Intranasal Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms Comprising Naloxone
a technology of naloxone and intranasal, which is applied in the direction of aerosol delivery, anti-noxious agents, inorganic non-active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of low bioavailability, unsuitable for such purposes, and addicts' deaths, and achieves high bioavailability of naloxone, fast onset of action, and long duration of action
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
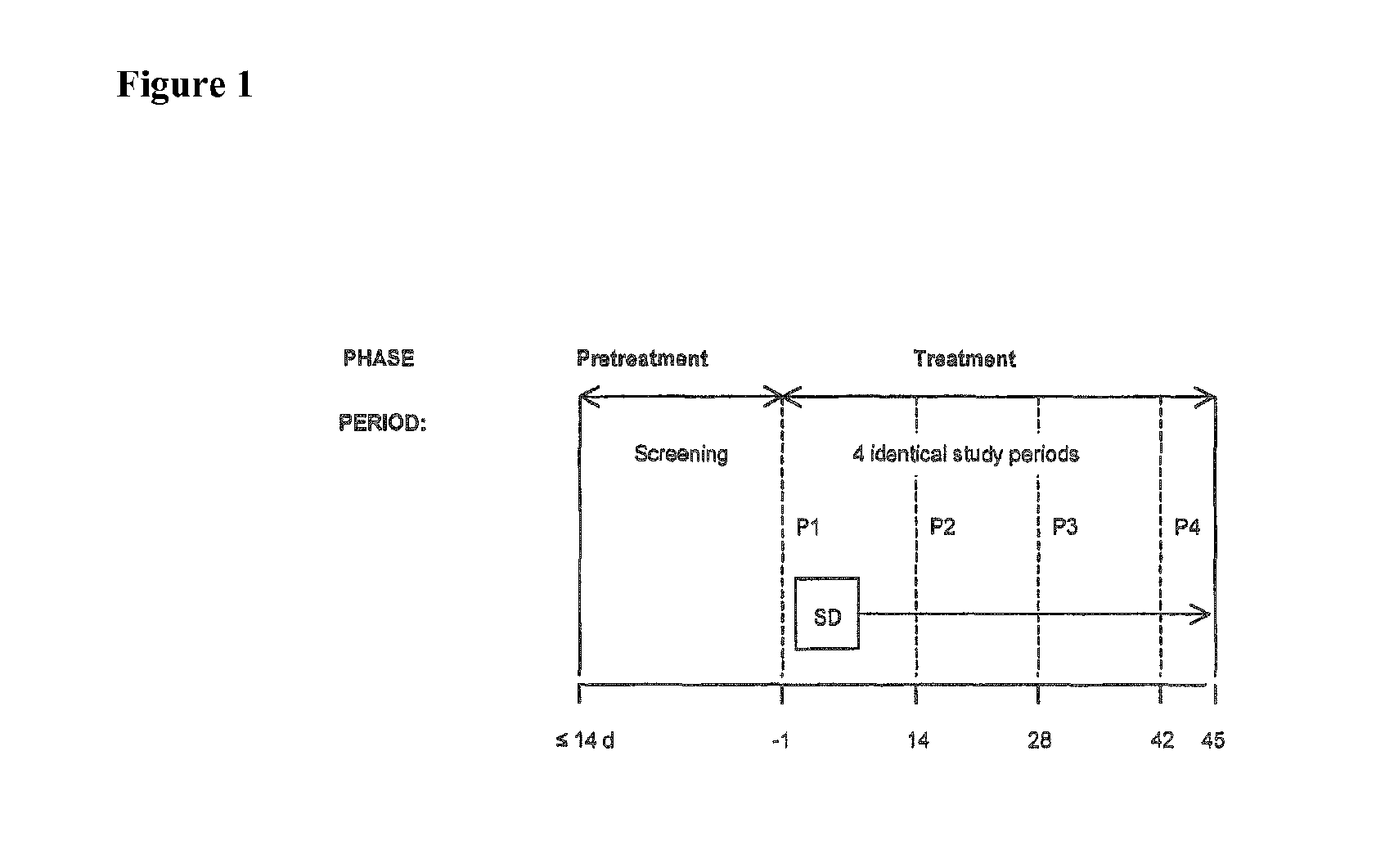
[0178]In the following, the results of a single-center, open-label, randomized investigation in healthy volunteers to determine the intranasal and sublingual bioavailabilities of naloxone in a four-way crossover study are set out.
Summary of the Study
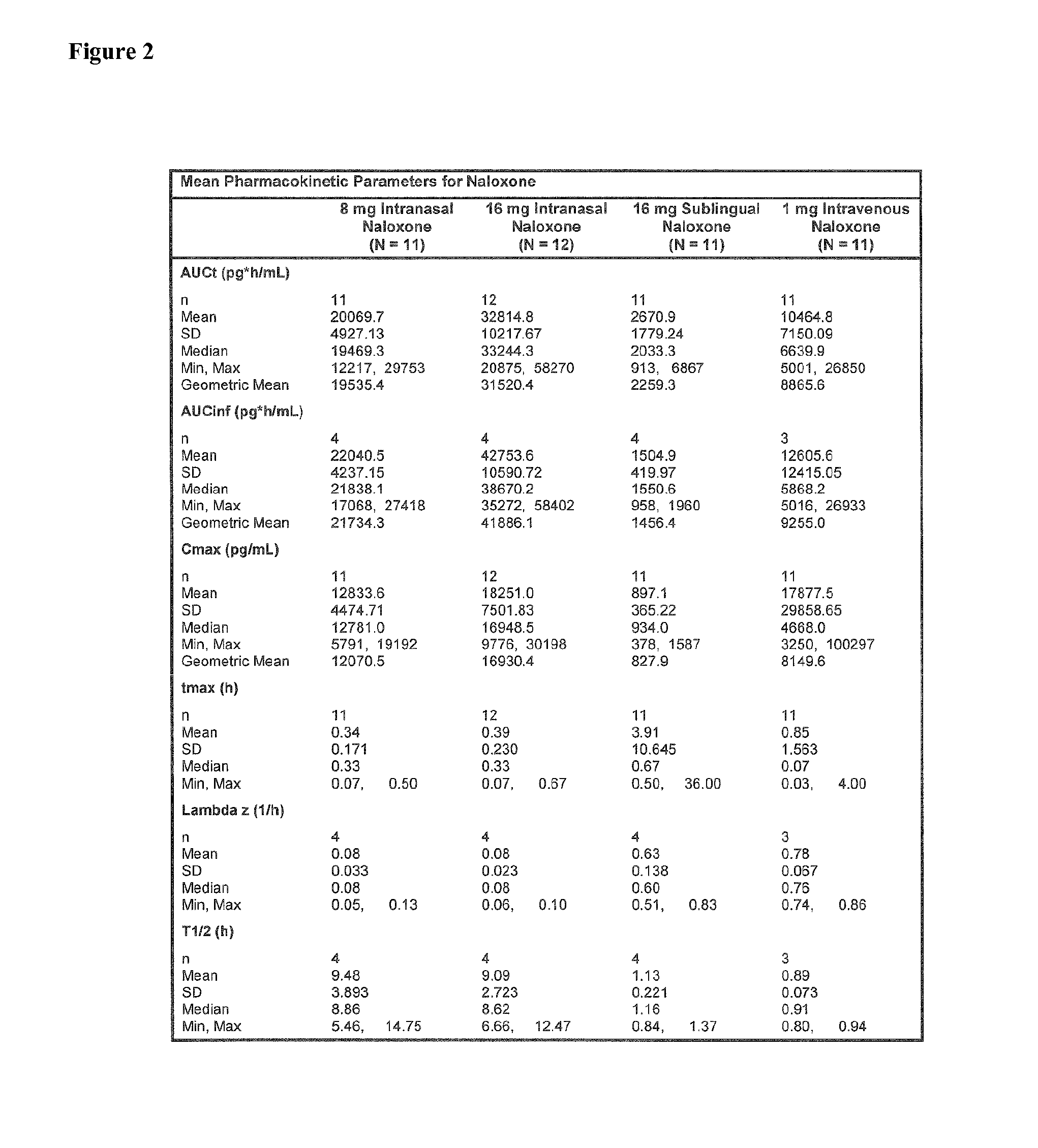
[0179]Objectives: To assess the absolute bioavailability of 8 mg and 16 mg intranasally and 16 mg sublingually administered naloxone compared with 1 mg of intravenously administered naloxone to healthy subjects.
Methodology: A single-center, open-label, randomized, 4-way crossover study using 8 mg and 16 mg intranasally, 16 mg naloxone sublingually, and 1 mg intravenous naloxone. A 4-sequence Williams design was used.
Number of Subjects: Planned: 12 subjects; full analysis for PK metrics: 12 subjects; Safety population: 12 subjects; Completed: 10 subjects; Discontinued: 2 subjects [due to their own choice].
Indication and Criteria for Inclusion: Subjects were males and / or females aged ≧18 and ≦55 years who were in good health as determined ...
example 2
[0227]Based on the data gained in Example 1, the following predictions of amounts of naloxone administered intravenously or intranasally were carried out.
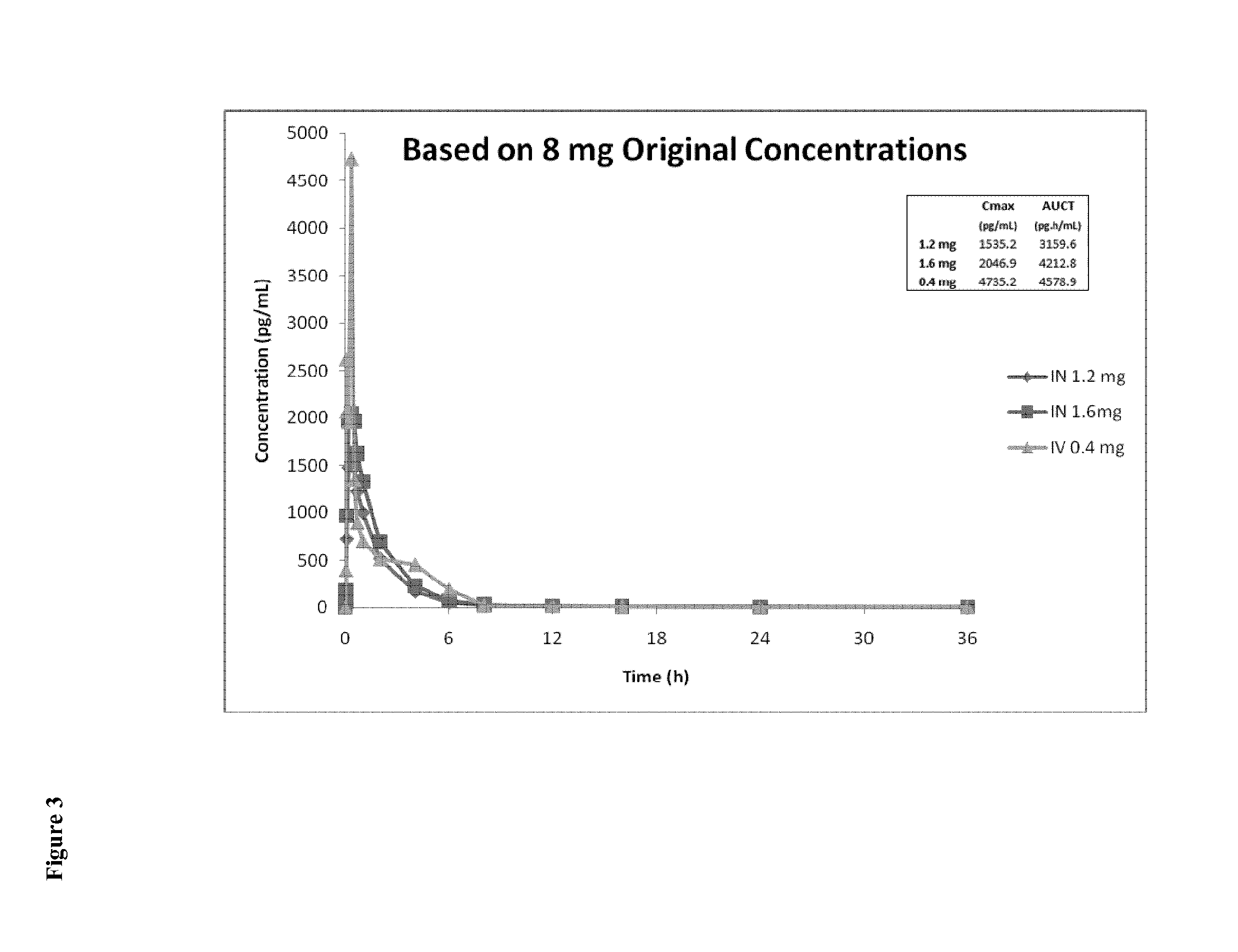
[0228]A typical starting point for an intravenous administration of naloxone is in the range of about 0.4 mg (IV). Based on the AUC-values for 1 mg IV naloxone, 8 mg IN naloxone and 16 mg IN of example 1, it can be estimated that the range of dose-proportionality to 1 mg IV is in the range of 3 mg to 4 mg for IN naloxone. For 0.4 mg IV naloxone, this results in typical starting amounts for naloxone administered intranasally ranging from 1.2 mg to 1.6 mg.
[0229]Based on the original data of the study of example 1 on either 8 mg naloxone or 16 mg naloxone administered intranasally (IN) and of 1 mg naloxone administered intravenously (IV), plasma concentrations were predicted for the following amounts: 0.4 mg naloxone IV, 1.2 mg naloxone IN and 1.6 mg naloxone IN.
[0230]Using a first method (Excel), the Cmax and AUCt-values based on the...
example 3
[0239]As evident particularly from FIGS. 4, 6, 7 and 8, the plasma concentration curve predicted for an amount of 0.4 mg naloxone IV displays two peaks, wherein the first peak after a few minutes is followed by a second peak corresponding to the Cmax-peak.
[0240]Due to this rather unusual IV profile, it was decided to exclude one outlying subject who was apparently responsible for the “double peak IV profile” when predicting the plasma concentration curve for an amount of 0.4 mg naloxone administered intravenously. The calculations using Excel and WinNonlin for the 1.2 mg naloxone IN and 1.6 mg naloxone IN correspond to the data as shown in Example 2.
[0241]Using Excel, the Cmax and AUCt-values based on the 1 mg naloxone IV data excluding the outlying subject were calculated by performing non-compartmental analysis on the mean profiles which had been scaled to the dose of 0.4 mg IV with the following results (depicted again with the IN-values based on the 8 mg IN data):
Cmax (pg / ml)AUC...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com