Methods and compositions for selectively removing potassium ion from the gastrointestinal tract of a mammal
a technology of gastrointestinal tract and composition, applied in drug compositions, synthetic polymeric active ingredients, metabolic disorders, etc., can solve the problems of high risk of hyperkalemia in certain groups, high risk of patients at the extreme of life, and limited current treatment options for hyperkalemia
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
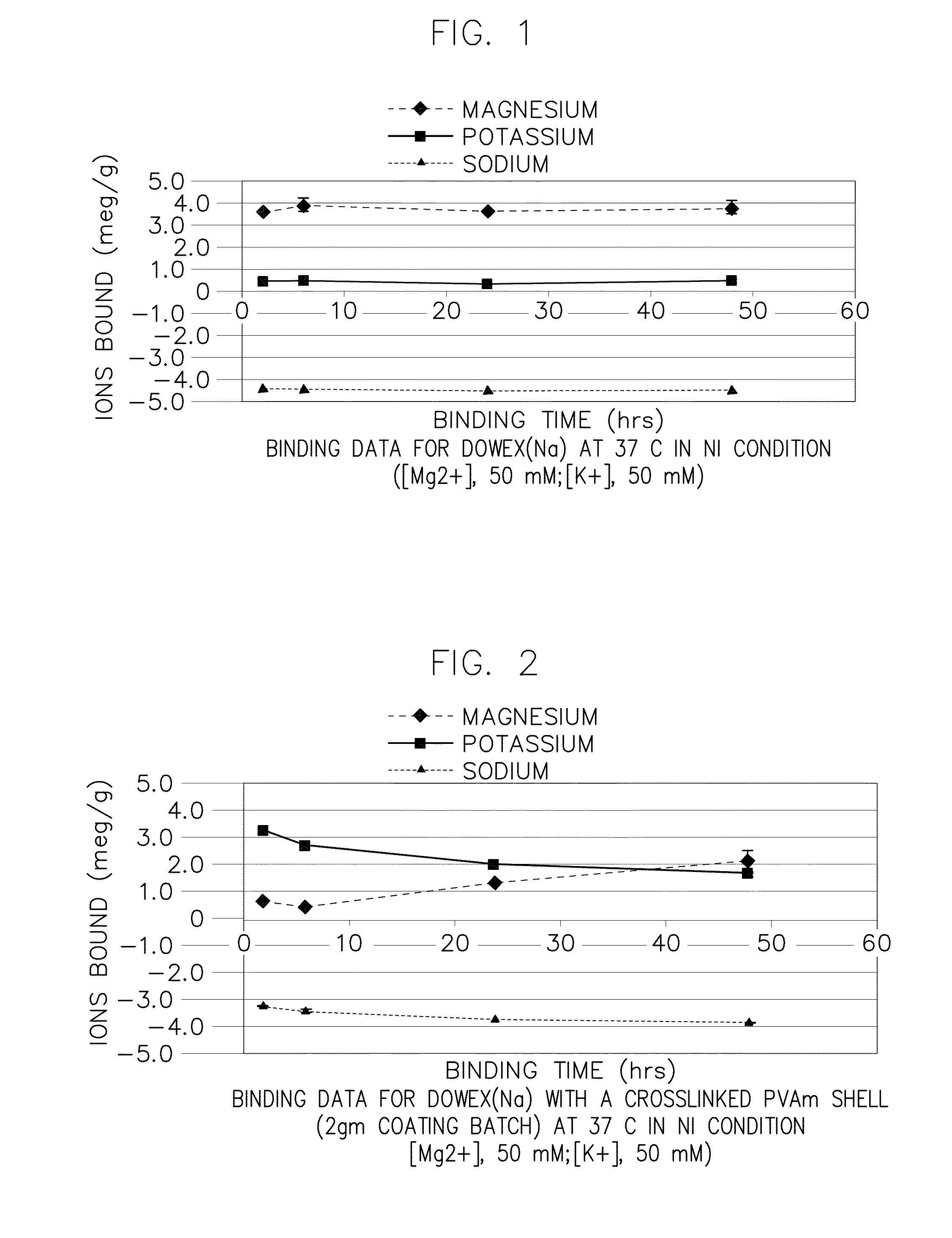
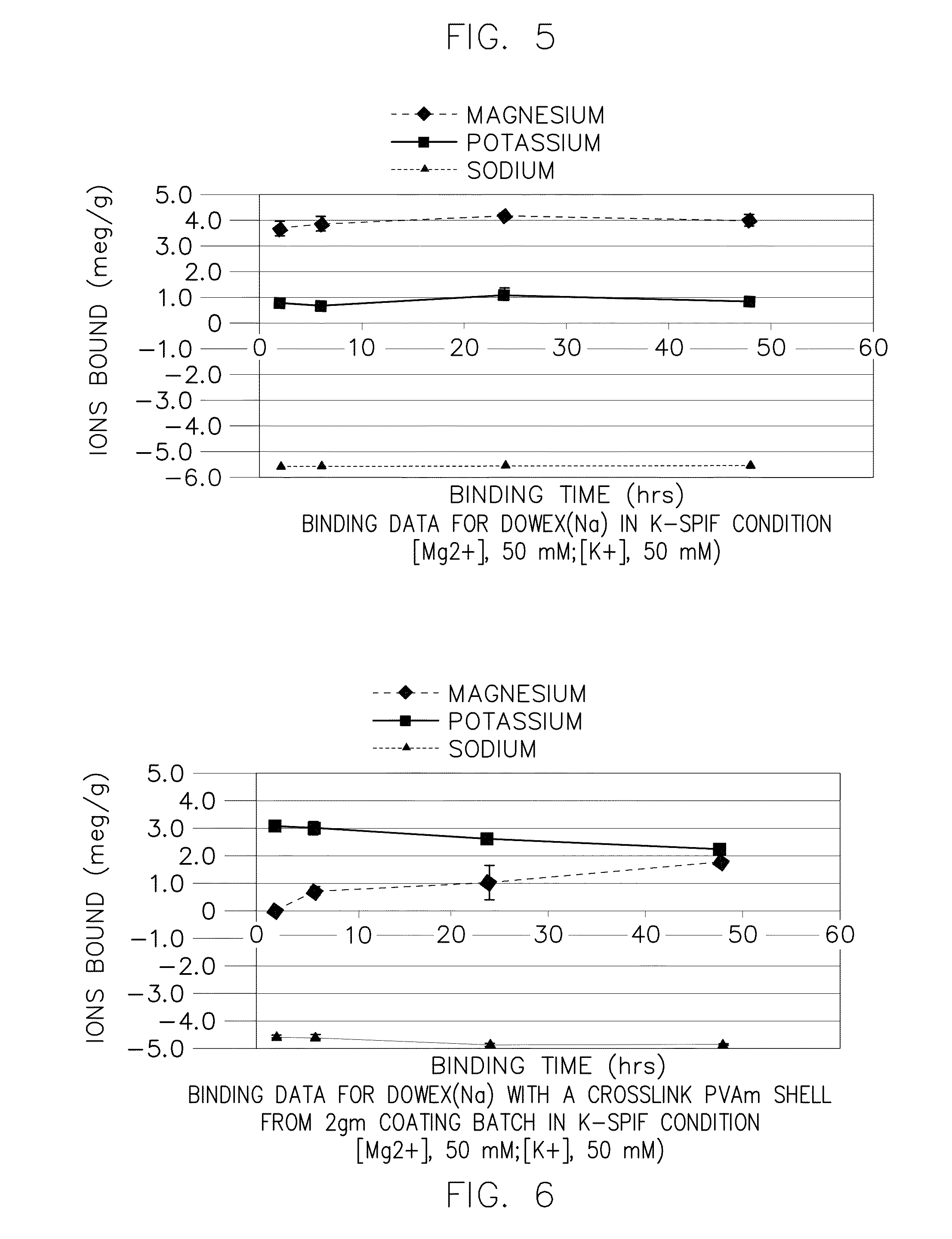
Preparation of Core-Shell Particles Having Crosslinked Polyvinylamine Shell (2 gm / 100 ml Scale) (Reference ID #253)
[0314]This example illustrates the preparation of a core-shell particle comprising a core component comprising polystyrenesulfonate and a shell component comprising a crosslinked polyvinylamine, using a multiphase in situ crosslinking process with 2 gm core polymer and epichlorhydrin crosslinker in a 100 ml scale reactor.
[0315]Shell Polymer
[0316]Polyvinylamine (Mw, 340,000; >90% hydrolyzed) was provided by BASF under trade name, lupamin9095 (20˜22 wt % in aqueous solution). As described herein, more than 90% of the polyvinylformamide was hydrolyzed (or deprotected) to produce polyvinylamine, but the balance of the polymer contained formamide groups, thus, a copolymer of polyvinylamine and polyvinylamide was used. In each example where the polymer was described as 90% hydrolyzed, this copolymer was generally the starting material. The solution was diluted with nanopure w...
example 2
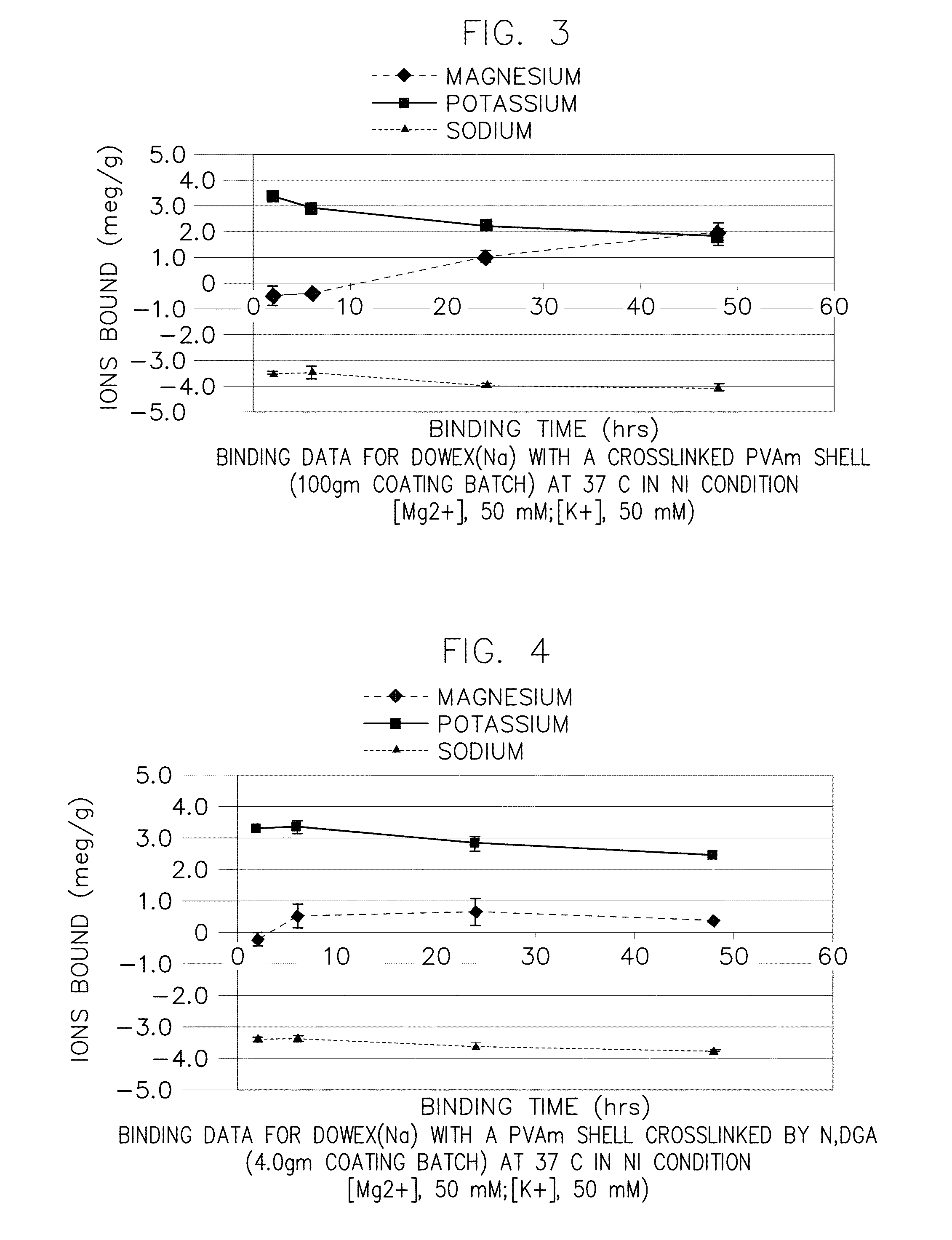
Preparation of Core-Shell Particles Having Crosslinked Polyvinylamine Shell (100 gm / 1 Liter Scale) (Reference ID #293)
[0330]This example illustrates the preparation of a core-shell particle comprising a core component comprising polystyrenesulfonate and a shell component comprising a crosslinked polyvinylamine, using a multiphase in situ crosslinking process with 100 gm core polymer and epichlorhydrine crosslinker in a 1 liter scale reactor.
[0331]Shell Polymer
[0332]A polyvinylmine solution (Mw, 45,000; >90% hydrolyzed) was provided by BASF under trade name, lupamin5095 (20˜22 wt % in aqueous solution). The solution was diluted with nanopure water to 2.5 wt %. The solution pH was adjust to pH8.5 by using 33.3 wt % NaOH before coating.
[0333]Core Polymer
[0334]The core polymer was a polystyrenesulfonate material, Dowex 50WX4-200, as described in connection with Example 1.
[0335]Crosslinking Agent
[0336]The crosslinking agent was epichlorohydrin (ECH). The ECH was provided in a toluene sol...
example 3
Preparation of Core-Shell Particles Having Crosslinked Polyvinylamine Shell (4 gm / 100 ml Scale) (Reference ID #291)
[0345]This example illustrates the preparation of a core-shell particle comprising a core component comprising polystyrenesulfonate and a shell component comprising a crosslinked polyvinylamine, using a multiphase in situ crosslinking process with 4 gm core polymer and N,N-diglycidylaniline crosslinker in a 100 ml scale reactor.
[0346]Shell Polymer
[0347]A polyvinylmine solution (Mw, 45,000; >90% hydrolyzed) was provided by BASF under trade name, lupamin5095 (20˜22 wt % in aqueous solution). The solution was diluted with nanopure water to 2.5 wt %. The solution pH was adjust to pH8.5 by using 33.3 wt % NaOH before coating.
[0348]Core Polymer
[0349]The core polymer was a polystyrenesulfonate material, Dowex 50WX4-200, as described in connection with Example 1.
[0350]Crosslinking Agent. N,N-diglycidylaniline (N,N-DGA) was used as received from Aldrich.
[0351]Reactor
[0352]100 ml...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time persistence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time persistence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time persistence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com