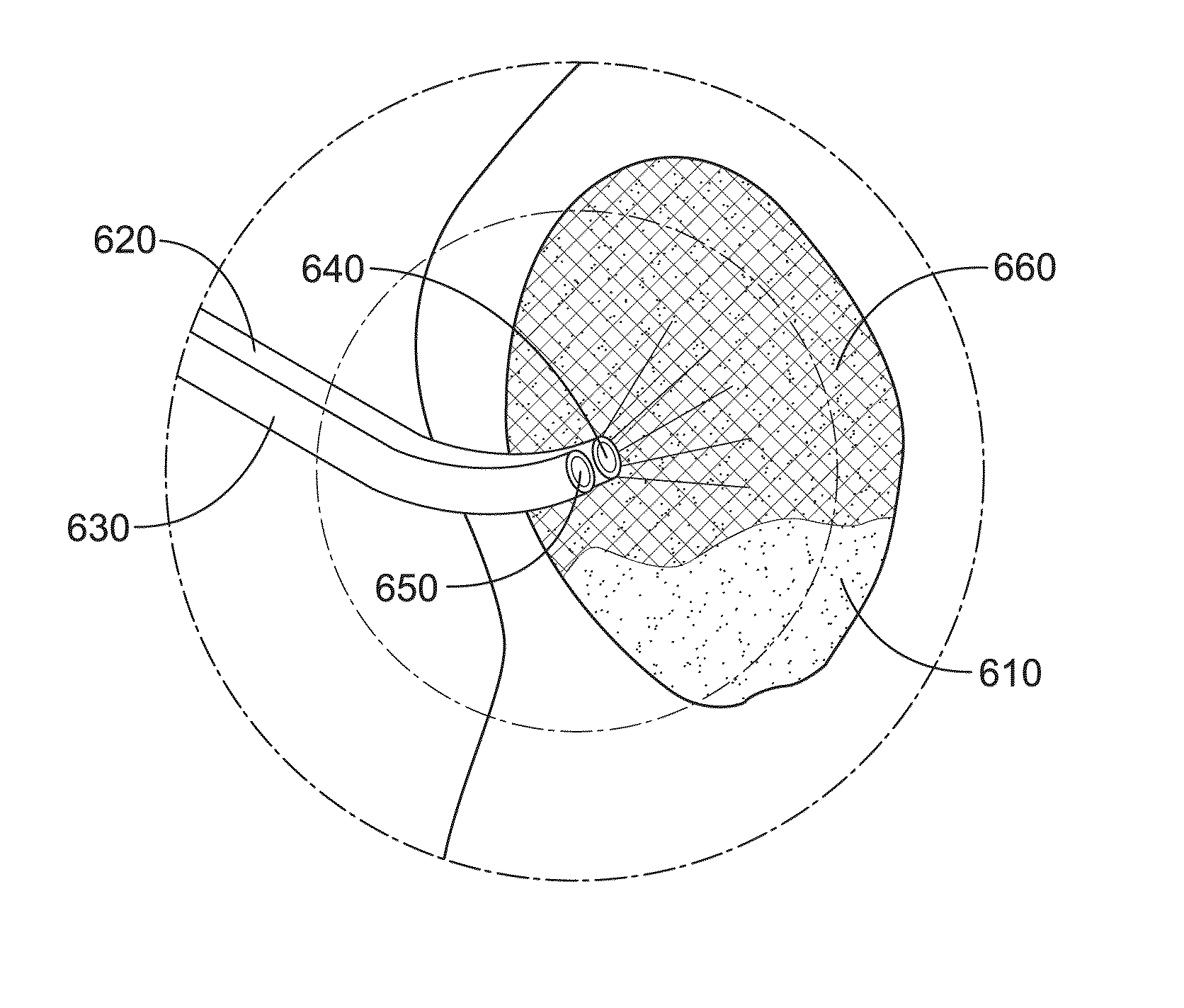
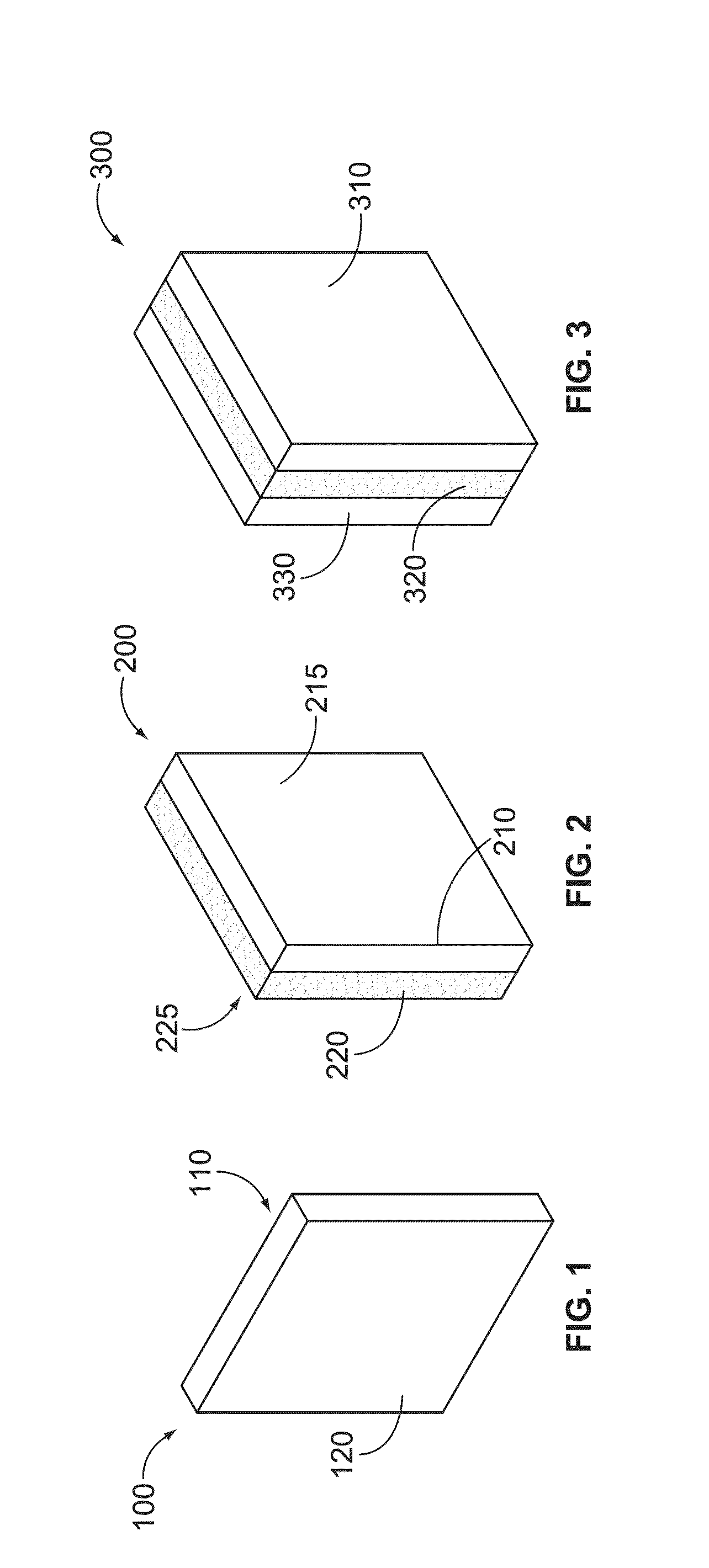
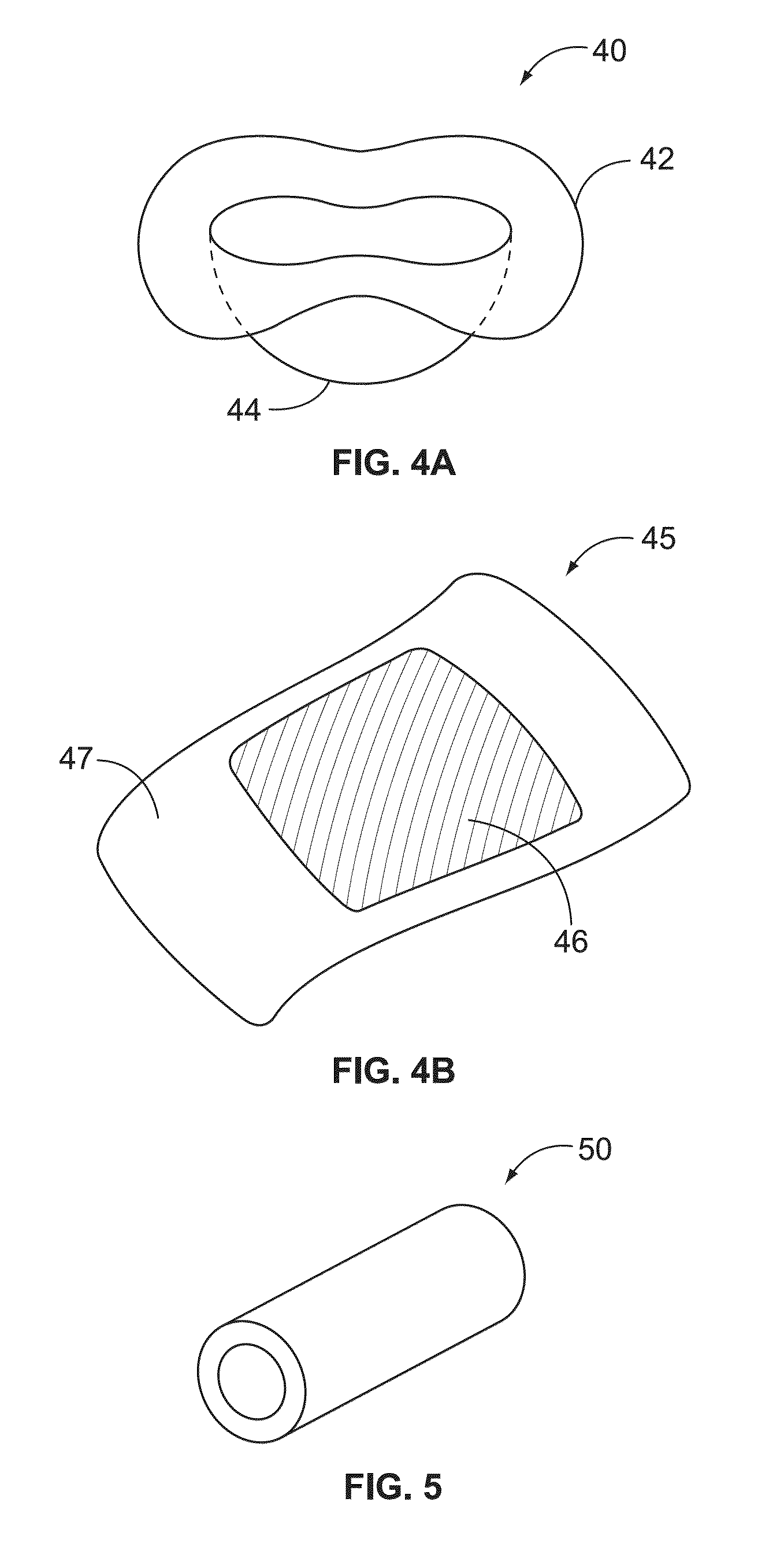
Mucosal tissue dressing and method of use
a technology of mucosal tissue and dressing, which is applied in the direction of bandages, dermatological disorders, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of nausea, post-operative bleeding, and children's general inability to eat solid food, and achieve the effect of reducing or eliminating pain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0119]In this example, dressings were made from films composed of modified cellulose.
[0120]Method—all the raw materials are prepared into solutions in certain concentrations respectively; then the solutions are coated on a PTFE sheet individually or in mixture with single or double layers to make different films.
[0121]1. Raw Materials
[0122]Polypropylene glycol (PPG), Alfa Aesar Cat# 40811, Lot#K28Q011, used as received.
[0123]DI water was prepared on site by DI water generation system.
[0124]The following raw materials are prepared into solutions for use:
[0125]Ethanol, Aldrich Cat# 493546-1 L, Lot# 06862EH
[0126]Ethyl cellulose (EC), Spectrum Cat# ET110, Lot# UT0371
[0127]Methyl cellulose (MC), Aldrich Cat# M0555-100G, Lot# 037K00611
[0128]Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC), Aldrich Cat# H3785-100G, Lot# 086K0115.
[0129]2. Solution Preparation
[0130]Ethyl Cellulose Solution Preparation
[0131]Composition: 20 wt % ethyl cellulose (EC) in USP grade ethanol.
[0132]Example: 37.5 g EC in 150 g ...
example 2
[0210]Film Adhesion Strength Test
[0211]For the evaluation of the adhesion strength of oral wound dressing film samples, An apparatus was set up, which can be used to evaluate the film samples for their adhesion performances. Two types of adhesion strength, i.e., lift-off strength and peel-off strength, can be measured through the use of the apparatus.
[0212]1. Lift-off Adhesion Strength Test Setup and Procedures
[0213]By measuring the vertical detaching force and time, the lift-off adhesion strength of the film adhering to fresh pork steak can be tested. The test apparatus 1600 is set up as shown in FIG. 16. Tests are performed at room temperature, 23 deg. C. The procedures are described below:
[0214]1) Cut a sample film 1610 in a certain size, e.g., 15×15 mm2;
[0215]2) Use superglue to fix a fresh, boneless pork steak 1620 to the bottom of a dish;
[0216]3) Use Scotch tape to fix the string at the center of sample (for single-layer film) or sample protective layer (for double-layer film)...
example 3
[0232]In this example, films were tested for properties desirable in a dressing. The set time, or the time it takes for a hydrogel to form, was measured for each of the adhesion films. Carboxymethyl cellulose performed better than hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, which in turn performed better than methyl cellulose. All adhesion films and the barrier film displayed good flexibility and lack of swelling. All adhesion films and the barrier film remained intact in artificial saliva. In degradation testing, after 5 days the carboxymethyl cellulose film was 70% degraded, the hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose film was 40% degraded, the methyl cellulose film was 25% degraded, and the barrier films was 15% degraded. All degradation values are given by weight.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com