Methods of treatment involving p21/CIP1
a technology of rheumatoid arthritis and p21cip1, which is applied in the field of molecules for suppressing inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis, can solve the problems of little evidence proving that these drugs arrest the progression of the disease, the inability to achieve total prevention of joint destruction through conventional treatments, and the inability to achieve the effect of preventing aberrant growth and/or inflammation of synovial tissue, promoting expression or function of p21cip1 protein, and the inability to
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Transfection of Adenoviral Vectors Incorporated with p16INK4a and p21Cip1 Gene Inhibits Synovial Cell Proliferation
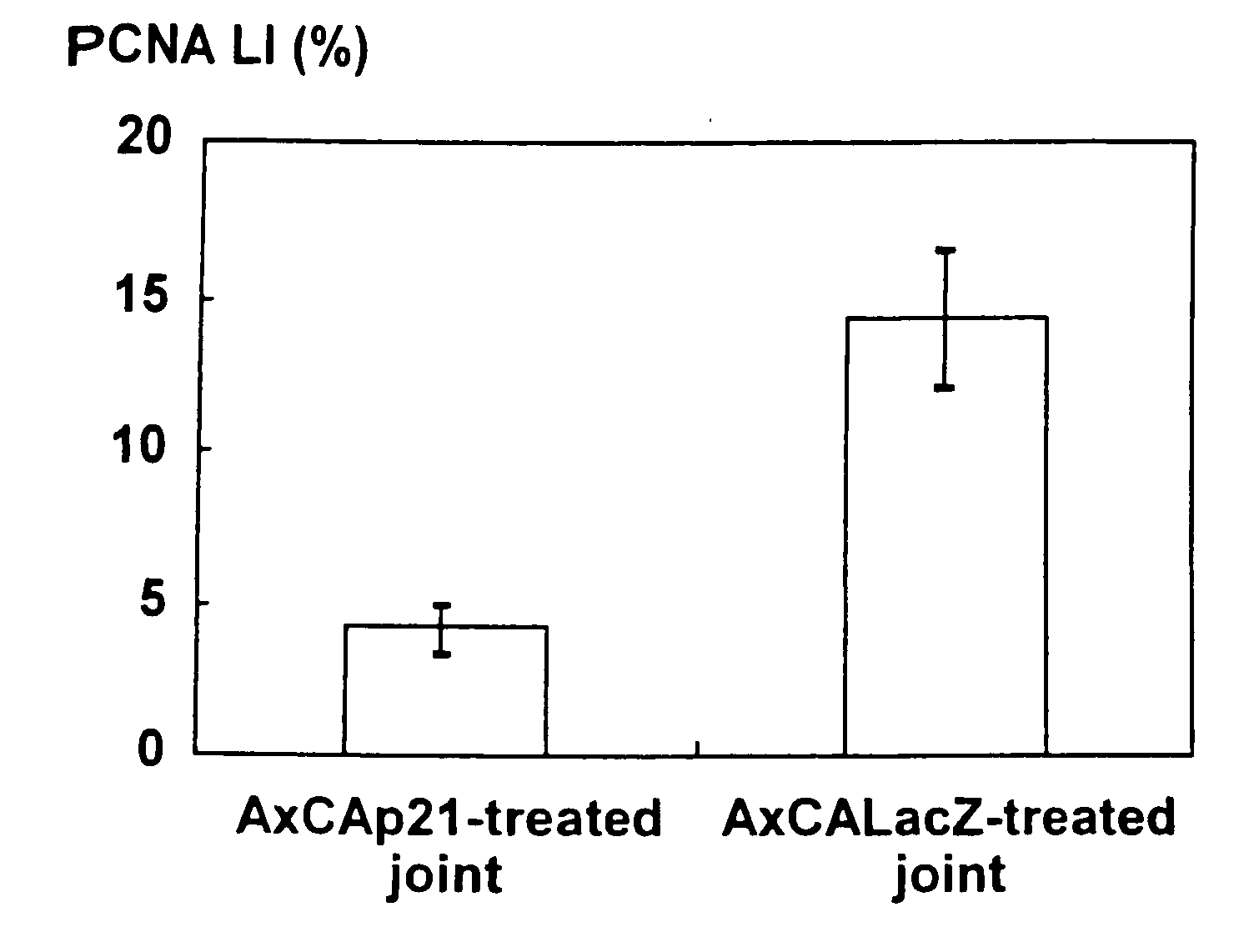
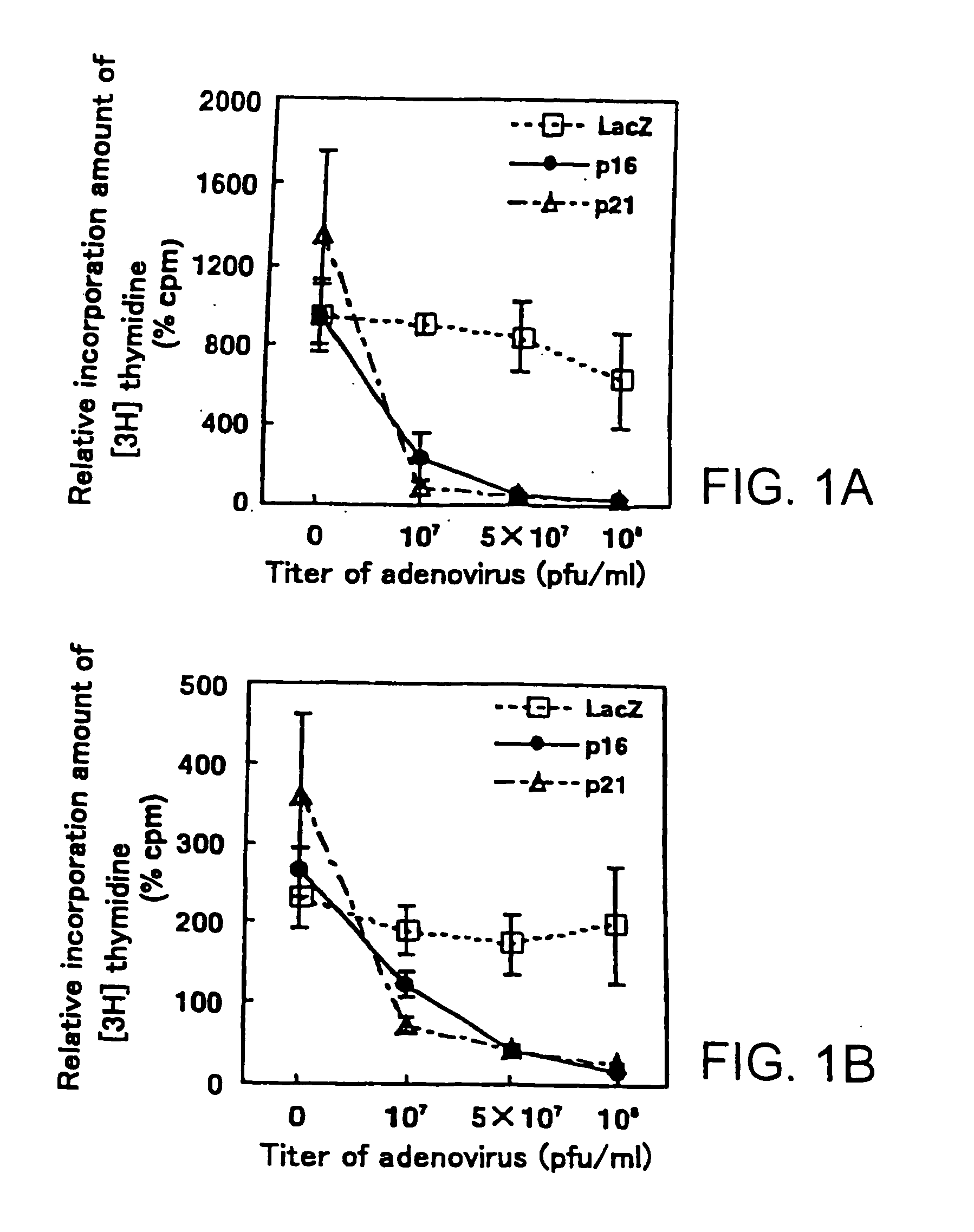
[0081]The anti-proliferative effects of the forced expression of p21Cip1 as well as p16INK4a on the synovial cells were examined using human synovial fibroblasts. RSFs prepared from the rheumatoid synovial tissues were infected with the recombinant adenoviruses AxCAp16, AxCAp21, or AxCALacZ, containing p16INK4a, p21Cip1, or E. coli lacZ, respectively. Replication-defective adenoviruses containing a human p16INK4a gene and a human p21Cip1 gene (AxCAp16 and AxCAp21, respectively) were kindly supplied by Drs. Terada and Ito (Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Tokyo, Japan) (Terada, Y. et al., 1997, J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 8: 51-60). A recombinant adenovirus encoding the lacZ gene (AxCALacZ) was kindly provided by Dr. Saito (University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan) (Kanegae, Y. et al., 1995, Nucleic Acids Res. 23:3816-3821). High-titer recombinant adenoviruses were prepared by am...
example 2
Effects of p16INK4a and p21Cip1 Gene Induction on the Pathology of CIA
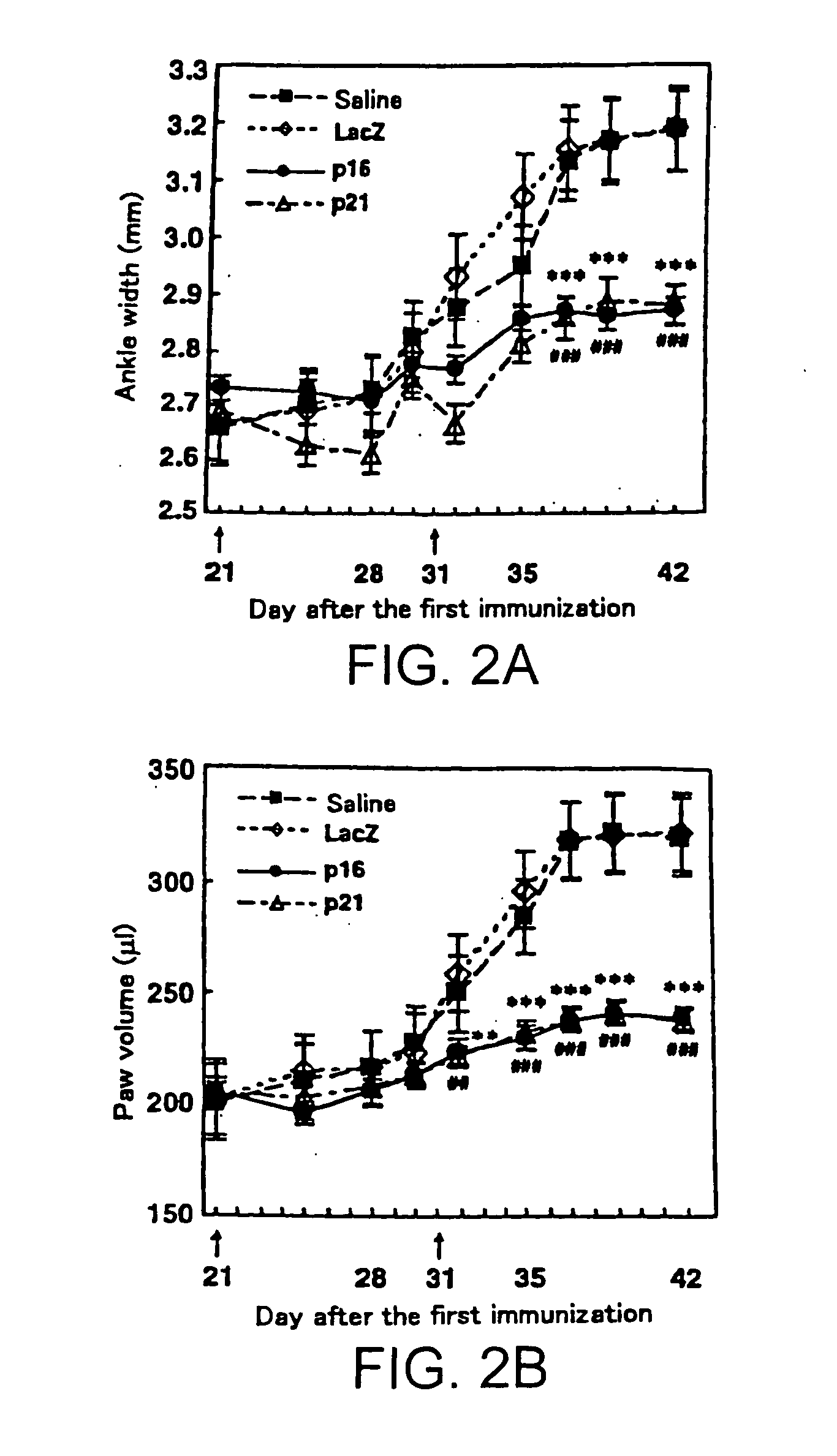
[0083]The same set of adenoviruses as in Example 1 was used to induce the p16INK4a, p21Cip1, or lacZ gene in vivo in the synovial tissues of CIA mice.
[0084]Induction of CIA was performed as follows. Male DBA / 1J mice were purchased from Japan Charles River Laboratories (Tokyo, Japan) and housed in the Tokyo Medical and Dental University Animal Research Center. Bovine type II collagen (Collagen Research Center, Tokyo, Japan) was dissolved at 2 mg / ml in 0.1 M acetic acid, then was emulsified with an equal volume of complete Freund's adjuvant (Iatron, Tokyo, Japan) . A hundred microliter of the immunogen was injected intradermally into 8-weeks-old mice at the tail base. After 3 weeks, the mice received the same antigen subcutaneously. Arthritis was developed within 10 days of the second immunization.
[0085]In vivo gene transfection into the joints was performed either on the same day as the second immunization and 10 d...
example 3
Effects of p16INK4a and p21Cip1 Gene Induction on the Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in the CIA-Affected Joints
[0091]As in the case of RA, TNF-α and IL-1, which are mainly secreted from the synovial cells, largely account for the pathology of CIA (Piguet, P. F. et al. , 1992, Immunology 77: 510-514; Williams, R. O. et al. , 1992, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 89: 9784-9788; Wooley, P. H. et al., 1993, J. Immunol. 151: 6602-6607; Joosten, L. A. B. et al., 1996, Arthritis Rheum. 39: 797-809). Thus, the inventors studied the expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokines, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, in arthritic joints administered with AxCAp16, AxCAp21, AxCALacZ adenovirus, or saline. The synovial tissues from the hind paws were collected on the day of histopathological examination. mRNA expression levels of these cytokines were analyzed by RT-PCR.
[0092]Total RNA was extracted from the arthritic synovial tissues with Isogen (Nippongene Co., Tokyo, Japan) for RT-PCR analysis. cDNA wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com