Method for culturing mammalian cells to improve recombinant protein production
a recombinant protein and cell culture technology, applied in the field of mammalian cell culture, can solve the problems of large-scale use of serum, inability to accurately detect and quantify inability to fully express the protein of interest, so as to improve cell viability, viable cell density, and protein expression. the effect of interes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
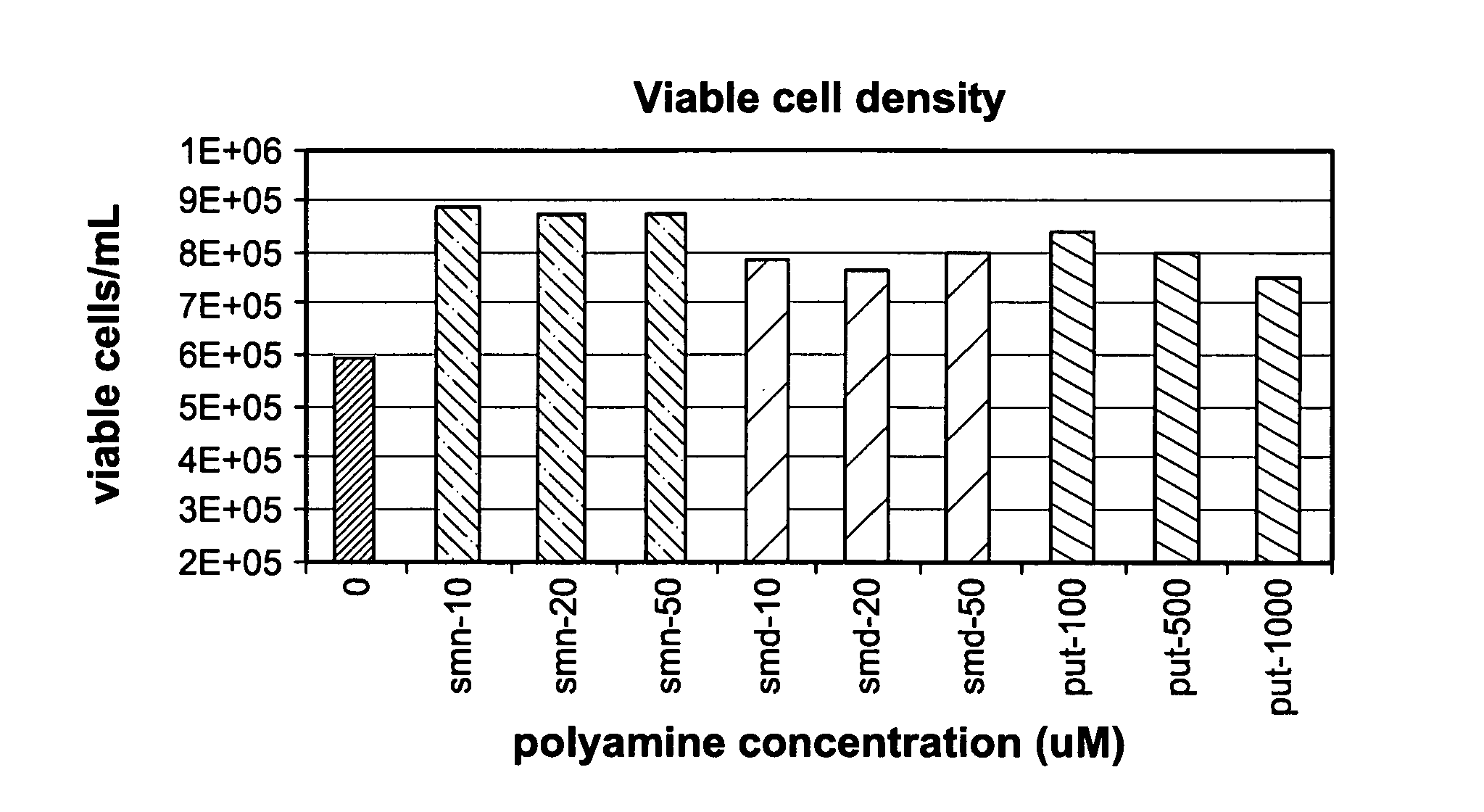
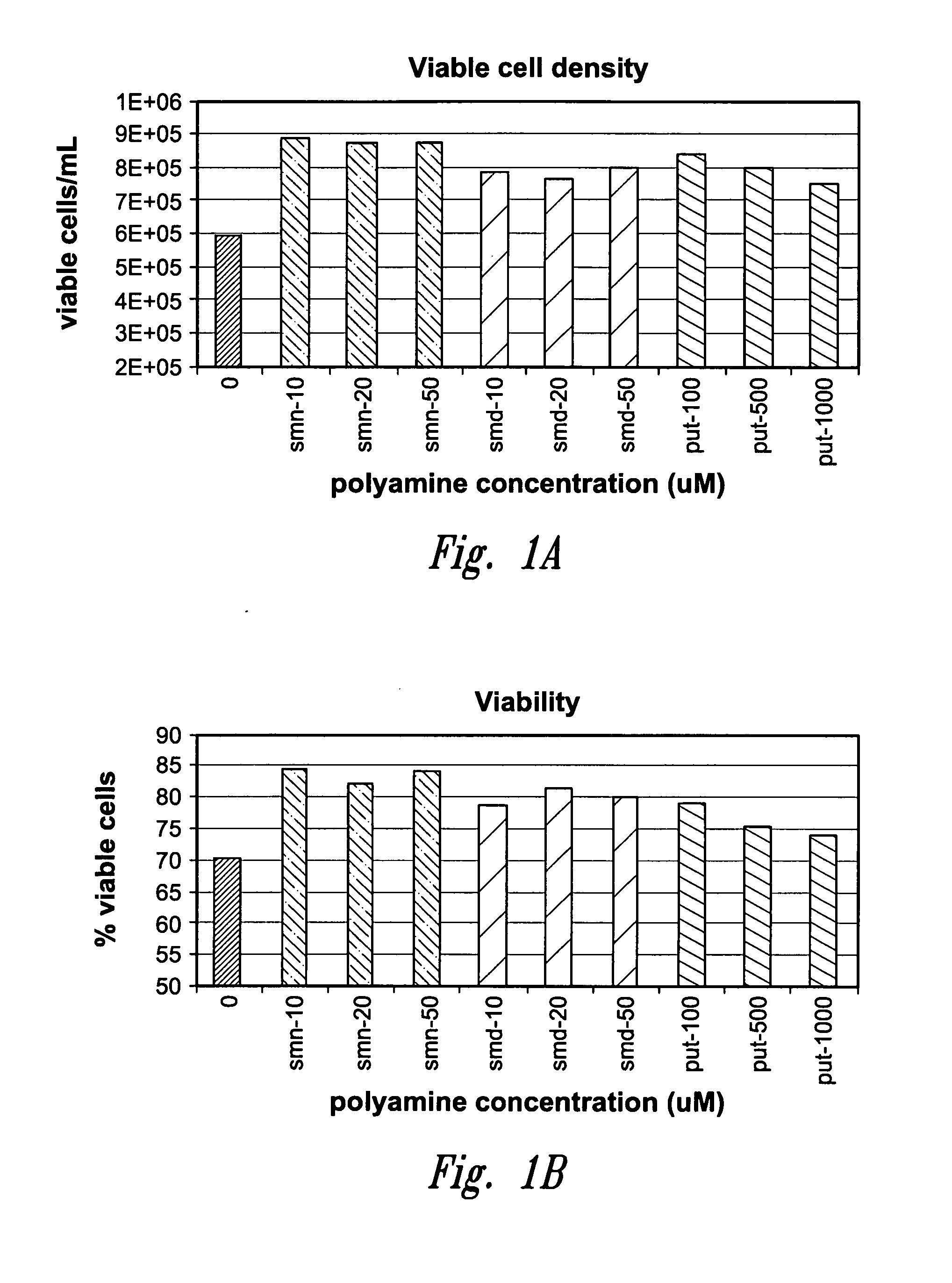
[0059]To test the effect of high concentration polyamine media formulations on cell culture performance a CHO cell line producing a recombinant IgG2 monoclonal antibody was seeded at 2.5×105 cells / ml in serum-free DMEM / F12 (SAFC, Lenexa, Kans.). DMEM / F12 contains 503 nM putrescine as a component of the commercial formulation. The media was supplemented with an additional 100-1000 μM putrescine dihydrochloride (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mo.); 10-50 μM spermidine tetrachdrochloride (Sigma-Aldrich), or 10-50 μM spermine tetrahydrochloride (Sigma-Aldrich). Cells were maintained in suspension culture for three days at 36° C. in 5% CO2. Total cell density and viable cell density were measured using a Guava Easy-Cyte™ flow cytometer and Guava Viacount® Flex reagent (Hayward, Calif.) according to manufacture's instructions.
[0060]Following three days culture in the polyamine-supplemented-DMEM / F12 media, viable cell density and culture viability were measured, see FIGS. 1a and 1b. Mean viabil...
example 2
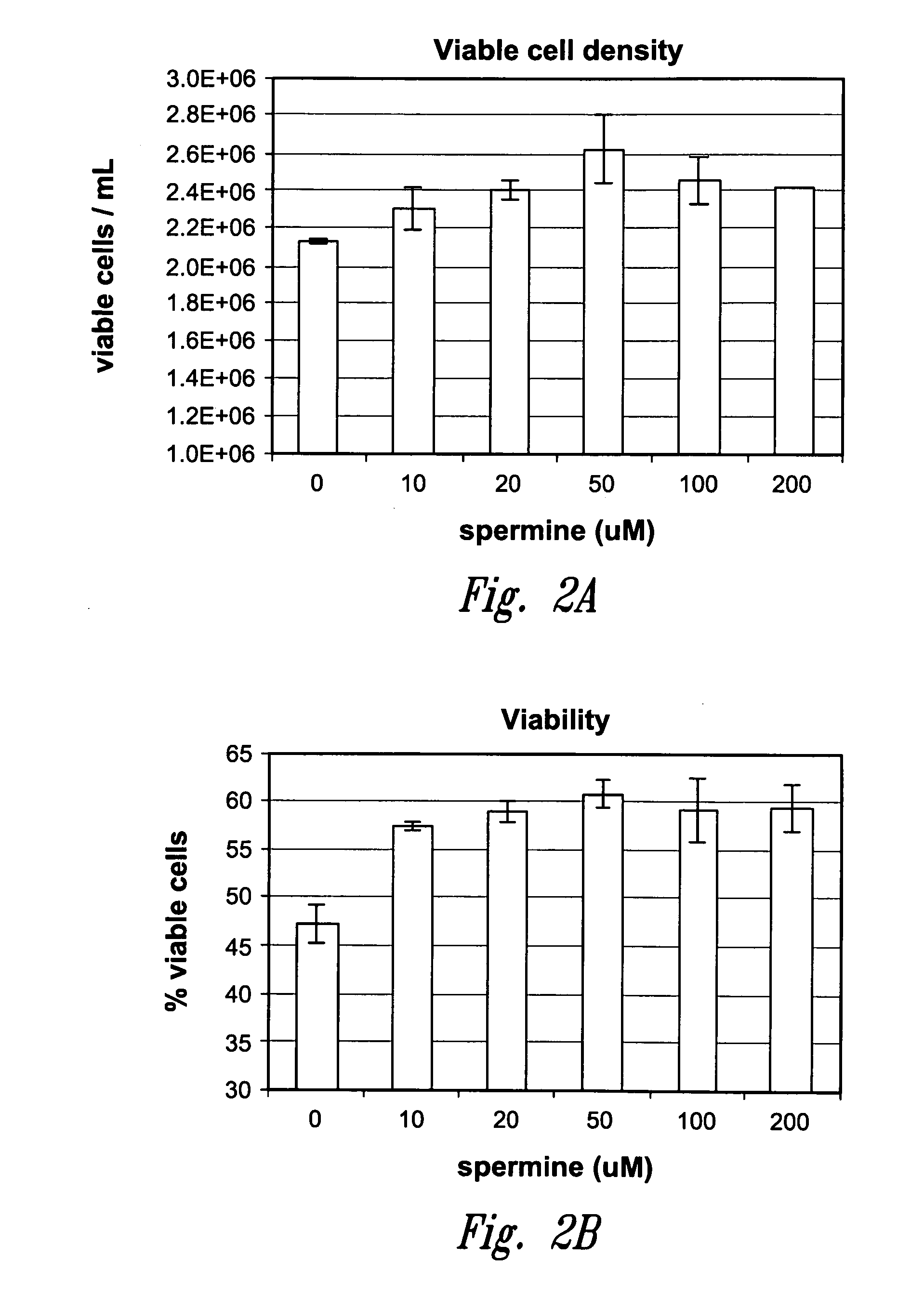
[0061]The antibody-expressing CHO cell line described in Example 1 was also grown in serum-free, soy hydrolysate containing media (VM-Soy, described in US Patent Application No. US2006-0115901), supplemented with spermine. VM-Soy basal media contains 0.98 μM (0.1620 mg / l) putrescine as a component of its formulation. The media was supplemented with spermine tetrahydrochloride (Sigma-Aldrich) to a concentration of 10-200 μM, each concentration was run in duplicate. Cells were seeded at 2.5×105 cells / ml and maintained for six days at 36° C. in 5% CO2. Viable cell density and cell viability were measured as described above. Once again cell viability and viable cell density were higher in those cultures supplemented with spermine compared to the unsupplemented control media (see FIGS. 2a and 2b). Viable cell density increased 8-23% and cell viability increased 22-29% compared to the unsupplemented control. The greatest increases in viable cell density and cell viability, 23% and 29% res...
example 3
[0064]To test the effect of spermine on cells in fed-batch production culture, four different recombinant monoclonal IgG2 antibody-producing CHO cell lines (each expressing a different IgG2 monoclonal antibody) were seeded at 5.0×105 cells / ml in serum-free, hydrolysate-free batch medium. The medium was an enriched formulation of DMEM / F12 medium (ingredients supplied by SAFC, Lenexa, Kans.). The medium contained putrescine at a concentration of 0.014 mM. In this experiment, cells were cultured in medium with or without 10 μM spermine tetrahydrochloride (Sigma-Aldrich). Cells were maintained in suspension culture for 11 days at 36° C., 5% CO2. Cultures were fed an enriched feed medium on the fourth, seventh, and ninth days of culture. The feed volume was equal to nine percent of the initial batch culture volume. The feed medium contained putrescine but not spermine and delivered 0.0025 mM putrescine as the final concentration in the cultures as a result of each feed. Glucose was also ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com