Proteasome inhibitors and uses thereof
a technology of proteasomes and inhibitors, applied in the field of proteasome inhibitors, can solve problems such as failure to predict the inhibitory activity of live cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0217]Reference is now made to the following examples, which together with the above descriptions illustrate some embodiments of the invention in a non limiting fashion.
[0218]Generally, the nomenclature used herein and the laboratory procedures utilized in the present invention include molecular, biochemical, microbiological and recombinant DNA techniques. Such techniques are thoroughly explained in the literature. See, for example, “Molecular Cloning: A laboratory Manual” Sambrook et al., (1989); “Current Protocols in Molecular Biology” Volumes I-III Ausubel, R. M., ed. (1994); Ausubel et al., “Current Protocols in Molecular Biology”, John Wiley and Sons, Baltimore, Md. (1989); Perbal, “A Practical Guide to Molecular Cloning”, John Wiley & Sons, New York (1988); Watson et al., “Recombinant DNA”, Scientific American Books, New York; Birren et al. (eds) “Genome Analysis: A Laboratory Manual Series”, Vols. 1-4, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York (1998); methodologies as set...
example i
Discovery of Novel Proteasome Inhibitors Using a High-Content Cell-Based Screening System
[0219]Materials and Methods
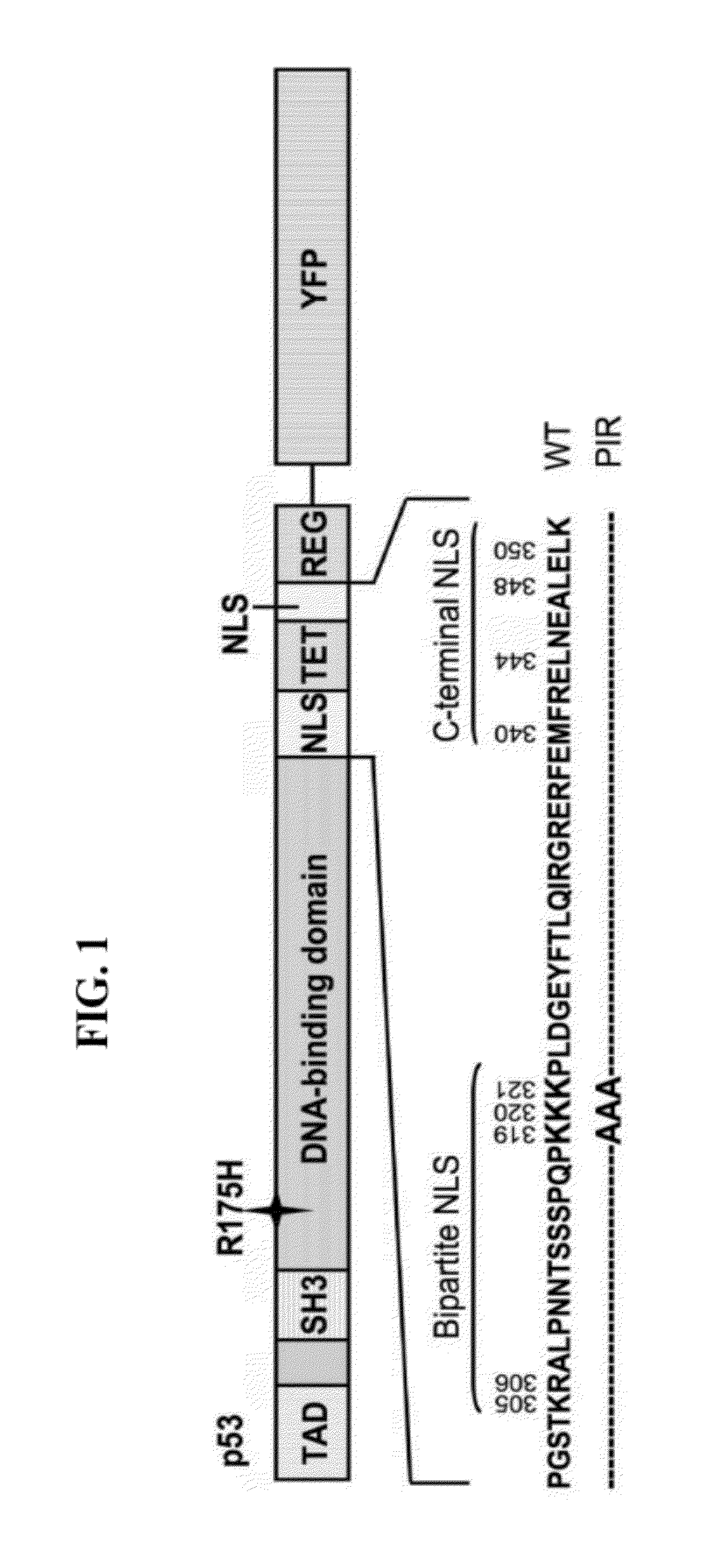
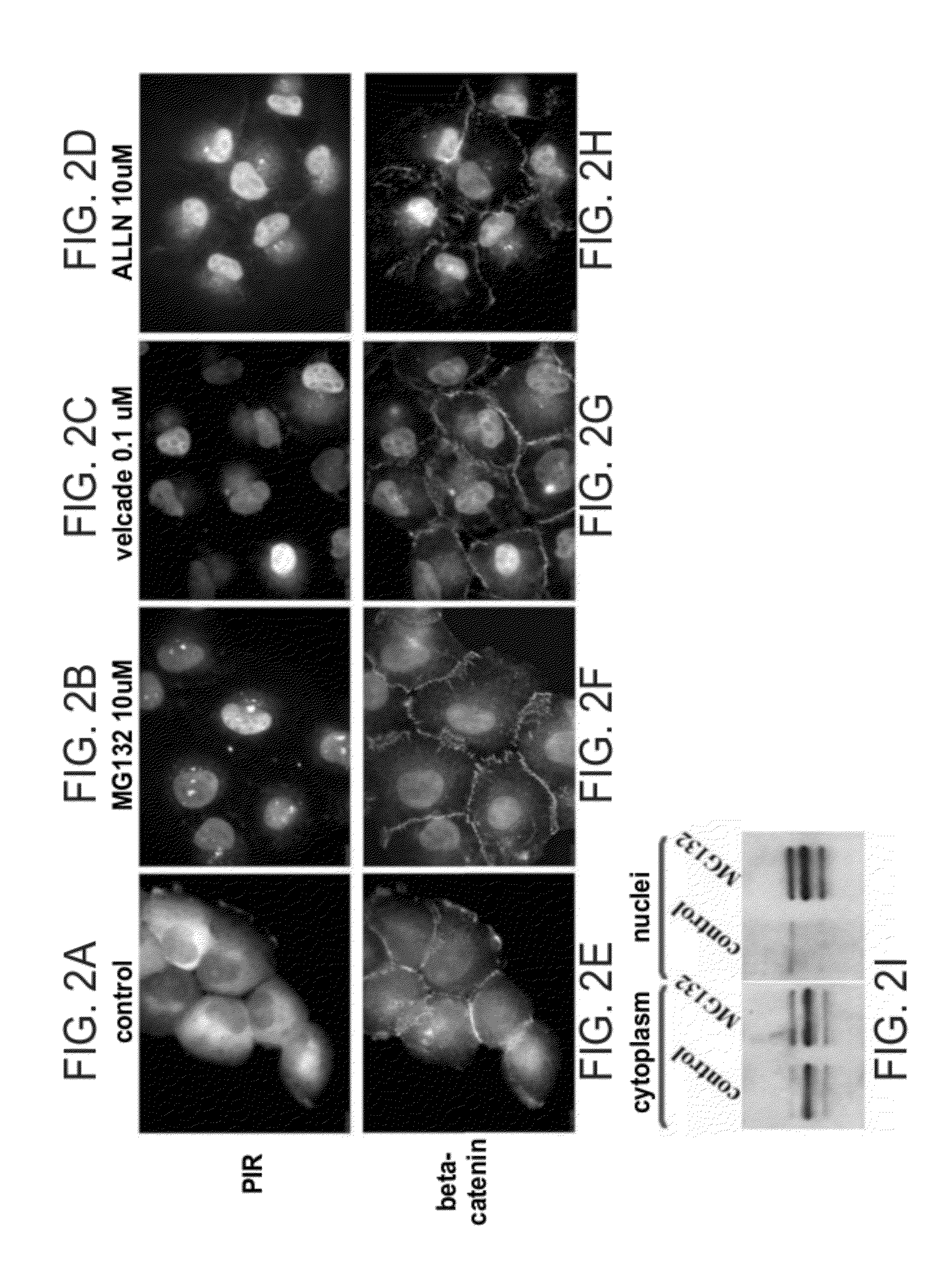
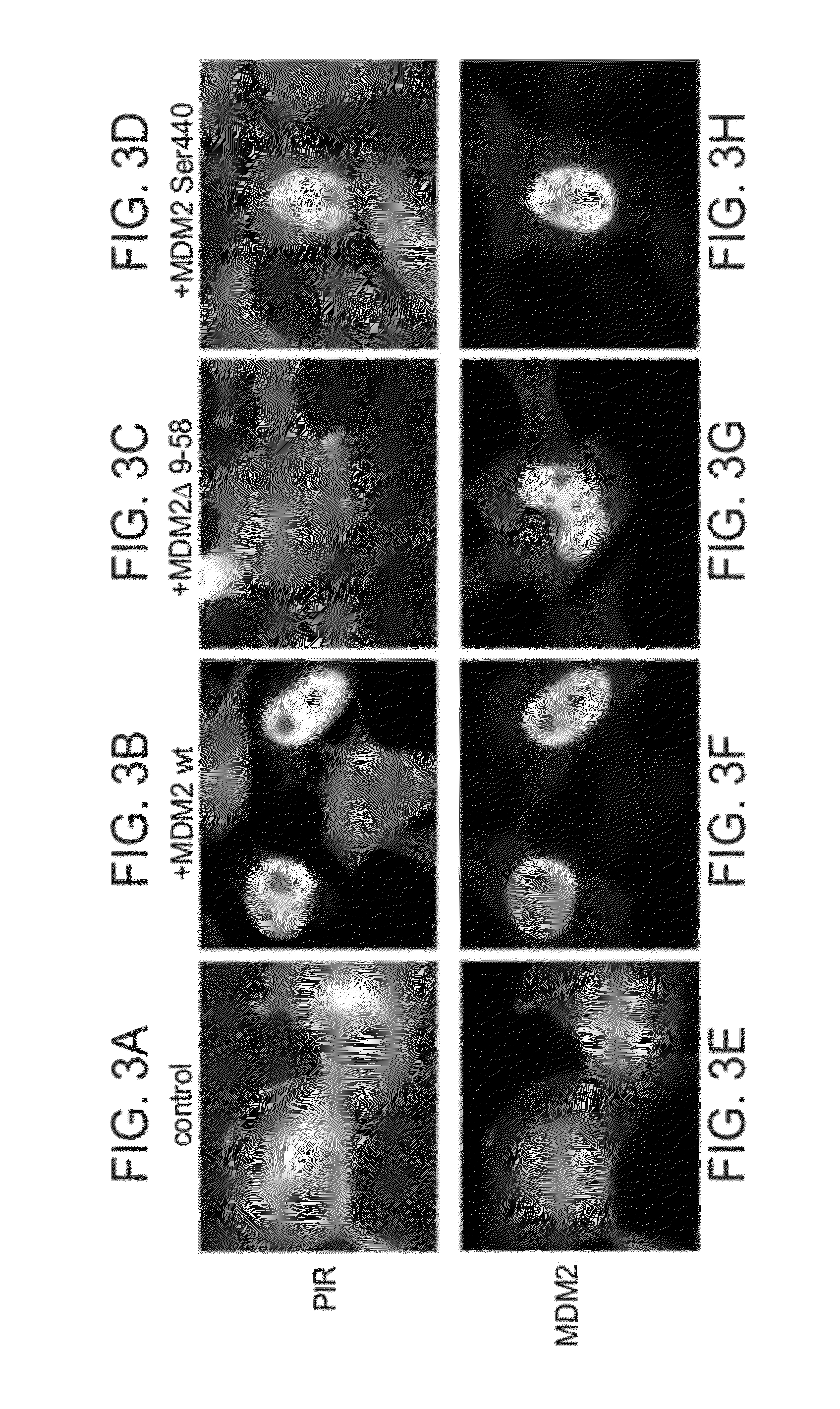
[0220]DNA constructs, generation of a stable reporter cell line and transient transfection: To construct a YFP-tagged Proteasome Inhibitor Reporter (PIR) protein, cDNA encoding a full-length human p53 R175H mutant was amplified by PCR from a cDNA clone, and three consecutive lysine residues in the bipartite Nuclear Localization Signal (NLS) were replaced with alanines by PCR-based, site-directed mutagenesis [Higuchi R, et al., (1988) Nucleic Acids Res 16: 7351-7367; Ho SN, et al (1989) Gene 77: 51-59]. The DNA fragment was cloned into the BglII and NotI sites of pLPCX retroviral vector (Clontech) in-frame to the N-terminus of the yellow fluorescent protein (YFP), using the NotI / ClaI restriction sites. The PIR protein was expressed in an H1299 non-small cell lung carcinoma cell line, following retroviral infection, and the cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium contain...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleic acid sequence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com