Method and Apparatus for Reducing Patterning Effects on a Substrate During Radiation-Based Heating
a technology of radiation-based heating and patterning, applied in the field of substrate thermal processing, can solve the problems of non-uniform spectral power distribution, general inability of substrates to adequately ameliorate these gradients, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing patterning effects on a substra
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
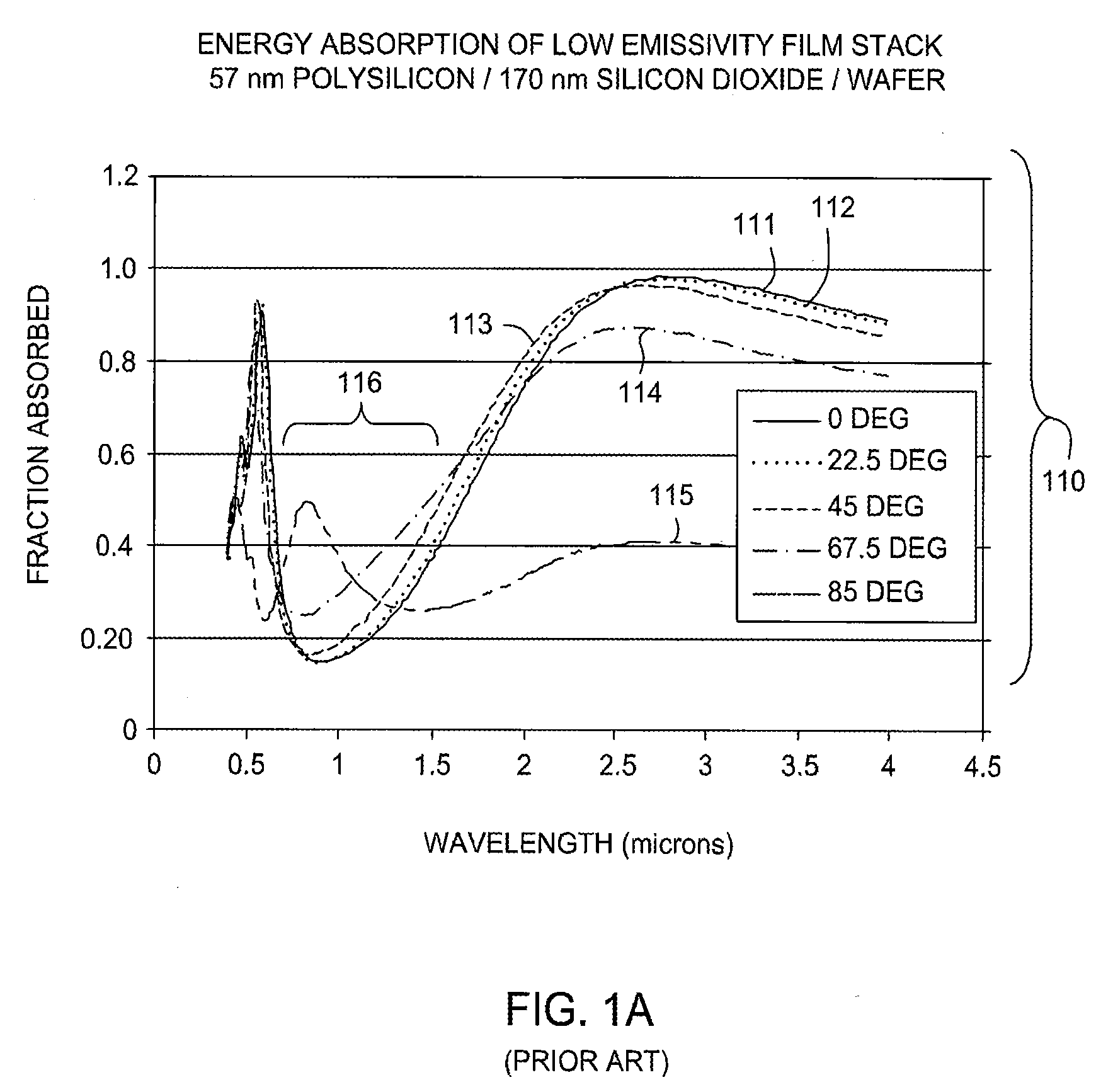
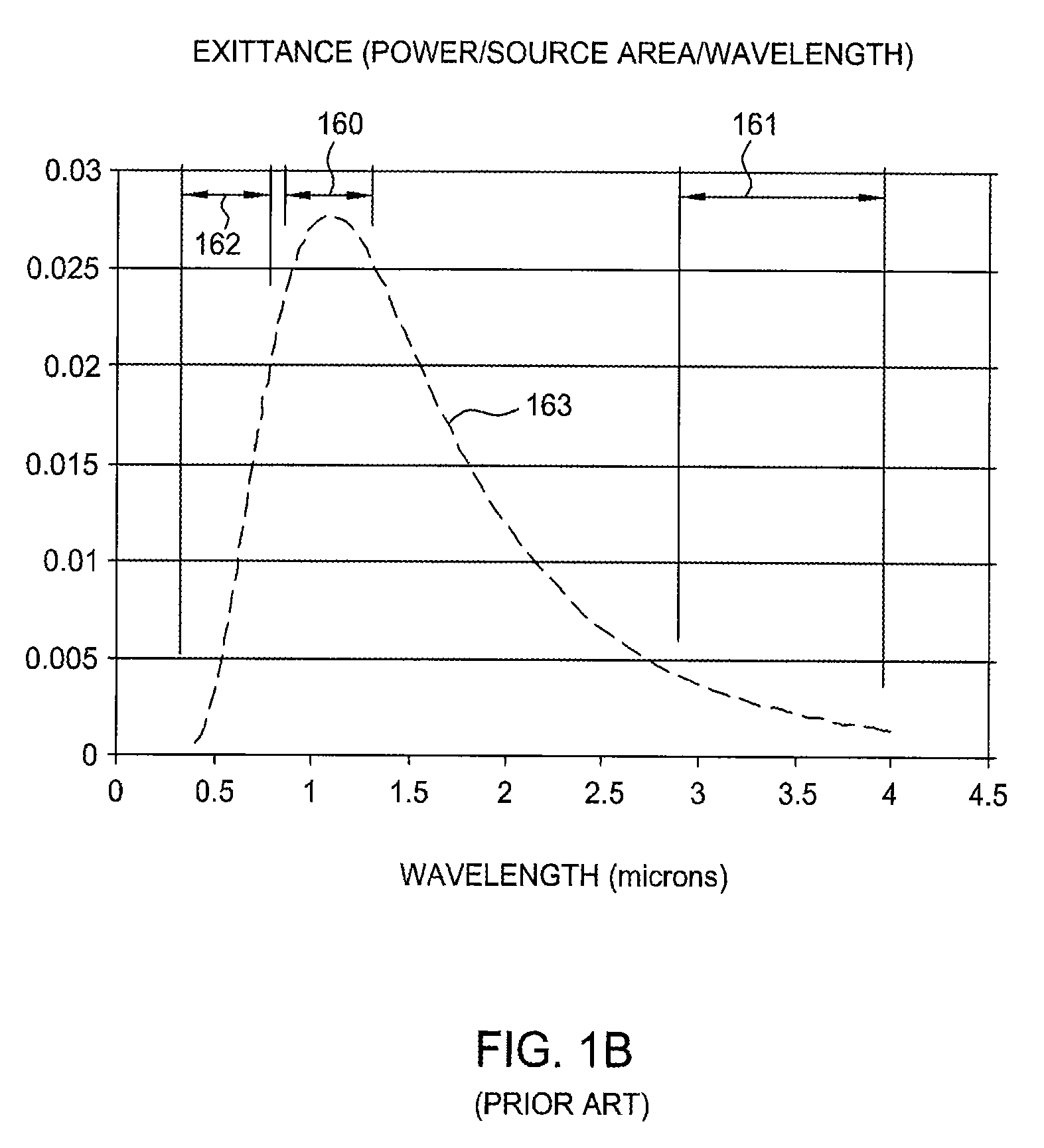
[0032]Typically in the art of radiation-based thermal processing of substrates, a single optimal radiation source type is selected for a particular thermal process. Embodiments of the invention contemplate the use of multiple radiation sources of different spectral characteristics to minimize the variation in absorbed power between different regions of a substrate surface, for example, between different regions of an IC die.
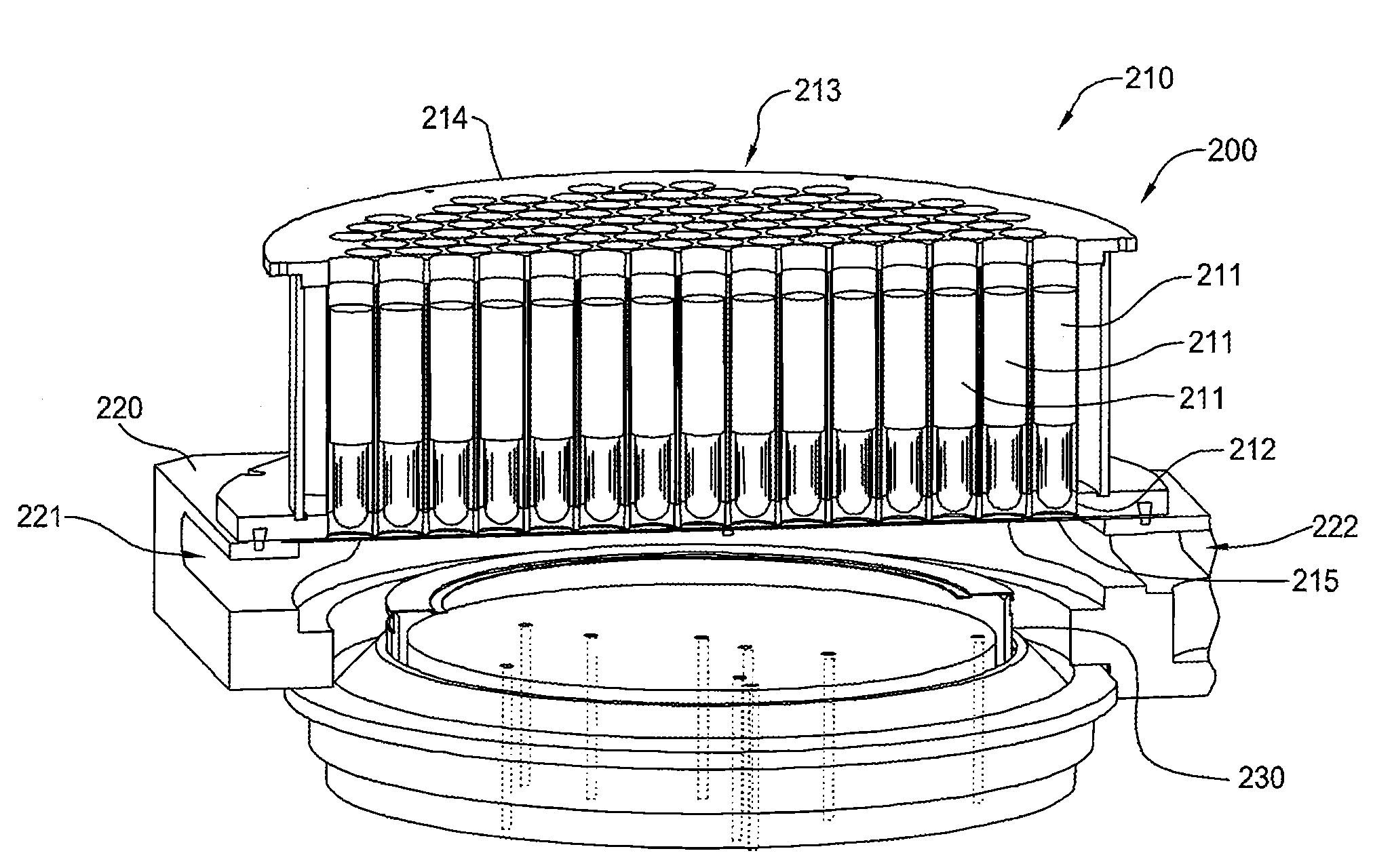
[0033]FIG. 2A is a partial perspective diagram of an exemplary radiation-based thermal processing chamber, in this case an RTP chamber, that may incorporate embodiments of the invention. The RTP chamber, hereinafter referred to as chamber 200, has been cross-sectioned for clarity. The chamber 200 generally consists of a lamp assembly 210, a chamber body 220 and a substrate support assembly 230. For clarity, only the upper portion of chamber body 220 is illustrated in FIG. 2A.
[0034]Lamp assembly 210 includes a plurality of radiation sources 211, each of which may ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com