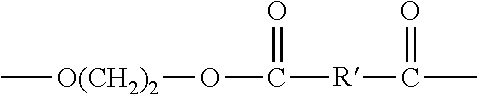
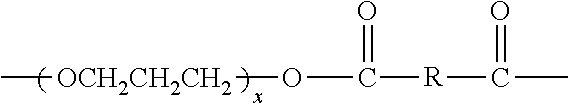Methods for preparing polyether ester elastomer composition
a technology of polyether ester and composition, which is applied in the field of thermoplastic polyether ester elastomers, can solve the problems of unsuitable injection molding applications for unmodified polyether ester, difficult pelletization or flaking of polymer, and limited application prospects, etc., to achieve rapid crystallization, effective utilization of polymer, and rapid rigidity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0130]This example illustrates the preparation of a polyether ester with the same stoichiometry as that prepared in Comparative Example 1, but in this case including trisodium phosphate nucleating agent.
[0131]A 25 gallon autoclave was charged with 33.2 lbs of dimethyl terephthalate, 30 lbs of PO3G (Mn of 2440), 14 lbs of ethylene glycol, 2 lbs of 1,4-butanediol, 80 g of ETHANOX® 330 antioxidant, 12 g of TYZOR® TPT as catalyst, and 136 g of trisodium phosphate as nucleating agent. The temperature was raised to 215° C., and methanol generated was removed with a nitrogen flush by distillation as a liquid condensate. The temperature was held at 210° C. for about 1.5 hours until no more methanol evolved indicating the end of the trans-esterification reaction.
[0132]The temperature was then raised to 250° C. and held at that temperature at a pressure of 0.3 mm Hg for 2.5 hours. The polymer was extruded into ribbons and converted into flakes.
example 2
[0136]This example illustrates the preparation of a polyether ester with the same stoichiometry as that prepared in Comparative Example 2 but including trisodium phosphate nucleating agent.
[0137]A 250 ml three-necked flask was charged with 42.1 g of dimethyl terephthalate, 29.3 g of PO3G (Mn of 1770), 20 g of ethylene glycol, 0.15 g of IRGANOX® 1098 anti-oxidant, 25 mg of TYZOR® TPT catalyst, and 0.36 g of trisodium phosphate (2100 ppm of sodium based on the final polymer) as nucleating agent. The temperature was raised to 215° C. under nitrogen, and the methanol generated was removed as a liquid condensate by distillation. The temperature was held at 210° C. for about 1.5 hours until no more methanol evolved, indicating the end of transesterification reaction.
[0138]The temperature was raised to 250° C. and held at that temperature at a pressure of 0.2 mm Hg for 2 hours. Then the reaction was stopped by removal of the heat and vacuum, and the polymer was collected.
example 3
[0139]A polyether ester was prepared as described in Example 2 except that the amount of trisodium phosphate used was 0.26 g (corresponding to 1700 ppm of sodium based on the final polymer).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com