Method for removing micro-debris and device of the same
a technology of micro-debris and a device, applied in the direction of sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmission, manufacturing tools, chemistry apparatus and processes, etc., can solve the problems of increasing surface roughness, affecting proper laser performance, and machining precision decreasing, so as to improve machining precision and facilitate operation. , the effect of reducing the machining precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030]The following illustrative embodiments are provided to illustrate the disclosure of the present invention, these and other advantages and effects can be apparently understood by those in the art after reading the disclosure of this specification. The present invention can also be performed or applied by other different embodiments. The details of the specification may be on the basis of different points and applications, and numerous modifications and variations can be devised without departing from the spirit of the present invention.
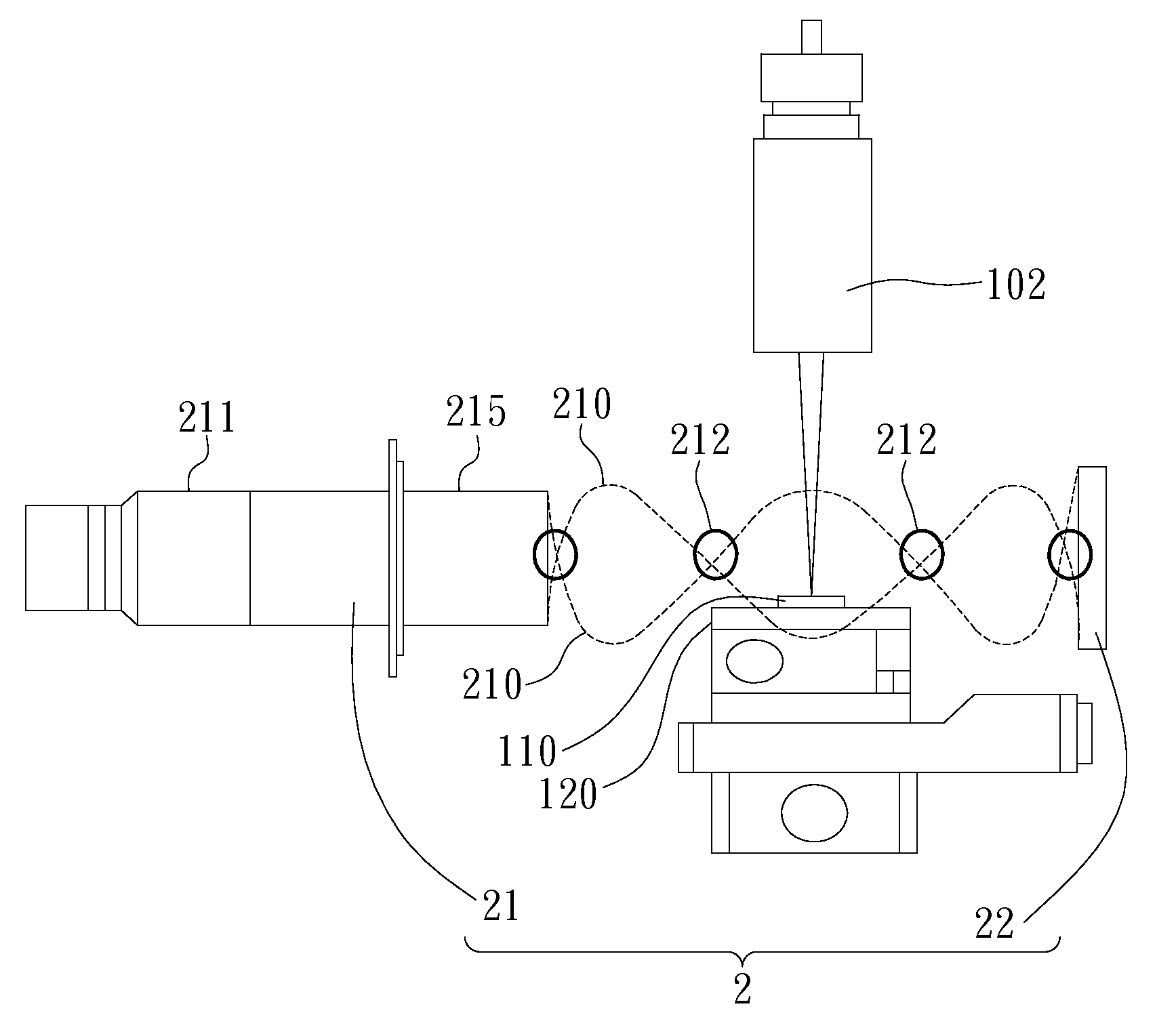
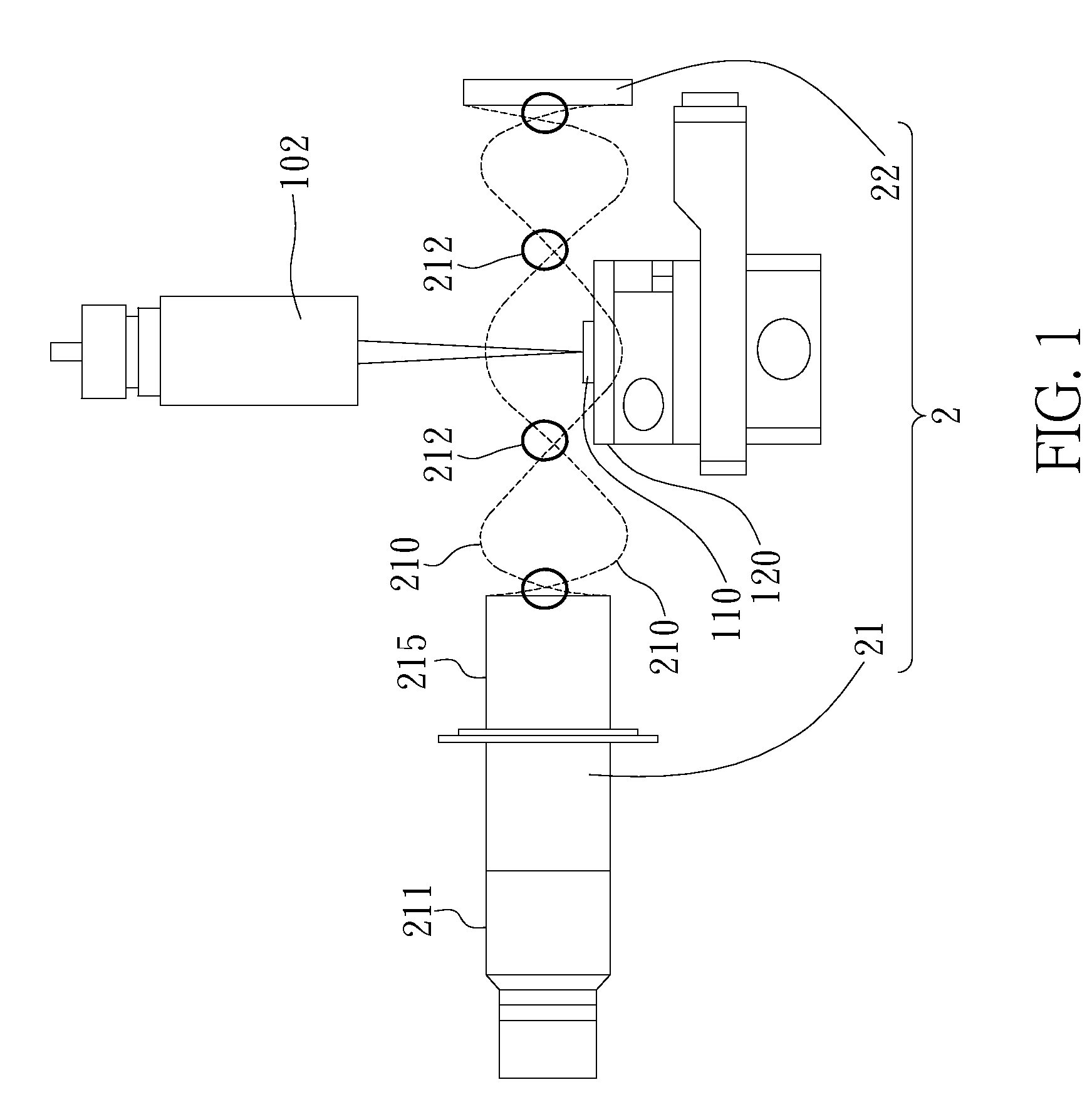
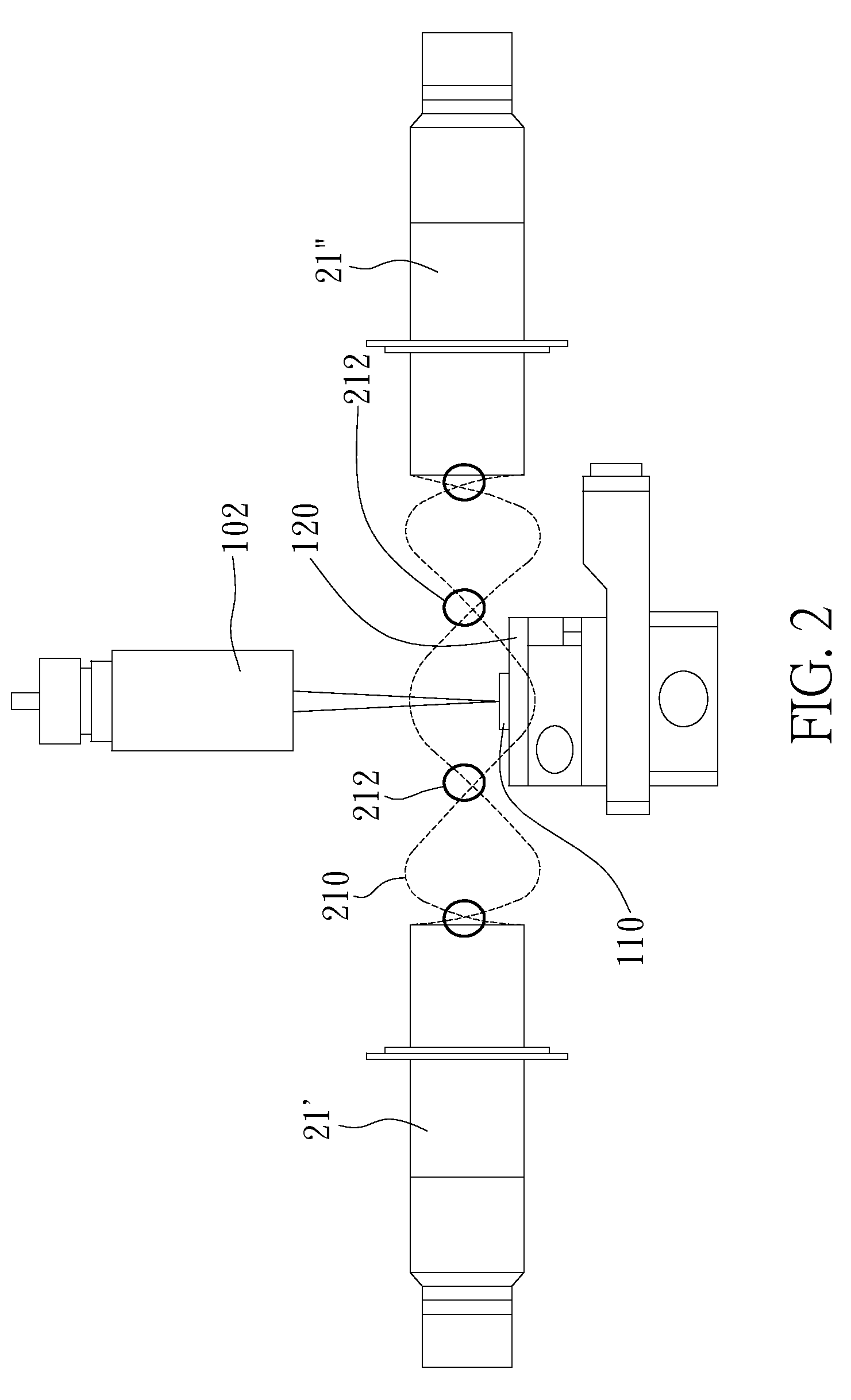
[0031]Please refer to FIG. 1, which is a diagram illustrating a first embodiment of method and device of the present invention for removing micro-debris; as shown in the FIG. the present invention is for removing micro-debris generated during a laser machining process performed on a machined object 110, the machined object 110 is placed on a movable machining platform 120 within a machining range, thereby performing machining on a machining locat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com