Method and compositions for treatment or prevention of inflammatory conditions
a technology of inflammatory conditions and compositions, applied in drug compositions, biocides, metabolic disorders, etc., can solve problems such as significant detrimental effects in patients, and achieve the effects of inhibiting nf-b-dependent inflammatory response, inhibiting monocyte adhesion and chemotaxis, and inhibiting tnf-
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Vinpocetine Inhibits NF-κB Activation in a Variety of Cell Types
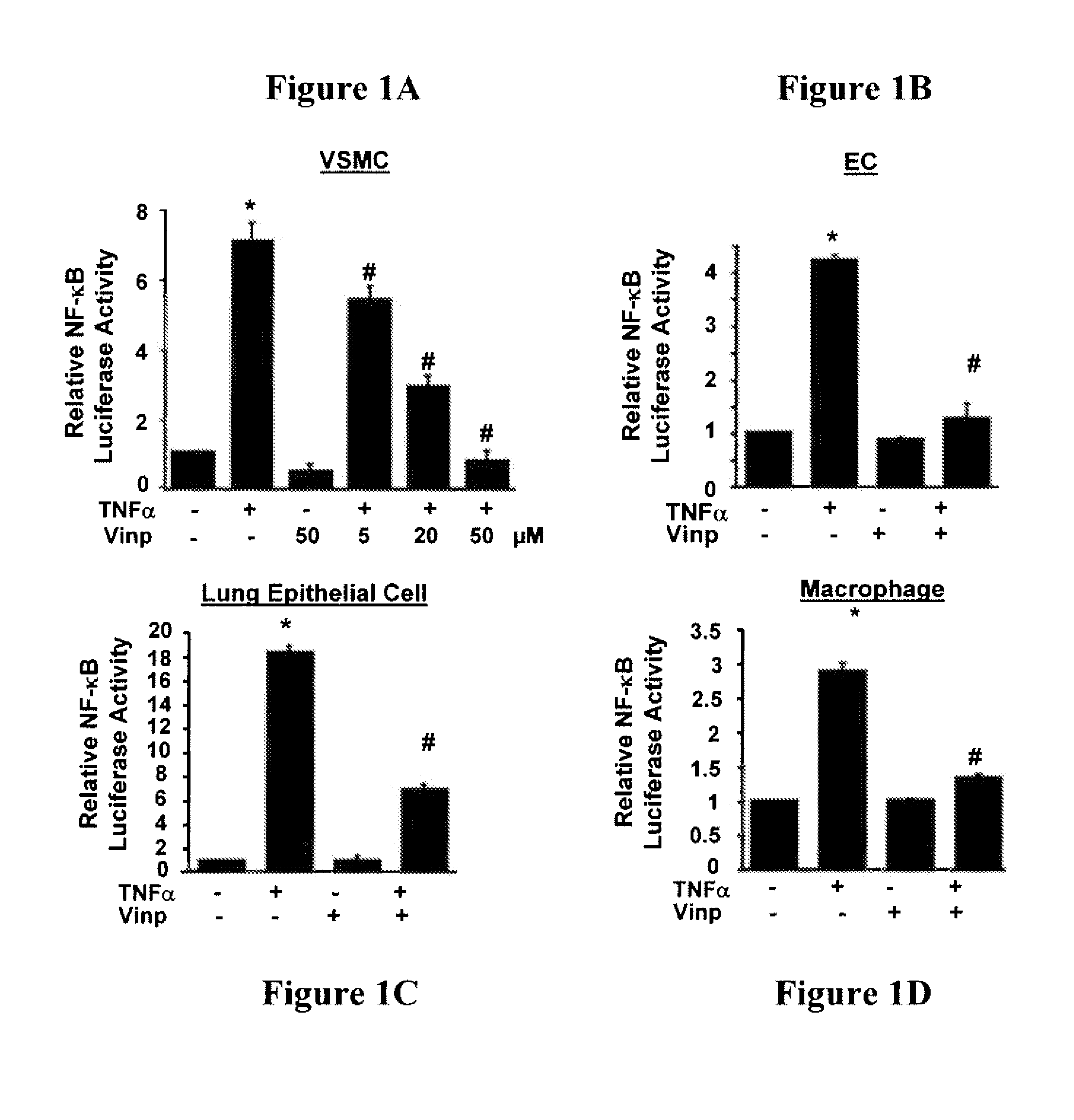
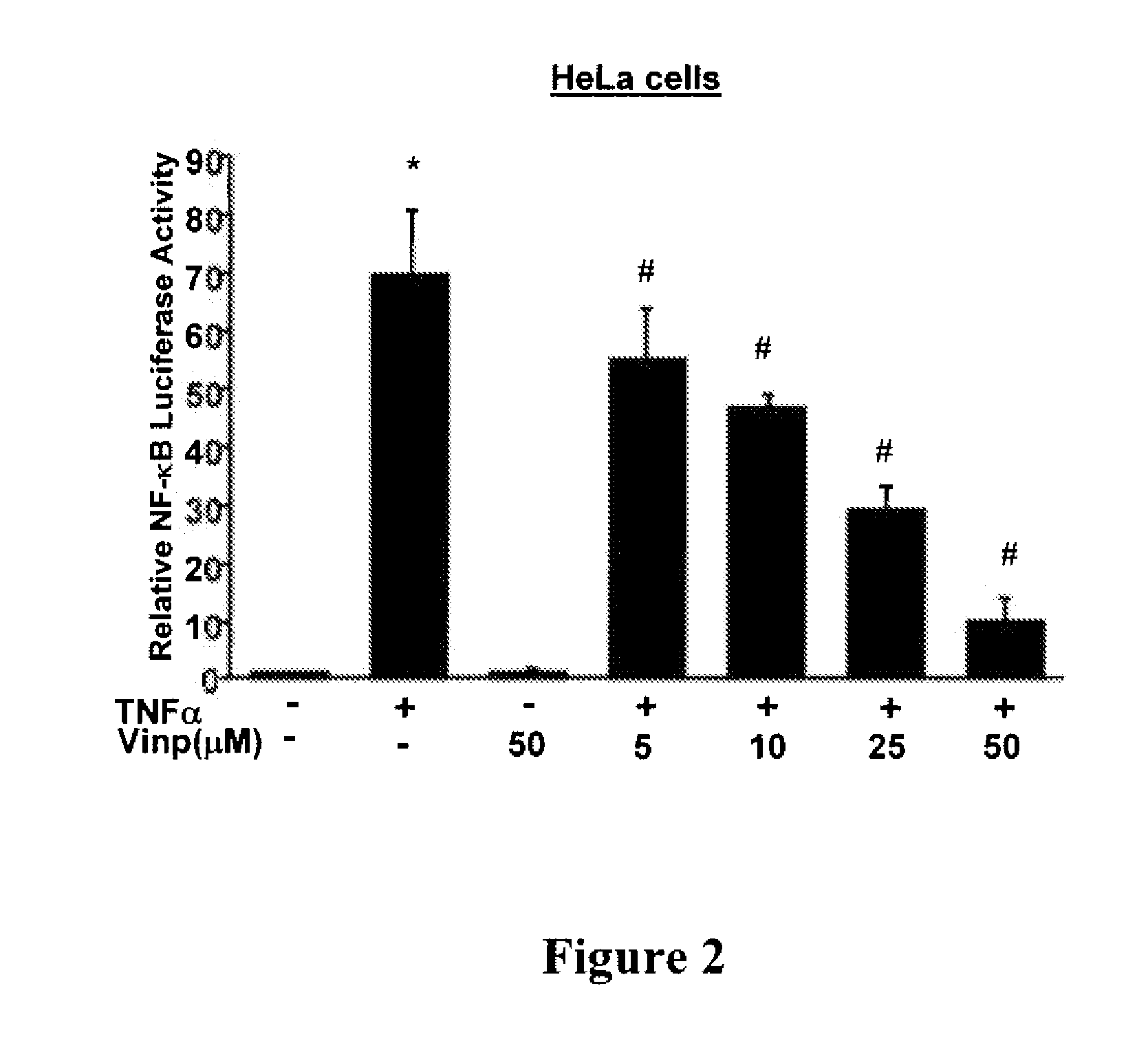
[0086]Because NF-κB plays a critical role in regulating inflammatory response, whether vinpocetine acts as an anti-inflammatory agent by inhibiting NF-κB was investigated. The effect of vinpocetine on NF-κB-dependent promoter activity was first evaluated by using luciferase reporter plasmids in a variety of cell types. As shown in FIG. 1A, vinpocetine potently inhibited TNFα-induced NF-κB-dependent promoter activity in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) in a dose-dependent manner. Similar results were also observed in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs, FIG. 1B), human lung epithelial A549 cells (FIG. 1C), and macrophage cell line (RAW264.7) (FIG. 1D). Similarly to TNFα, IL-1- and LPS-induced NF-κB-dependent promoter activity was also inhibited by vinpocetine. It should be noted that no significant cytotoxic effects on cell morphology and viability were observed at the tested doses.
[0087]This experiment wa...
example 2
Vinpocetine Inhibits TNFα-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Mediators in a Variety of Cell Types
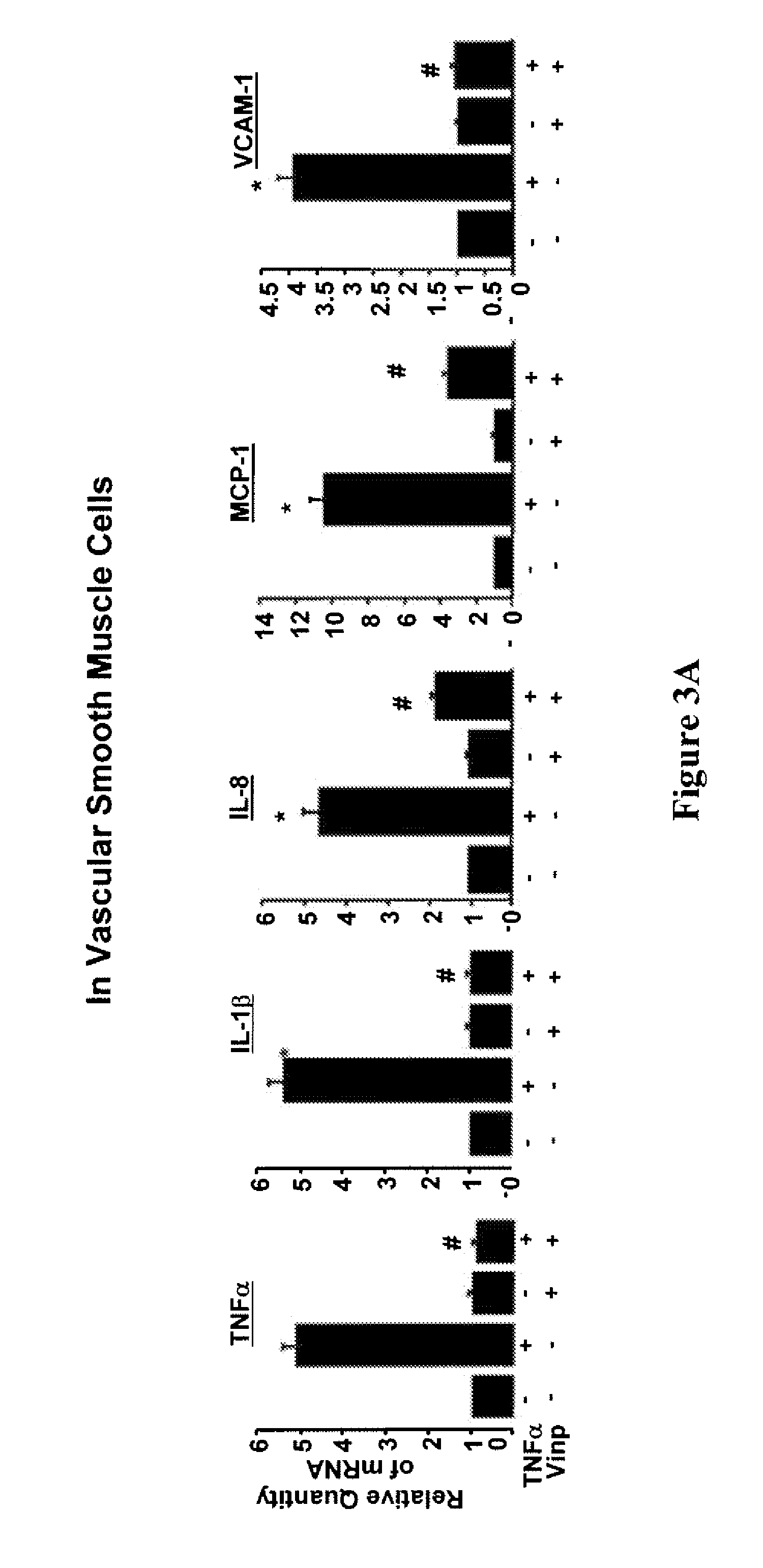
[0088]Next it was determined whether vinpocetine also inhibits TNFα-induced up-regulation of NF-κB-dependent pro-inflammatory mediators including cytokines, chemokines and adhesion molecules at the mRNA level. As shown in FIG. 3A, vinpocetine potently inhibited TNFα-induced expression of TNFα, IL-1β, IL-8, monocot chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) in VSMCs, as assessed by real-time RT-PCR analysis. Similarly, vinpocetine was also found to inhibit TNFα-induced expression of TNFα, IL-1β, IL-8, MCP-1, VCAM-1, and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) in HUVECs (FIG. 3B), expression of TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-8 in A549 cells (FIG. 3C), and expression of TNFα, IL-1β, and macrophage-inflammatory protein 2 (MIP-2) in RAW264.7 (FIG. 3D).
[0089]This experiment was repeated with A549 cells using substantially the same procedures, except with varying doses of a comm...
example 3
Vinpocetine Inhibits Monocyte Adhesion of EC and Chemotactic Activity of VSMC
[0090]To further evaluate the physiological consequences of the inhibitory effect of vinpocetine on induction of pro-inflammatory mediators, monocyte adhesion and chemotactic activities in ECs and VSMCs were measured, respectively. These cells types are known to be dependent on adhesion molecules (such as ICAM-1 and VCAM-1) and chemokines (such as MCP-1) (Kunsch et al., “Oxidative Stress as a Regulator of Gene Expression in the Vasculature,”Circ Res 85:753-66 (1999), which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety). As shown in FIG. 5A-B, monocyte adhesion to HUVECs was markedly inhibited by vinpocetine, as assessed by adhesion assay. Moreover, vinpocetine also inhibited monocyte chemotaxis to VSMCs induced by TNFα in a dose-dependent manner (FIG. 5C), as measured by transwell migration with Boyden chamber.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| body weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com