Method of pretreatment of cellulose containing textiles
a technology of textiles and cellulose, applied in the field of pretreatment of cellulose containing textiles, can solve the problems of reduced strength, loss of mechanical resistance of textiles, and lower abrasion resistance of treated products compared to non-treated products, and achieve the effect of higher dye absorption and higher uptake of any desired chemical
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0051]The Examples which follow are set forth to aid in the understanding of the invention but are not intended to, and should not be construed to limit the scope of the invention in any way.
Test Procedure with the Denim Example
Pre-Treatment:
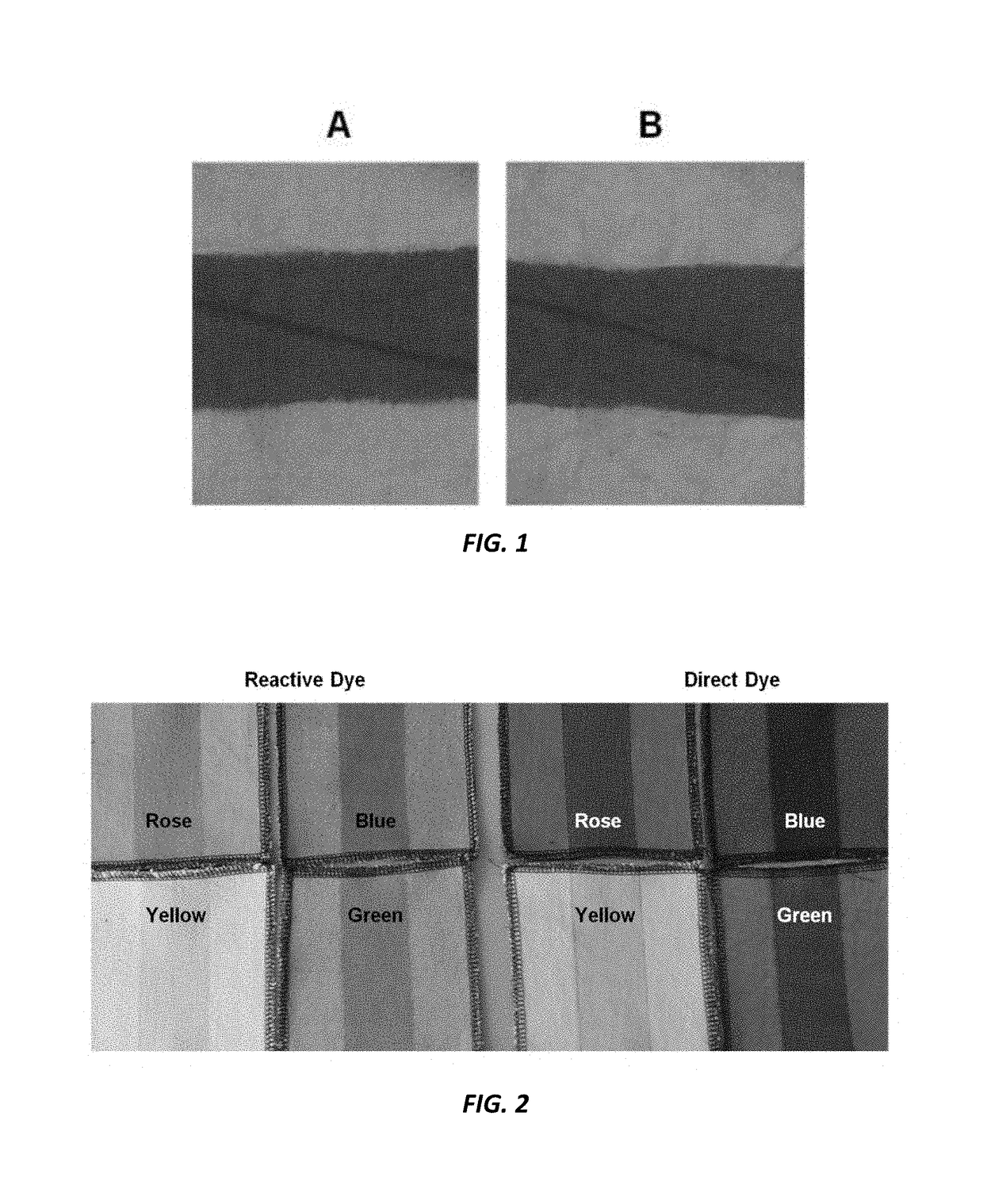
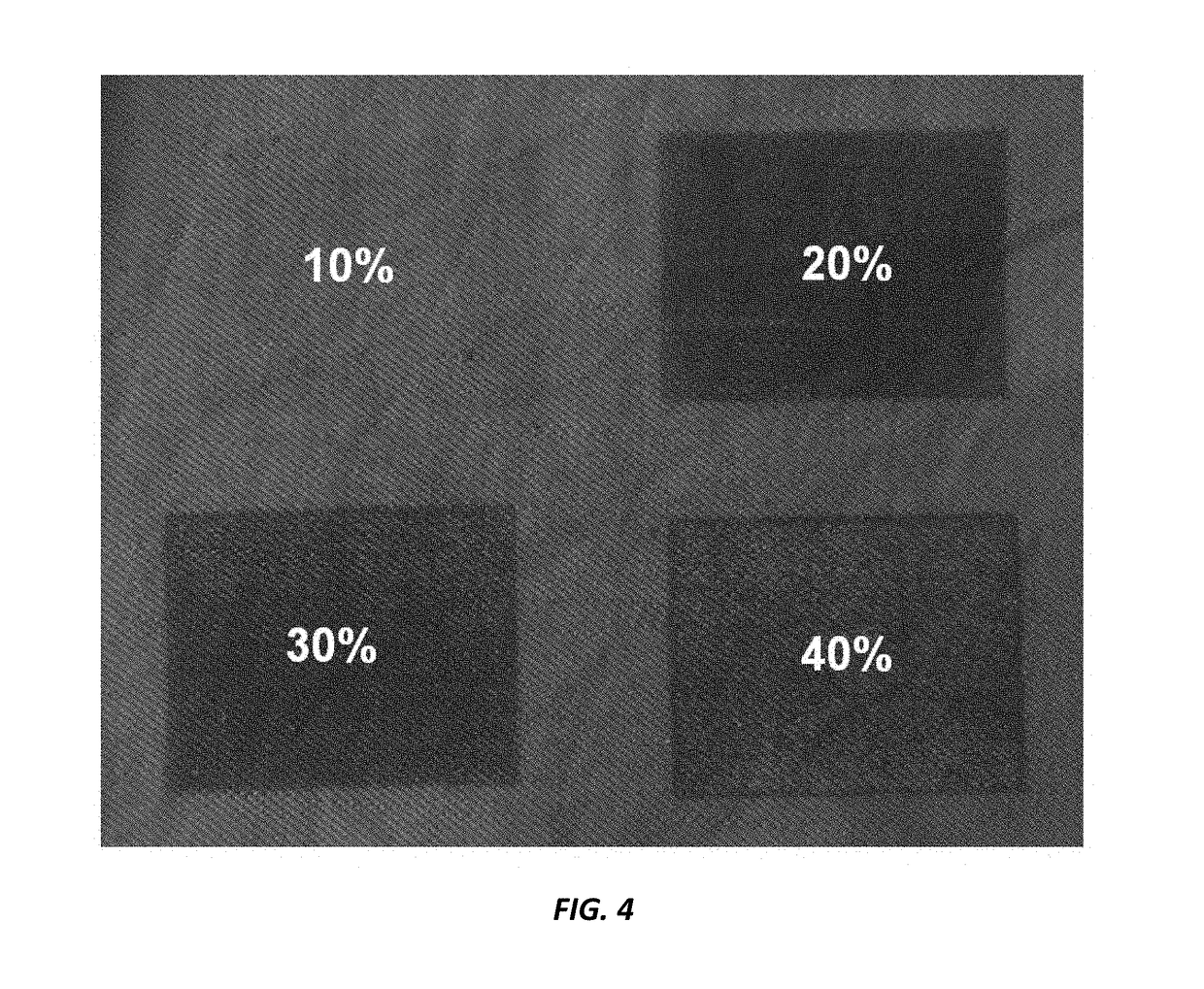
[0052]Specimens (denim, 10×15 cm, approx. 7.5 g, 500 g / m2) are treated with the test solution. Application is effected at the surface, in this case by dabbing with a sponge. One pattern is treated with the soft side of the sponge (A), another one with the rough side of the sponge (B). The exposure time to the chemicals is 30 minutes.
[0053]Then, the specimen may be pressed through the squeezer of a Foulard (e.g. 5 bar), causing the chemicals to penetrate far into the interior of the fabric.
[0054]One specimen is immediately rinsed, a second part is dried at 60° C. for 5 min and then rinsed, each one for approx. 5 min under running water. No intermediate drying is conducted before the enzyme treatment.
Enzyme Treatment:
[0055]The wet specimens are in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface morphology | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Morphology | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com