Cobalt-base alloy with high heat resistance and high strength and process for producing the same
a technology of cobalt-base alloy and high heat resistance, which is applied in the field of cobase alloy, can solve the problems of low stability of 3/sub>ta at high temperature, low strength of ni-base alloy, and low operating temperature, and achieve high alloy strengthening and good compatibility with the matrix
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
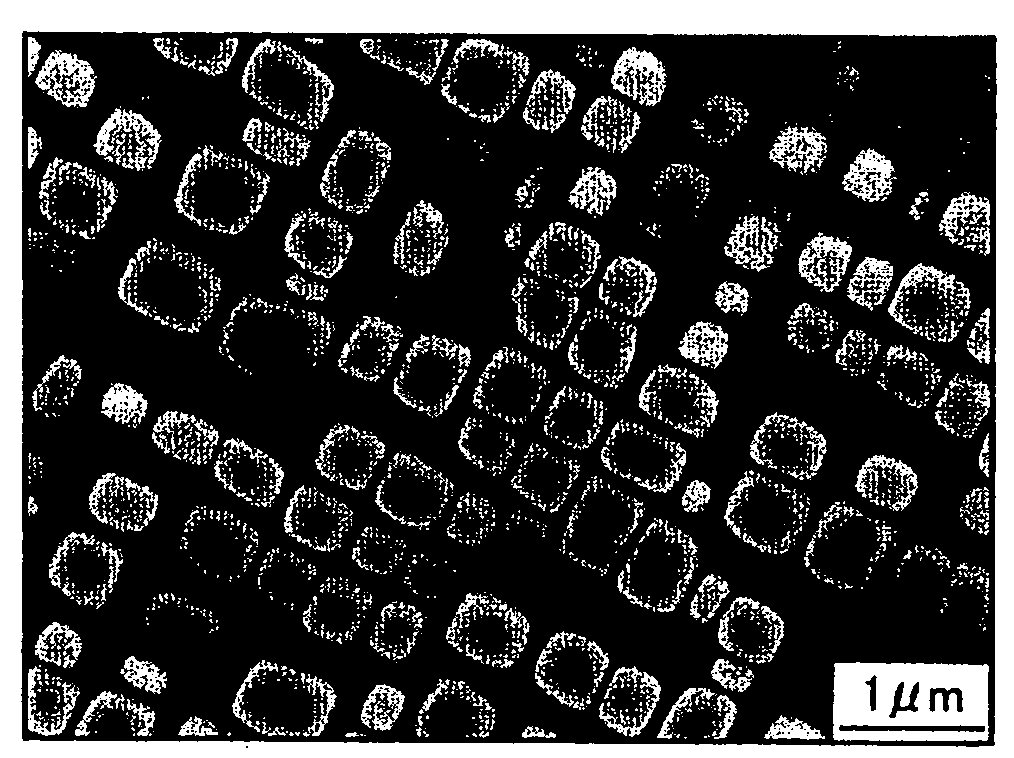
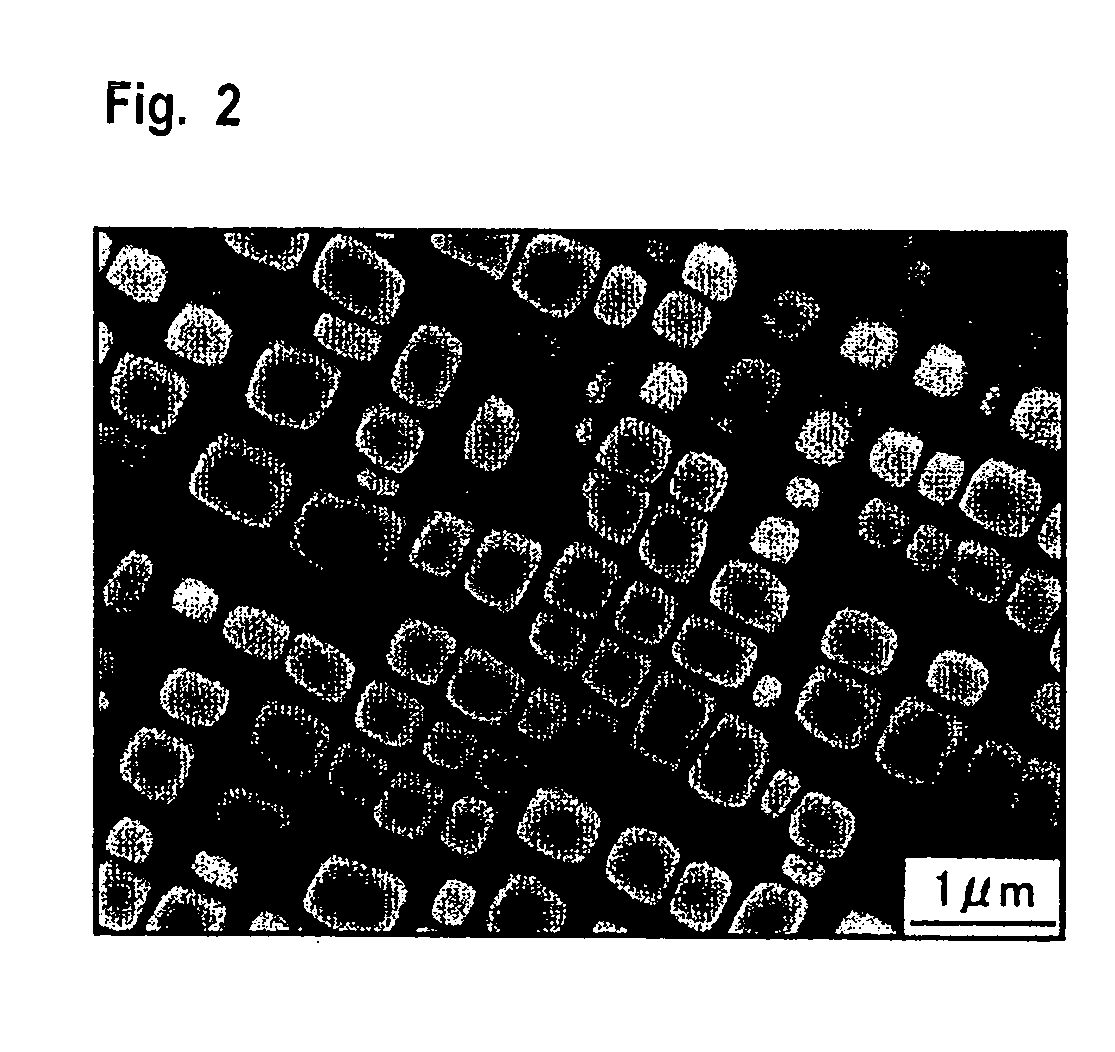
[0046]The Co-base alloy with the composition of Table 1 was smelted by high-frequency-induction dissolution in an inert gas atmosphere. The resulting product was casted to form an ingot, and then hot-rolled to a plate thickness of 3 mm at 1200° C. The test pieces obtained from the ingot and the hot-rolled plate were subjected to the solution treatment and aging treatment shown in Table 2, followed by texture observation, composition analysis, and characteristic test.
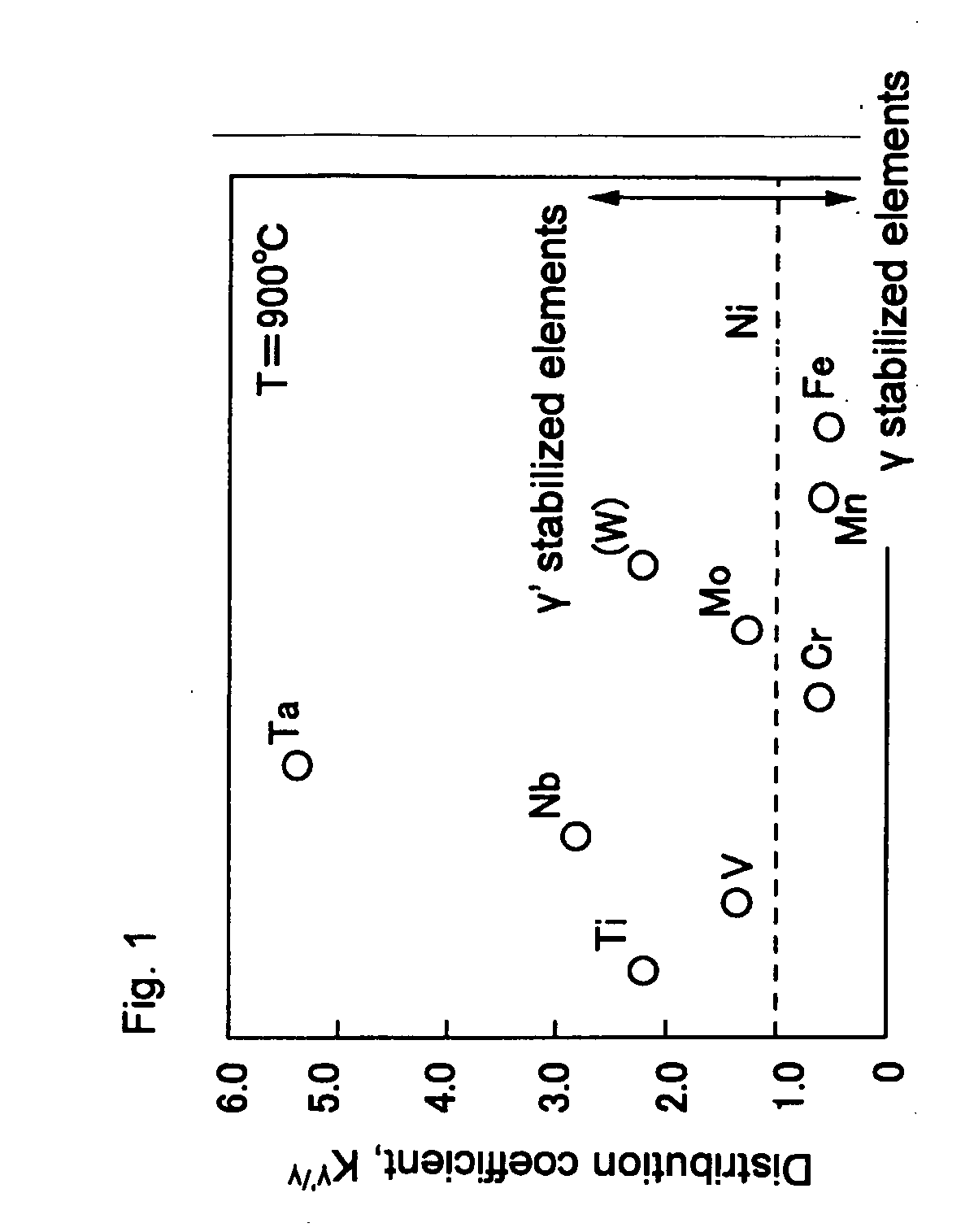
[0047]Each of the test results is shown in Table 3. In the Table, γ′ / D019 shows that precipitates are two types of γ′ phase and D019(Co3W) phase, D019 / μ shows that precipitates are two types of D019 phase and μ phase, and B2 / μ shows that precipitates are two types of B2 (CoAl) phase and μ phase.
[0048]In the samples of Test Nos. 1 to 13, one type of the γ′ phase was observed as a precipitate. As is apparent from the case of Test Nos. 1 and 2, it is found that a mechanical property such as hardness can be controlled by cha...
example 2
[0056]Table 4 shows alloy designs in which alloy components of Group (I) were added to Co—W—Al alloy. The amounts of Al and W were determined based on Alloy No. 3 of Table 1. The cobalt-base alloy adjusted to a predetermined composition was dissolved, casted, and hot-rolled in the same manner as described in Example 1, followed by heat-treating. The characteristics of the obtained hot-rolled plates are shown in Table 5.
TABLE 4Smelted cobalt-base alloy (Co; impurities removed fromthe remainder)Alloy component and content(% by mass)Alloy No.AlWBCYLa143.725.00.2 ———153.725.0—0.7 ——163.725.0——0.4—173.725.0———0.4183.725.00.030.03——
[0057]Since all components other than C were added trace elements in Group (I), a major change in the texture other than the addition of C was not observed. When a carbide is precipitated by addition of C, the Co-base alloy becomes hard. Both C and B tend to be segregated in the grain boundary segregation and they contribute to the improvement in high temperatu...
example 3
[0058]Table 6 shows alloy designs in which alloy components of Group (II) were added to Co—W—Al alloy. The Co-base alloy adjusted to a predetermined composition was dissolved, casted, and hot-rolled in the same manner as described in Example 1, followed by heat-treating. The characteristics of the obtained hot-rolled plates are shown in Table 7. For comparison, physical properties of Ni-base super alloy Waspaloy (Cr: 19.5%, Mo: 4.3%, Co: 13.5%, Al: 1.4%, Ti: 3%, C: 0.07%) are shown in Table 7 as Alloy No. 33.
TABLE 6Smelted cobalt-base alloy (Co; impurities removed fromthe remainder)Alloy component and content(% by mass)Alloy No.AlWAlloy component of Group (II)194.026.9Ni: 4.3203.425.4Ir: 5.4213.526.4Fe: 1.6223.526.4Cr: 1.5233.426.1Mo: 2.8243.425.4Re: 5.3253.526.4Ti: 1.4263.426.1Zr: 2.6273.425.5Hf: 5.0283.526.4V: 1.5293.426.1Nb: 2.7303.425.4Ta: 5.1313.623.9Cr: 3.7, Ta: 5.2323.826.0Ni: 16.6, Ta: 5.1
TABLE 7Alloy components, metal compositions in accordance with heat treatment condition...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com