Nano-encapsulated triggered-release viscosity breakers
a technology of triggered release and viscosity breakers, which is applied in the direction of enzyme stabilisation, sealing/packing, and wellbore/well accessories, etc., can solve the problems of subterranean formation closing and crushing beads, and achieves environmental and economic favorable effects, simple operation, and huge flexibility in material composition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
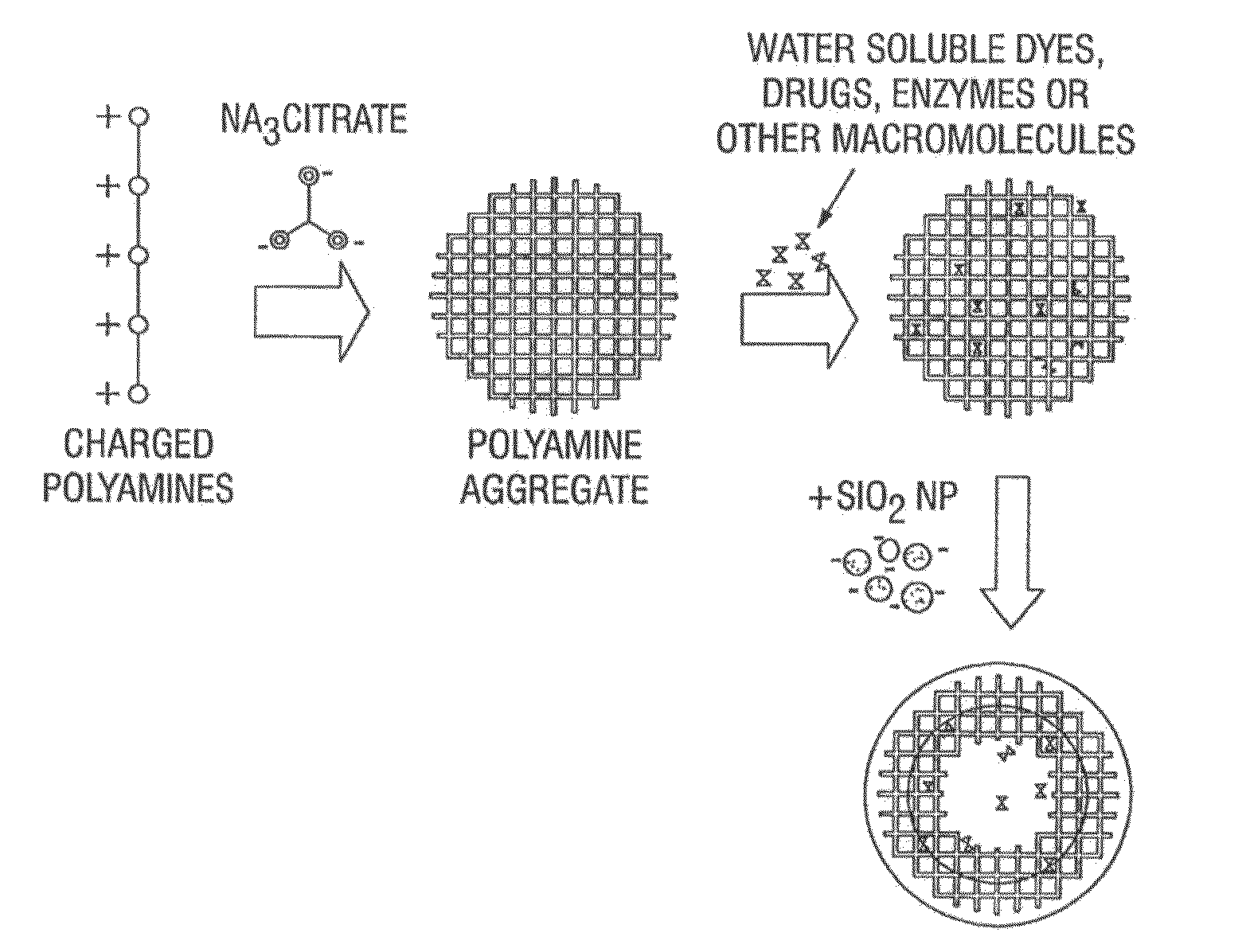
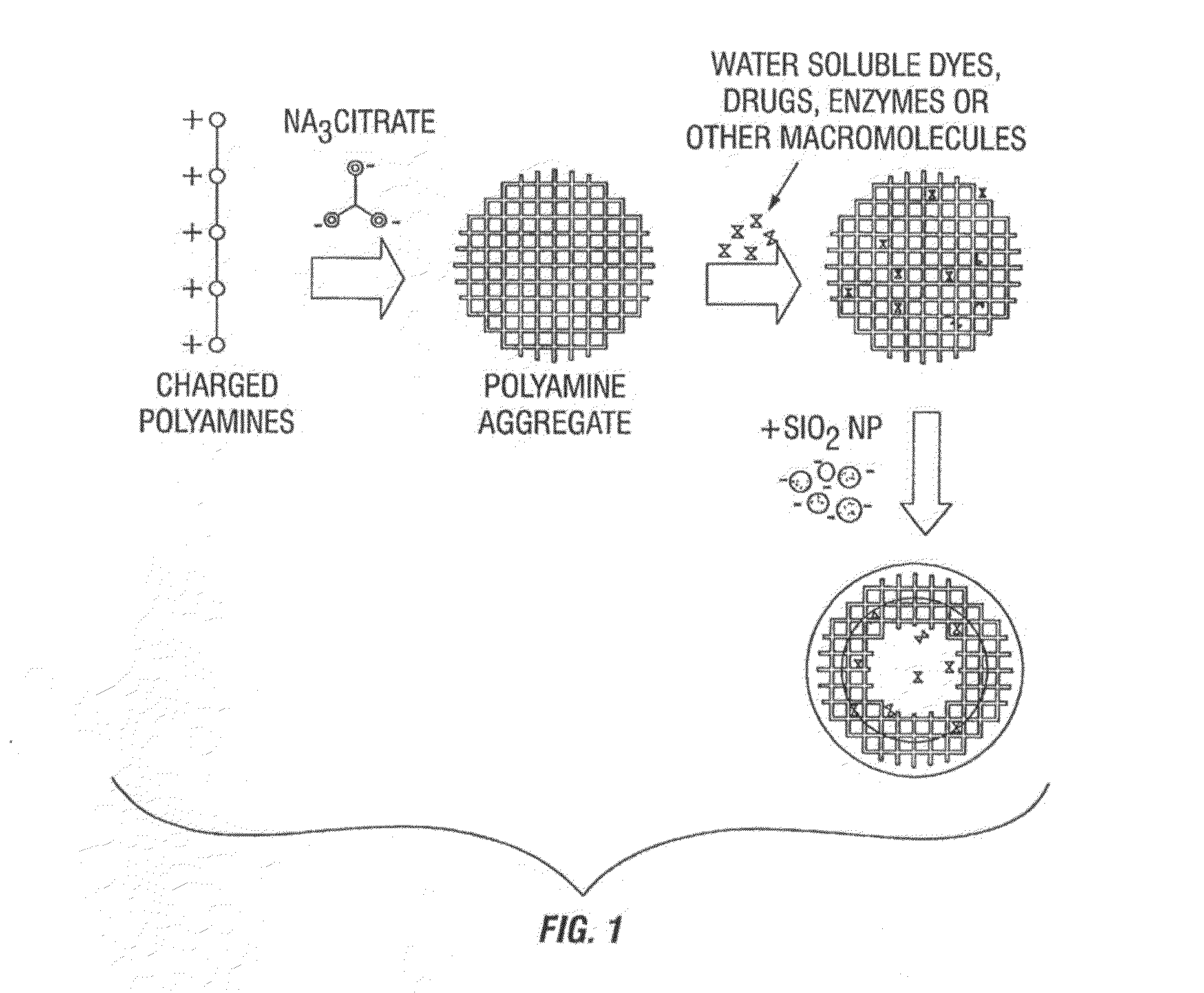
[0029]According to preferred embodiments, one method for preparing nanoparticle assembled microcapsules (NACs) involves poly-L-lysine (PLL) as the polyamine, citrate (cit) as the multivalent anion and silica nanoparticles. β-Mannanase (Megazyme) is used as the enzymatic breaker. For the enzyme encapsulation in NACs, 25 μL of the enzyme solution (9 U / ml β-Mannanase) was mixed with 21 μL of PLL and aged for 25 minutes. The resulting solution was added to a previously aged (25 min) PLL / cit suspension. The suspension was then aged for another 5 minutes. To this, a colloidal sol of silica nanoparticles was added and formed a thick shell surrounding the aggregates.
[0030]Optical brightfield and confocal images of silica microcapsules encapsulating β-Mannanase enzyme show circular microcapsules. The composition comprises: 21 μL PLL-FITC (2 mg / ml, 68.6 kD)+125 μL Na3Cit (5.36 mM)+50 μL β-Mannanase enzyme (9 units / ml)+125 μL SiO2 NP (20 wt %).
[0031]The encapsulation of the enzyme within the r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Solution structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Magnetism | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com