Inducible System for Highly Efficient Production of Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus (rAAV) Vectors
a production system and adenovirus technology, applied in the field of inducible system for highly efficient production of raav vectors, can solve the problems of high production cost of clinical grade gene therapy vectors, and the original protocol had not been widely adopted
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
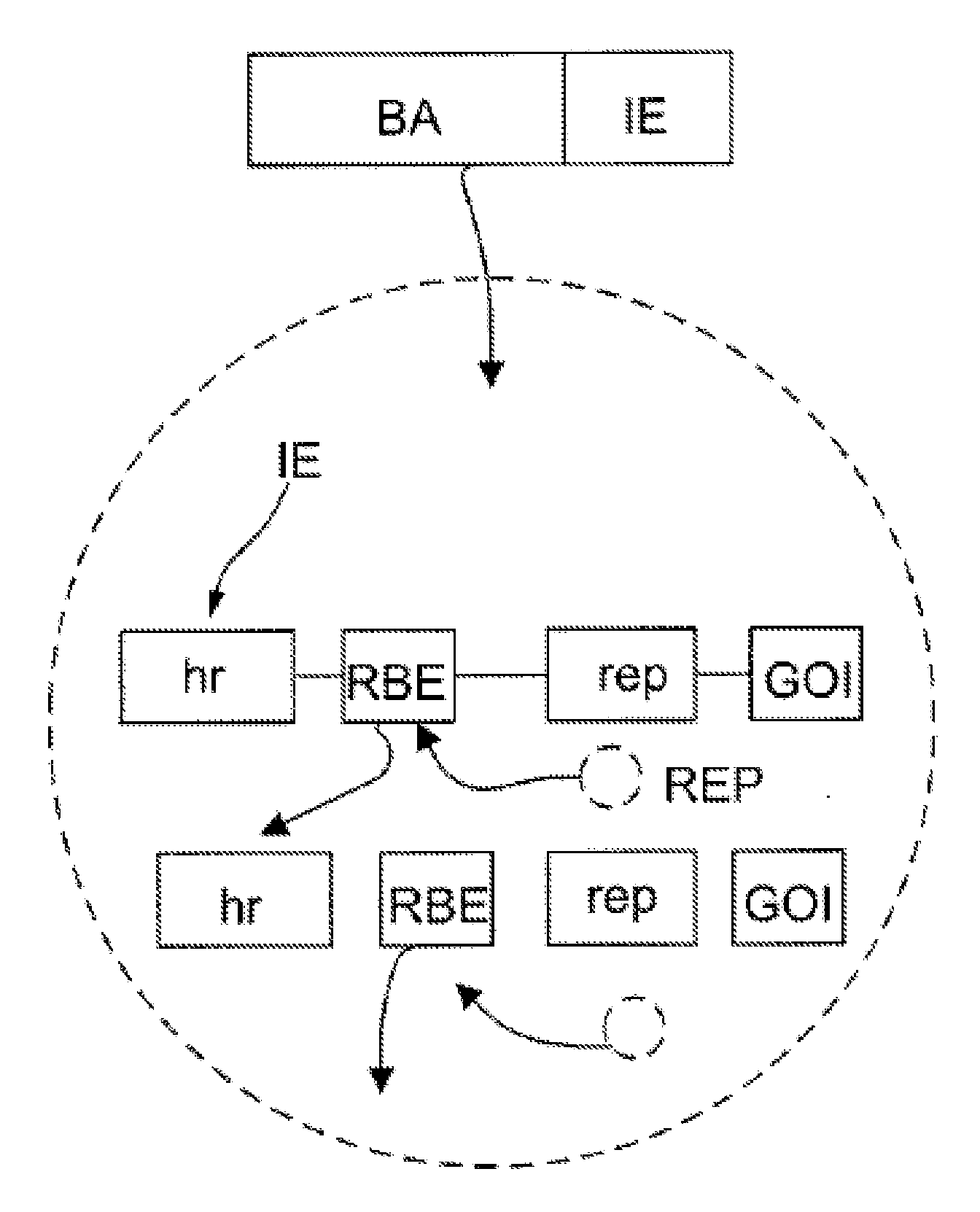
[0040]Cloning of AcMNPV (Accession No. NC—001623) homologous region 2 (hr2). In order to simplify this system embodiment and reduce the number of components, the inventors sought to derive Sf9-based stable lines expressing AAV rep and cap genes. The challenge of expressing AAV helper genes in the heterologous environment of an insect cell necessitates the use of baculovirus-derived promoters (e.g. polh) which are fully functional only in the context of the whole genome, i.e. next to other viral regulatory elements. Simple cassettes with rep and cap ORFs placed downstream of baculovirus promoters and integrated into the host chromosome, will not achieve similar expression levels as compared to the same modules in the context of a BEVs. Therefore, the inventors set forward to develop a novel modular cassette capable of highest levels of expression when remotely separated from BEV. An additional challenge in constructing such cassettes is that in the wt AAV genome, genes encoded by col...
example 2
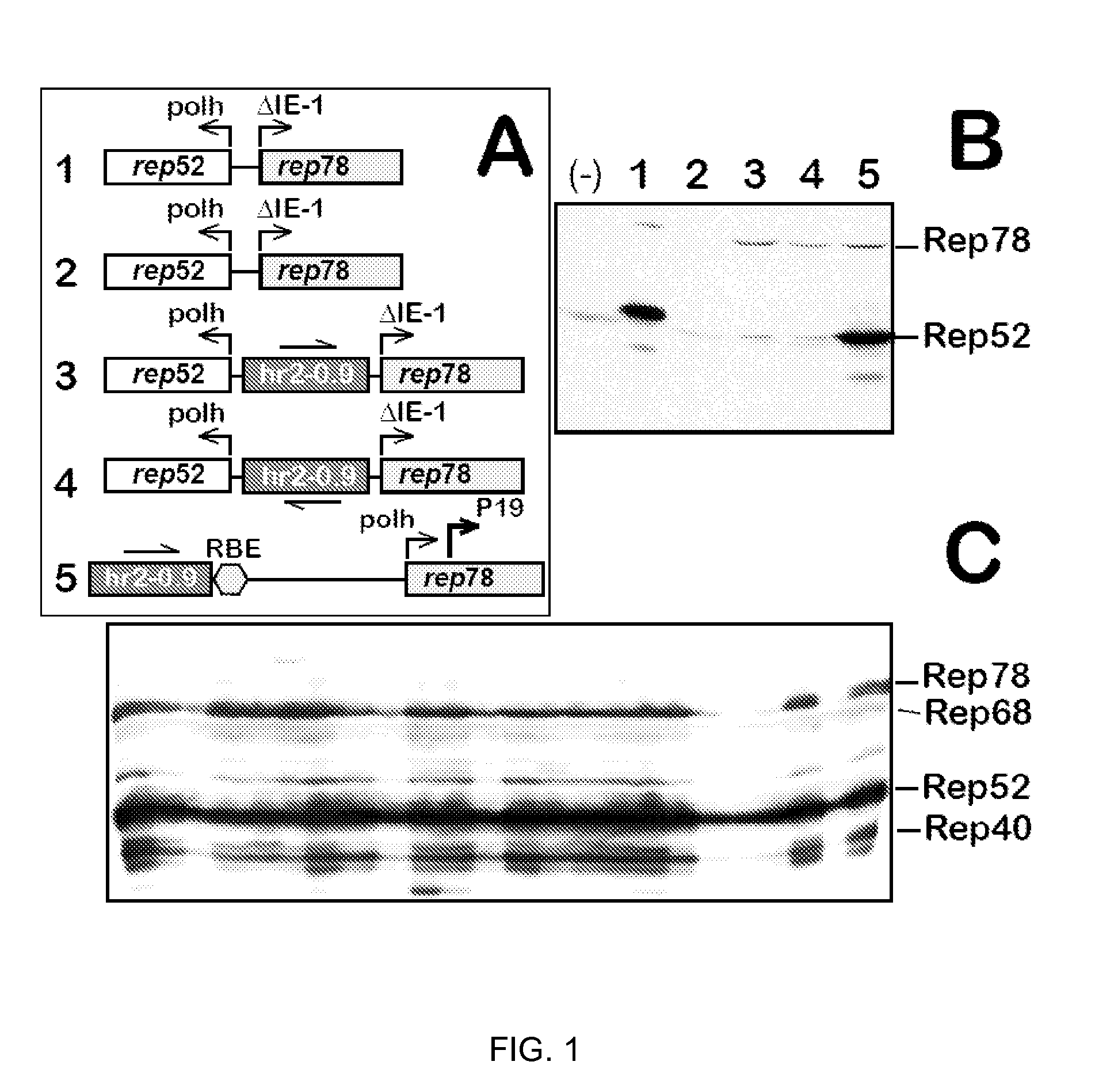
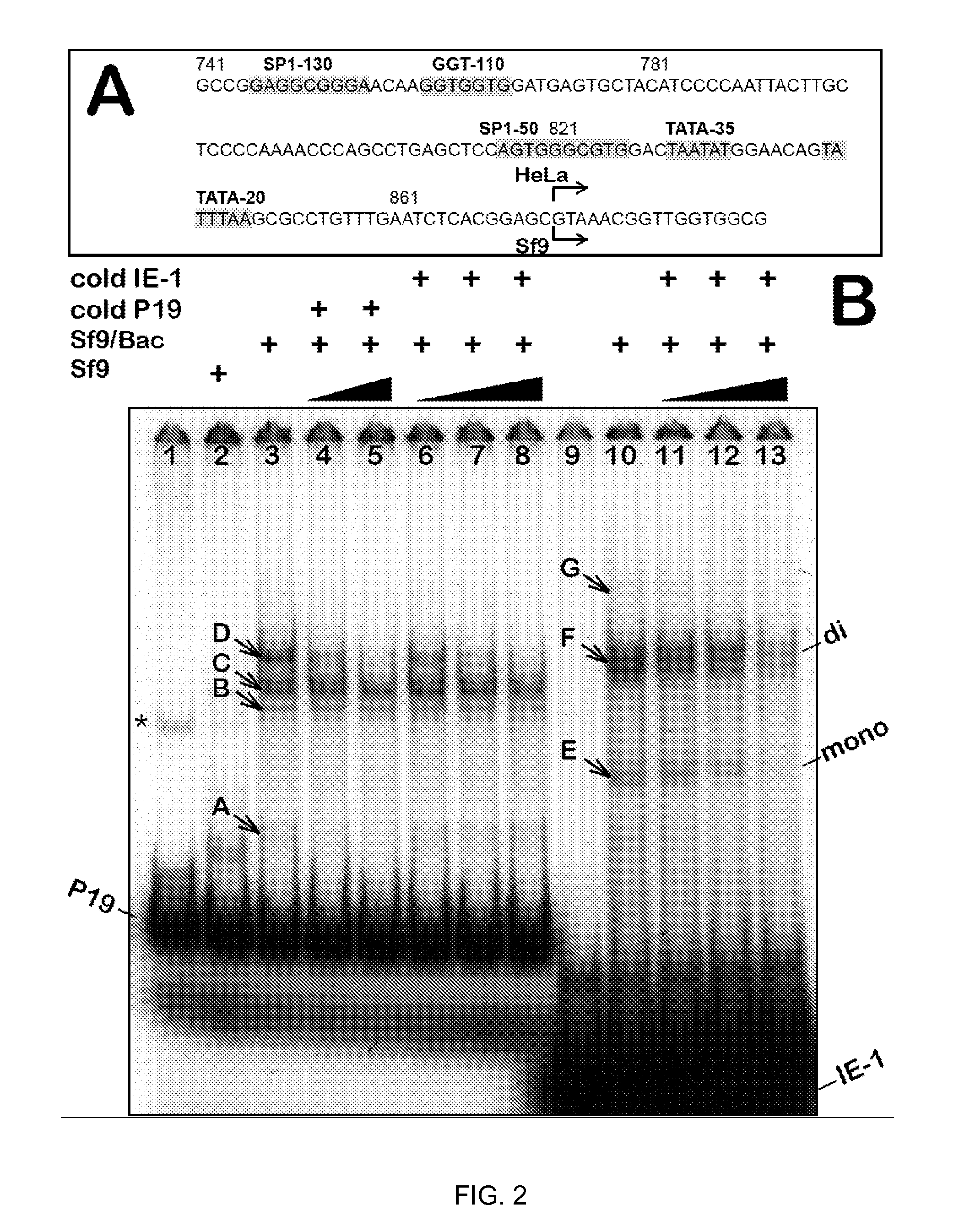
[0043]Rep-expressing cassettes. To test whether hr2-0.9 could enhance the transcription from wt AAV2 P19 promoter, a series of plasmid vectors (FIG. 1A) were constructed and the expression of rep52 and rep78 genes were tested in a transient transfection assay in insect Sf9 cells. As reported earlier (2), infection Sf9 cells with Bac-Rep harboring head-to-head rep78 and rep52 genes resulted in the expression of both Rep52 and Rep78 proteins (FIG. 1B, lane 1). The same cassette in the context of a transfer plasmid pFBD-LSR (2) did not produce any Rep proteins (FIG. 2B, lane 2) suggesting a requirement for an enhancer apparently present in a context of Bac-Rep BEV vector carrying Rep-expression cassettes. Insertion of hr2-0.9 between head-to-head polh and ΔIE-1 promoters created a cassette reminiscent of a transcription control element described earlier (8), with the exception of a hr2-0.9 substituted for hr5. As expected, in the presence of BEV-derived IE-1 transregulator (supplied by...
example 3
[0044]Rep-expressing stable cell lines. For the purpose of rAAV production, stable mammalian cell lines expressing AAV Rep78 / 52 are notoriously difficult to generate due to the genotoxic effect of the rep component (11). To make a stable line, a complete shutoff of the integrated rep ORF is therefore required. Until now, no similar stable insect cell-based lines expressing AAV rep / cap functions have been reported. Having designed the vector with hr2-0.9-mediated robust expression of both Rep78 and Rep52 in Sf9 cells, the inventors wondered whether the Rep-expression cassette could be utilized to derive stable cell lines.
[0045]The plasmid pIR-rep78-hr2-RBE (#5 in FIG. 1A), in addition to Rep expression cassette was constructed to harbor OpIE1 viral promoter-driven bsd (blasticidin S deaminase) gene conferring resistance to blasticidin S. This plasmid had been used to transfect Sf9 cells and select for BS-resistance to derive 24 individual stable cell lines. Remarkably, all analyzed B...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com