Cancerous lesion identifying method via hyper-spectral imaging technique
a hyper-spectral imaging and lesion technology, applied in the field of cancerous lesion identification methods, can solve the problems of time-consuming data reading, high cost, limited reading speed of spectrum data, etc., and achieve the effect of efficiently increasing the diagnostic rate of clinicians
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
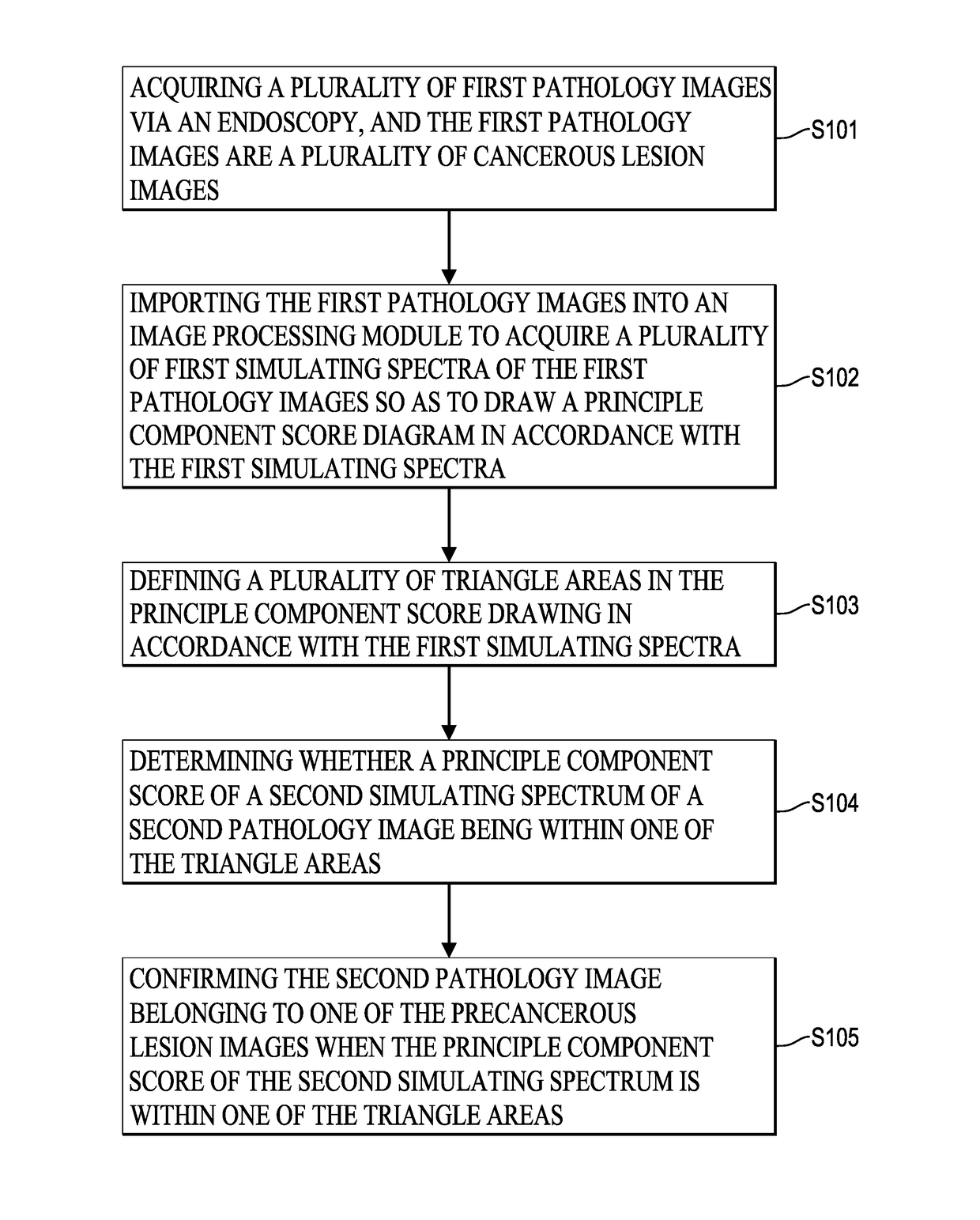
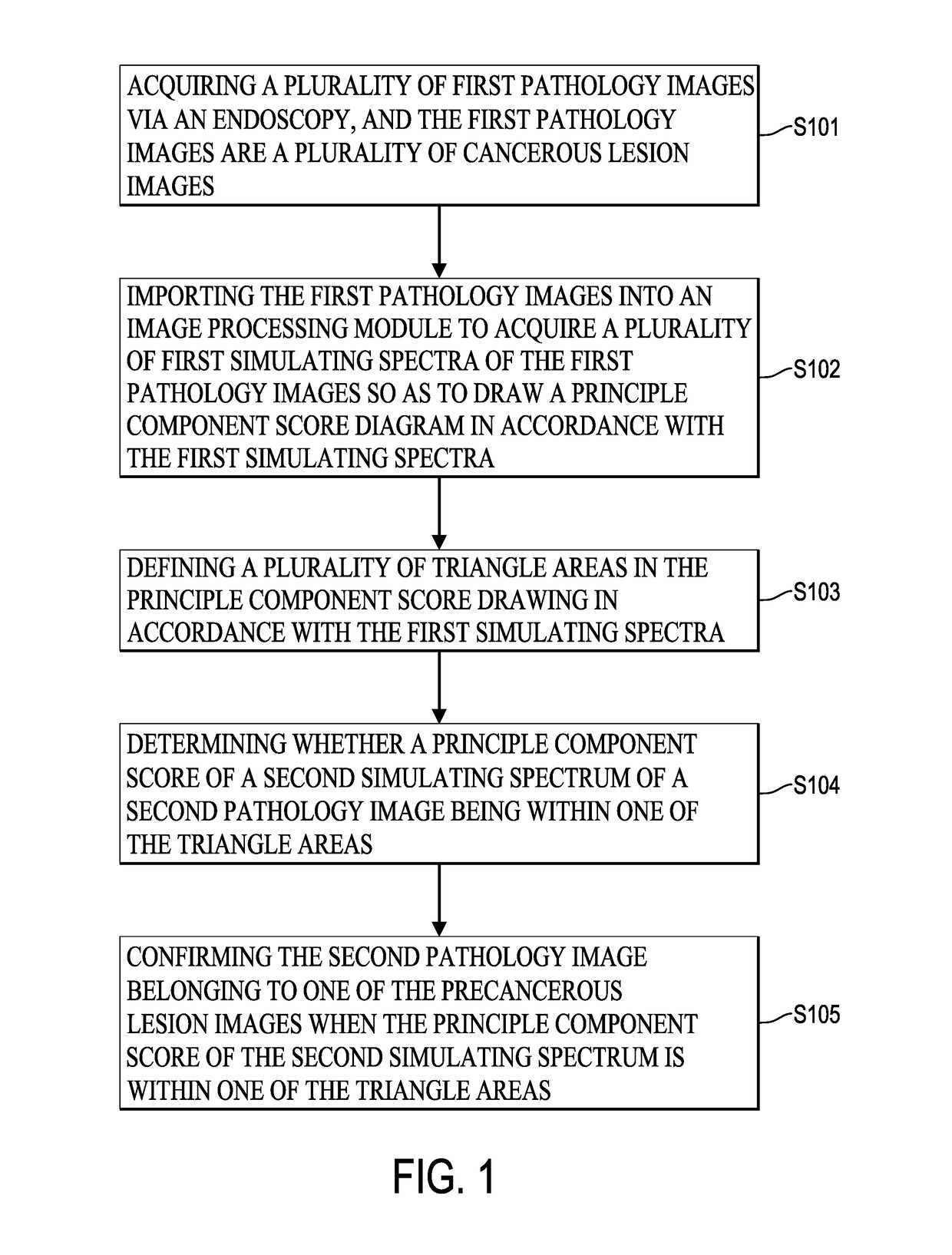
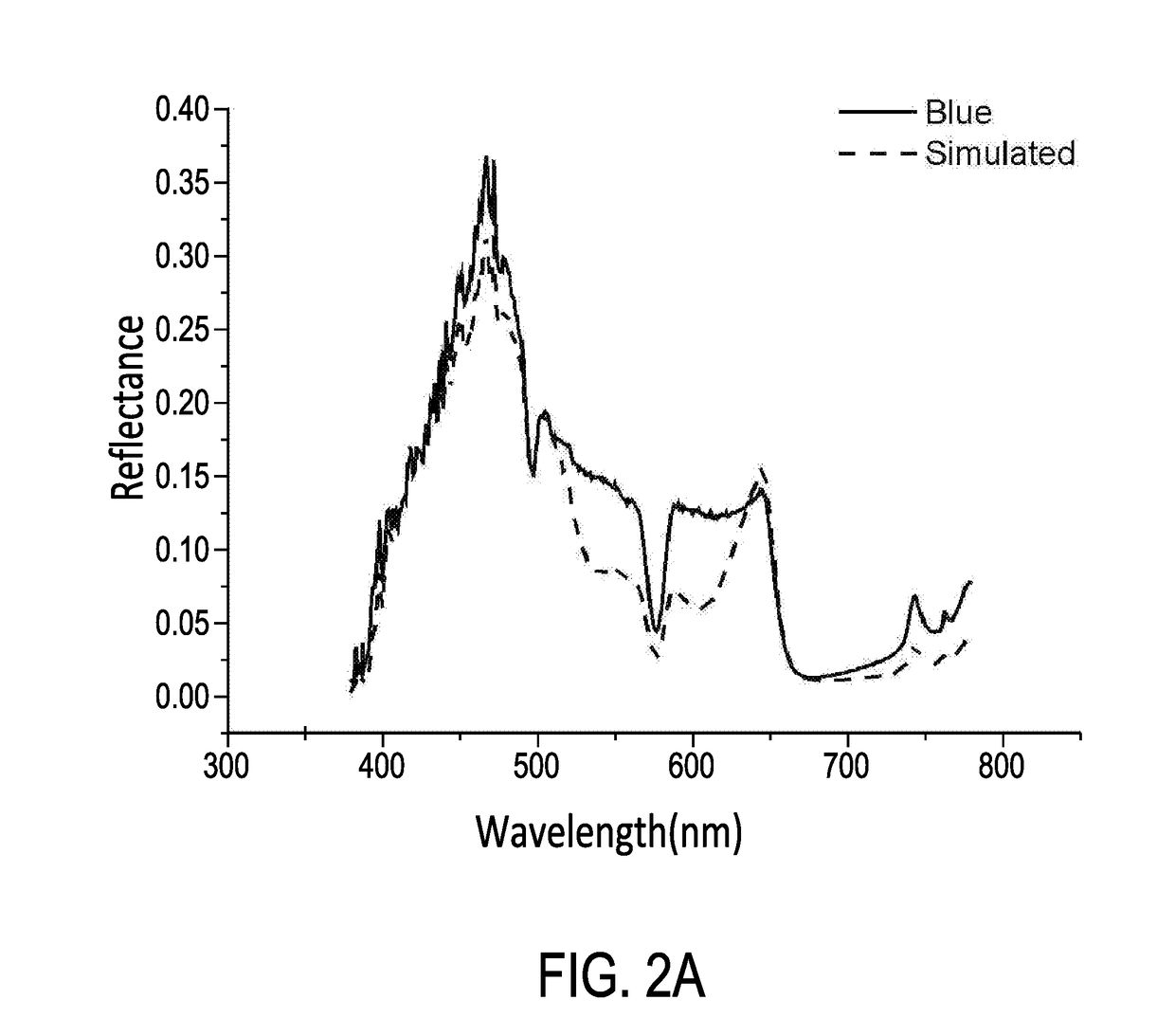
[0025]FIG. 1 is a flow chart of a cancerous lesion identifying method via hyper-spectral imaging technique in an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 1, in step S101, a plurality of first pathology images are acquired via an endoscopy and the first pathology images are cancerous lesion images. The hyper-spectral imaging system is built within the endoscopy and a high resolution spectrometer. The hyper-spectral imaging system can acquire image information of 24 mini color checkers. In order to determine cancerous lesions, the spectra at each of the pixels in each of the first pathology images may be acquired and a relationship matrix between the spectrometer and the endoscopy has to be found first. The spectra of the 24 mini color checkers are measured by the spectrometer under the environment of the endoscopy. The range of the spectra is set at the wave band of visible light (380 nm-780 nm). For analytical purposes, each column of the matrix is the corresponding str...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com