Treatment of inflammatory diseases
a technology for inflammatory diseases and diseases, applied in the field of inflammatory diseases, can solve the problems of increased potential for tissue injury, illness or disease, and inability to regulate the inflammatory respons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
f Human Airway Stem Cells
[0606]Human (upper) airway stem cells can be isolated and clonally expanded according to the method described in the co-pending co-owned application filed on the same day (Mar. 15, 2013), entitled “Isolation of Non-Embryonic Stem Cells and Uses Thereof,” as U.S. Provisional Application No. 61 / 792,027 (incorporated herein by reference). Also see Section 2 above.
[0607]In this experiment, human airway biopsy was digested with 2 mg / mL collagenase type IV (Gibco, cat. no. 17104-109), and epithelial cells were isolated and cultivated onto a feeder layer of lethally irradiated 3T3-J2 cells (originally from the Howard Green laboratory of Harvard Medical School, Boston, Mass.) in CFAD media based on the previously described methods for epidermal stem cells and airway epithelial stem cells (see Barrandon and Green, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:2302-2306, 1987; Kumar et al., Cell 147:525-538, 2011; Senoo et al. 2007, Cell 129:523-536). CFAD culture medium contains thr...
example 2
Methods Using Sensitized Test Cells from an Asthma Patient
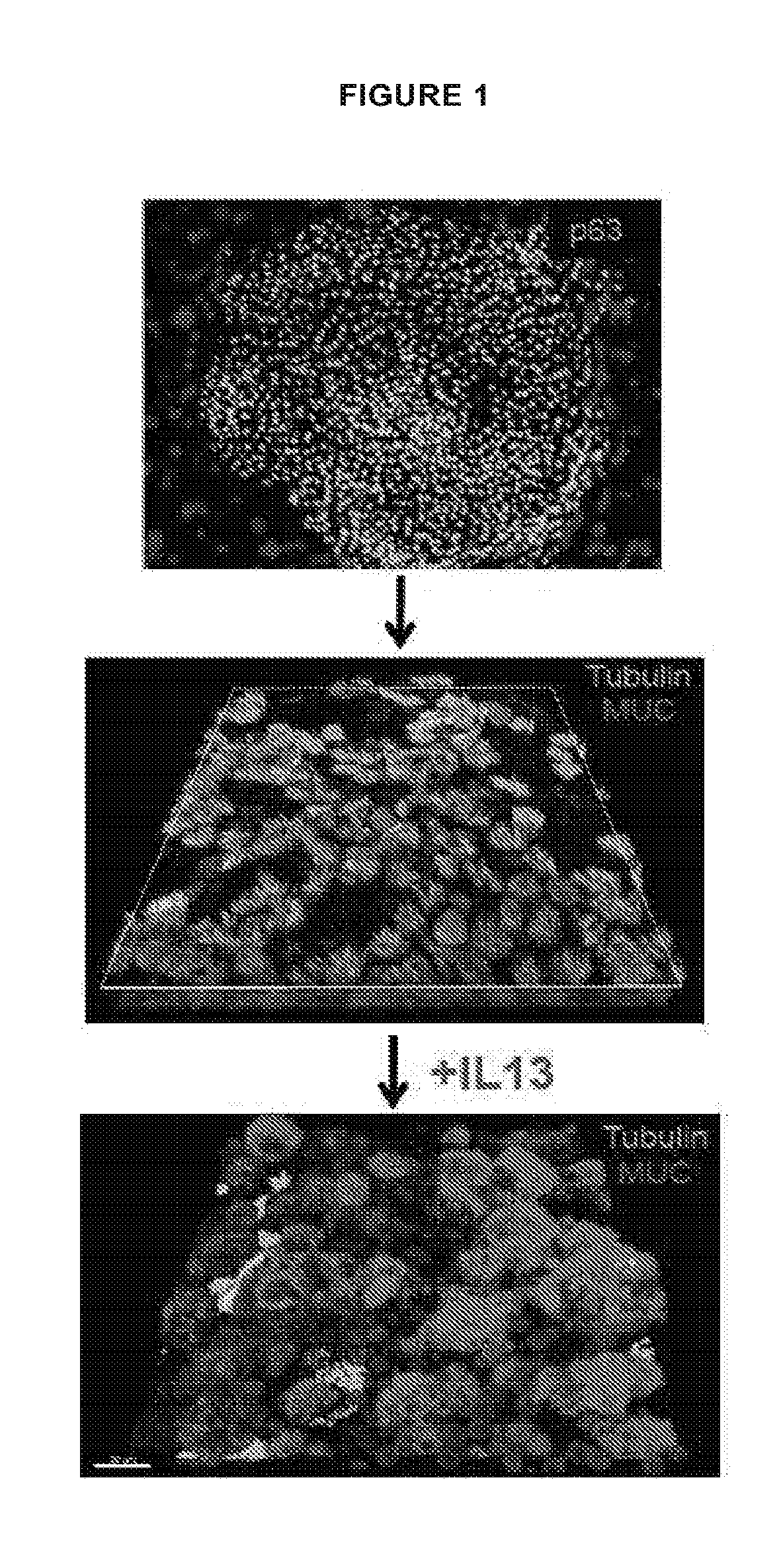
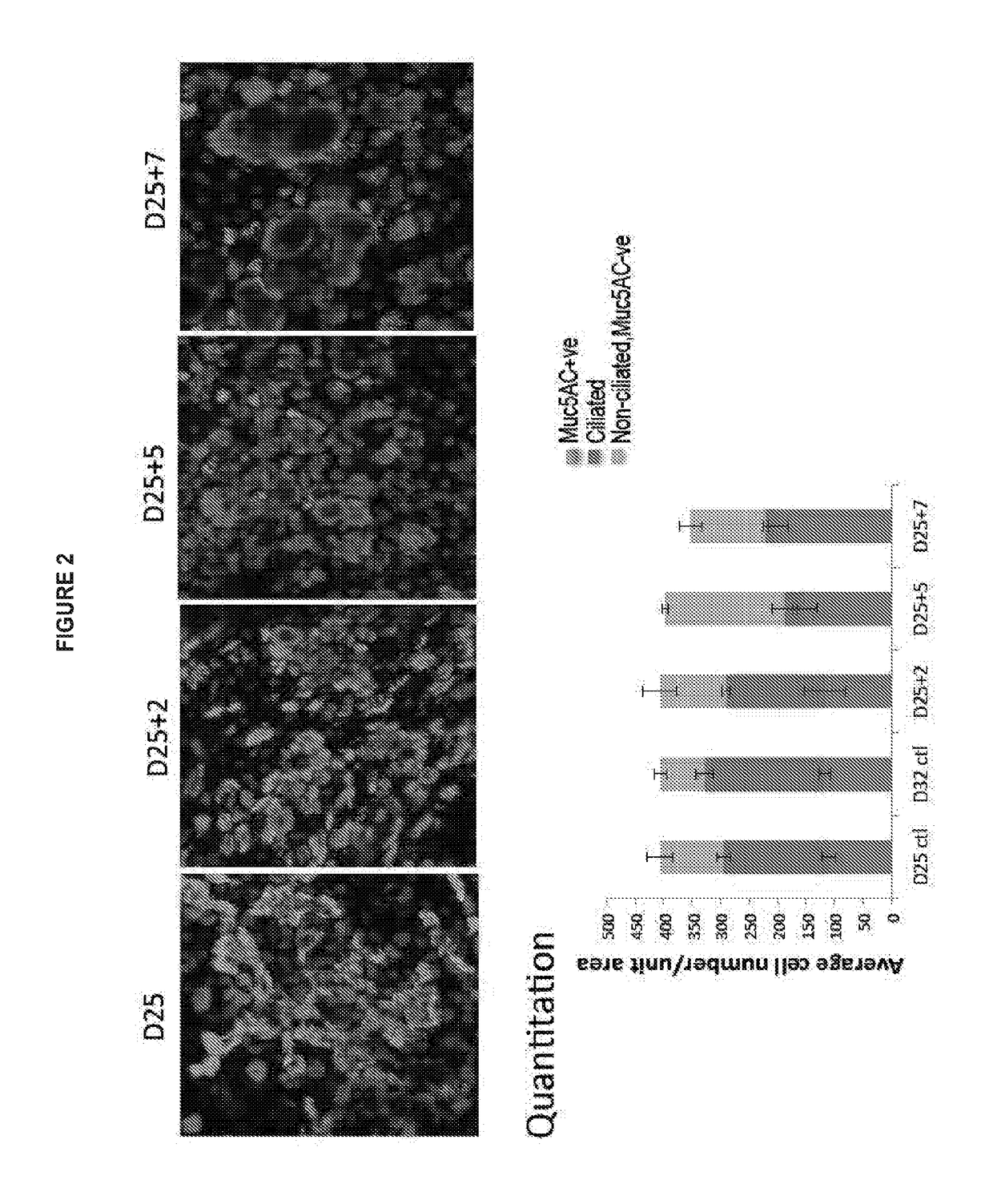
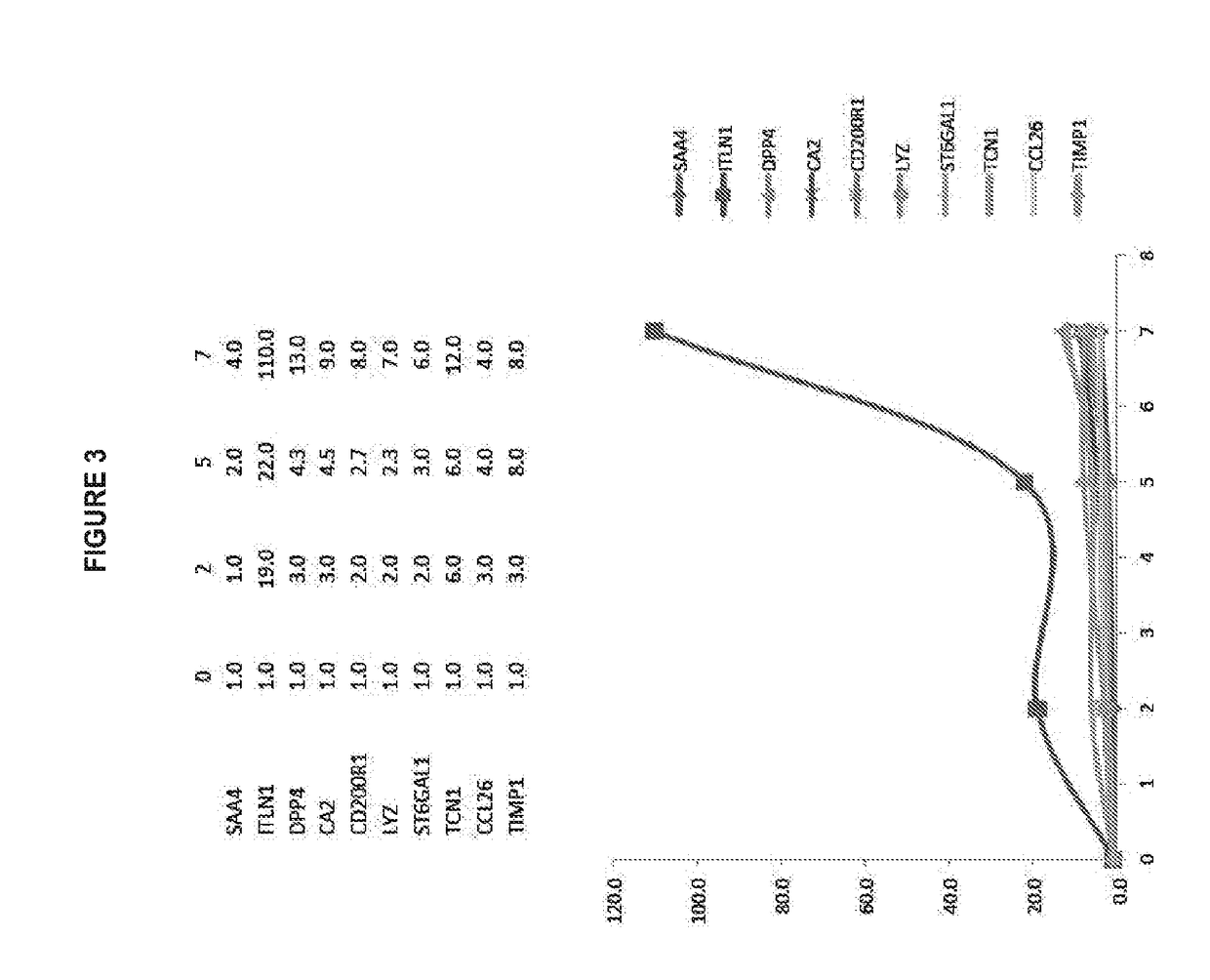
[0608]Upper airway stem cells were isolated using the methods of the invention from an asthma patient. Microarray analysis revealed that, without IL-13 treatment, in about 13 days, normal upper airway stem cells differentiate into both ciliated cells and goblet cells. However, Asthma patient stem cells have extremely limited or no ability to form ciliated cells. Based on the microarray data, AMTN expression in the patient cells was already 35-fold lower, and TCN1 expression in the patient was already 45-fold higher compared to normal control at day 13. Consistently with this observation, Asthma stem cells were more susceptible to IL-13 treatment, and gave rise to goblet cell metaplasia much faster and stronger than normal upper airway epithelial stem cells. See FIG. 19.
[0609]Note that on Day 15, without IL-13 treatment, normal upper airway stem cells differentiate into both goblet cells and ciliated cells. IL-13 treatment led...
example 3
Differentiation Assays for Human and Rat Cells
[0612]Air-liquid interface culture of upper airway epithelial cells was performed as described (Schmidt et al., Toxicol. Lett. 88:75-79, 1996; Kumar et al, supra, both incorporated by reference). Briefly, upper airway stem cells were cultured on Transwell plates (Corning) coated with irradiated 3T3-J2 feeder cells in the presence of CFAD medium (a base medium). At confluence, the medium on the inserts was removed and the medium outside the insert was changed to differentiation medium (DMEM / F12 1:1, 50 mg / mL penicillin; 50 mg / mL streptomycin; Fungizone 2.5 mg / mL (GIBCO); 10 ng / mL cholera toxin, retinoic acid 10−7 M; 10% Knockout SR serum replacement (GIBCO)).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com