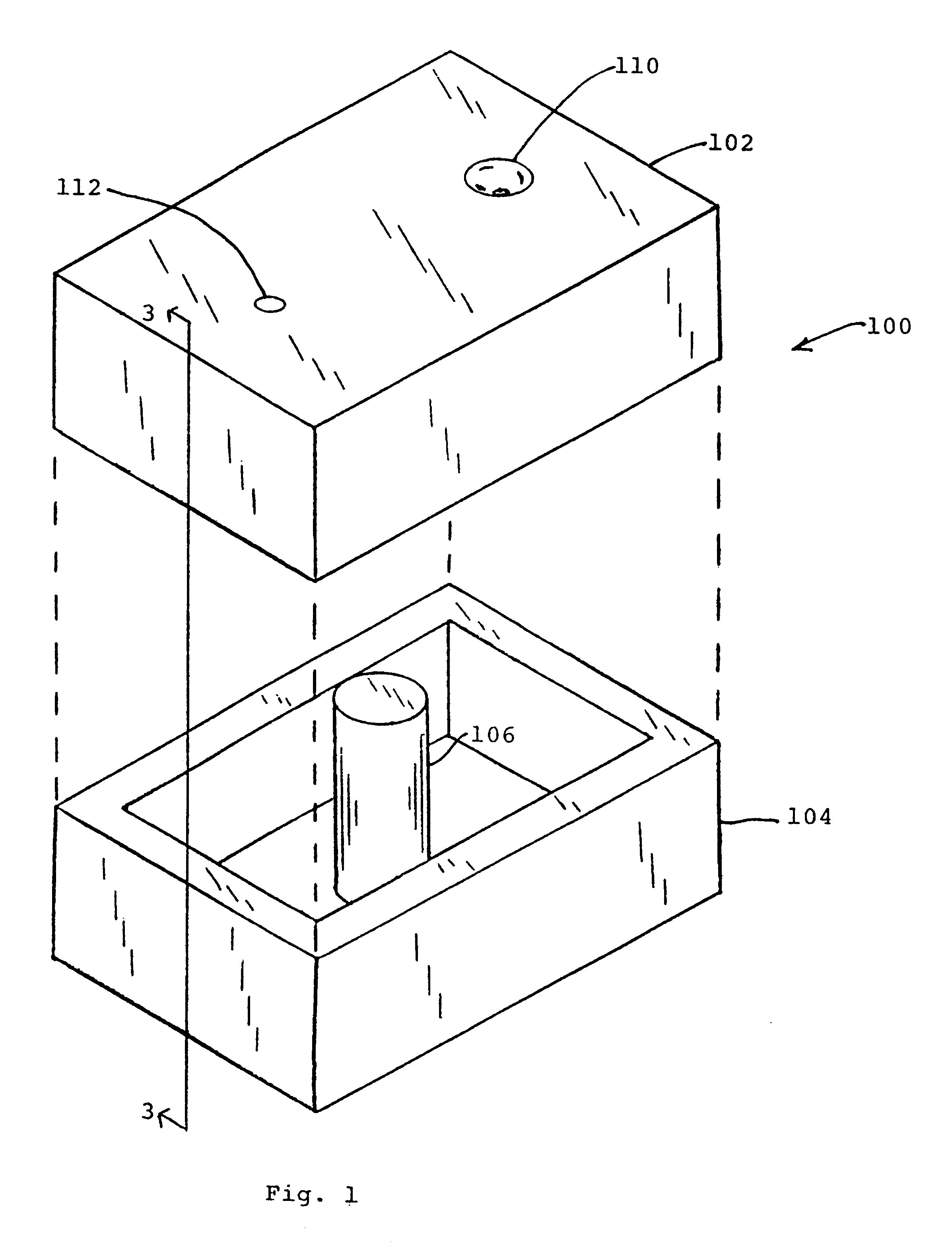
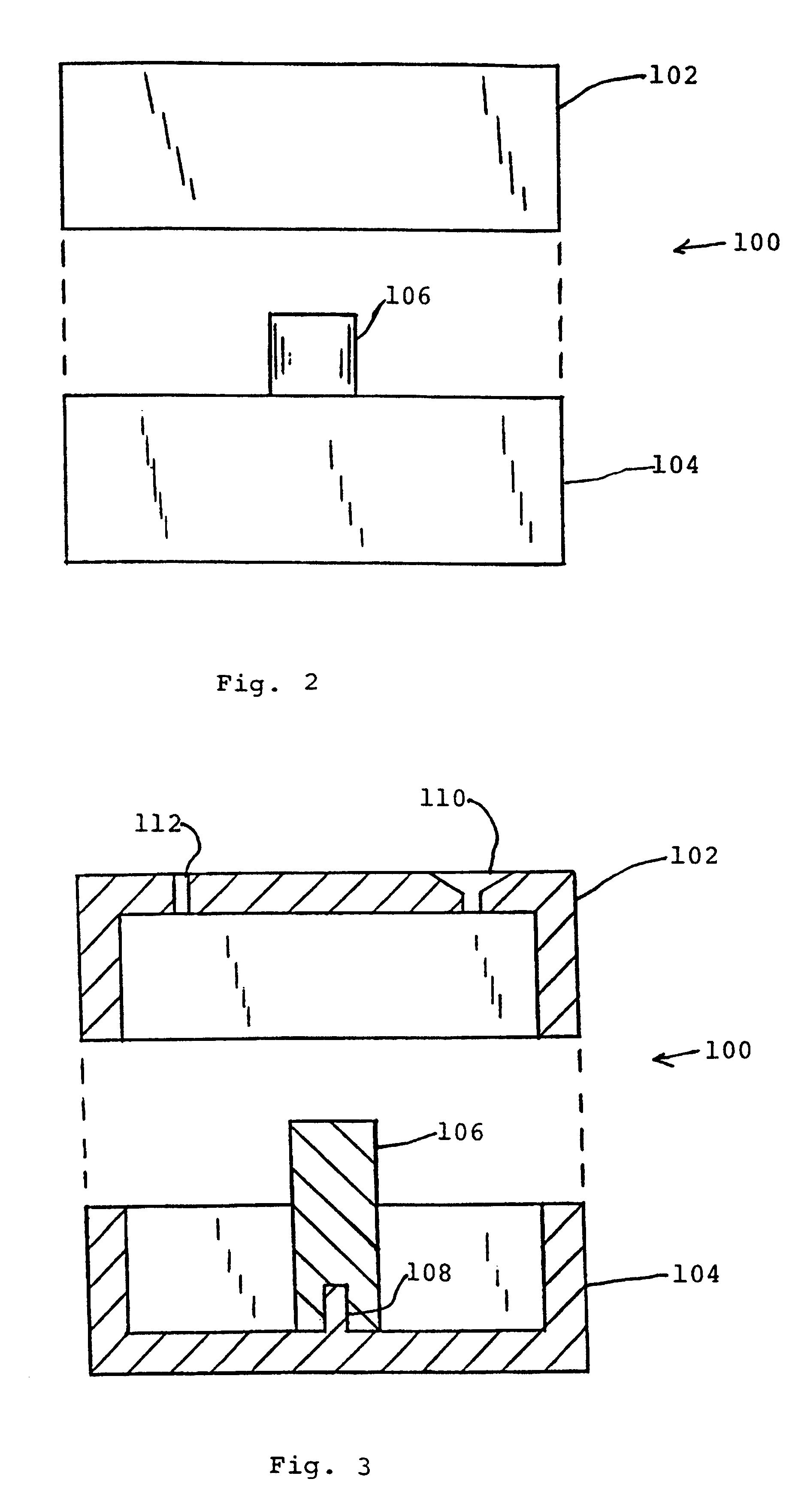
Pulse reverse electrodeposition for metallization and planarization of semiconductor substrates
InactiveUS6319384B1Avoid excessive depositionExcessive depositionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPrinted element electric connection formationSemiconductorElectroplating
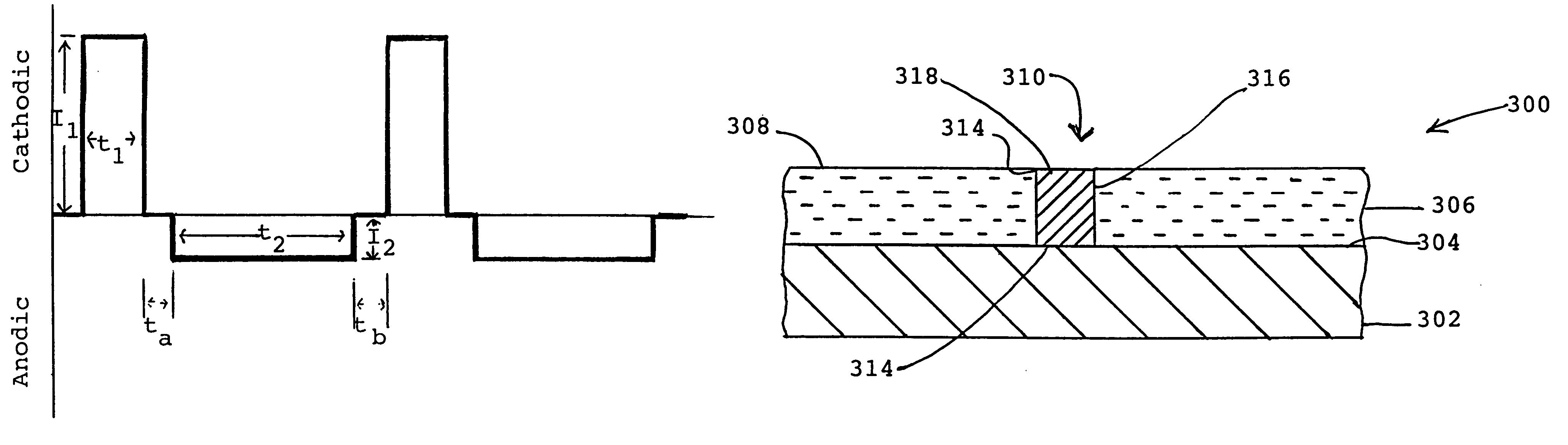
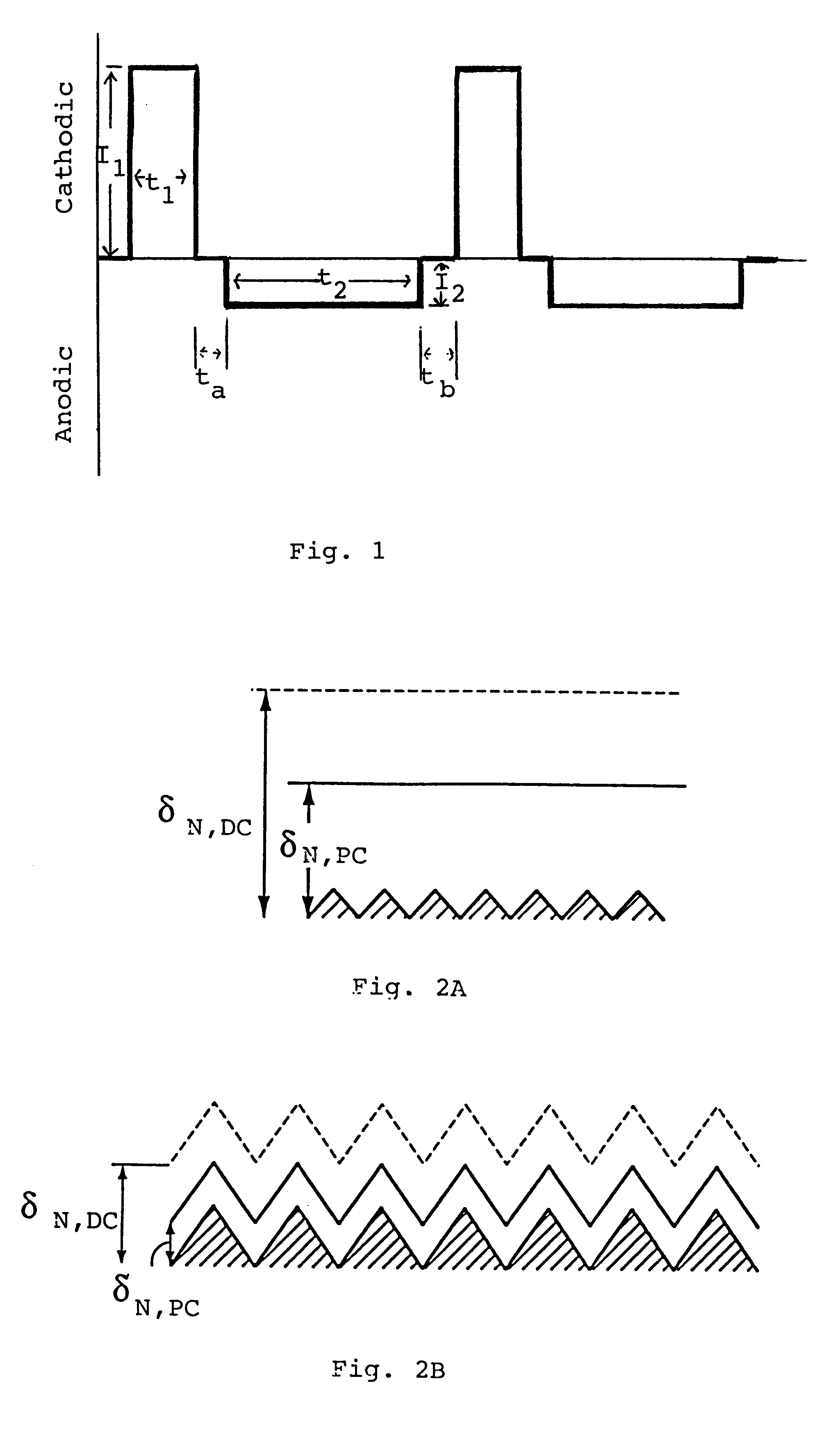
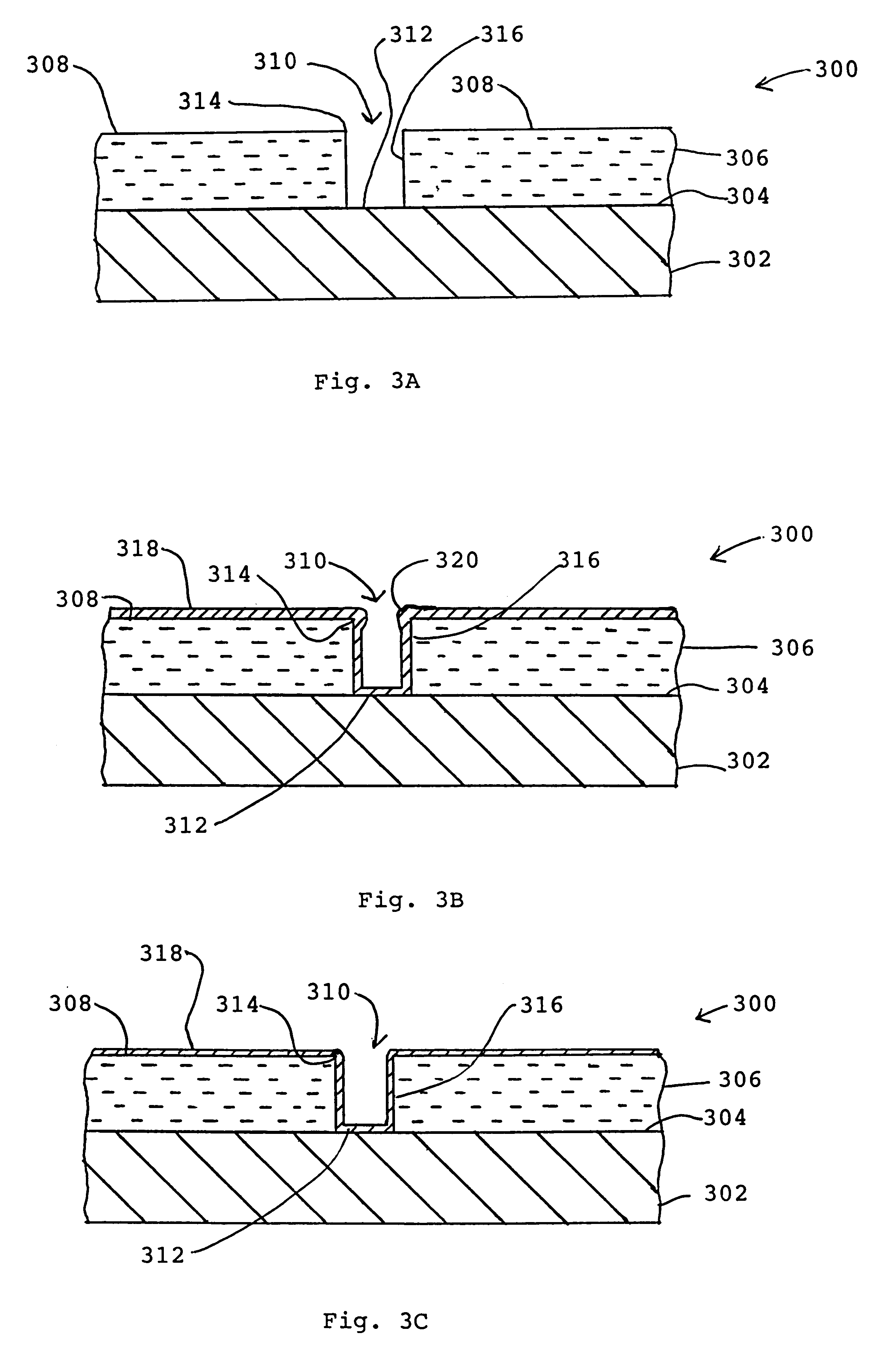
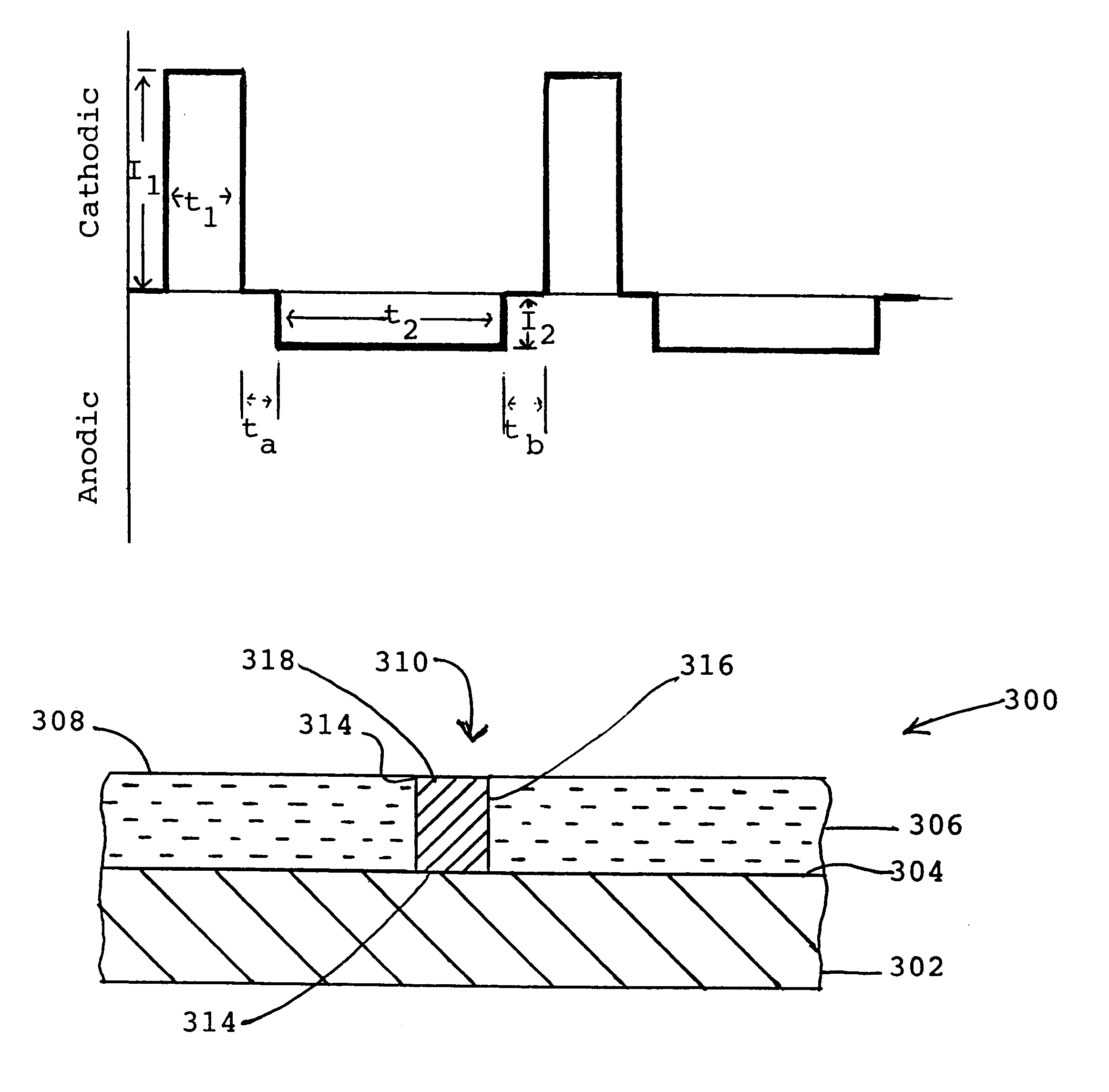
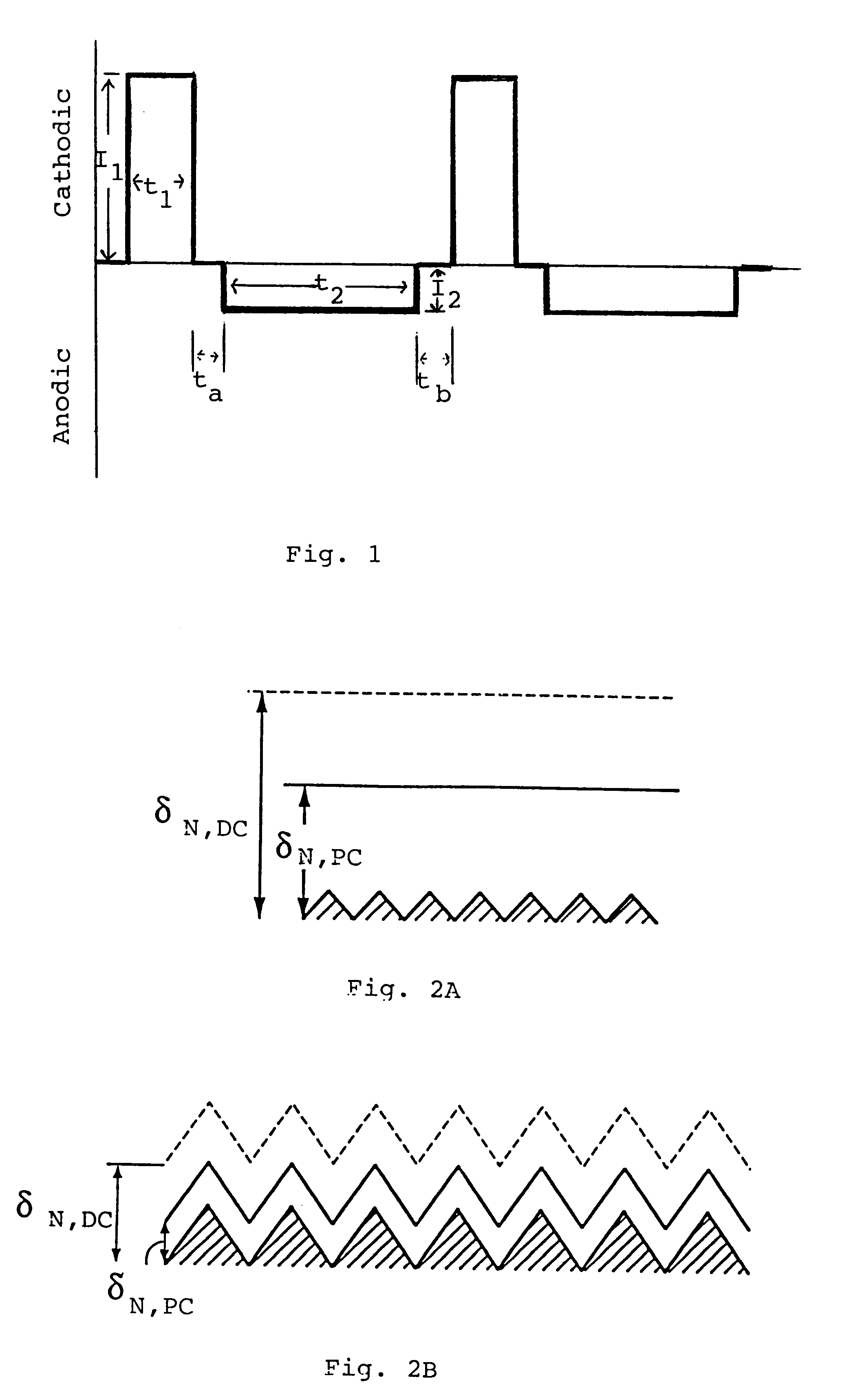
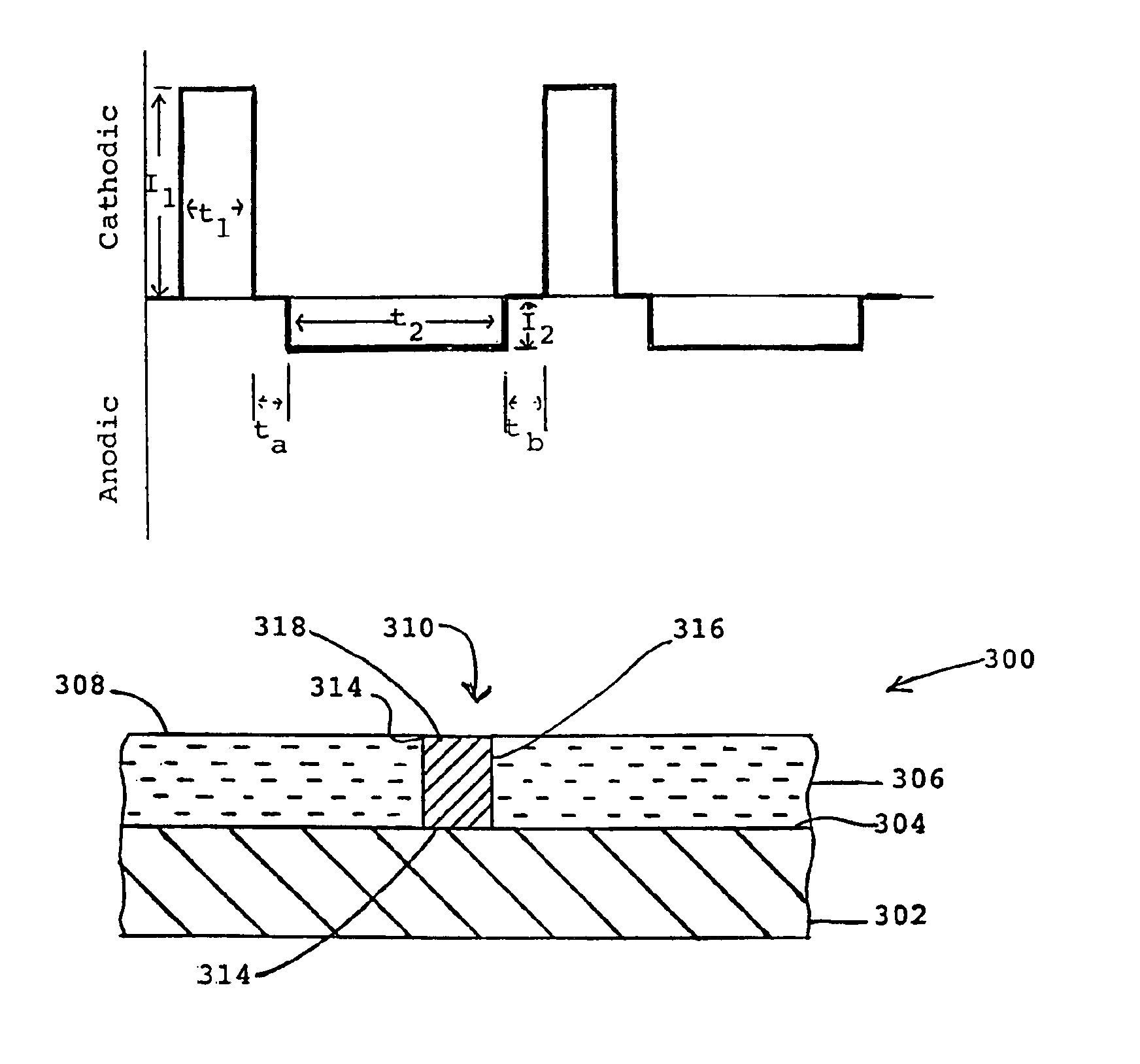
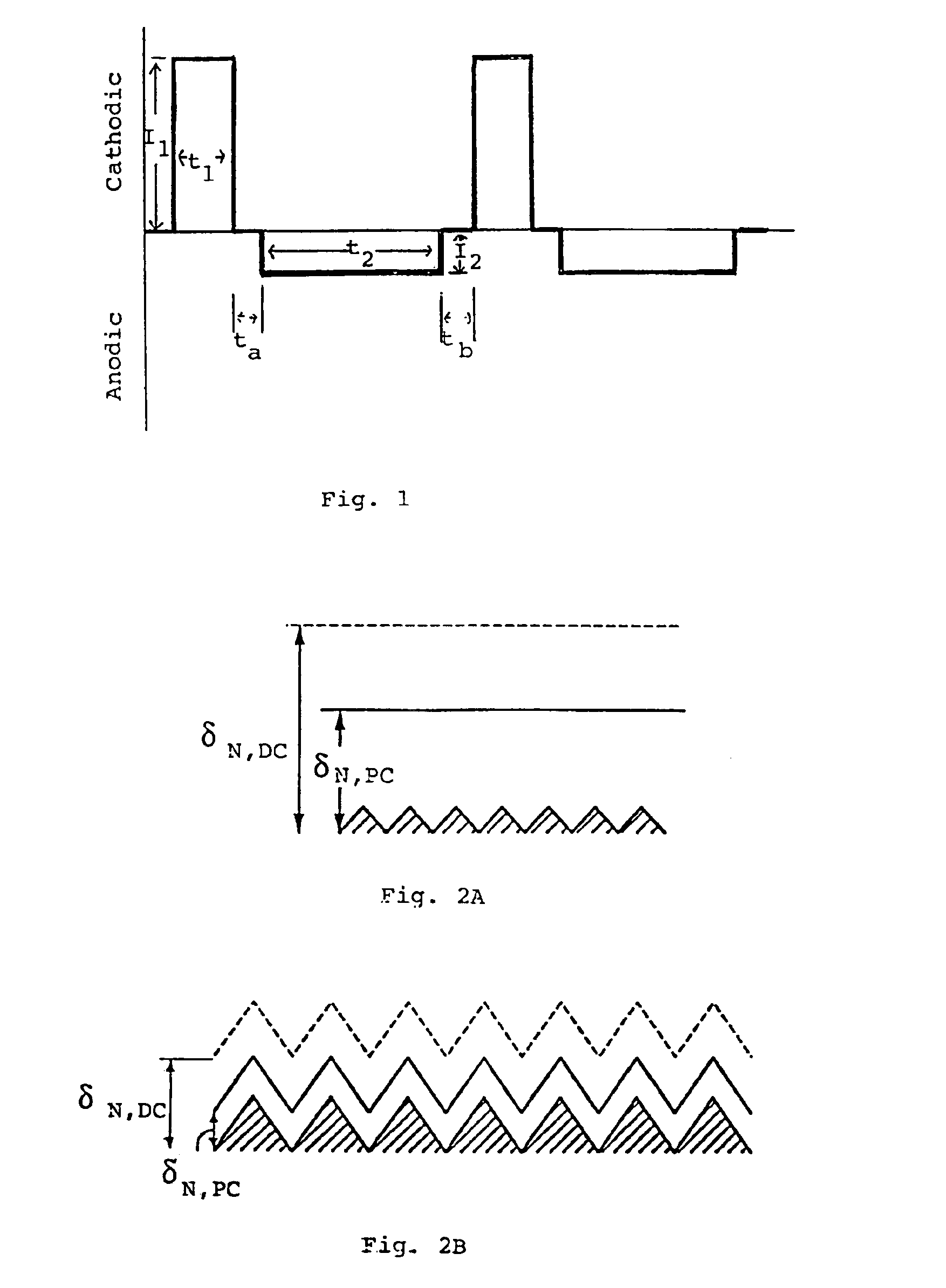
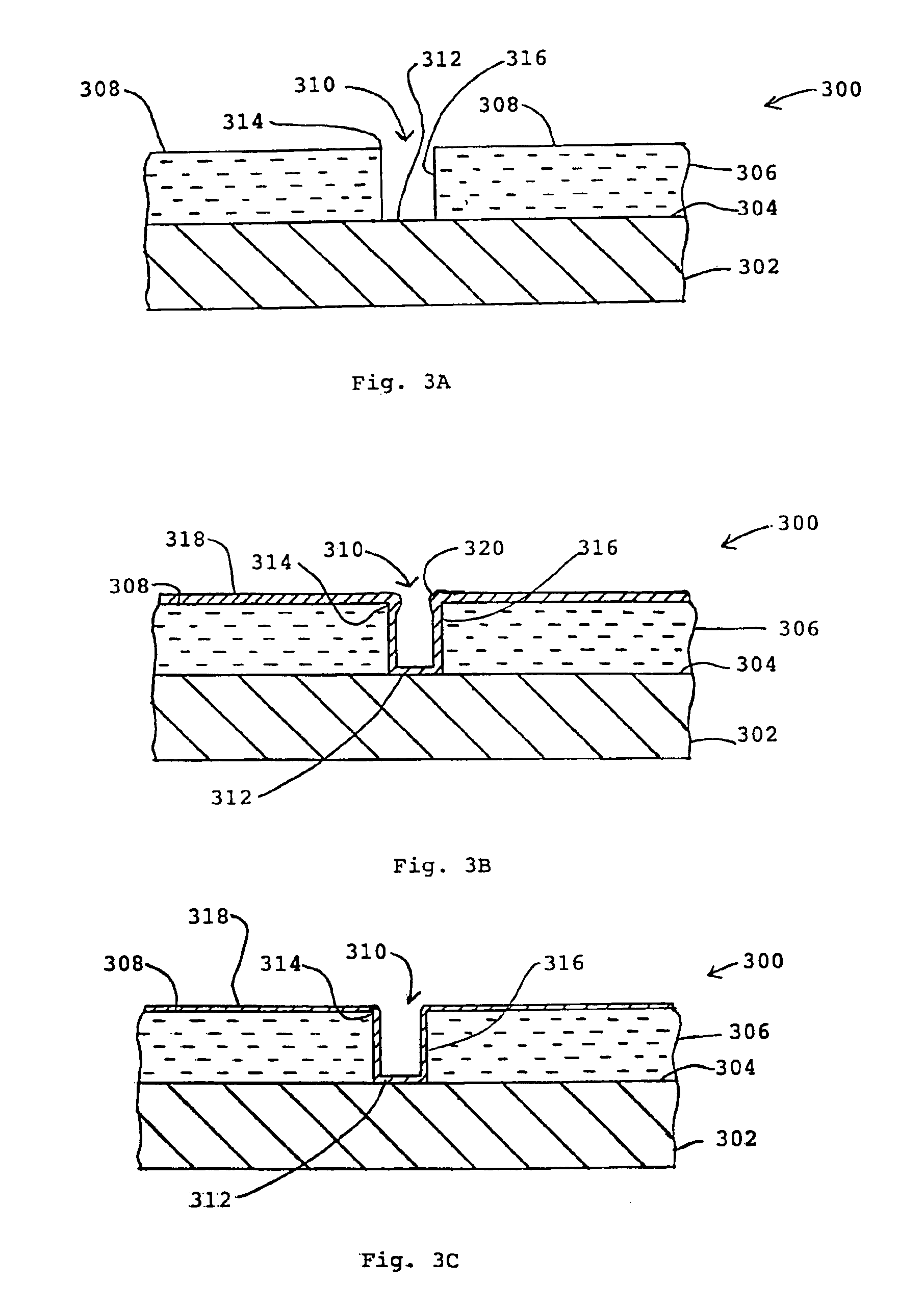
A smooth layer of a metal is electroplated onto a microrough electrically conducting substrate by immersing the substrate and a counterelectrode in an electroplating bath of the metal to be electroplated and passing a modulated reversing electric current between the electrodes. The current contains pulses that are cathodic with respect to said substrate and pulses that are anodic with respect to said substrate. The cathodic pulses have a duty cycle less than about 50% and said anodic pulses have a duty cycle greater than about 50%, the charge transfer ratio of the cathodic pulses to the anodic pulses is greater than one, and the frequency of said pulses ranges from about 10 Hertz to about 12000 Hertz. The plating bath is substantially devoid of levelers and may be devoid of brighteners.
Owner:INVENSAS CORP
Pulse reverse electrodeposition for metallization and planarization of a semiconductor substrates
InactiveUS6203684B1Avoid excessive depositionExcessive depositionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPrinted element electric connection formationSemiconductorElectroplating
A smooth layer of a metal is electroplated onto a microrough electrically conducting substrate by immersing the substrate and a counterelectrode in an electroplating bath of the metal to be electroplated and passing a modulated reversing electric current between the electrodes. The current contains pulses that are cathodic with respect to said substrate and pulses that are anodic with respect to said substrate. The cathodic pulses have a duty cycle less than about 50% and said anodic pulses have a duty cycle greater than about 50%, the charge transfer ratio of the cathodic pulses to the anodic pulses is greater than one, and the frequency of said pulses ranges from about 10 Hertz to about 5000 Hertz.
Owner:INVENSAS CORP
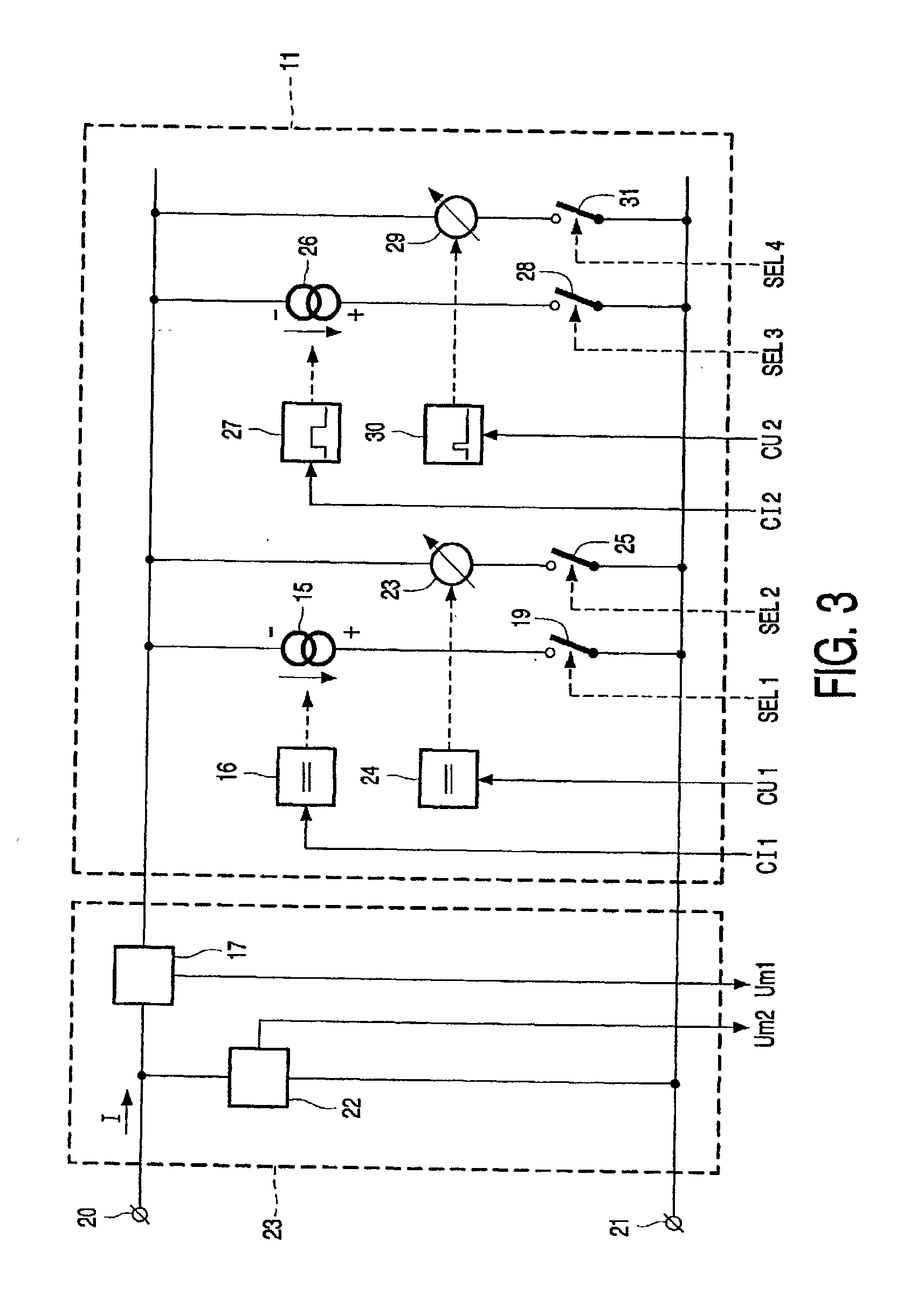
Method of controlling an electrochemical machining process
InactiveUS20020169516A1Improve machining accuracyAvoid large gapsMachining electric circuitsElectric circuitsElectrochemistryElectrochemical machining
A method of controlling a process of electrochemically machining an electrically conductive workpiece employing the spectral composition of the measured voltage within a predetermined measuring period such as induced by an applied current between the electrically conductive workpiece and an electrode tool. A process of electrochemically machining employing a material removing step with electric current supplied continuously and an a workpiece shaping step with electric current supplied intermittently. An advantageous embodiment employs extreme short pulses.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
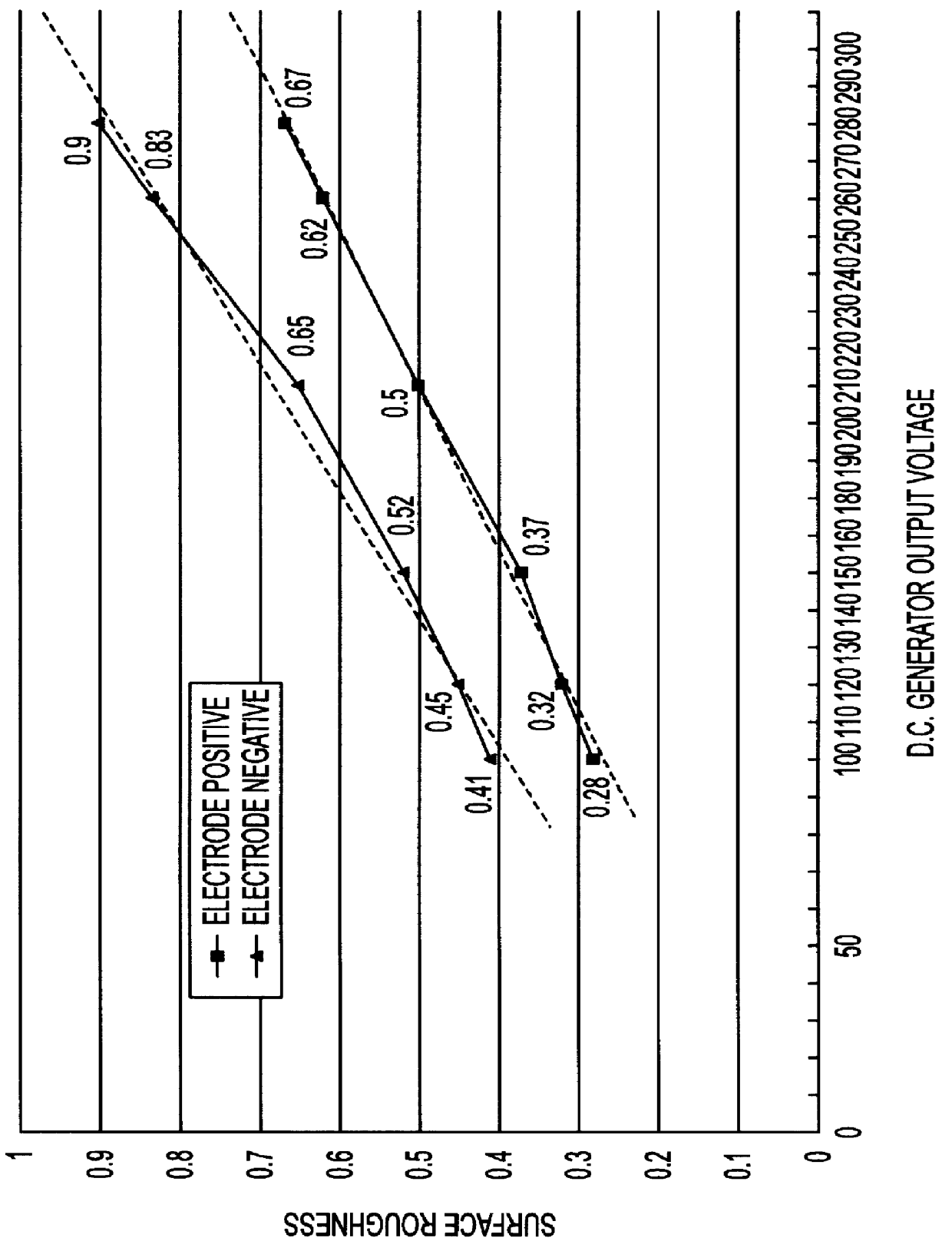
Method and apparatus for achieving a fine surface finish in wire-cut EDM
InactiveUS6130395AImprove surface roughnessStable processingArc welding apparatusElectric circuitsSurface finishRough surface
A wire-cut EDM method and apparatus for machining to a fine surface roughness of 1 mu m Rmax or less. Two power supplies and a electrode polarity switching system are used. A first high energy power source is used for initial profile cutting and may also be used for one or more later cuts while the machining pulse parameters, and feed rate and offset are adjusted for increasing less rough surface finishes. The wire electrode is held at negative machining potential. A second power supply and smaller offset values are used for later cuts to create lower values of surface roughness, while still maintaining the wire electrode at a negative machining potential. Finally, in order to create a fine finished surface (Rmax
Owner:SODICK CO LTD
System and method for providing electrochemical machining of a device
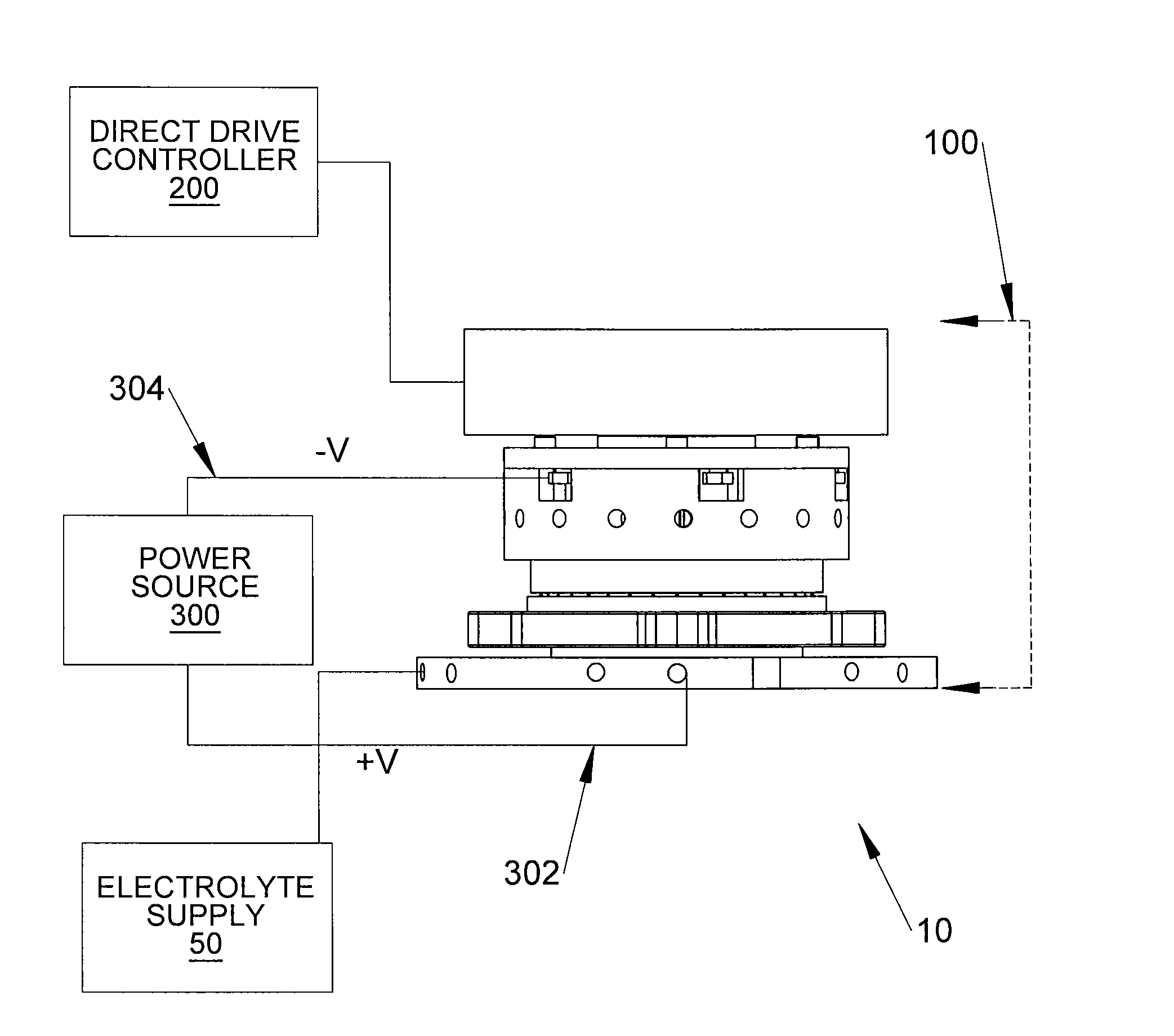
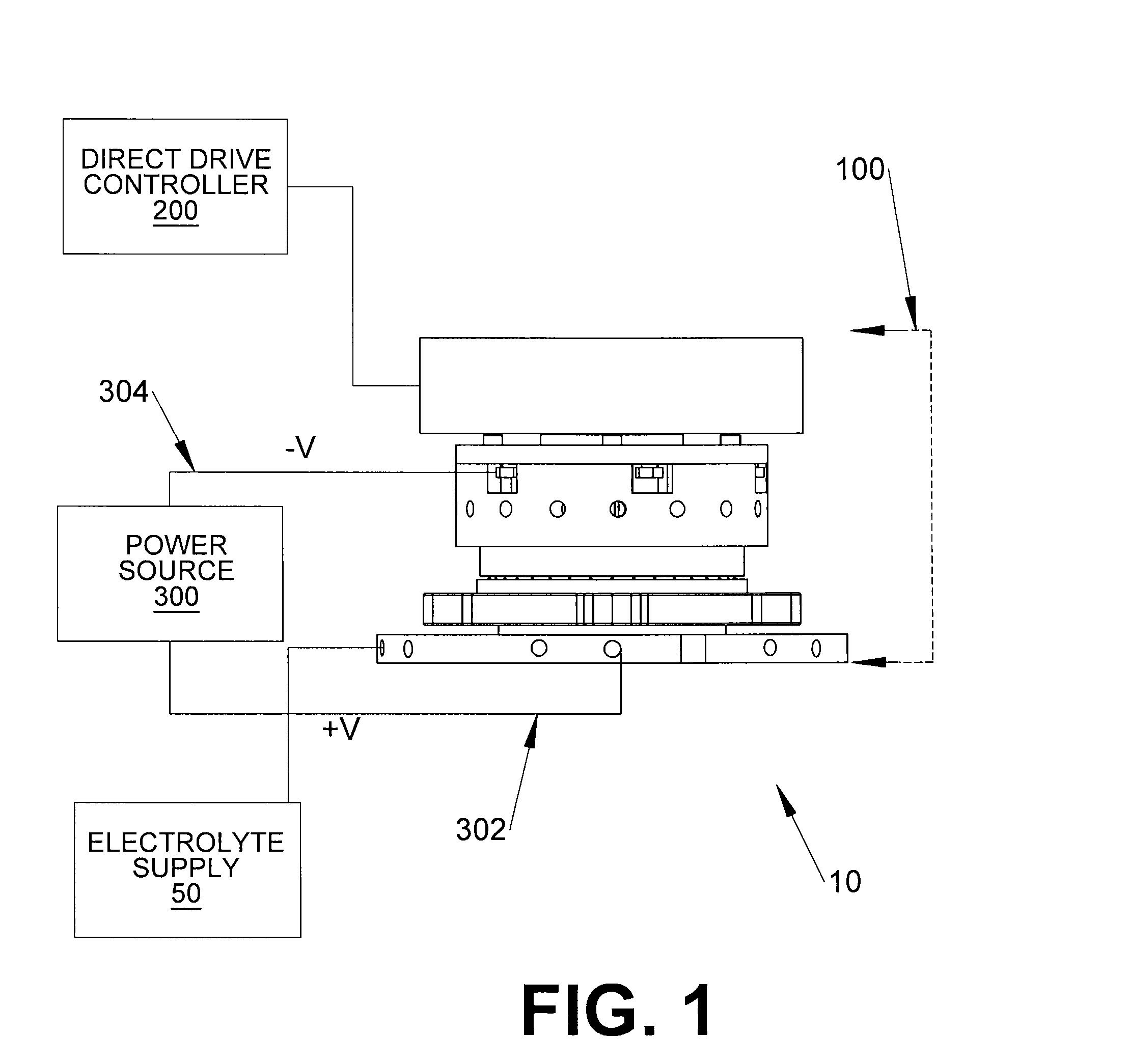
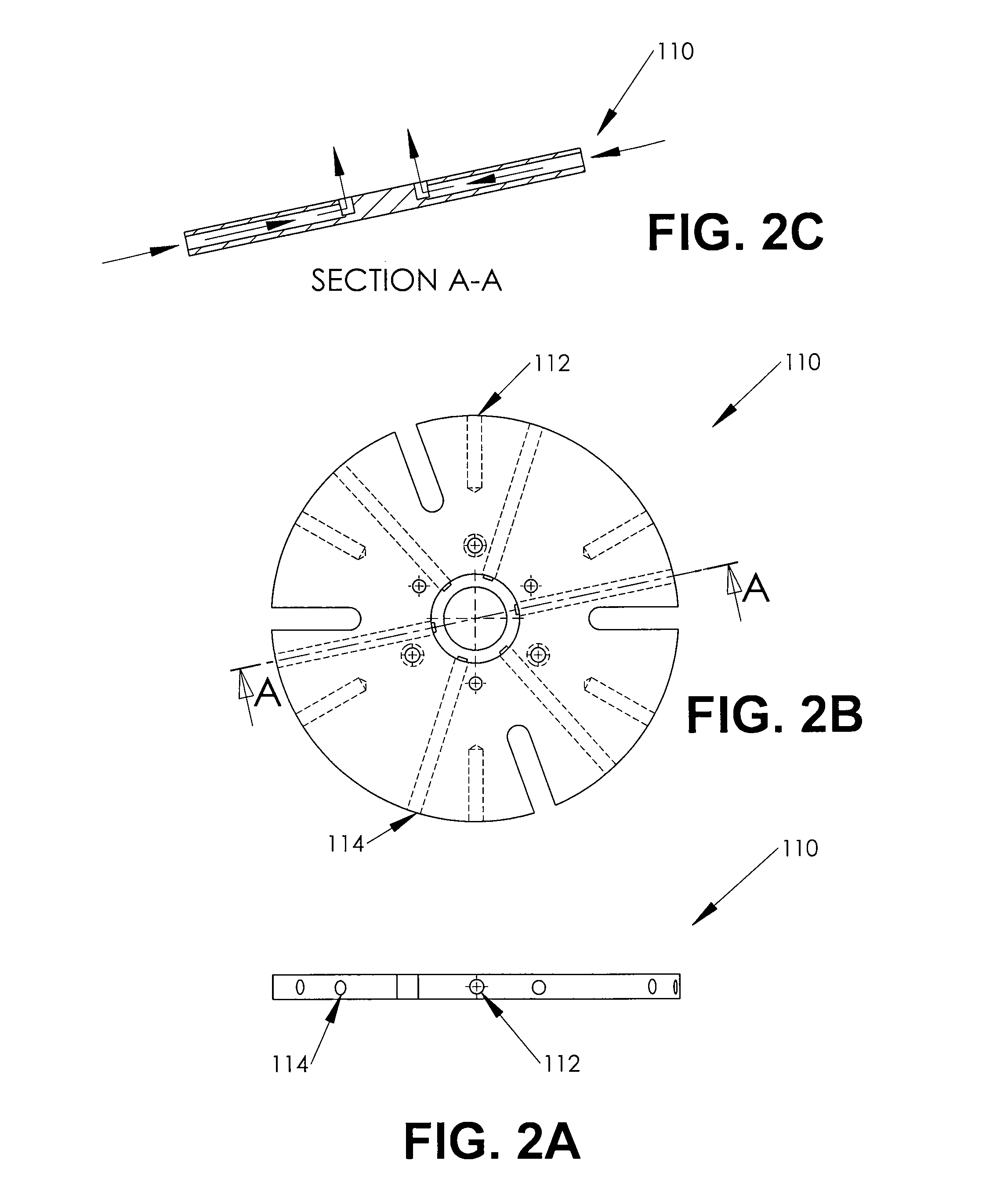
A system and method for electrochemically machining a work-piece contains a fixture capable of receiving a work-piece and securing the work-piece to the fixture. An electrolyte source is also provided. In addition, the system contains a rotary drive subassembly capable of receiving a portion of the work-piece therein, motion of the rotary drive assembly being determined by a received control signal, wherein frequency and amplitude of the control signal increases and decreases motion of the rotary drive subassembly, and wherein the control signal is a trapezoidal waveform.
Owner:TURBOCAM
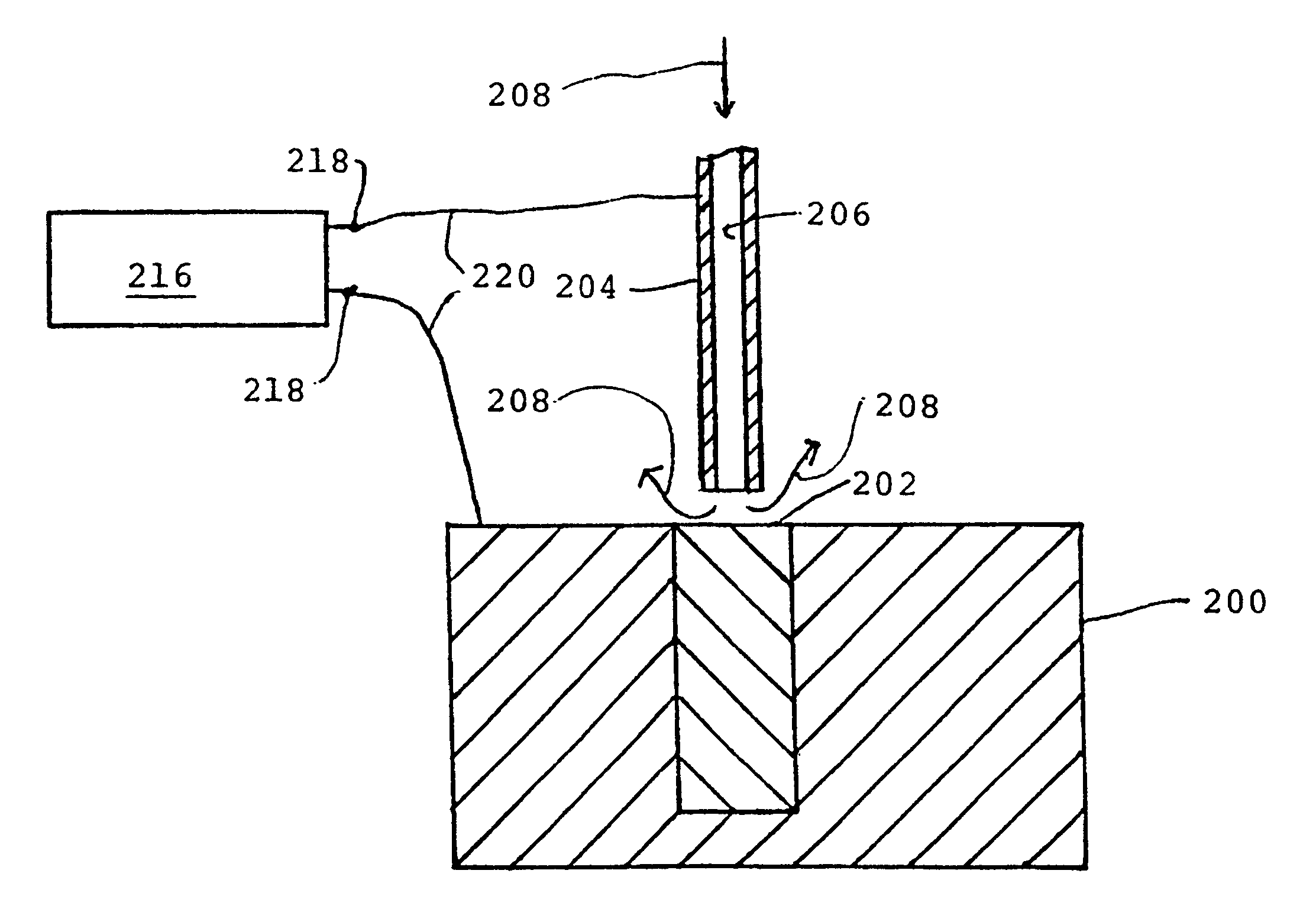
Removal of sacrificial cores by electrochemical machining
InactiveUS6676825B1Electrolysis componentsFrom normal temperature solutionsElectrolysisMaterials science
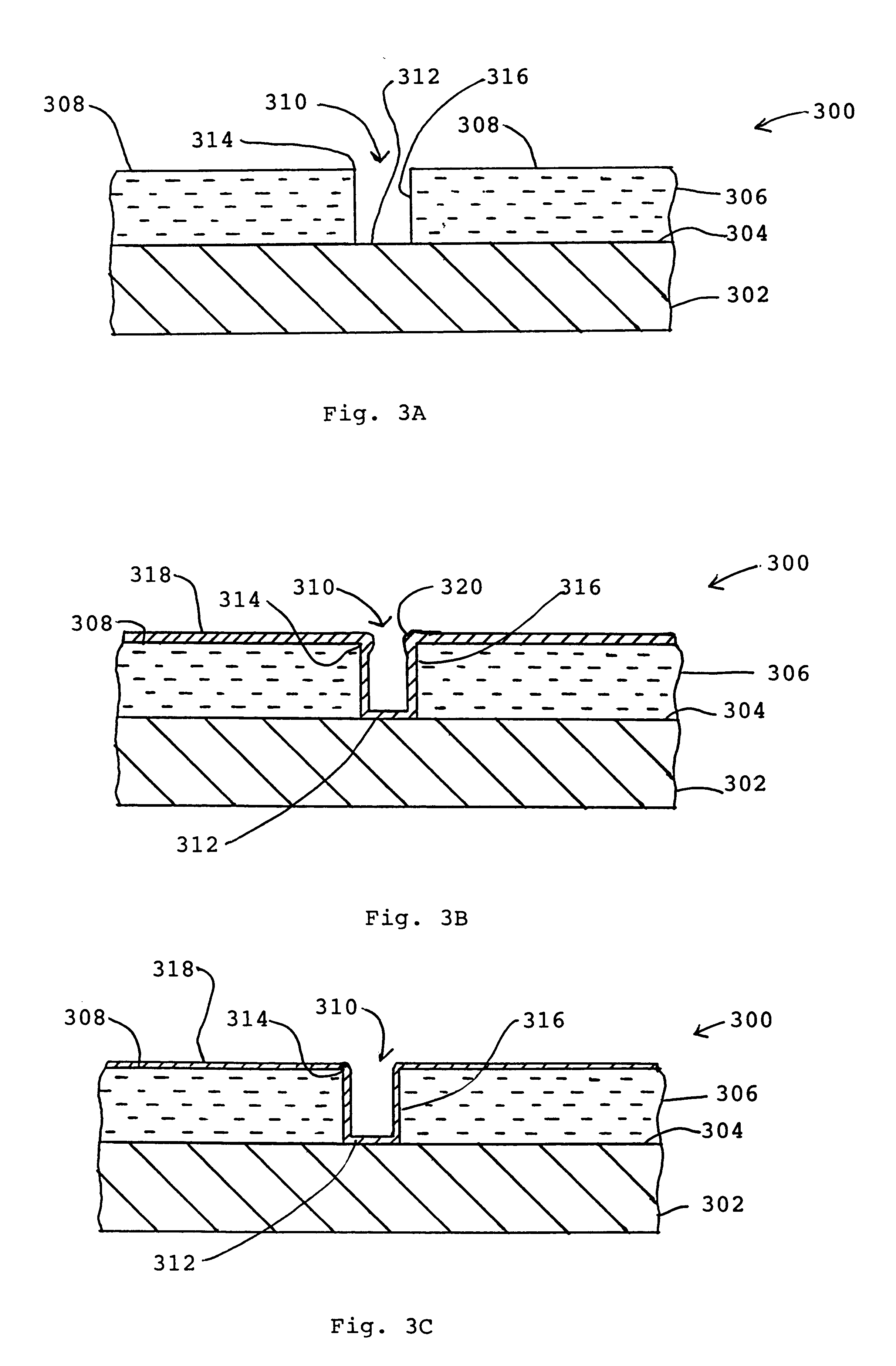
A sacrificial core (304) defining a cavity in a metallic or non-metallic shaped article of manufacture, e.g., a casting (302), is made from a metal that can be electrolytically dissolved. The sacrificial core (304) is removed from the article (302) by electrochemical machining. The sacrificial core (304) may be a hollow shell (306) incorporating an integral electrode (308) within the shell and electrically insulated from the shell.
Owner:FARADAY TECH INC
Electrochemical machining method and apparatus
InactiveUS20080099343A1Reduce conductivityAffect performanceElectrolysis componentsMachining electric circuitsReverse currentElectrochemistry
An electrochemical machining system and method includes at least one tube arranged in a first fixture, a second fixture arranged adjacent to the first fixture, the second fixture adapted for supporting a workpiece relative to the tube, a translation mechanism which causes relative movement between the first fixture and the second fixture, a power supply which supplies a current to the workpiece and the tube, and a control unit which controls the power supply to alternately apply a forward current and a zero current (C0) to the workpiece and the tube for a total time interval (tt) wherein deplation of the workpiece occurs and bubbles are separated from the tube. This may be followed by a reverse current (CR) or voltage to the workpiece and the tube for a second time interval (tR), wherein deplation of the workpiece occurs.
Owner:CORNING INC
Discharge-processing power source device
InactiveUS20060054600A1High currentReduce lossElectric circuitsElectric variable regulationElectric dischargeLow speed
A power supply device for electric discharge machining includes a switching circuit that supplies a discharge pulse current to an inter-electrode portion that is a portion between an electrode and a workpiece serving as another electrode arranged to be opposed to the electrode at a predetermined interval; and a pulse-width control unit that generates a control pulse signal of a predetermined pulse width in response to a detection signal for starting a discharge at the inter-electrode portion. The switching circuit includes a switching circuit including a switching element suitable for a high-speed operation and a switching circuit including a switching element suitable for a low-speed operation, and receives the control pulse signal in parallel.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
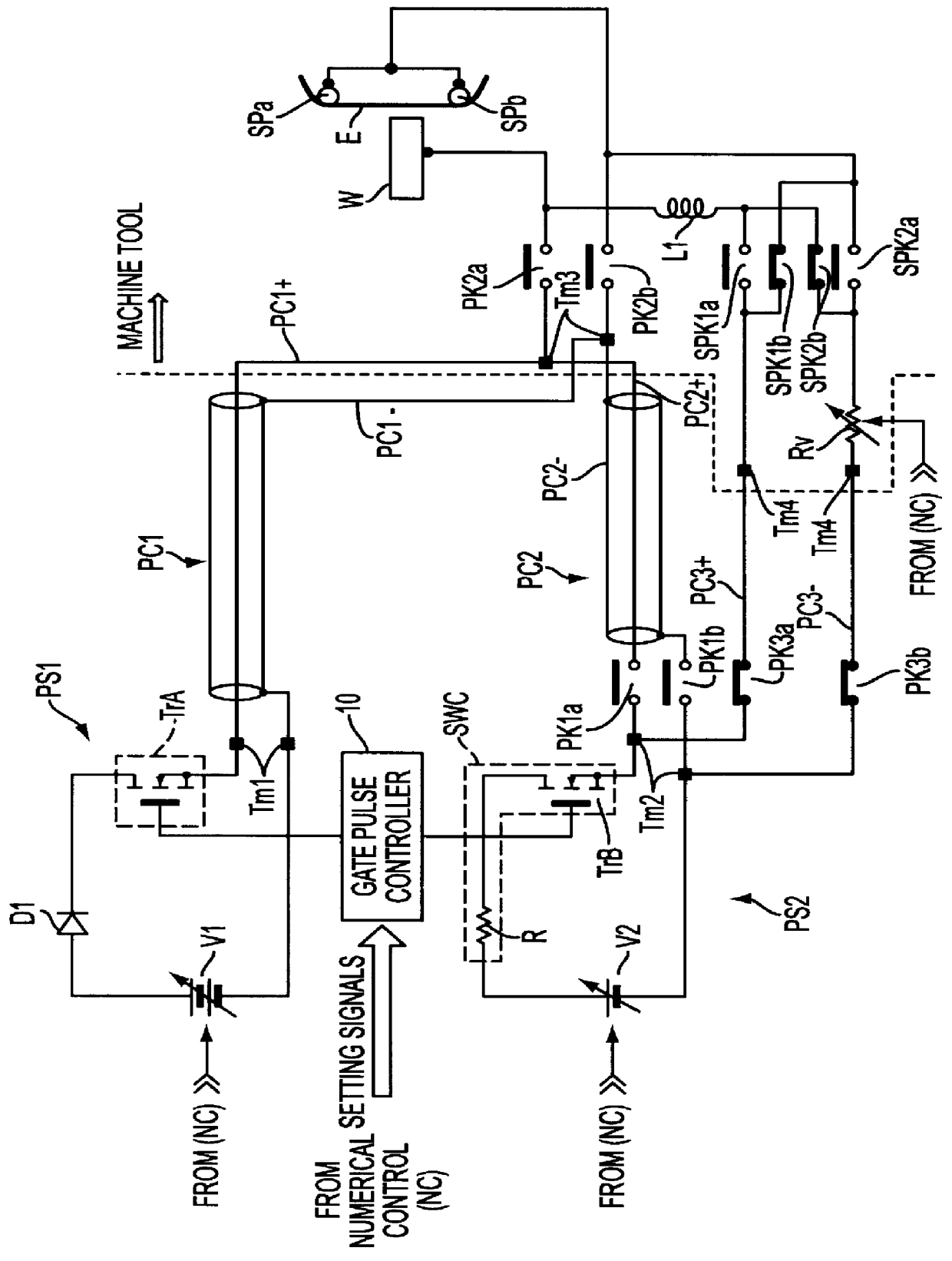
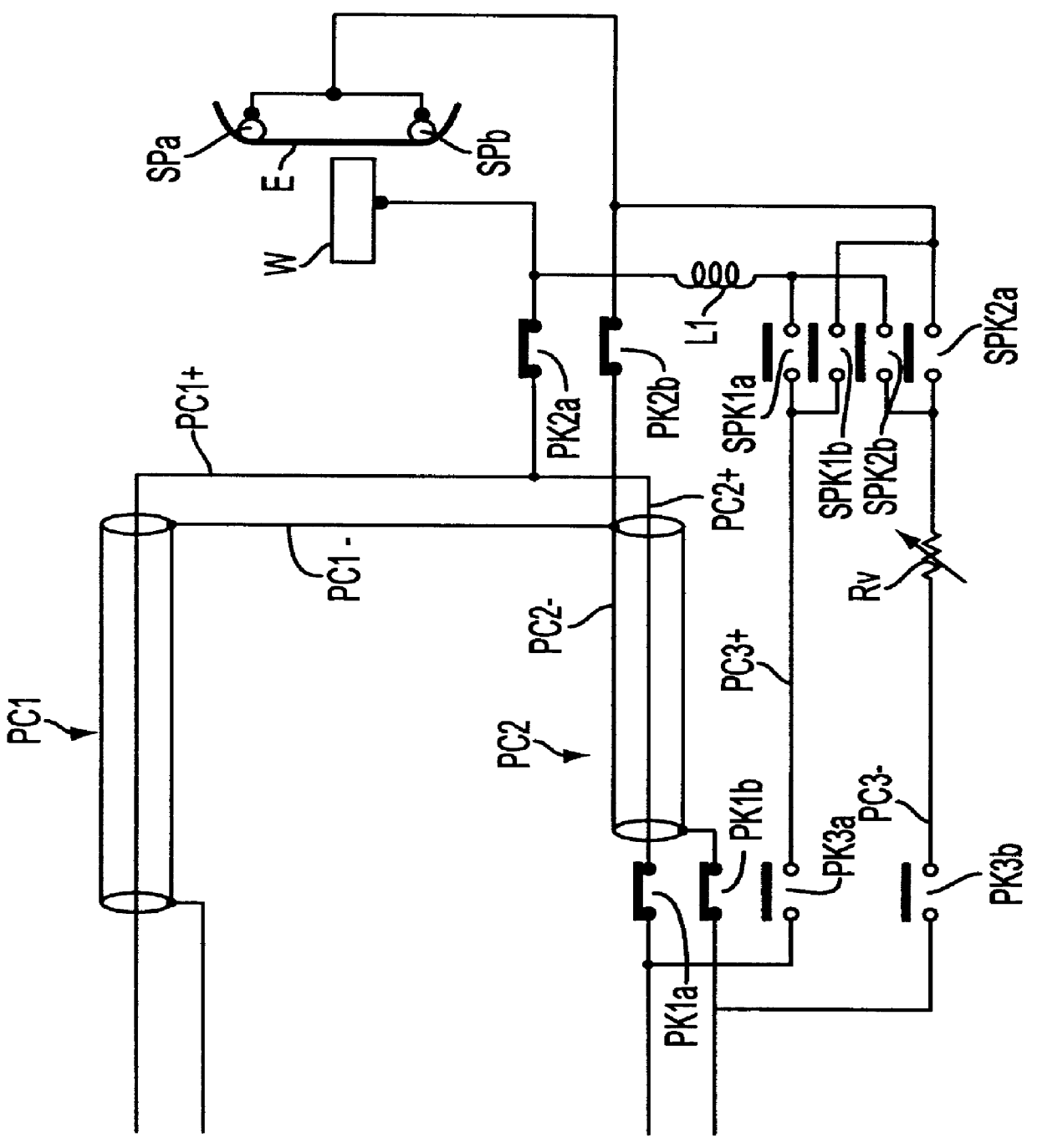
Wire electric discharge machine
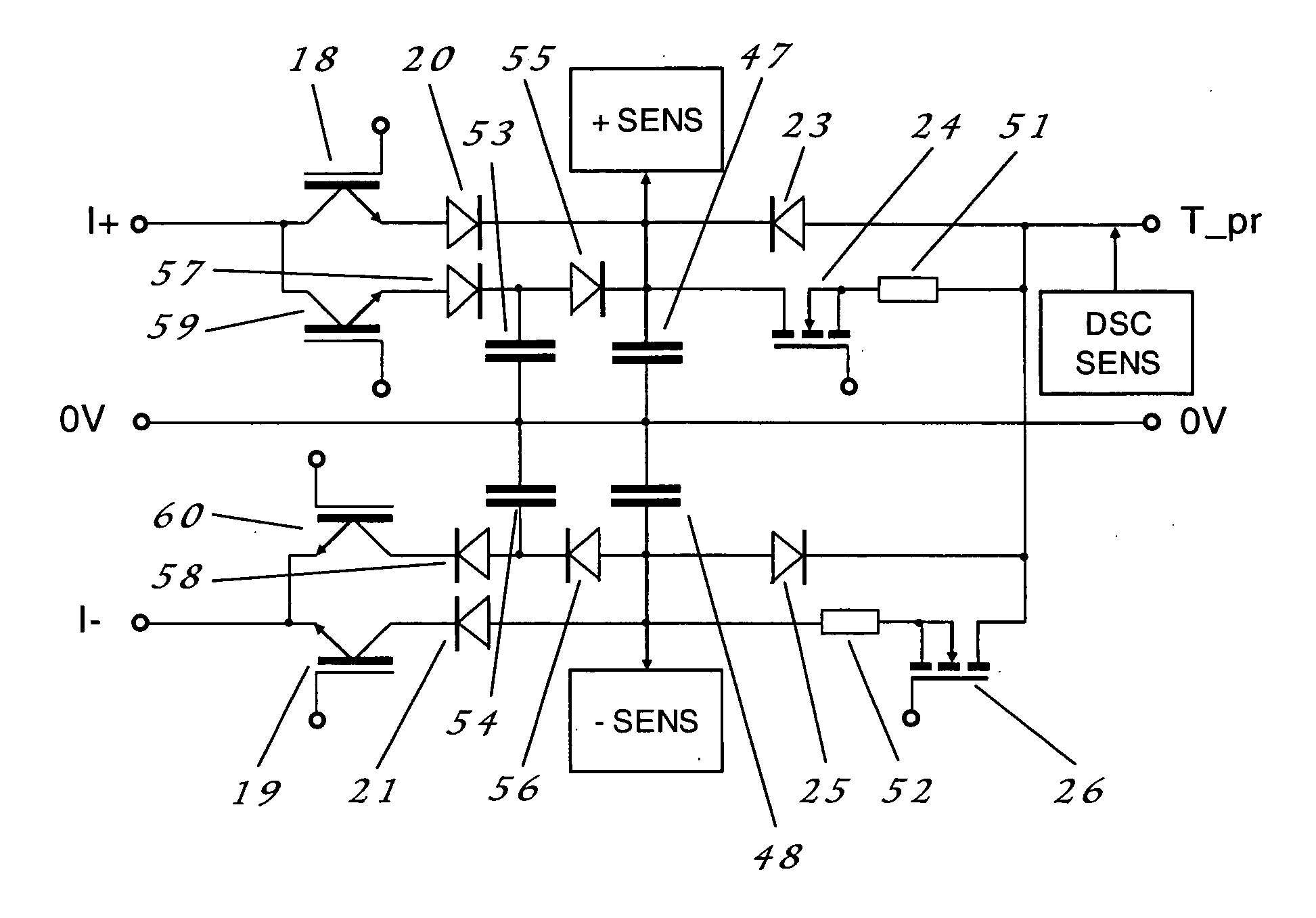
InactiveUS20090314747A1Easy to controlLow costElectric circuitsPower source circuitsElectricityElectric discharge
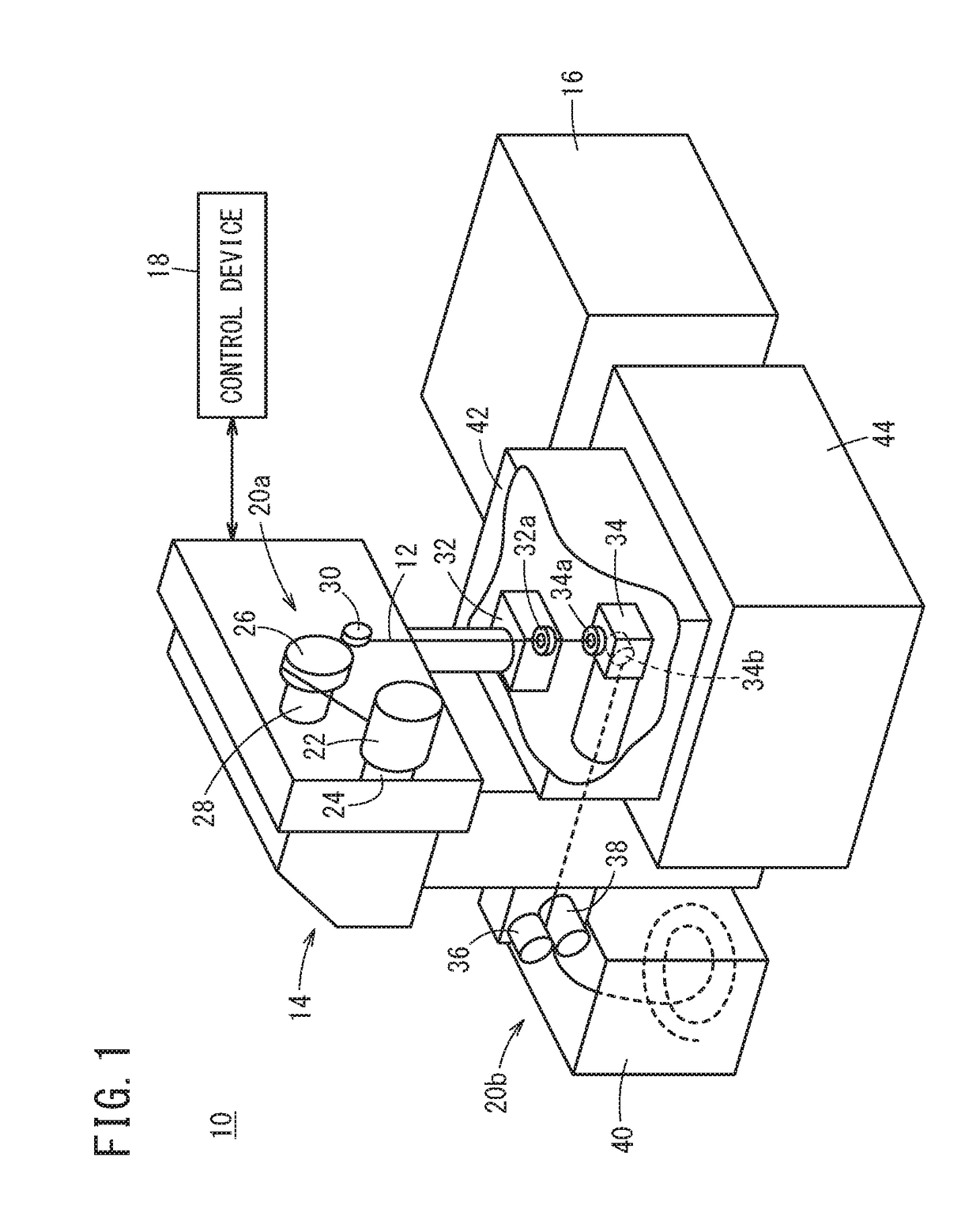
A wire electric discharge machine includes a wire electrode; a machining power supply that supplies a machining current to between the wire electrode and a workpiece; a first power feed contact and a second power feed contact that respectively feed power to the wire electrode; a first machining-current loop that lets a first machining current to flow from the first power feed contact toward the workpiece; a second machining-current loop that lets a second machining current to flow from the second power feed contact toward the workpiece; an impedance switching circuit that is provided in at least any one of the first machining-current loop and the second machining-current loop; and a control unit that controls a flow ratio of the first machining current and the second machining current by changing an impedance of the impedance switching circuit.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
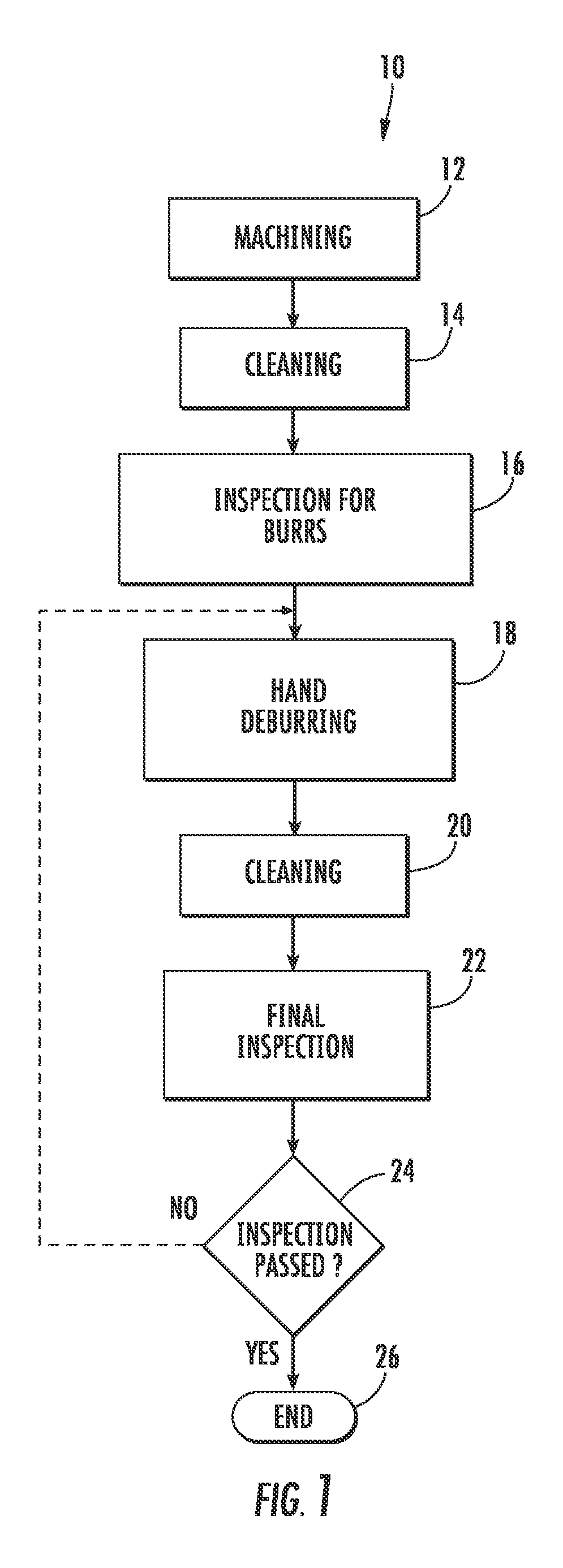
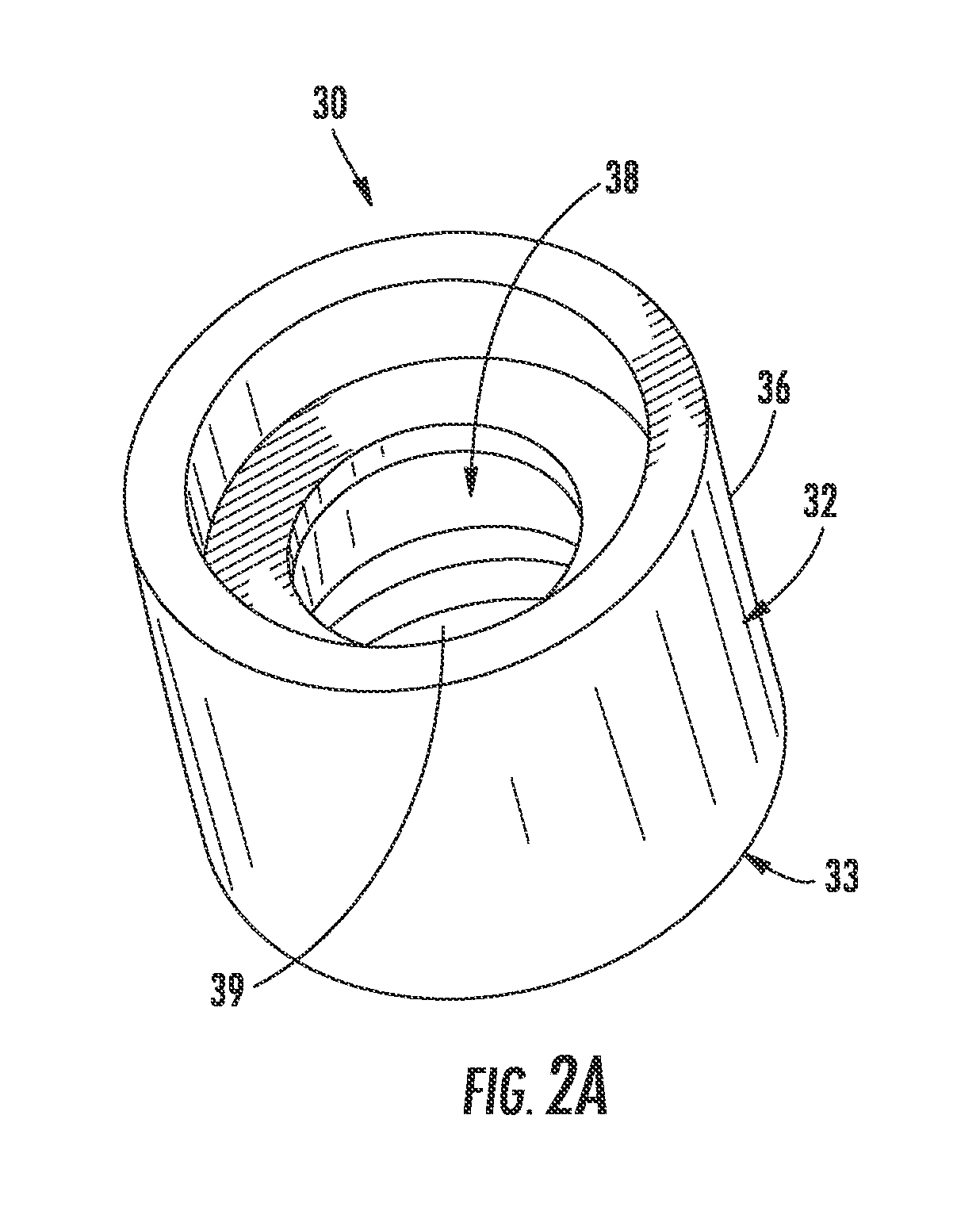
Electrodes, components, apparatuses, and methods for burr-free or substantially burr-free electrochemical machining
InactiveUS20120217163A1Reduce and eliminate formation of burrAvoidance of stray erosionMachining electrodesCellsEngineeringElectrochemistry
Electrodes, components, apparatuses, and methods for electrochemical machining (ECM) are disclosed. ECM may be employed to provide burr-free or substantially burr-free ECM of electrically-conductive workpieces (e.g. shrouds). As one non-limiting example, the electrically-conductive workpiece may be a shroud that is used as an electrical component in electronics boards. While the ECM components, apparatuses, and methods disclosed herein reduce burrs, ECM can provide imprecise machining and cause stray erosions to occur in the machined electrically-conductive workpiece. In this regard, the electrodes, components, apparatuses, and methods for ECM disclosed herein provide features that allow for precise machining of the machined electrically-conductive workpiece and also allow avoidance of stray erosions in the machined electrically-conductive workpiece.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
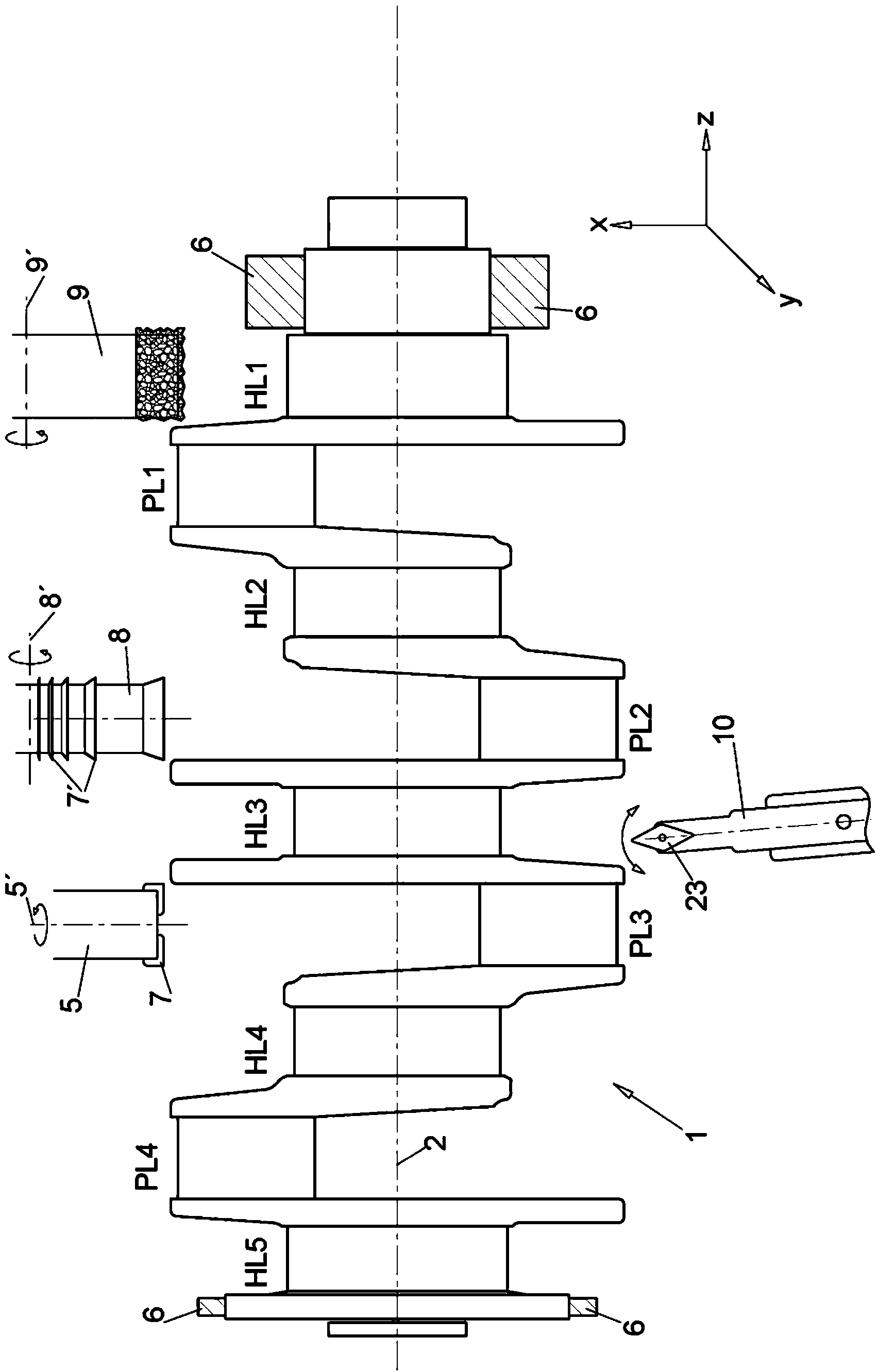
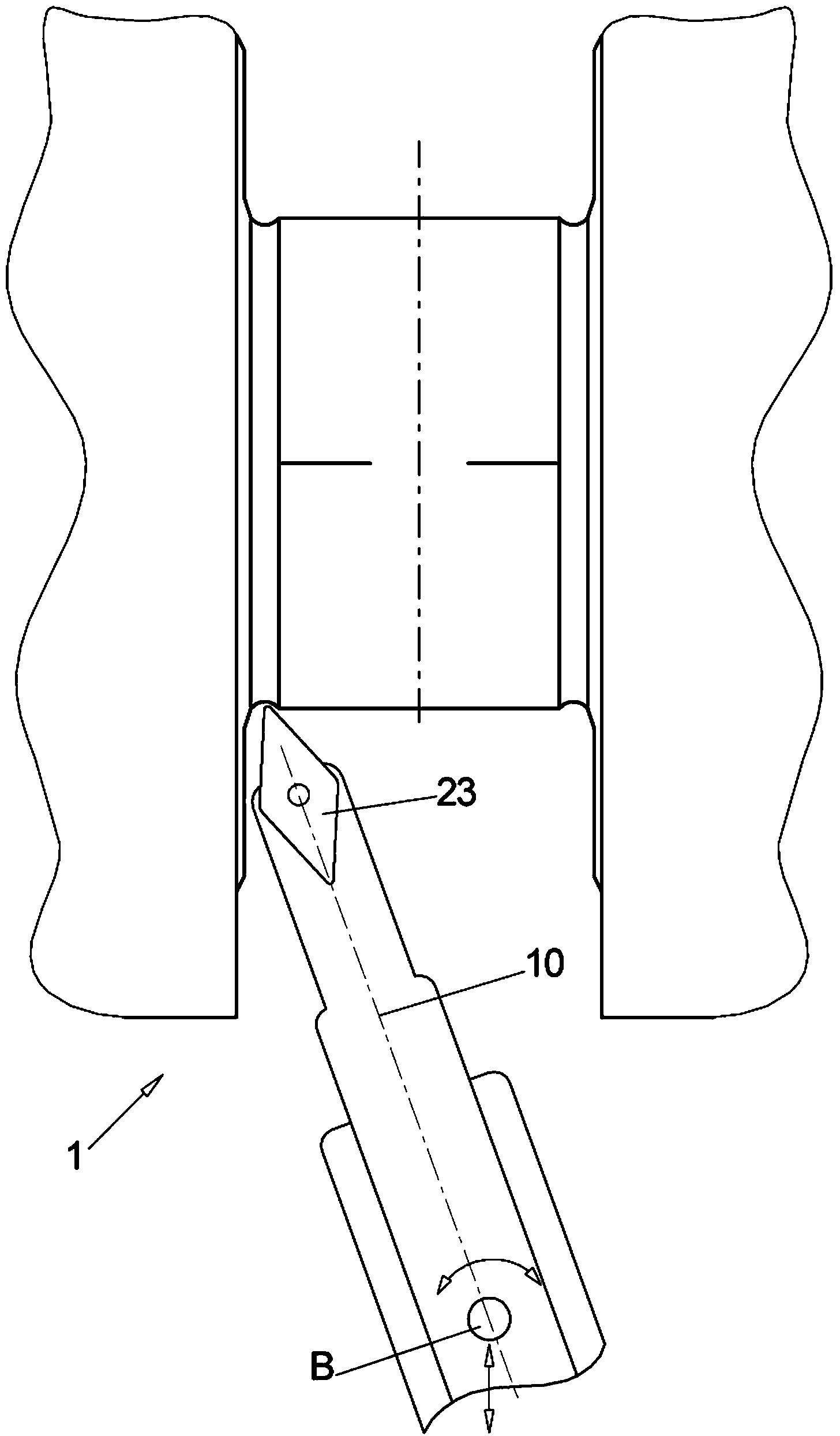
Method and device for finishing workpieces
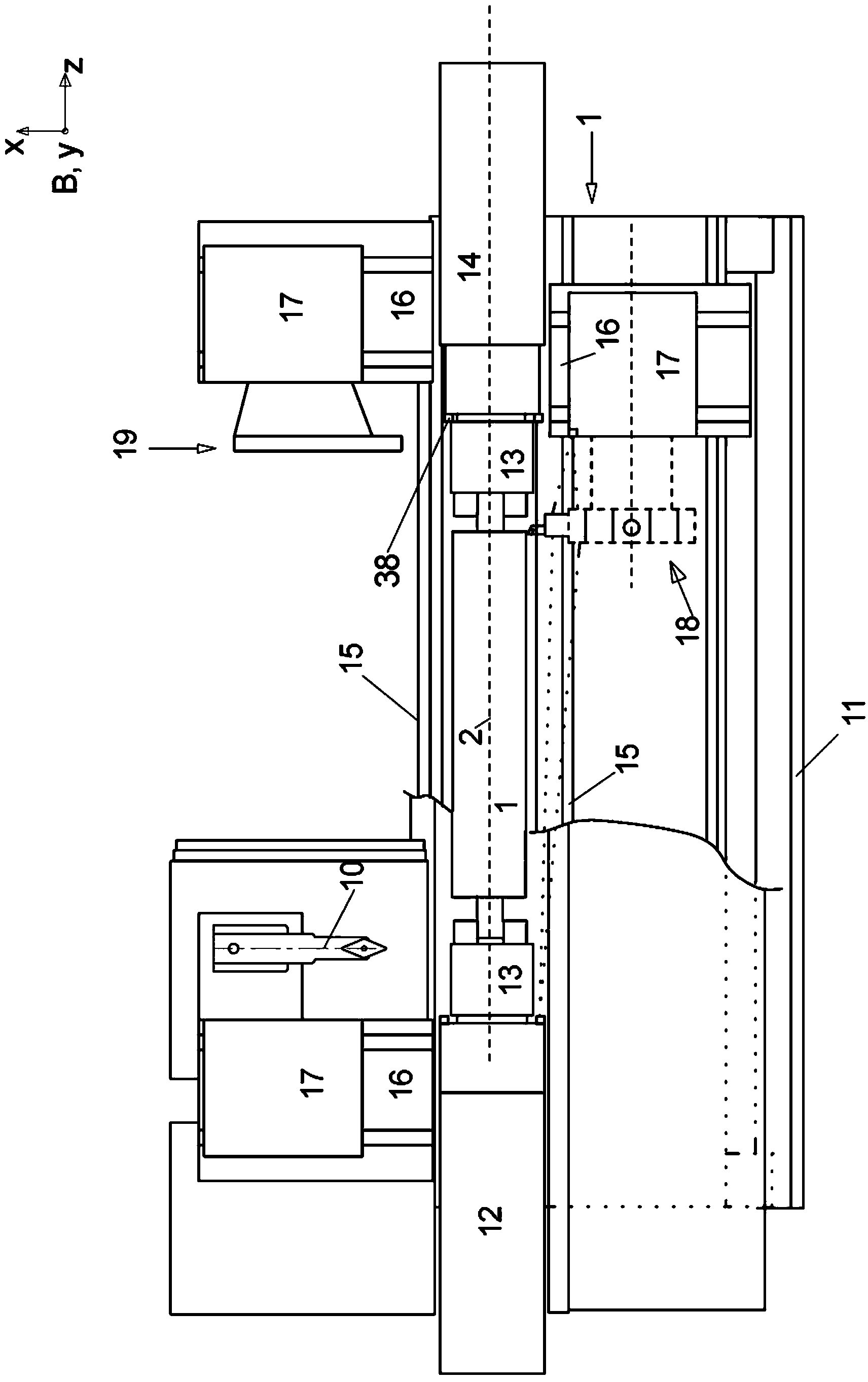
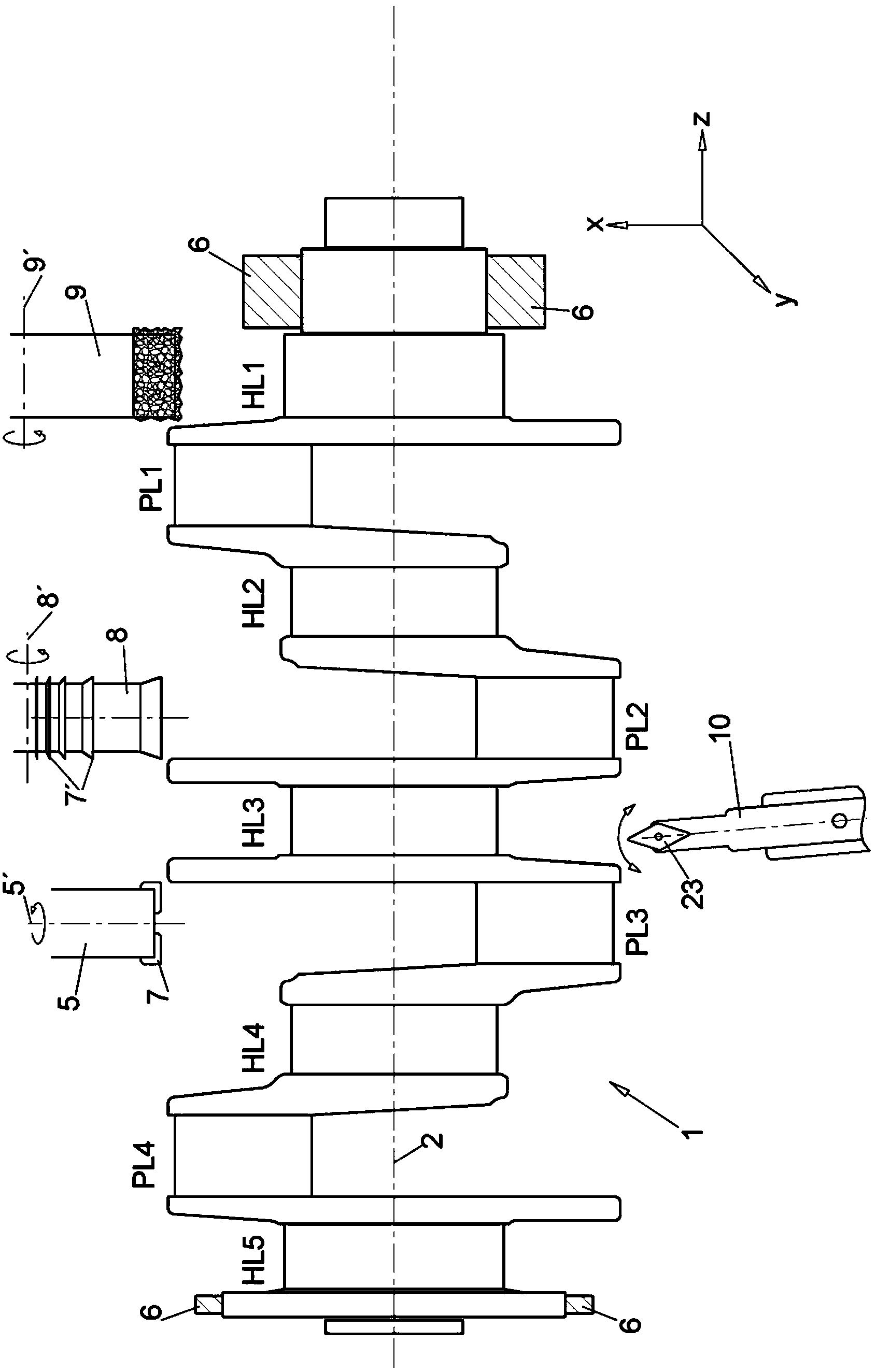
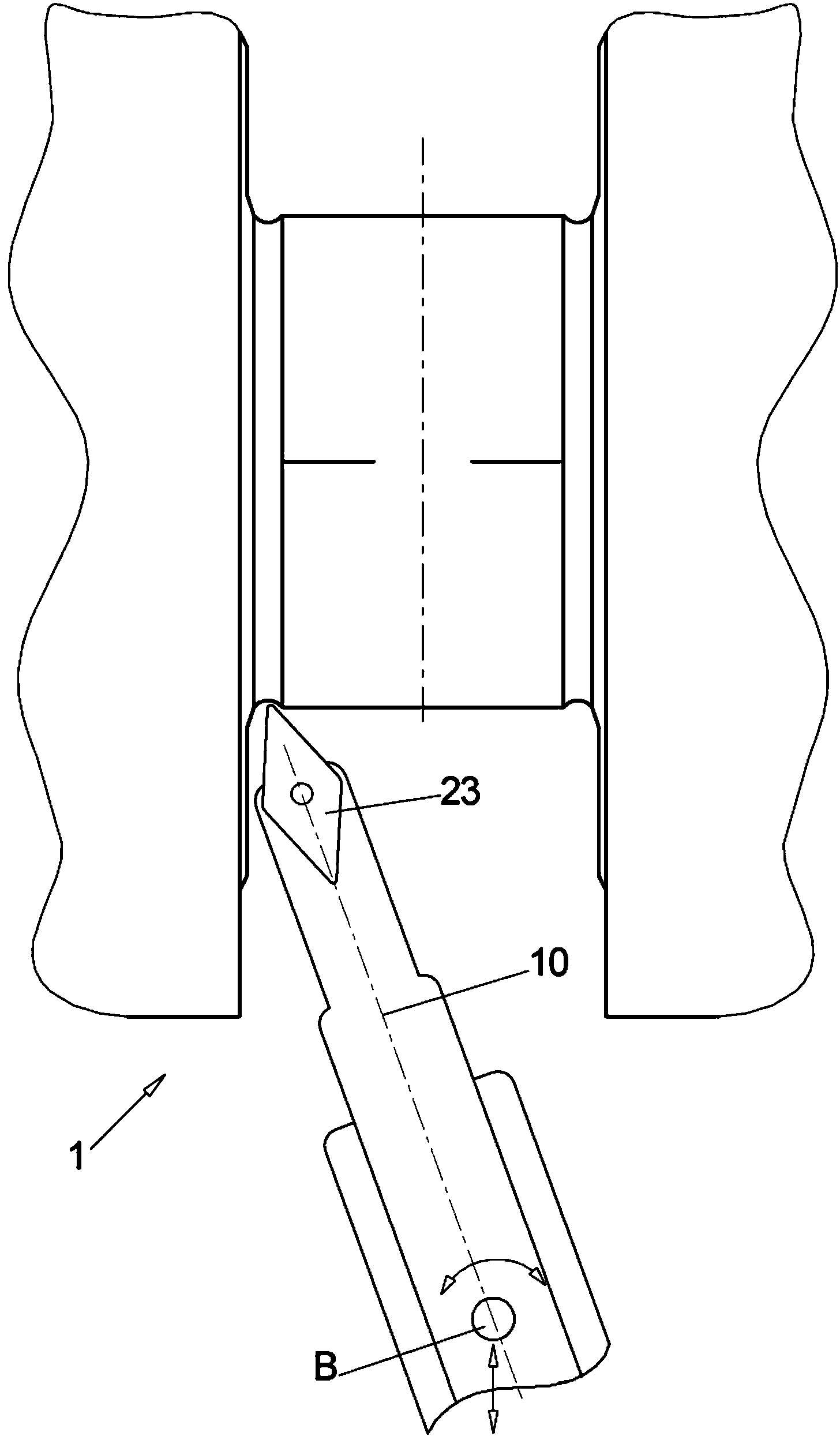
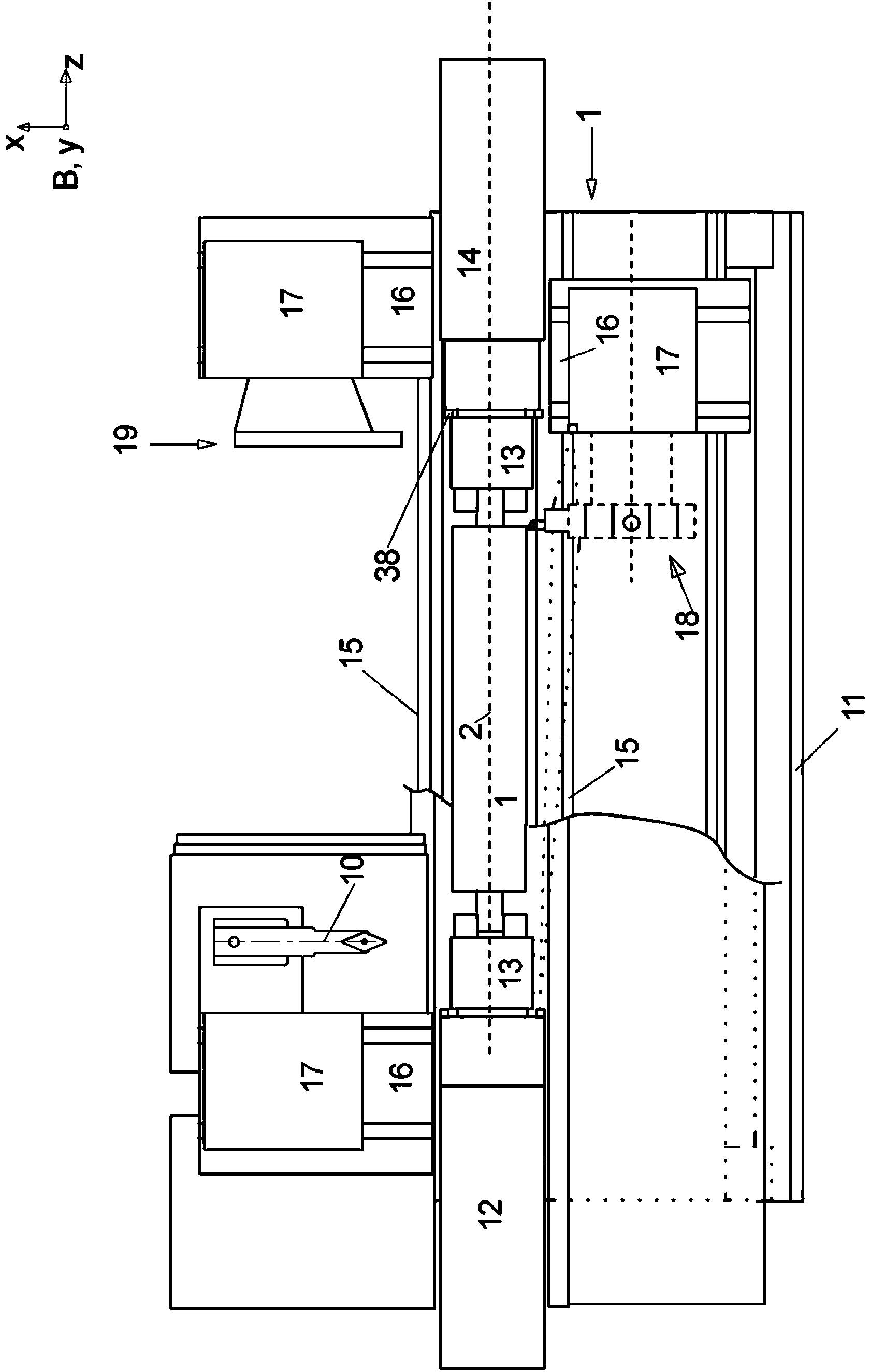
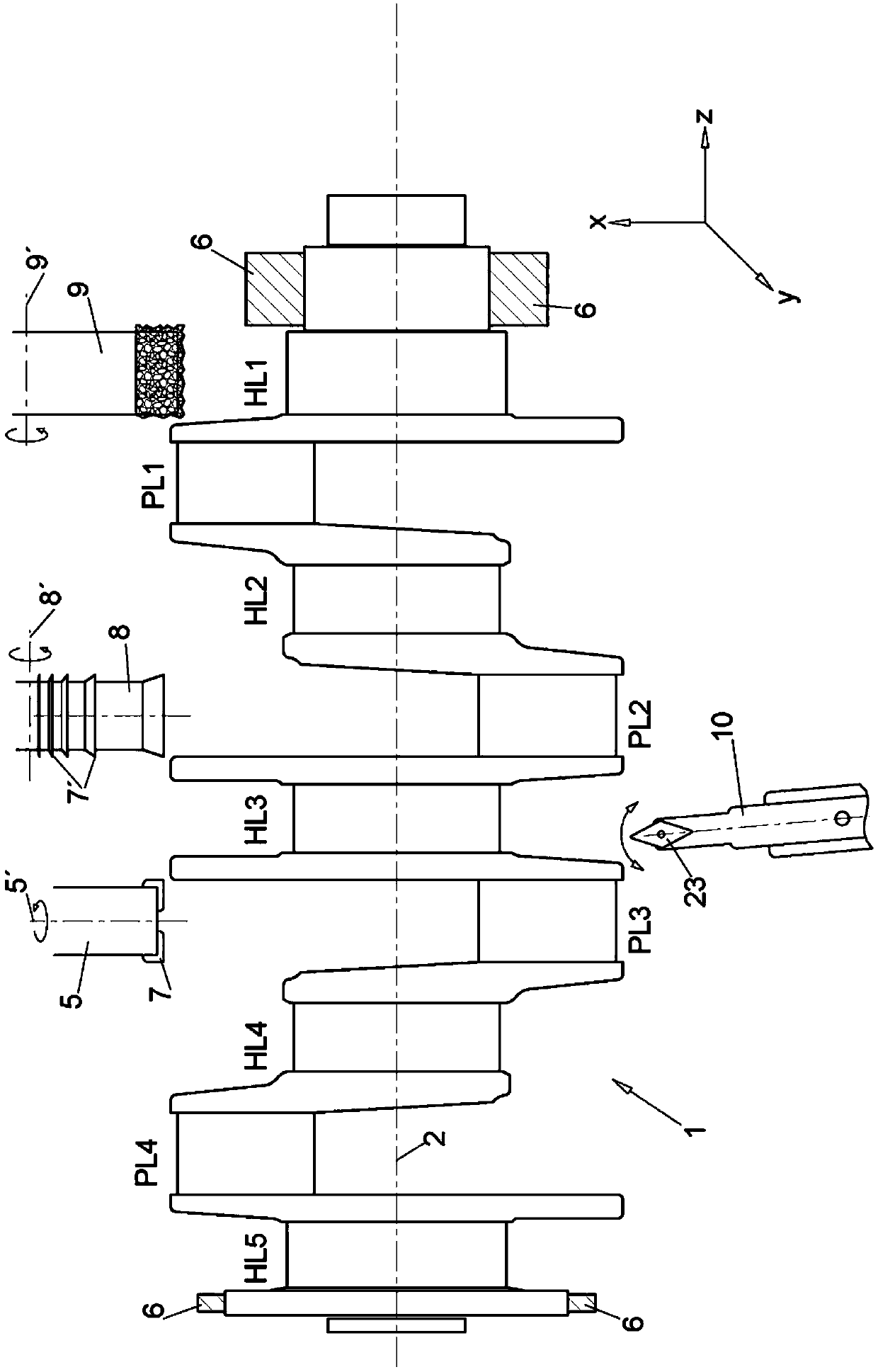
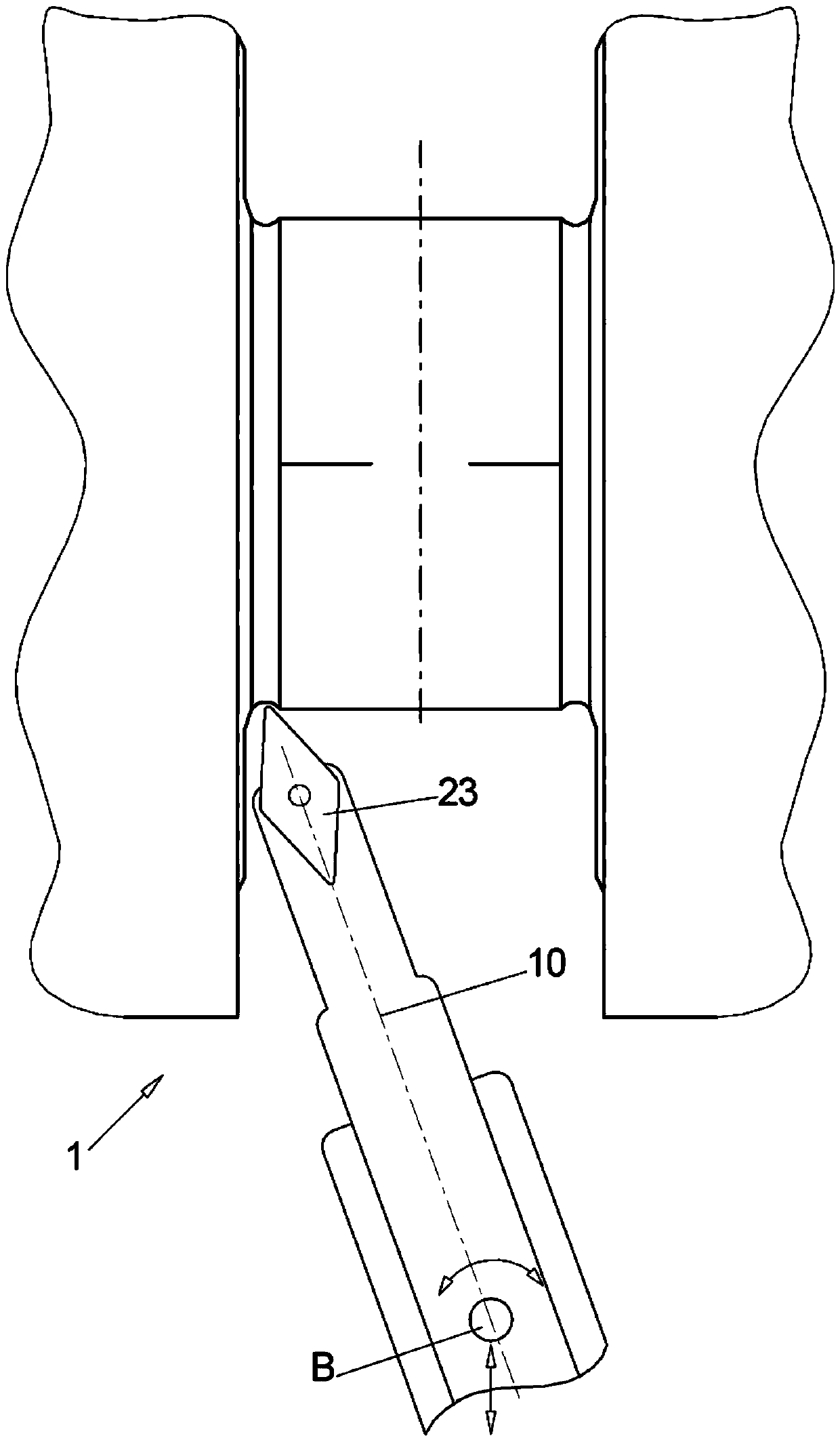
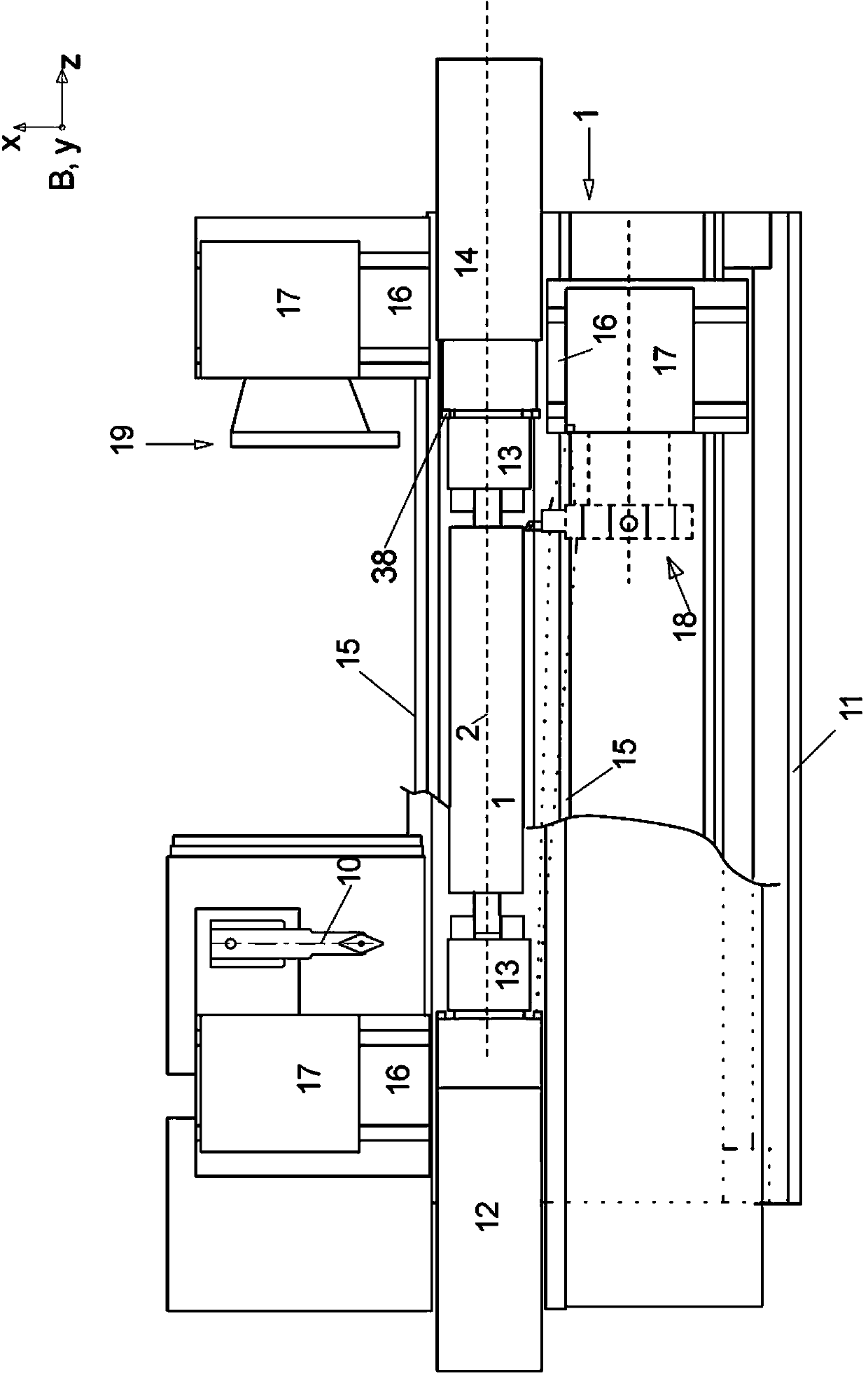
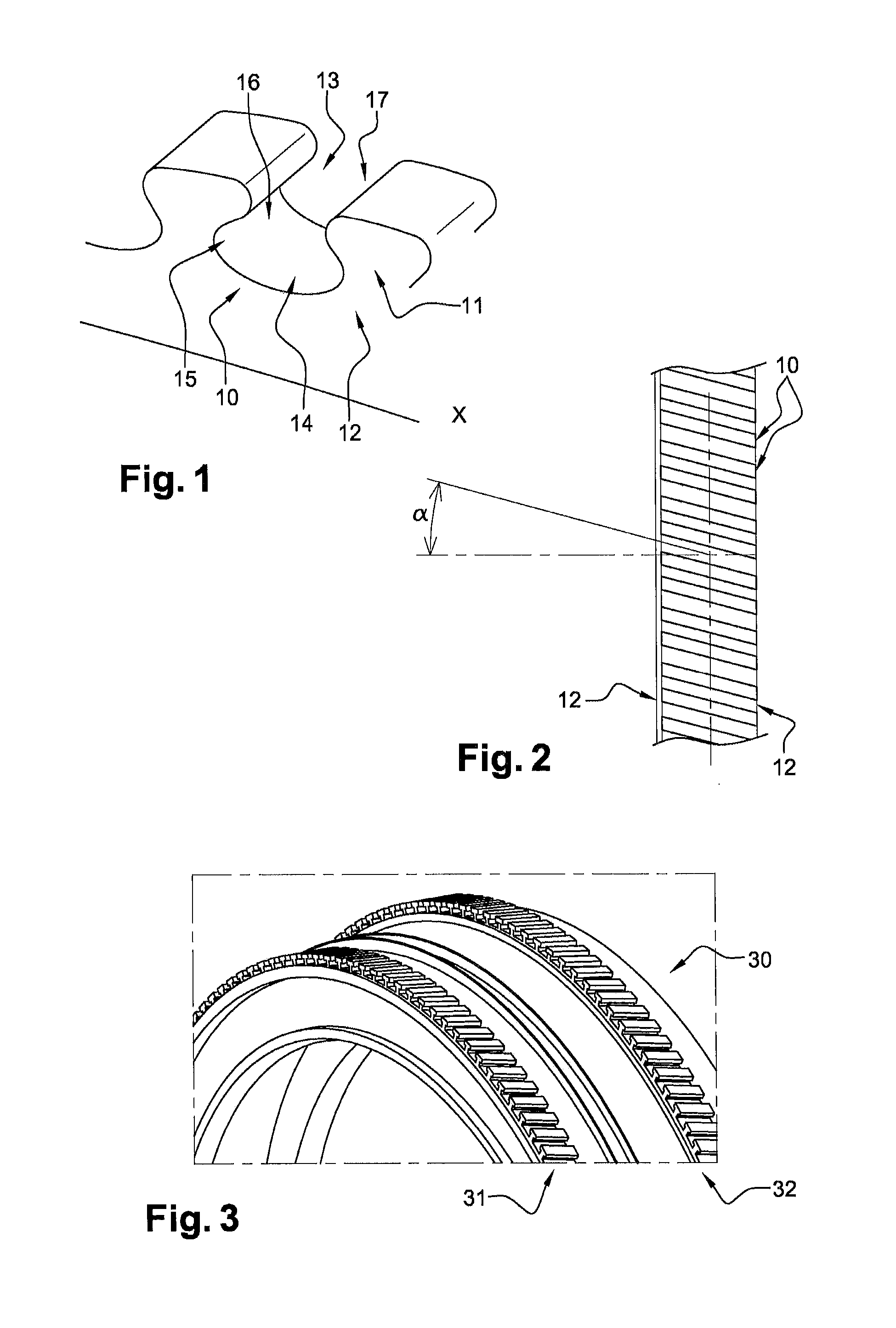
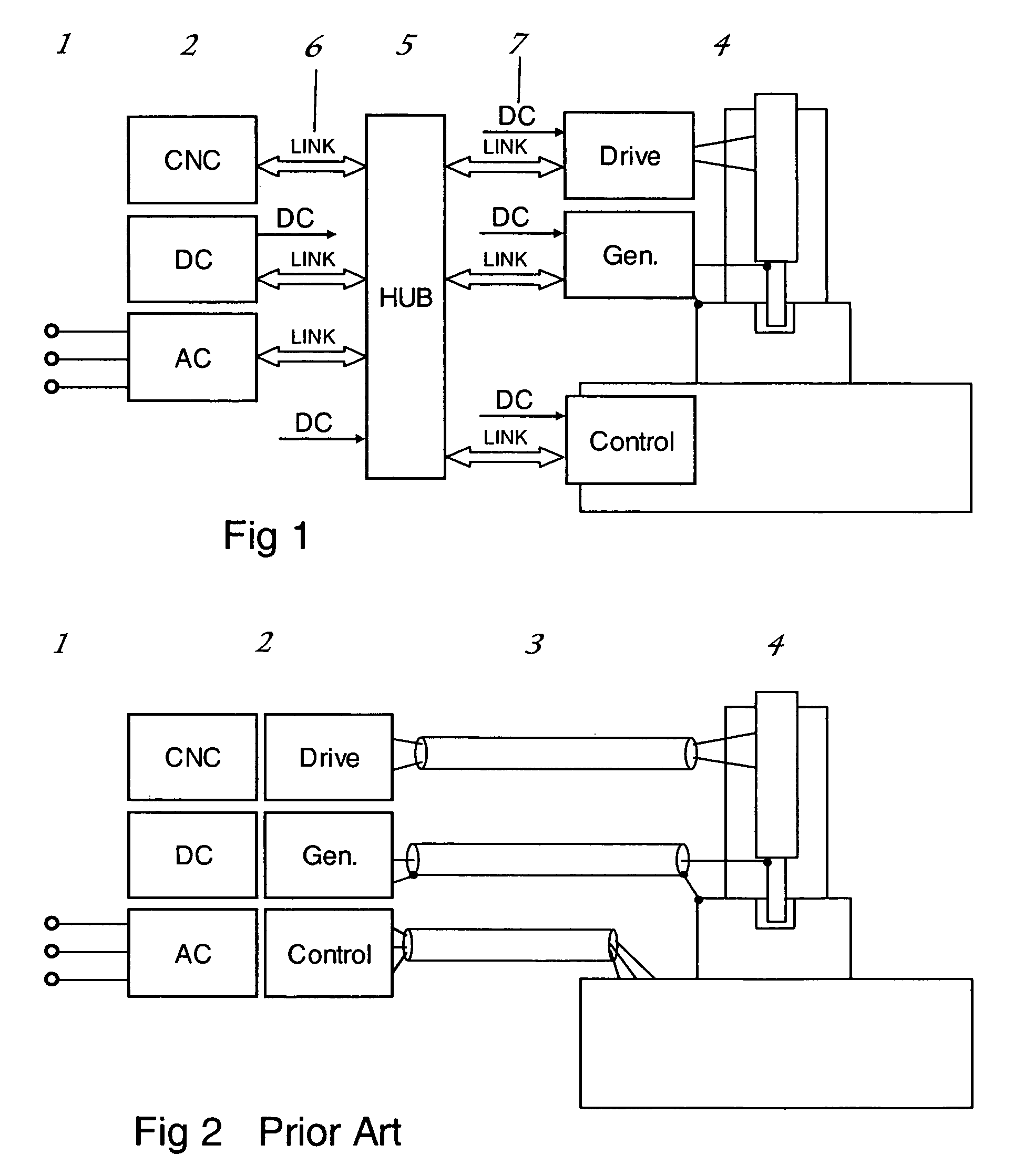
The aim of the invention is to shorten the process chain during the material-removing machining of in particular a crankshaft (1) following the rough machining and substantially after hardening. In order to achieve said aim, it is proposed, according to the invention, to combine peripheral rotary milling as a first step and subsequent dry grinding as a second step.
Owner:美艾格工业自动化系统股份有限公司
Method and device for finishing workpieces
The aim of the invention is to shorten the process chain during the material-removing machining of in particular a crankshaft (1) following the rough machining and substantially after hardening. In order to achieve said aim, it is proposed, according to the invention, to combine rotary milling or single-point milling as a first step and the subsequent fine machining step by means of finishing, electrochemical etching.
Owner:美艾格工业自动化系统股份有限公司
Method and generator for electrical discharge machining
InactiveUS20070023400A1Reduce power lossIncrease the output frequencyElectric circuitsPower source circuitsCapacitorElectrical discharge machining
The invention relates to a method and a generator for generating a time sequence of discharge pulses separated from each other by pulse pauses for electrical discharge machining. At least two pulse capacitors are discharged each in the form of a partial pulse into the spark gap for forming together a discharge pulse. A discharge pulse having a predetermined waveform is selected from a plurality of discharge pulses having differing predetermined waveforms. The discharge of the at least two pulse capacitors is controlled such that the selected discharge pulse is generated with the predetermined waveform.
Owner:AGIE CHARMILLES +1
Power supply device for electric discharge machining
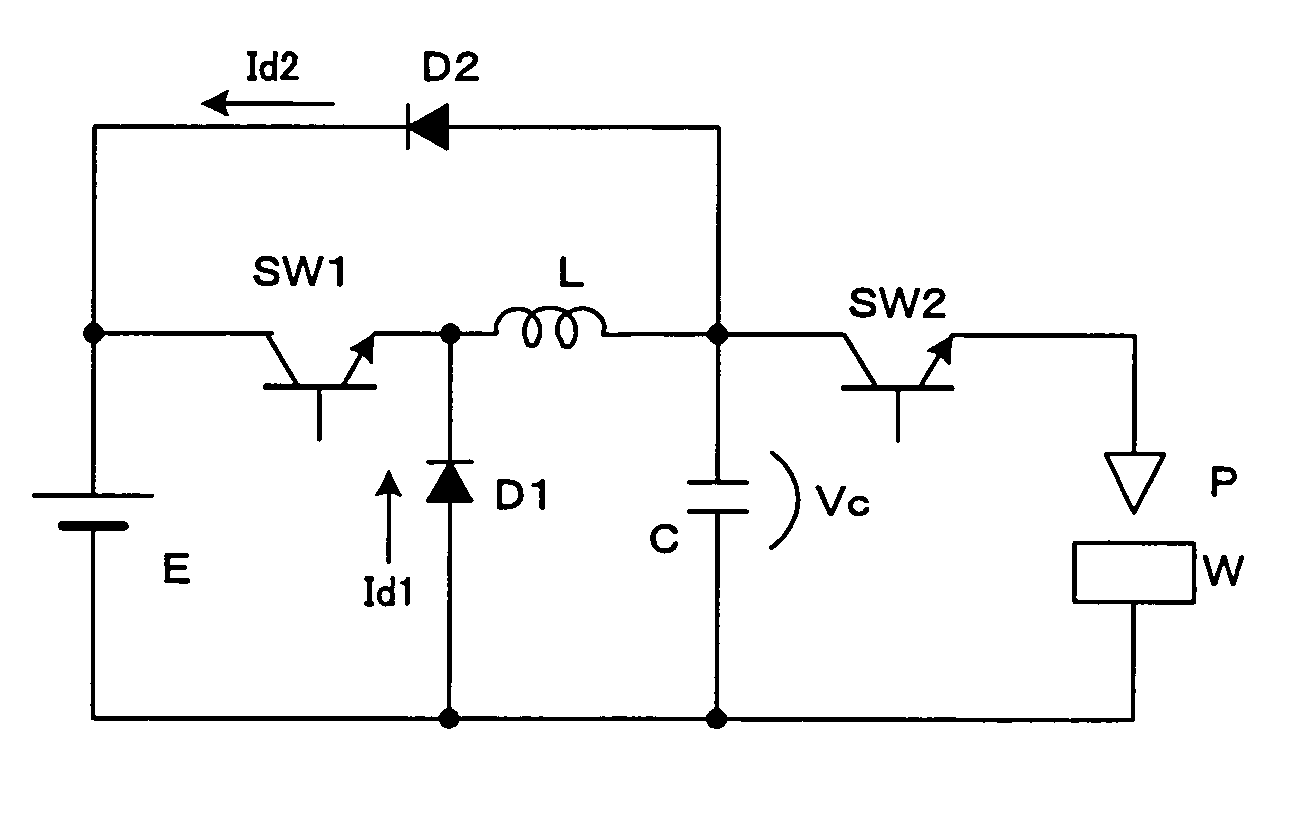
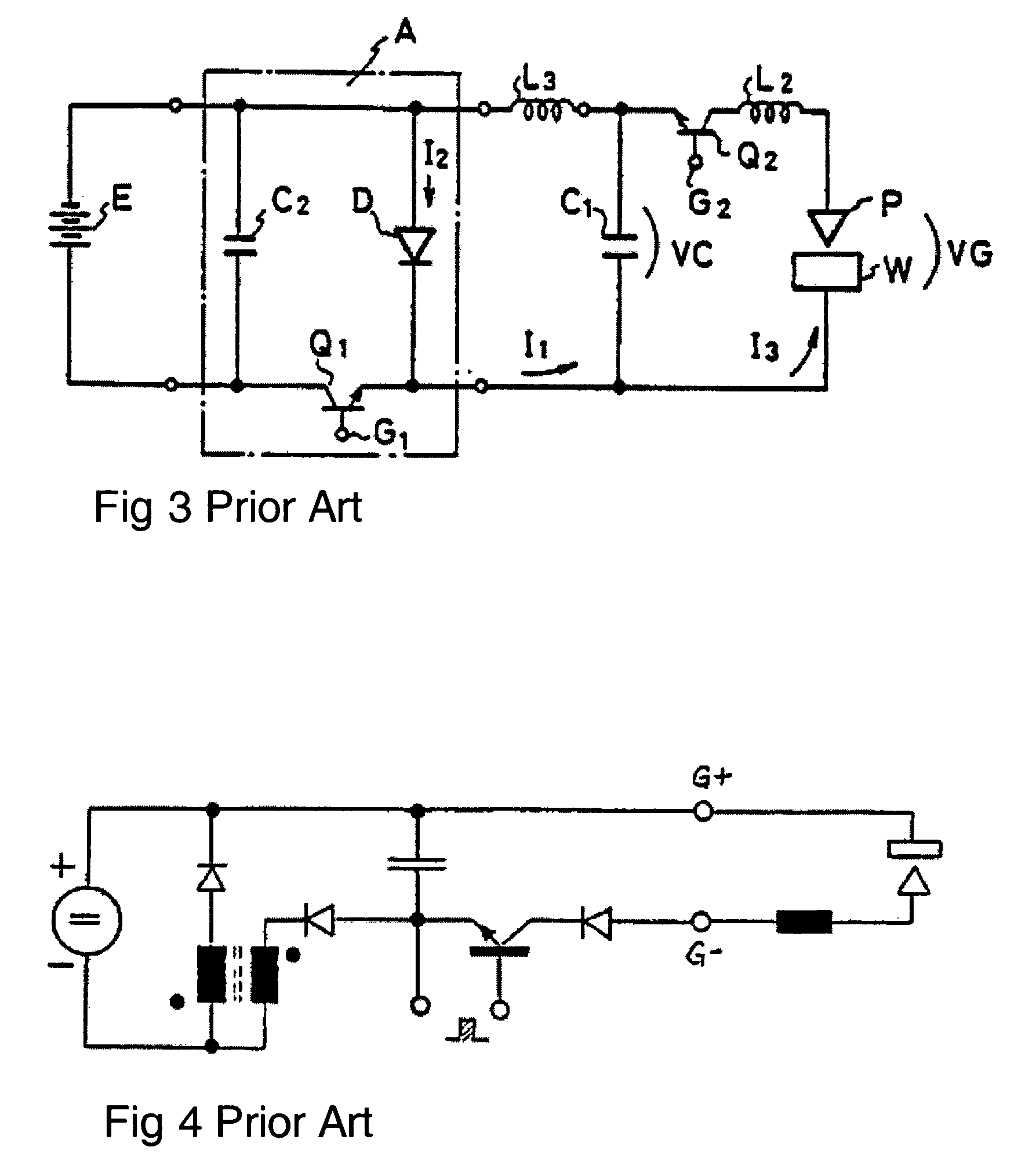
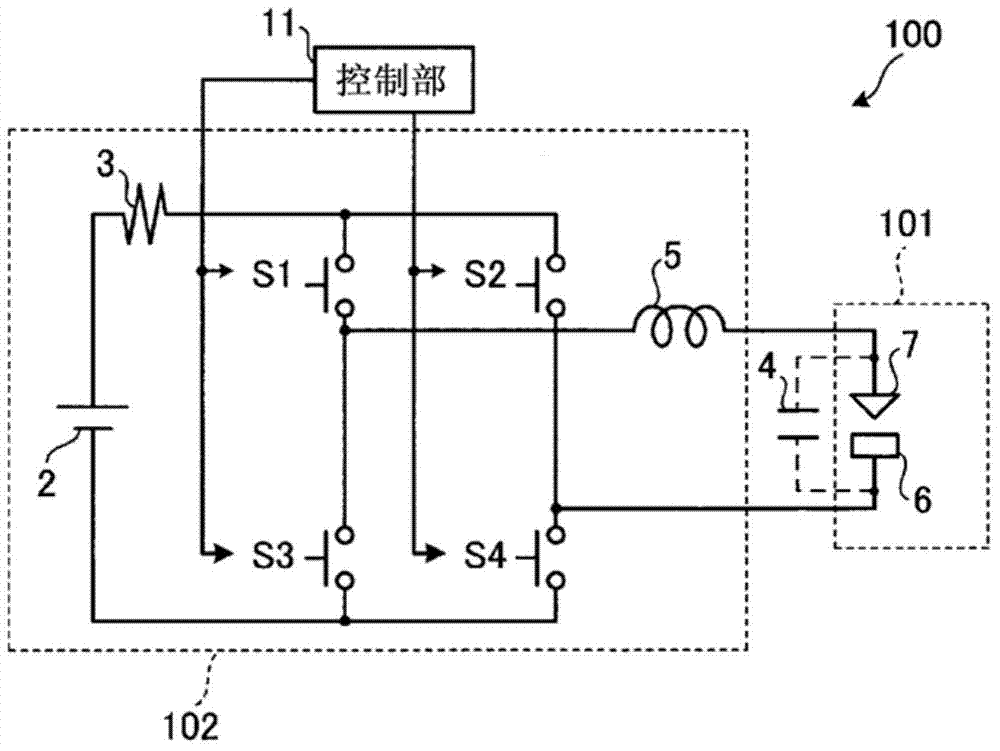
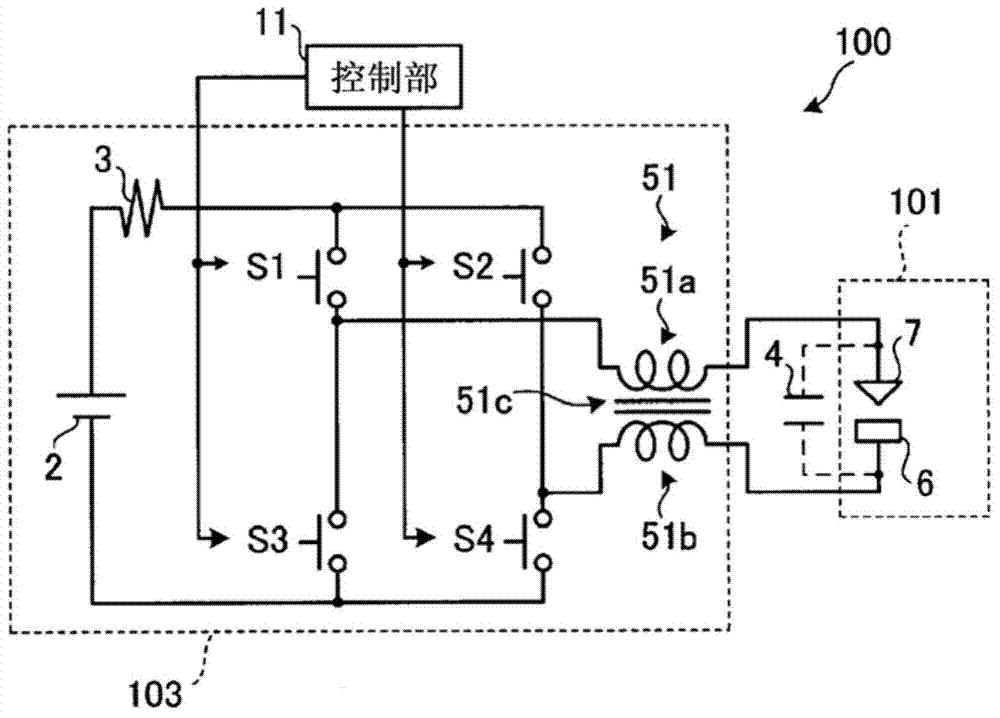
InactiveUS7148442B2Energy loss is hardlyLimit charging voltageBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerElectric dischargeEngineering
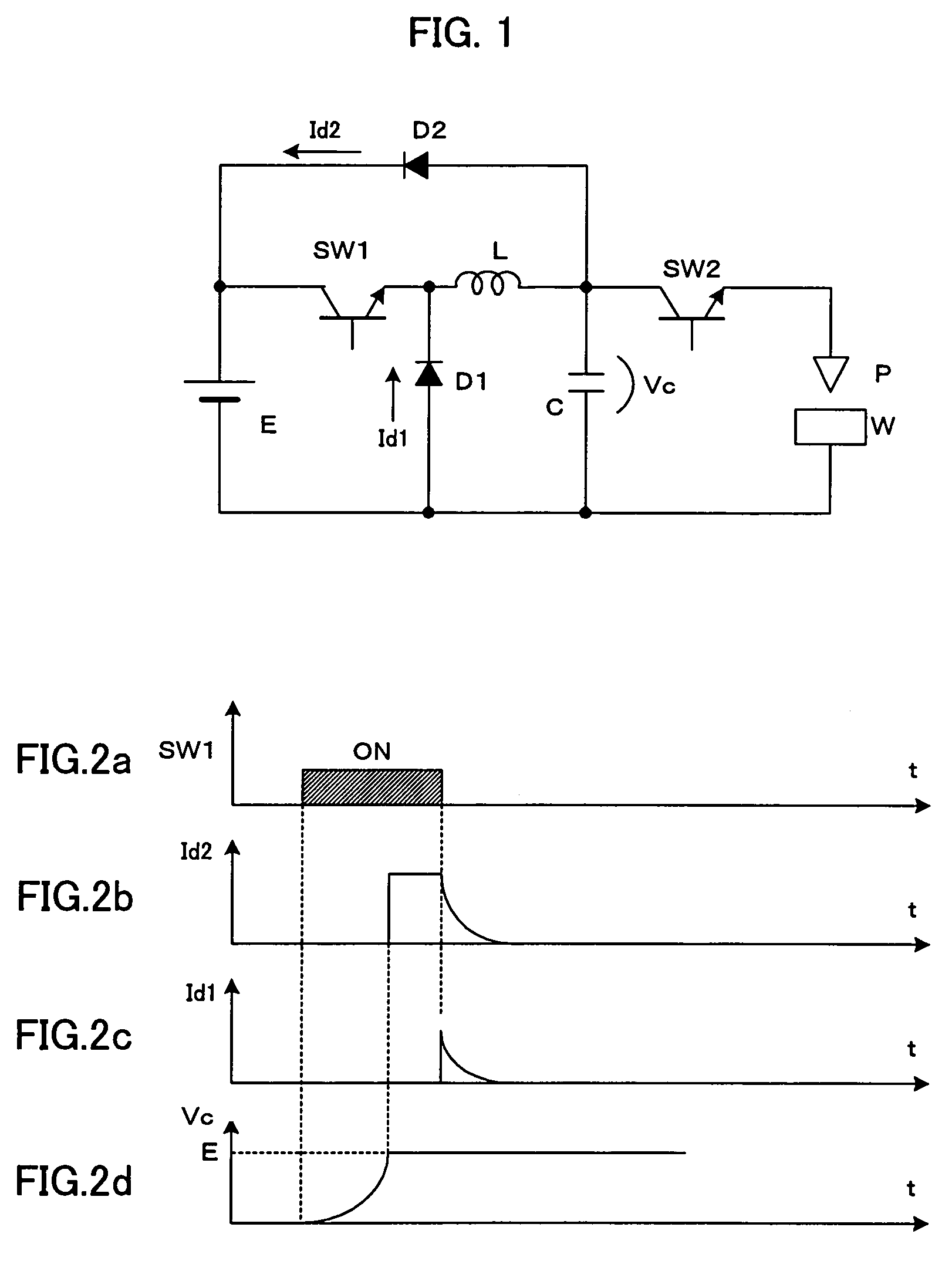
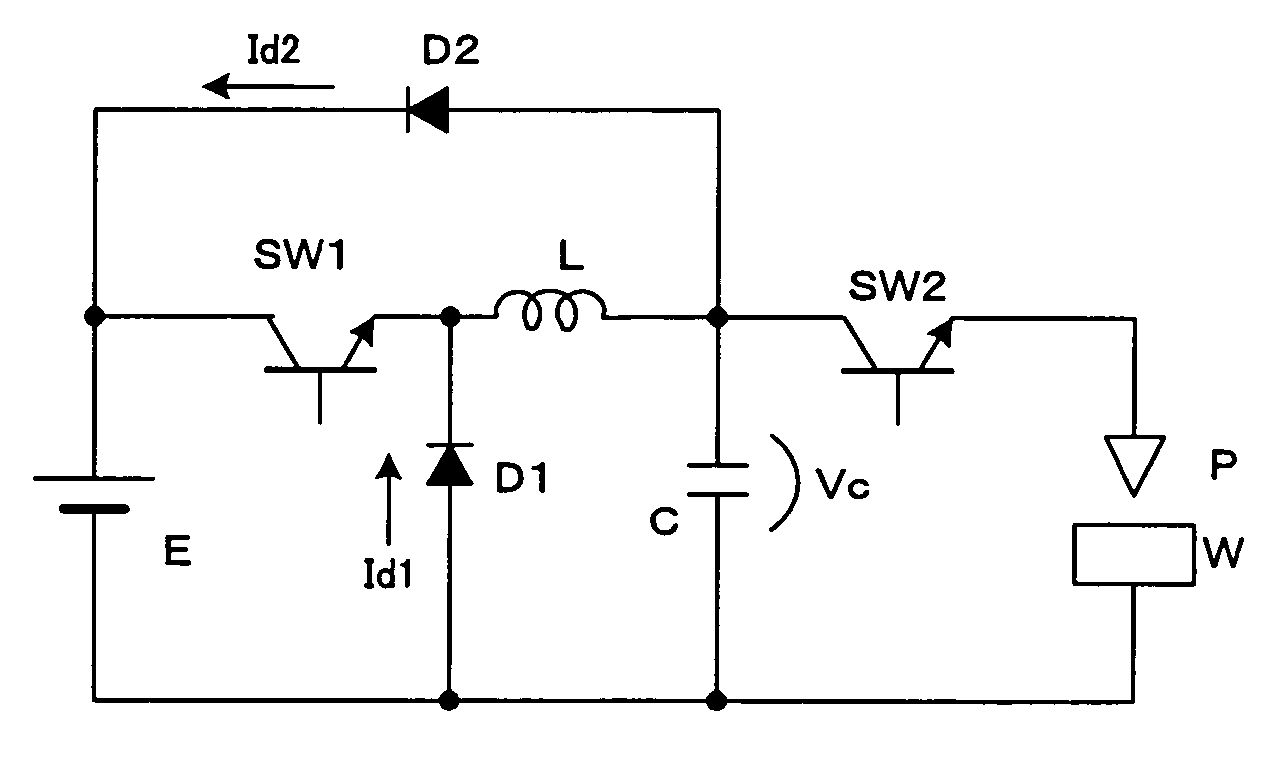
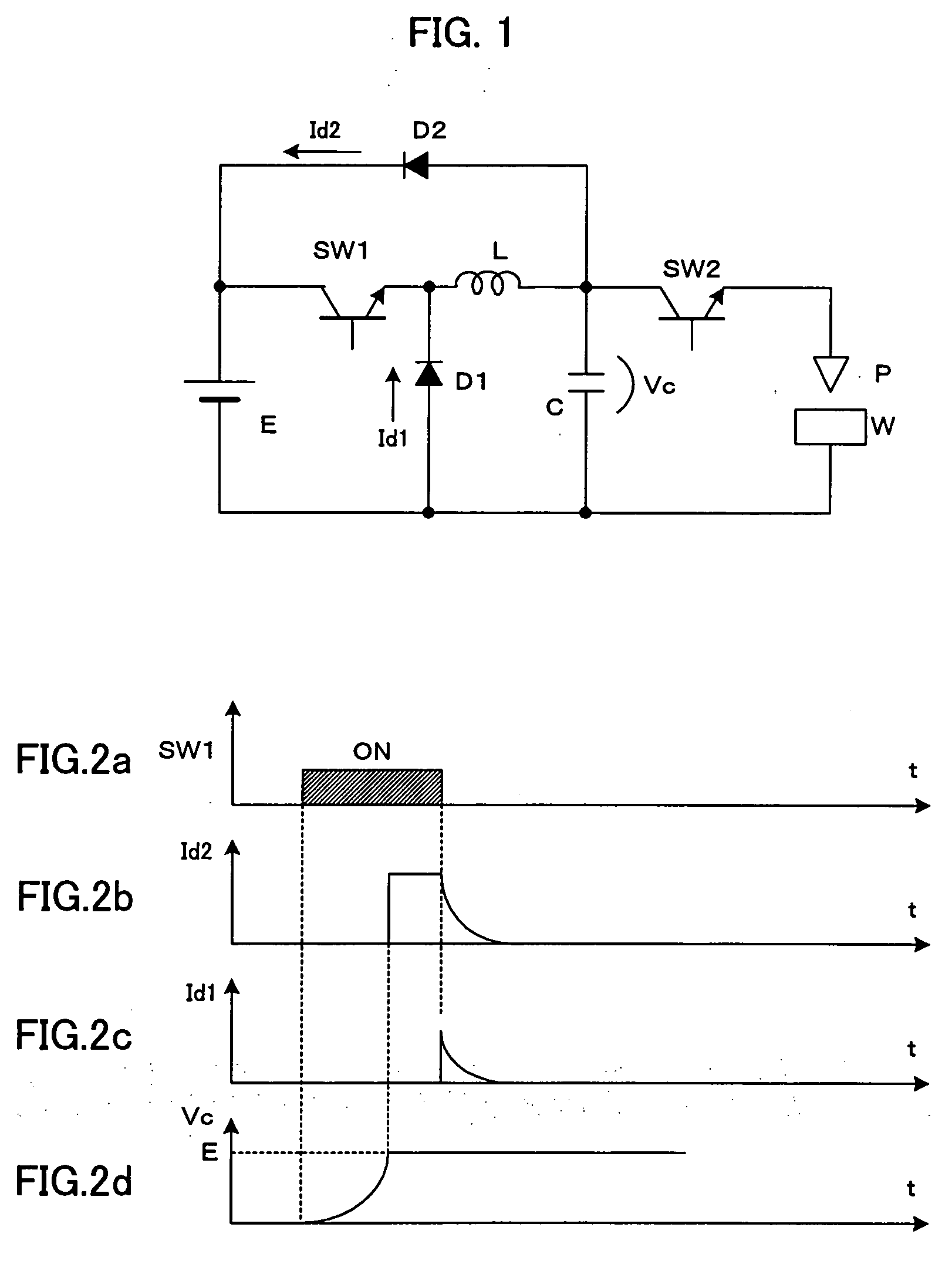
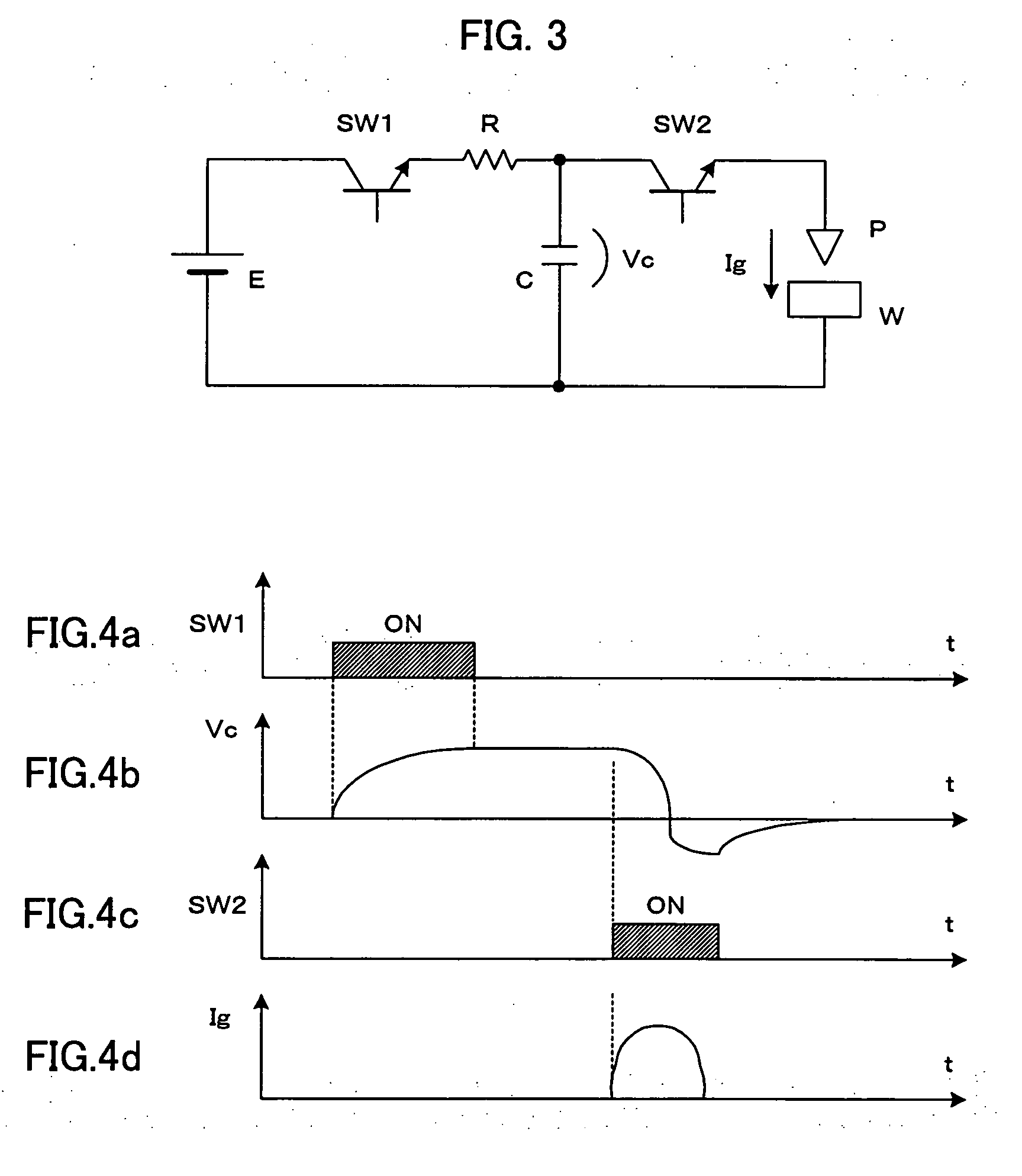
An electric-discharge-machining power supply device in which energy loss is hardly produced and a charge voltage of a capacitor is easily controlled. When a switching element SW1 is turned on, a capacitor C is charged via an inductor L. When the voltage Vc of the charged capacitor exceeds the voltage of a direct-current power source E, a current is returned to the power source E via a diode D2. When the switching element SW1 is turned off, energy stored in the inductor L flows from the inductor L through the diode D2, the power source E and the diode D1, so that the voltage Vc of the capacitor C is kept at the power source voltage. When a switching element SW2 is turned on, the voltage of the capacitor is applied between an electrode and a workpiece.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Method and device for finishing work pieces
In order to shorten a process chain for chip removing processing of a crank shaft after coarse machining and after hardening according to the invention a combination of turn milling or single point milling is proposed as a first step and a subsequent line machining step through finishing or electro chemical etching is proposed.
Owner:MAG IAS
Pulse reverse electrodeposition for metallization and planarization of semiconductor substrates
InactiveUS6878259B2Reduce decreaseLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHertzSemiconductor
Owner:INVENSAS CORP
Power supply device for sinker electric discharge machining
ActiveUS20110220615A1Improve material removal rateSmall amplitudeElectric circuitsPower source circuitsPower flowElectric discharge
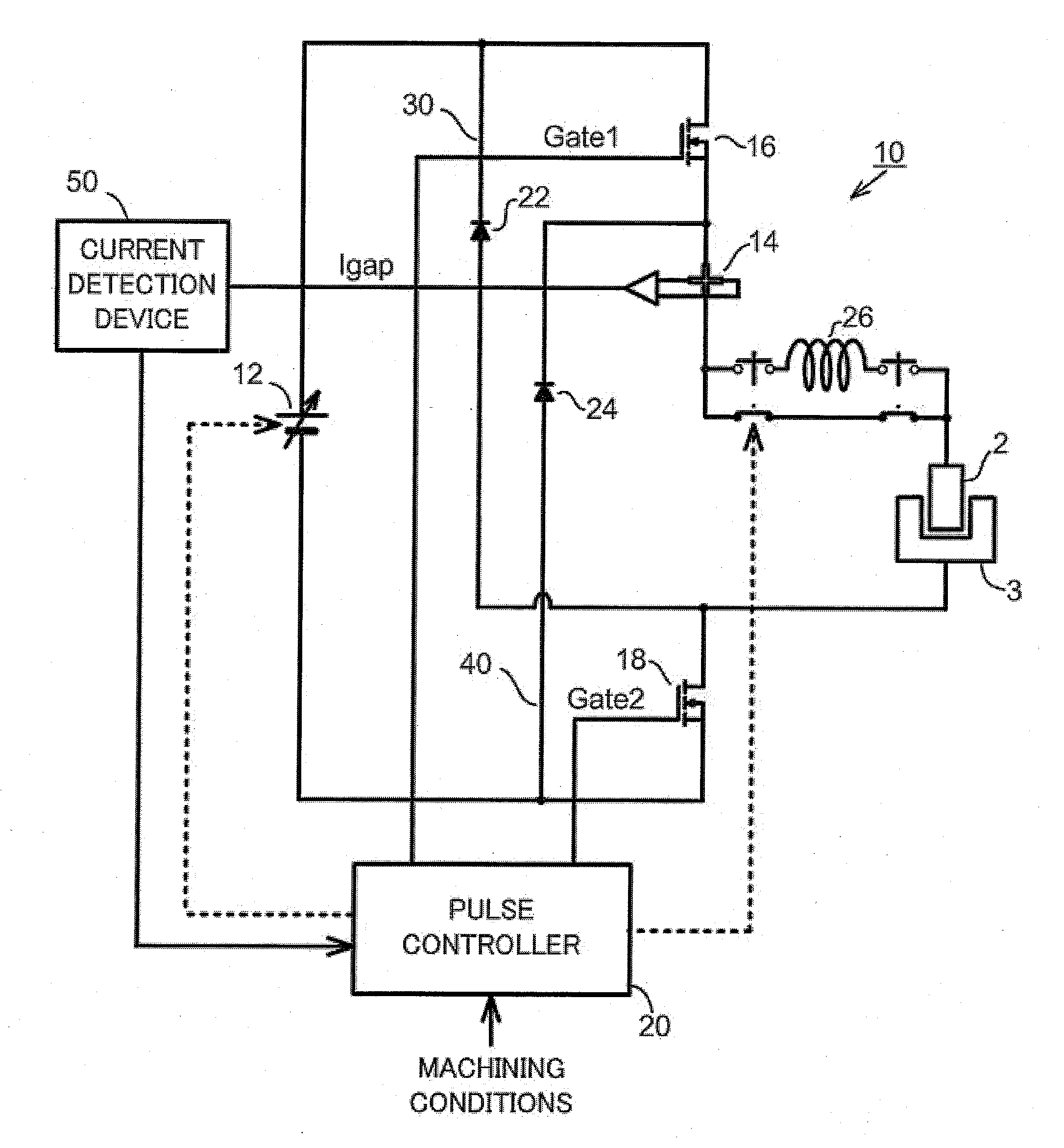
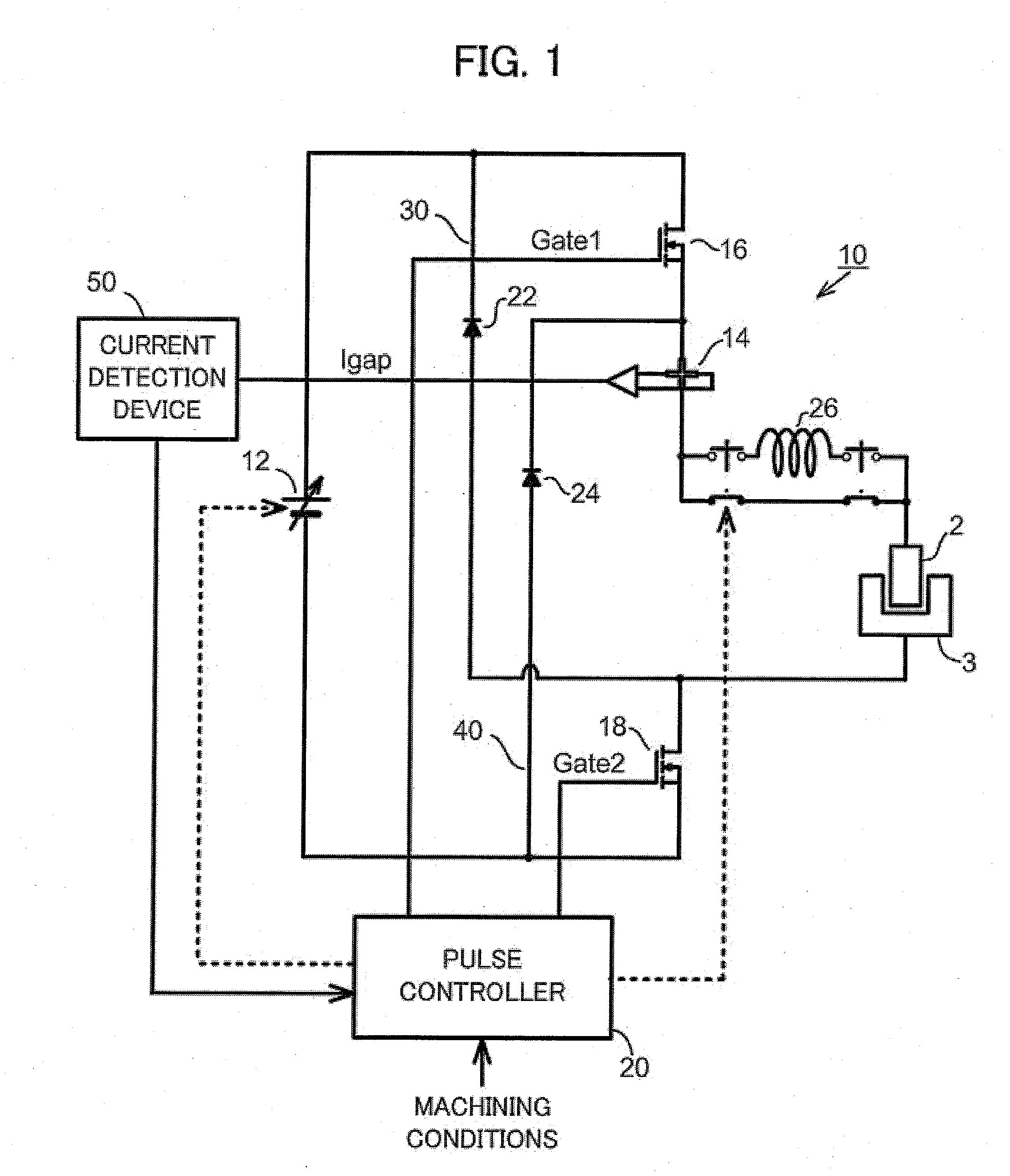
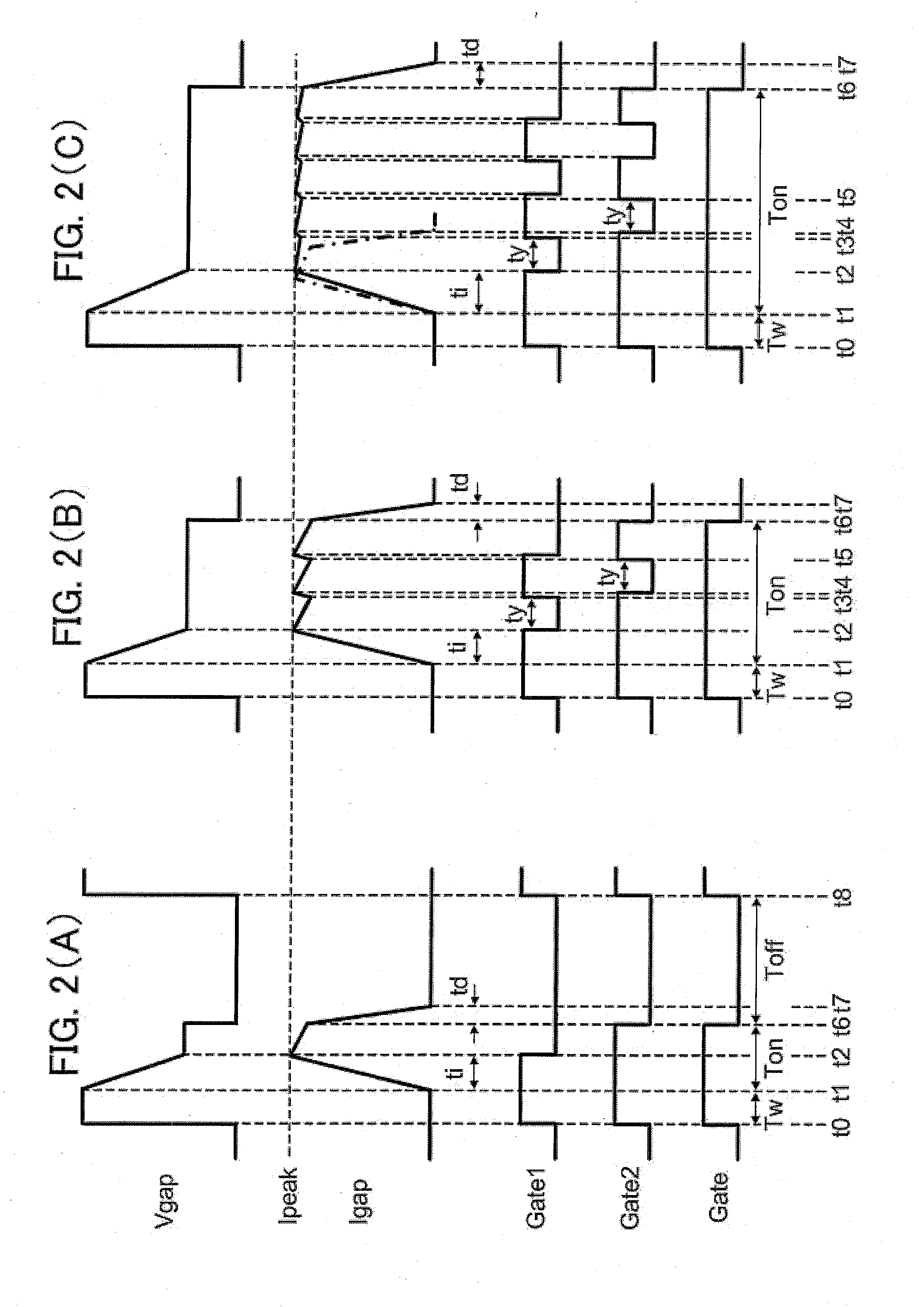
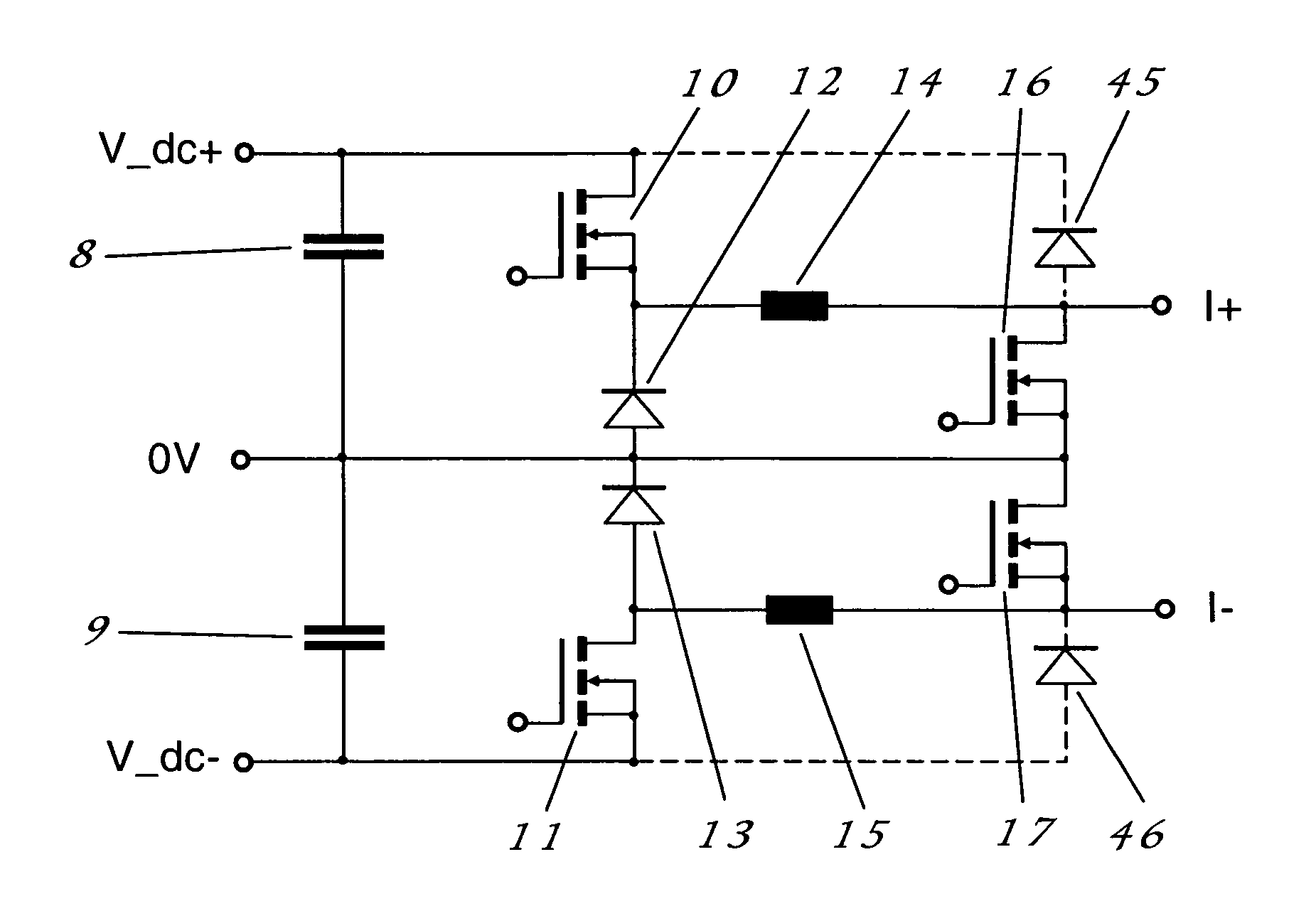
A power supply device comprises a DC power supply (12), a current sensor (14) for detecting gap current (Igap) flowing through the machining gap, a first switching element (16) connected in series between the DC power supply and the tool electrode (2), a first reverse current prevention diode (22) connected in parallel with the DC power supply and connected in series with the first switching element (16), a second switching element (18) connected in series between the DC power supply and the workpiece (3), a second reverse current prevention diode (24) connected in parallel with the DC power supply and connected in series with the second switching element (18), and a pulse controller (20) for controlling the first and second switching elements in response to gap current (Igap). From a first time (t1) when electric discharge is generated across the machining gap, until a second time (t2) when the gap current reaches the peak current during the ON time, both of the first and second switching elements are on. At the second time (t2) only one of the first and second switching elements is turned off.
Owner:SODICK CO LTD
Method of electrochemical machining
InactiveUS20120181179A1Quality improvementReduce concentration of toxicCellsMachining electric circuitsLow voltageMachined surface
Owner:PECM IND
Method for producing aerodynamic structures in the manufacturing of integrally bladed gas turbine rotors
ActiveUS8262897B2Reduce processing timeCost-effectiveElectrolysis componentsMachining electric circuitsEngineeringGas turbines
The invention relates to a method for the production of aero-dynamic structures during the production of integrally bladed gas turbine rotors. Aerodynamic structures of an integrally bladed gas turbine rotor are produced on a rotor disk base body, whereon the end contours are precise, by removing material according to an electrochemical removal process, i.e. by means of an electrochemical machining (ECM)-process. The method comprises the following steps: a) preparing a rotor disk base body which is made of a material which is difficult to machine; b) removing the material which is between the blade wings until a specific dimension is obtained, according to a removal process; c) preparing at least one working electrode in order to finish at least one aerodynamic structure of an integrally bladed gas turbine rotor. The contours of the or each of the working electrodes are adapted to the contours of the aerodynamic structure, which are produced by means of the respective working electrode, such that a gap between the rotor disk base body and a working electrode are produced in an approximately identical manner during the removal process of the material; d) electrochemically machining the or each aerodynamic structure in an electrochemical sinking by placing the rotor disk base body and the or each working electrode in an electrolyte and by applying voltage and / or current, whereby the applied current and / or voltage is temporally pulsed; e) pressure-rinsing the gap which is filled with electrolytes between the aero-dynamic structure and the or each working electrode by a pulsed movement of the or each working electrode.
Owner:MTU AERO ENGINES GMBH
Method and device for finishing workpieces
The aim of the invention is to shorten the process chain during the material-removing machining of in particular a crankshaft (1) following the rough machining and substantially after hardening. In order to achieve said aim, it is proposed, according to the invention, to combine single-point milling with subsequent tangential milling and / or finishing and / or fine dry grinding and / or electrochemical etching.
Owner:美艾格工业自动化系统股份有限公司
Power supply device for electric discharge machine
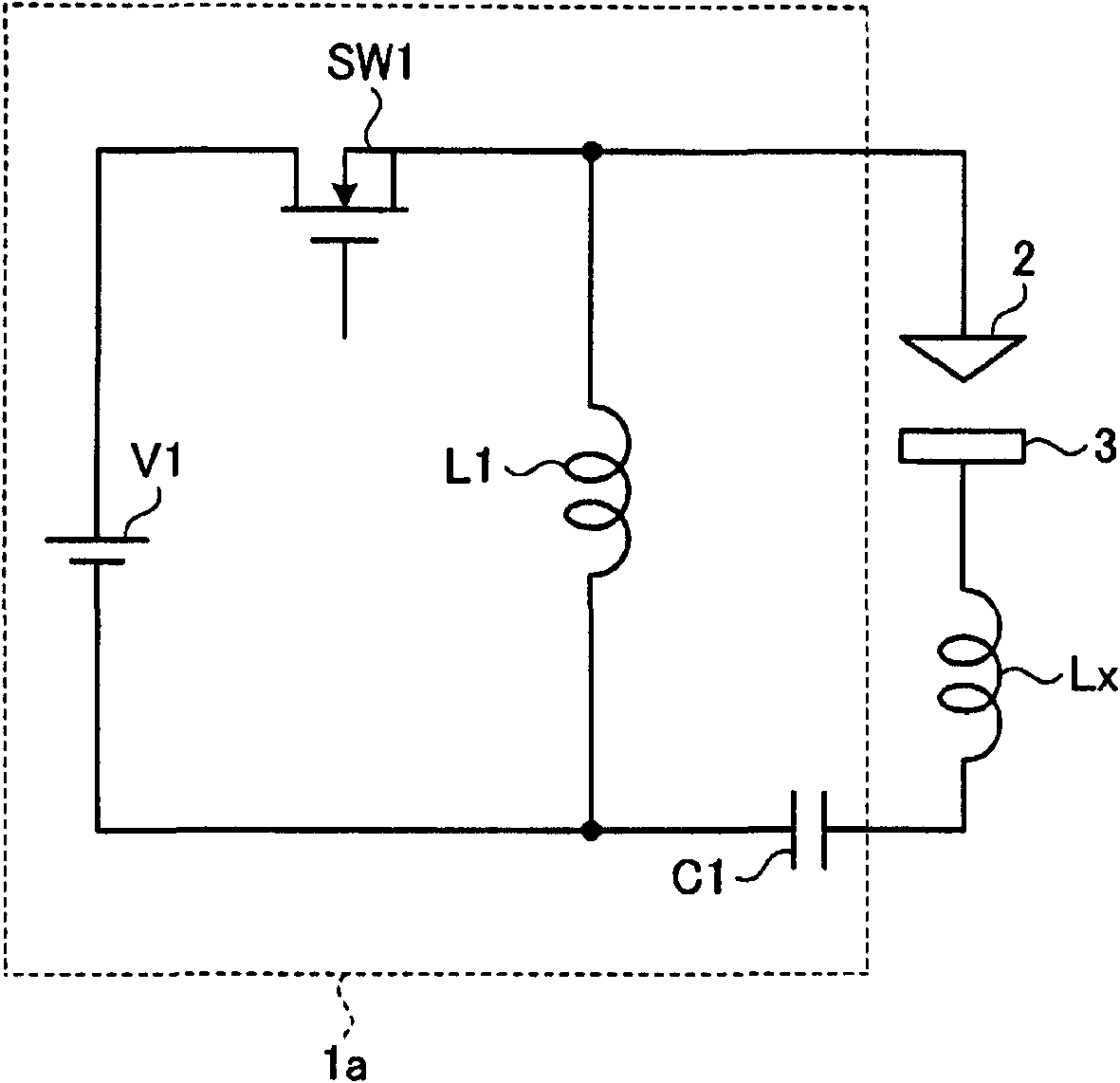
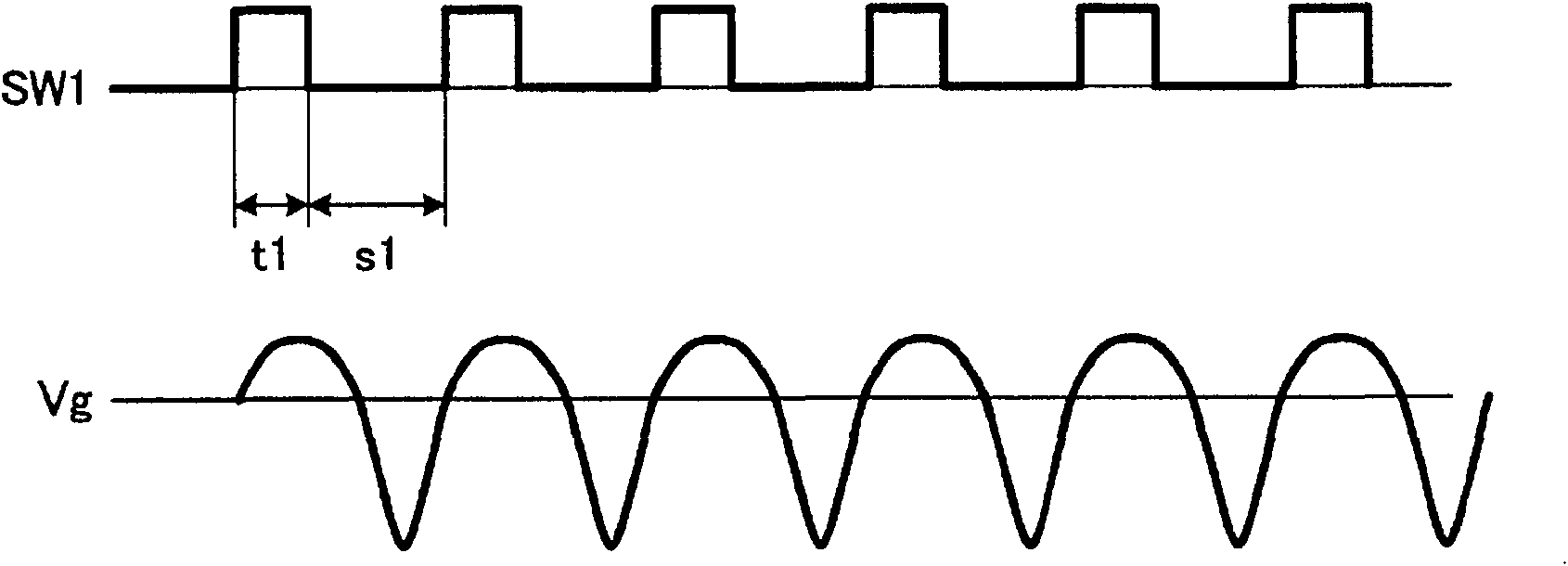
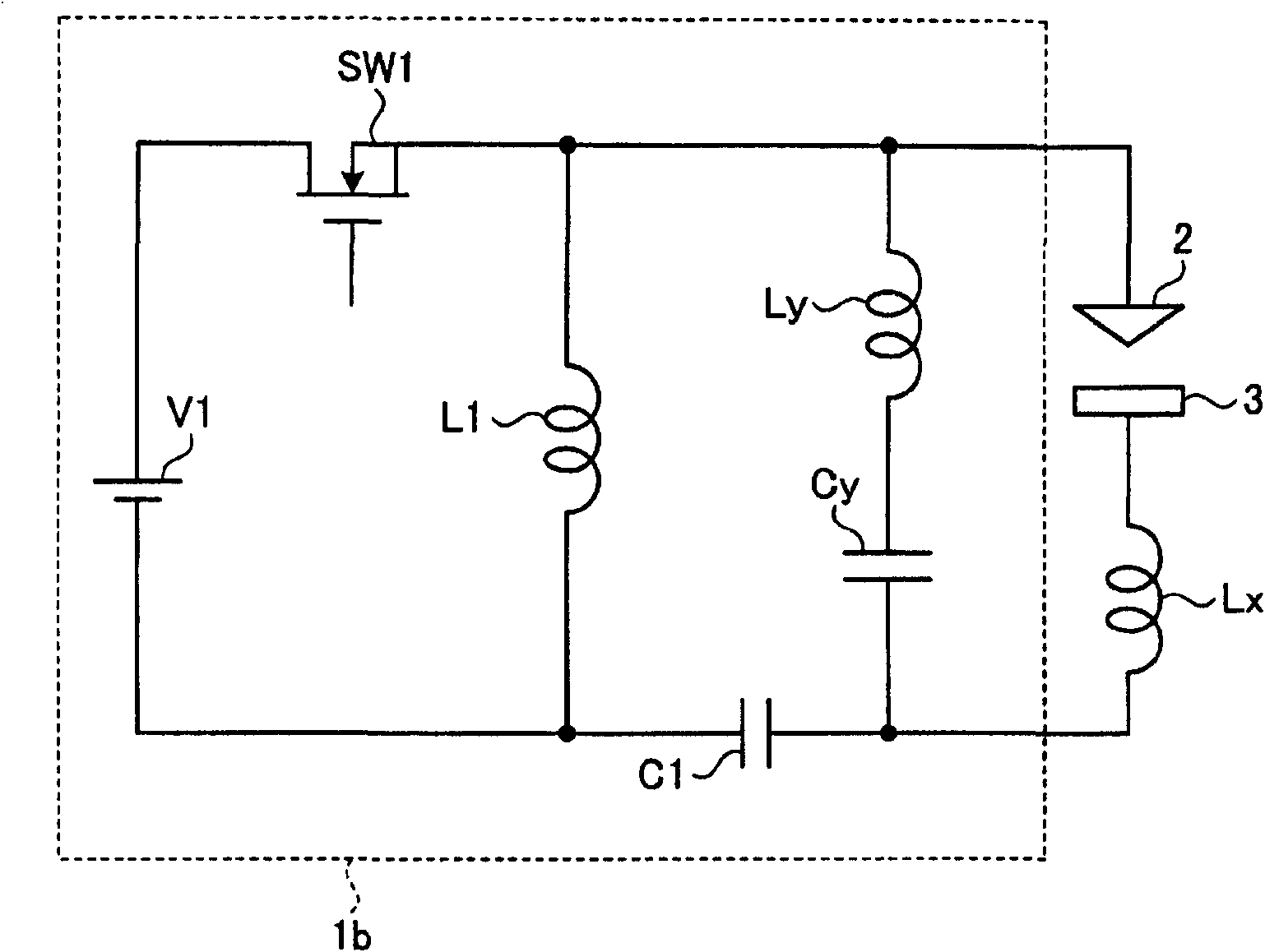
ActiveCN102143821AEliminate stabilityEliminate lossEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionStray inductanceResonance
A switching element (SW1) opens and closes in the frequencies of MHz-order. A reactor (L1) resonates with the stray capacitance between the electrodes and supplies the resulting resonant current to between the electrodes. The resonant current does not flow through a DC power supply (V1). A series resonance between a capacitor (C1) and a stray inductance (Lx) allows the resonant current to be ideally supplied from the rector (L1) to between the electrodes without receiving the influence of the stray inductance (Lx). A high-frequency voltage asymmetrical in the positive and negative directions is applied between the electrodes and a current pulse can be shortened, so that finish machining with a high degree of surface roughness can be performed.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method for a removal of cathode depositions by means of bipolar pulses
InactiveUS6620307B2Extended durationCellsMachining electric circuitsVoltage pulseElectrical polarity
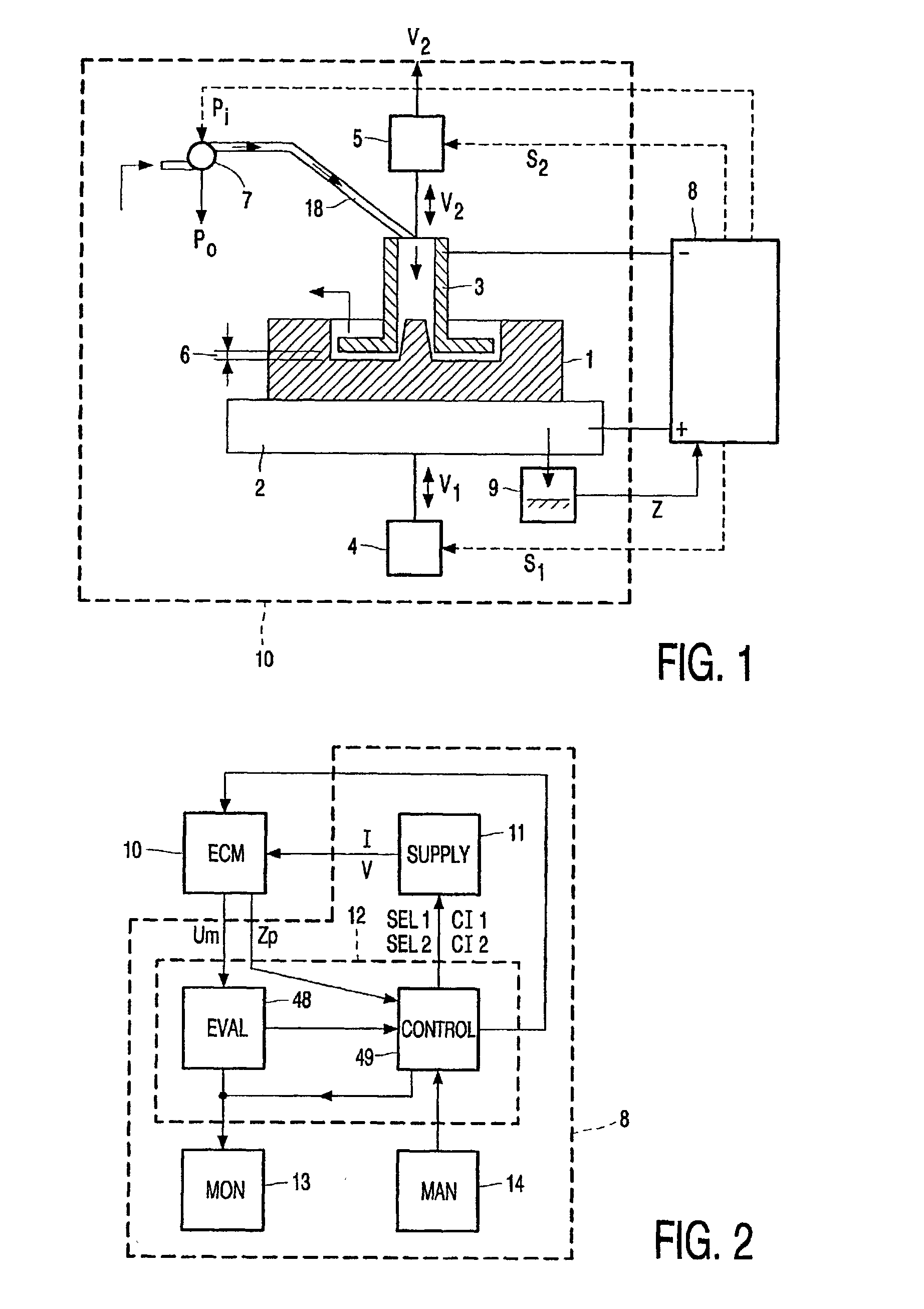
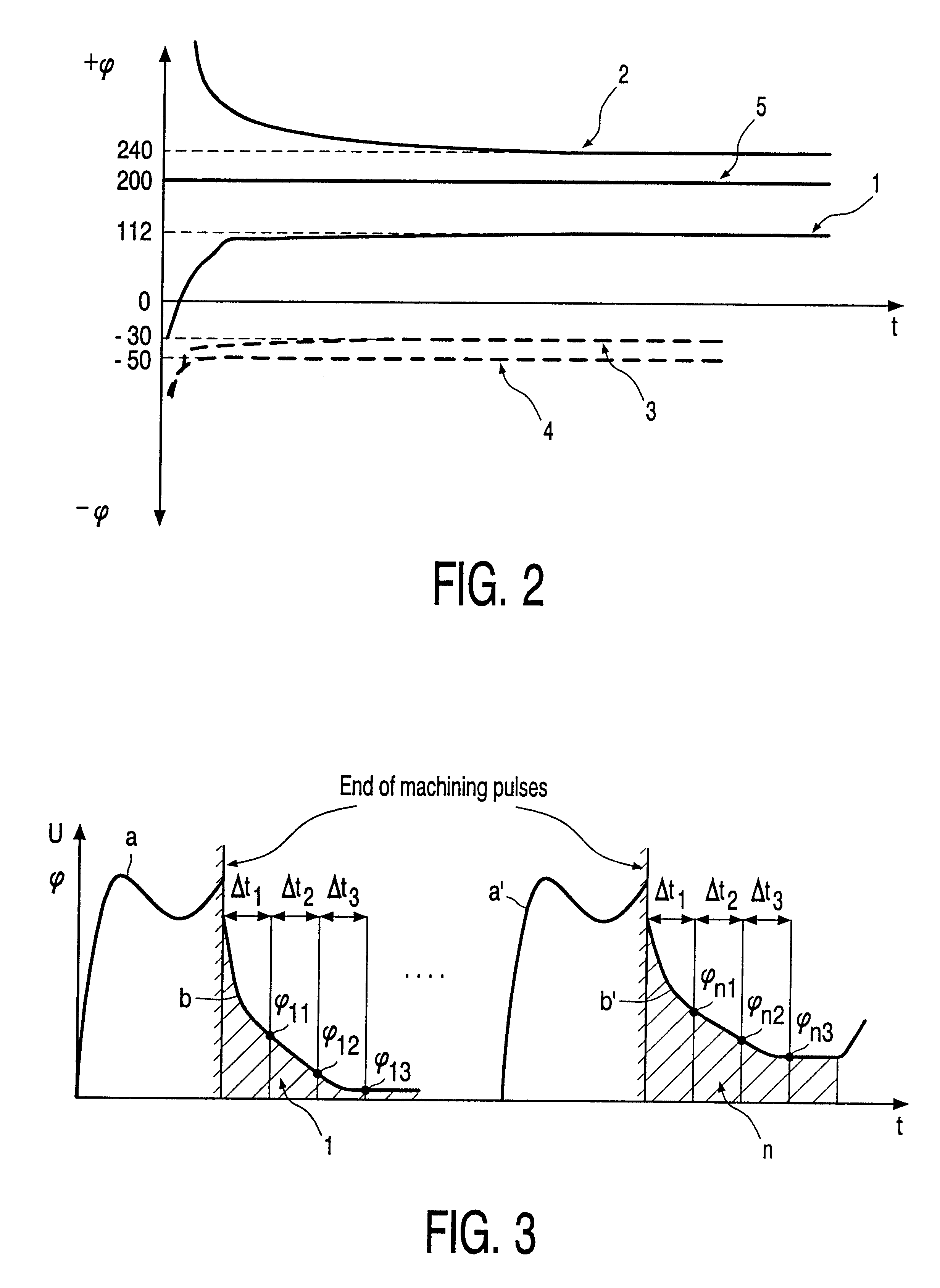
A method for on-line removal of cathode depositions during electrochemical process. The process control unit (30) is arranged to alternate the unipolar machining voltage pulses U1 with the voltage pulses of opposite polarity U2 to the work piece (2) and the cathode (3). The process control unit comprises an arrangement to determine the amount of cathode depositions on-line based on the operational parameter. Only in case the operational parameter exceeds the allowable level, the process control unit (30) alternates the unipolar machining voltage pulses U1 with the voltage pulses of opposite polarity U2. In this case the cathode wear is minimized.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Wire electrical discharge machine
ActiveUS20180056421A1Increase processing volumeImprove machine efficiencyElectrical-based machining electrodesElectric circuitsEngineeringVoltage
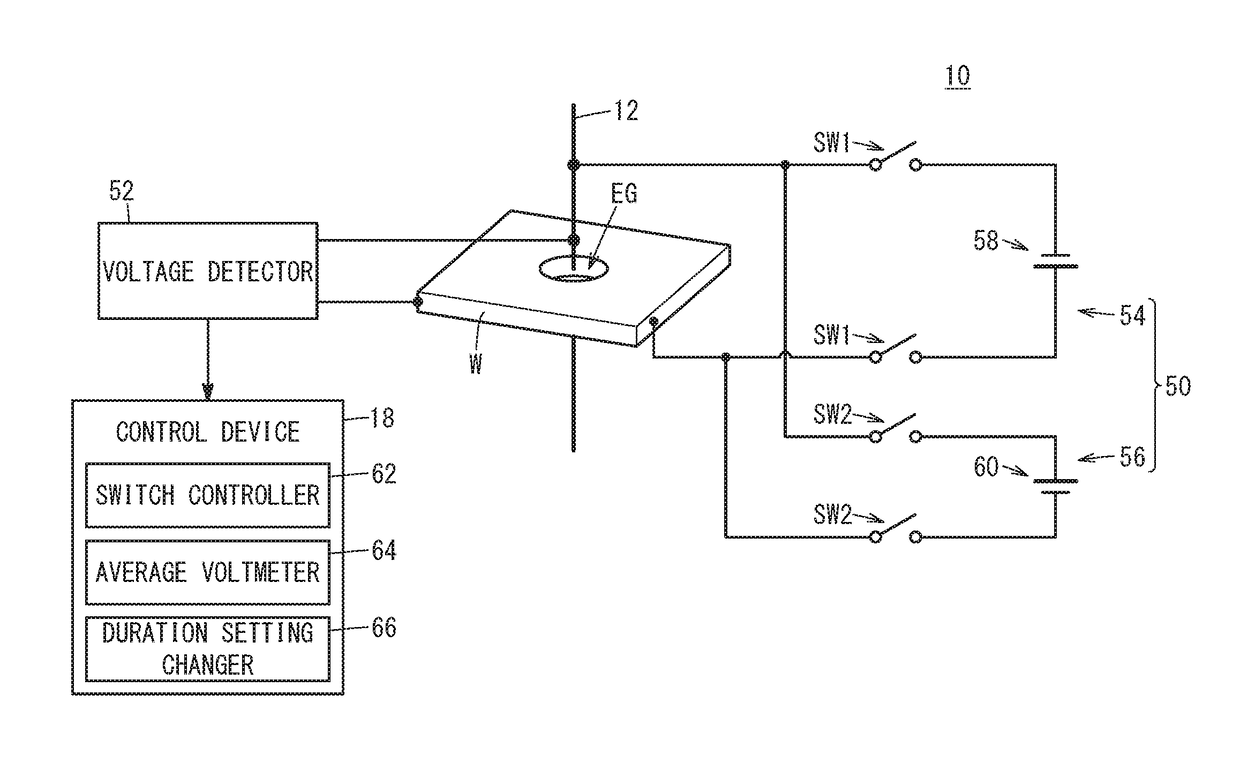
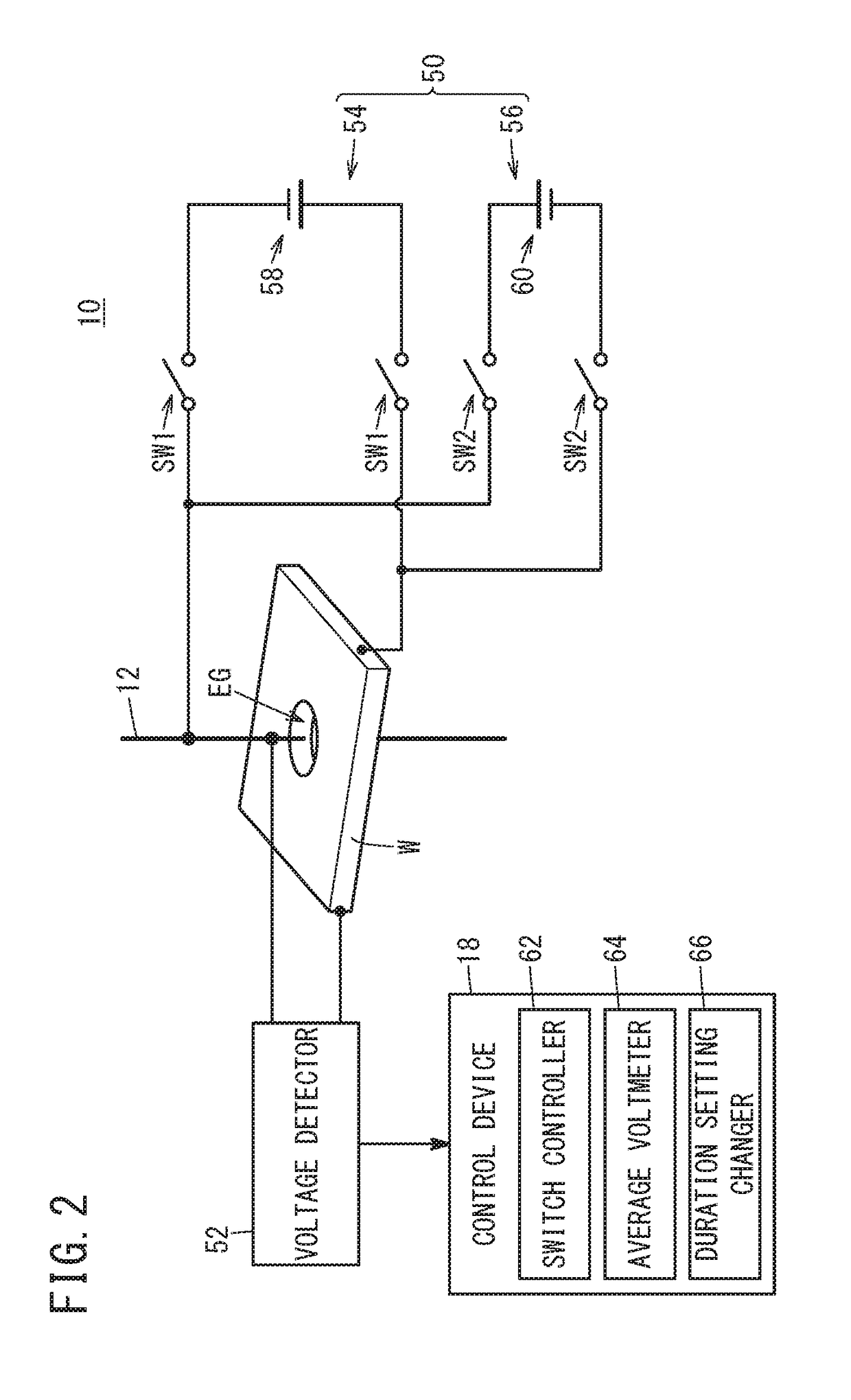
A wire electrical discharge machine includes a first voltage applying circuit, a second voltage applying circuit, and a switch controller. The first voltage applying circuit includes a first DC power source for applying a positive polarity voltage across an electrode gap, and a first switch for on / off-switching of application of the positive polarity voltage. The second voltage applying circuit includes a second DC power source for applying a reverse polarity voltage to the electrode gap, and a second switch for on / off-switching of application of the reverse polarity voltage. The switch controller controls the first switch and the second switch so that the first switch and the second switch are not turned on simultaneously. The first DC power source and the second DC power source are set up so that the absolute value of the reverse polarity voltage is lower than the absolute value of the positive polarity voltage.
Owner:FANUC CORP
Power supply device for electric discharge machining
InactiveUS20050194947A1Limit charging voltageEnergy loss is hardlyBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerCapacitanceResistor
An electric-discharge-machining power supply device in which energy loss is hardly produced and a charge voltage of a capacitor is easily controlled. When a switching element SW1 is turned on, a capacitor C is charged via an inductor L. When the voltage Vc of the charged capacitor exceeds the voltage of direct-current power source E, a current is returned to the power source E via a diode D2. When the switching element SW1 is turned off, energy stored in the inductor L flows from the inductor L through the diode D2, the power source E and the diode D1, so that the voltage Vc of the capacitor C is kept at the power source voltage. When a switching element SW2 is turned on, the voltage of the capacitor is applied between an electrode and a workpiece. Since the charging circuit does not include a resistor and energy stored in the inductor L is returned to the direct-current power source E, no energy loss is produced. Further, the voltage Vc of the charged capacitor C can be controlled by adjusting the power source voltage.
Owner:FANUC LTD
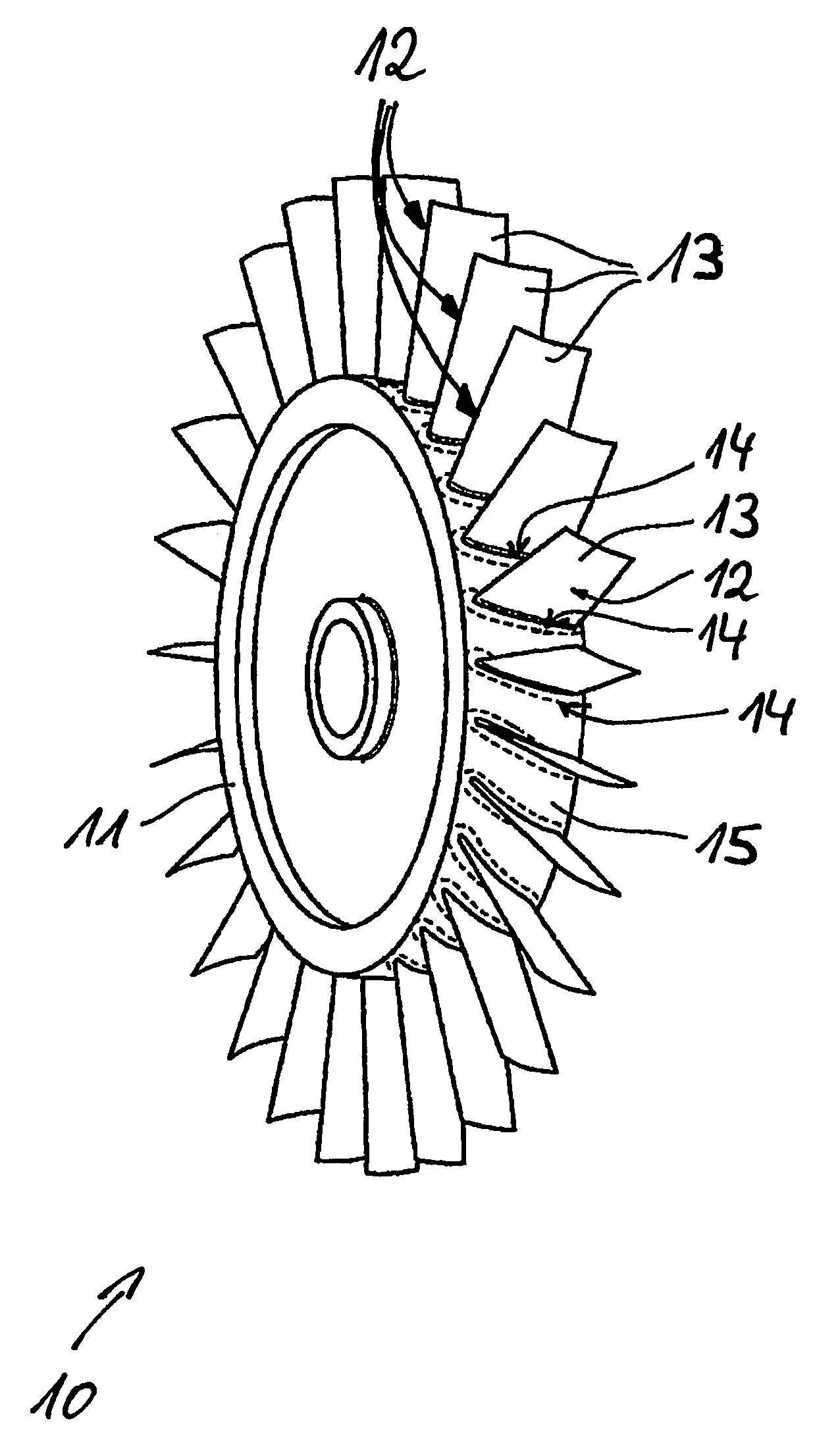
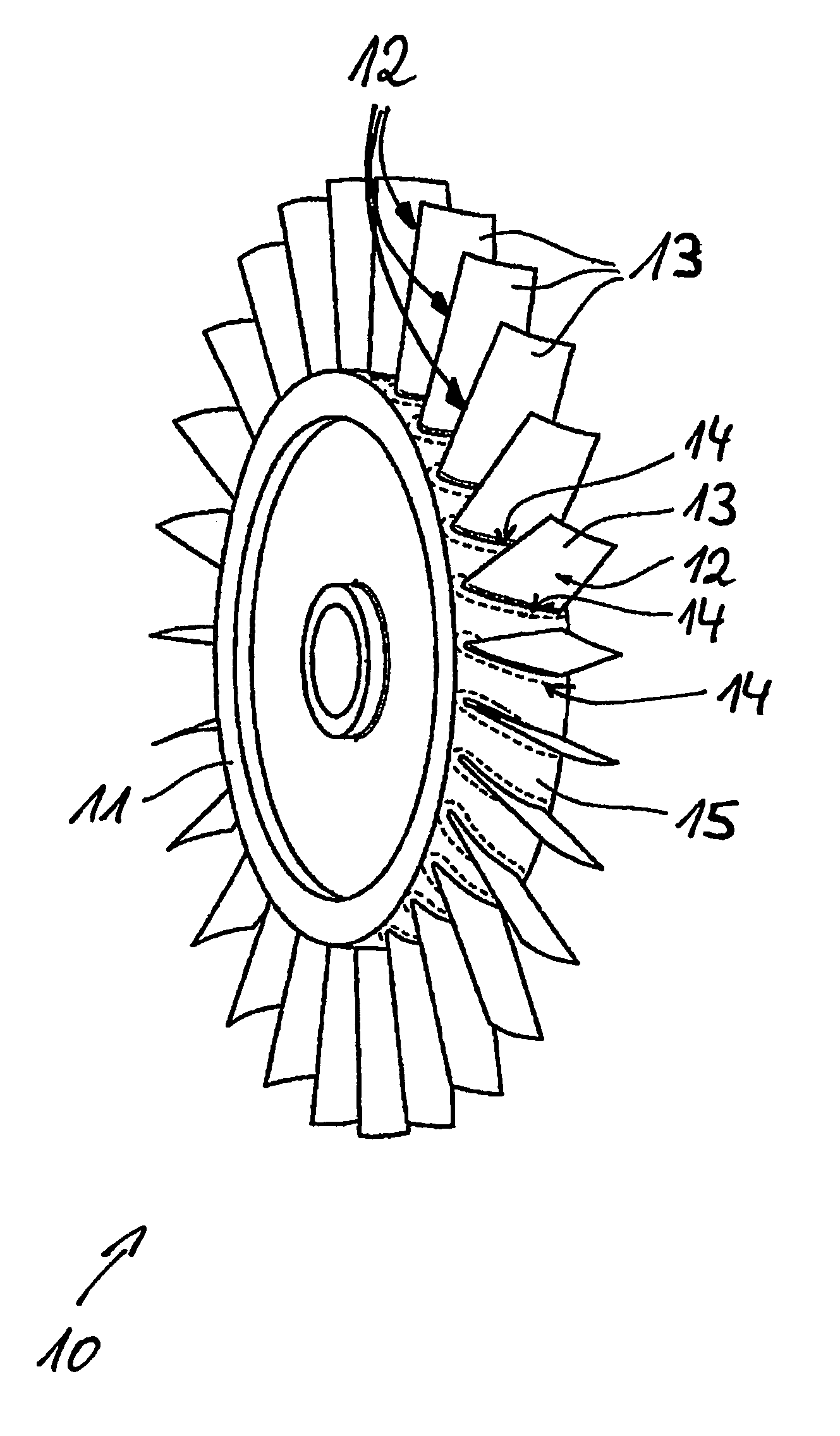
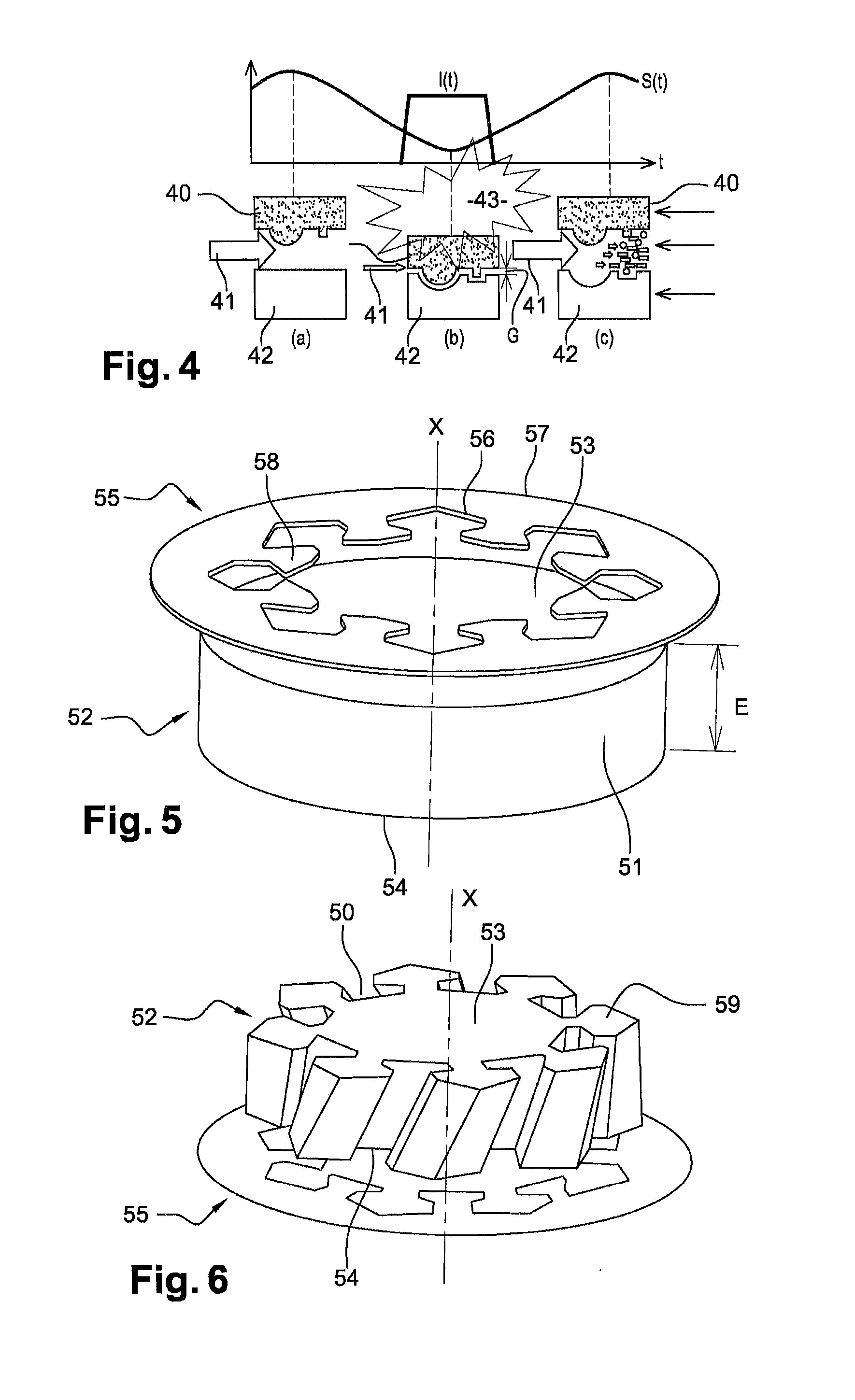
Method for producing cavities for a turbomachine disk
A method for producing cavities in a turbomachine disk, the cavities extending between first and second lateral surfaces of the disk, the method including positioning a ring facing the first surface, the ring including an inner periphery including protrusions complementary in shape to the cavities that are to be produced; circulating an electrolyte close to the protrusions on the ring; activating a first translational movement of the ring towards the second surface; activating a rotation of the disk; generating an electric current pulse in the electrolyte when the ring is substantially at the first surface, the pulse resulting in the ionic dissolution of the disk at the protrusions; reducing the speed of rotation to a first reduced speed, when the ring is substantially at the first surface, for a first period of time; and stopping the first translation of the ring when the ring is beyond the second surface.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Method and device for finishing work pieces
In order to shorten a process chain for material removing machining of a crank shaft after rough machining and after hardening a combination of circumferential turn milling as a first step and subsequent dry grinding as a second step is proposed according to the invention.
Owner:MAG IAS
Method of electrochemical machining
The invention relates to a method of electrochemical machining. In the initial step, the unipolar electrochemical machining by operating current pulses of normal polarity is carried out forming a layer enriched with chromium ions in the electrolyte area adjacent to the workpiece surface, then, upon achievement of the predetermined machining depth, shape and size of the workpiece, the operational current pulses of normal polarity and the machining electrode feeding are turned off and the residual polarization voltage value at the interelectrode gap is measured using the test high-frequency pulses of normal polarity, then low voltage pulses of opposite polarity synchronized with the phase of maximal approximation of the electrodes to each other are turned on and chromium cathode deposition onto the machined workpiece surface is carried out by means of alternating the pulses of opposite polarity with test high-frequency pulses of normal polarity and controlling the chromium deposition by increment of residual polarization value relative to its value after operational current pulses of normal polarity is applied.
Owner:PECM IND
Method and generator for electrical discharge machining
The invention relates to a method and a generator for generating a time sequence of discharge pulses separated from each other by pulse pauses for electrical discharge machining. At least two pulse capacitors are discharged each in the form of a partial pulse into the spark gap for forming together a discharge pulse. A discharge pulse having a predetermined waveform is selected from a plurality of discharge pulses having differing predetermined waveforms. The discharge of the at least two pulse capacitors is controlled such that the selected discharge pulse is generated with the predetermined waveform.
Owner:AGIE CHARMILLES +1
Pulse current and vibration matched feeding device
InactiveCN107322112AQuick updateReduce consumptionElectrochemical machining apparatusElectrical-based auxillary apparatusEngineeringPulse power supply
The invention discloses a pulse current and vibration matched feeding device which comprises a housing, and a cam and a sliding block that are arranged in the housing; the upper part of the cam is connected with a motor; a groove is formed in the upper part of the sliding block; the lower part of the cam is movably sleeved in the groove in the upper part of the sliding block; profile curves are formed in the cam; cylindrical pins are arranged on the sliding block, and are limited in the profile curves of the cam, and thus rotary motion of the cam is converted to up-down vibration of the sliding block; a permanent magnet is arranged on the sliding block; a hall switch is arranged at the place where the sliding block is in the lowest position after the sliding block vibrates downwards, in the housing; and when the sliding block is in the lowest position after the sliding block vibrates downwards, the hall switch sends out a voltage signal to a driving module, and thus a pulse power source sends out a packet high frequency pulse. An electrolytic solution in a machining gap can be renewed effectively; pulse current and vibration are matched for feeding, a cathode is vibrated to be fed to a place closest to an anode and the pulse power source sends out pulse, thus dispersion corrosion is reduced, energy consumption is reduced, and the precision of electrolytic machining is improved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF TECH
Electrical discharge machining apparatus
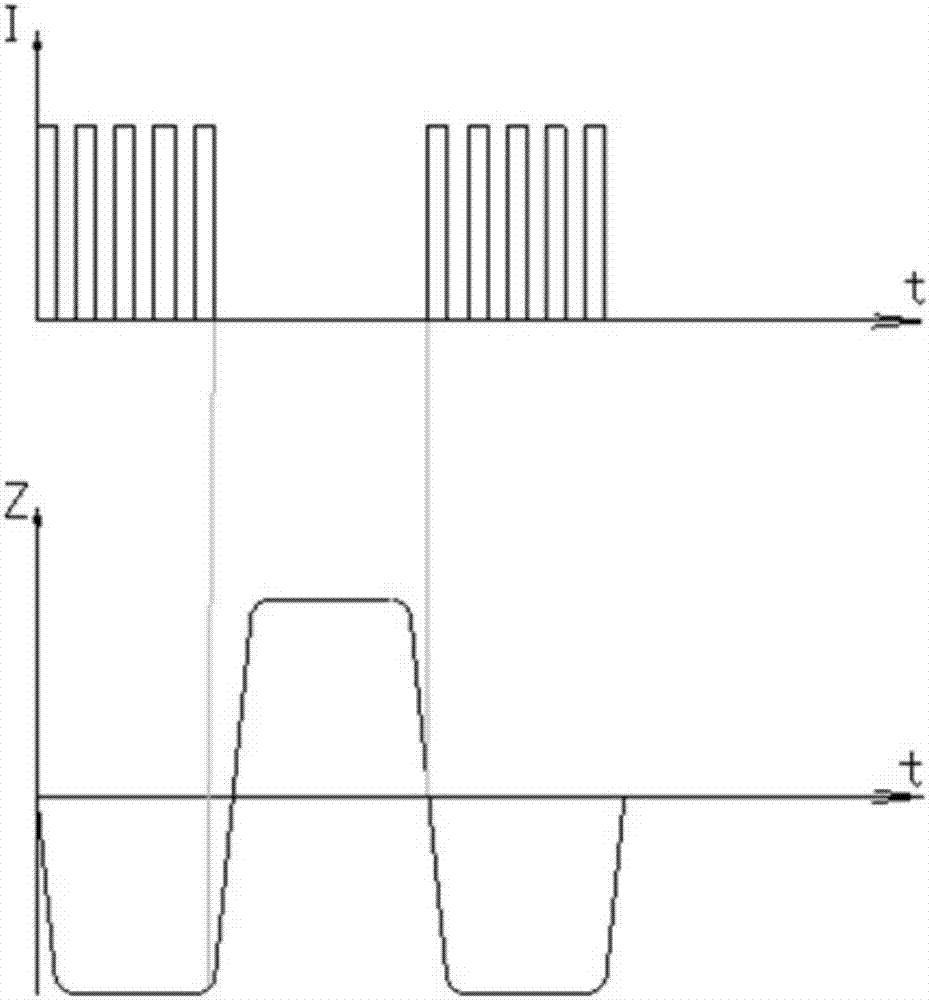
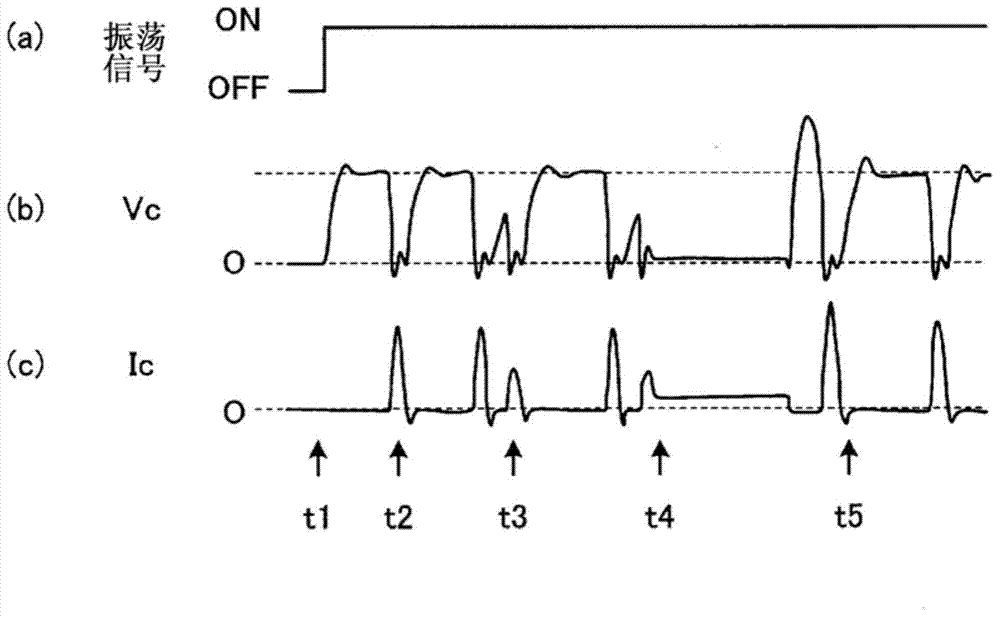
ActiveCN104781029AAvoid flowSuppresses discharge frequency reductionElectric circuitsPower source circuitsCapacitanceResting time
The present invention is capable of improving machining accuracy and machining efficiency by providing a regular rest time during a cycle in which machining is considered to become unstable during machining performed by the self-oscillation of a capacitor discharge in which the inter-electrode capacitance of a capacitor is used. This electrical discharge machining apparatus is provided with: a power source; an inter-electrode space formed by an electrode and the workpiece; a current-limiting resistor connected between the power source and the inter-electrode space; a switching element for turning on and off the application of voltage from the power source to the inter-electrode space; an inductance element connected serially between the switching element and the inter-electrode space; and a control unit for controlling the switching element, the control unit causing the switching element to turn on and off according to a switching pattern having an on-pulse duration (ΔT on) such that during the on-pulse time the voltage of the inter-electrode space can reach the voltage of the power source, and a rest duration (ΔT off) that ranges from the duration (ΔT ic) of the discharge current flowing during discharge of the capacitor, to less than the self-oscillation cycle (ΔT so).
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Popular searches
Special data processing applications Conductive material chemical/electrolytical removal Liquid separation by electricity Isotope separation From melt solutions Electroforming processes Polycrystalline material growth Single crystal growth details Metal working apparatus Revolution surface grinding machines
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com