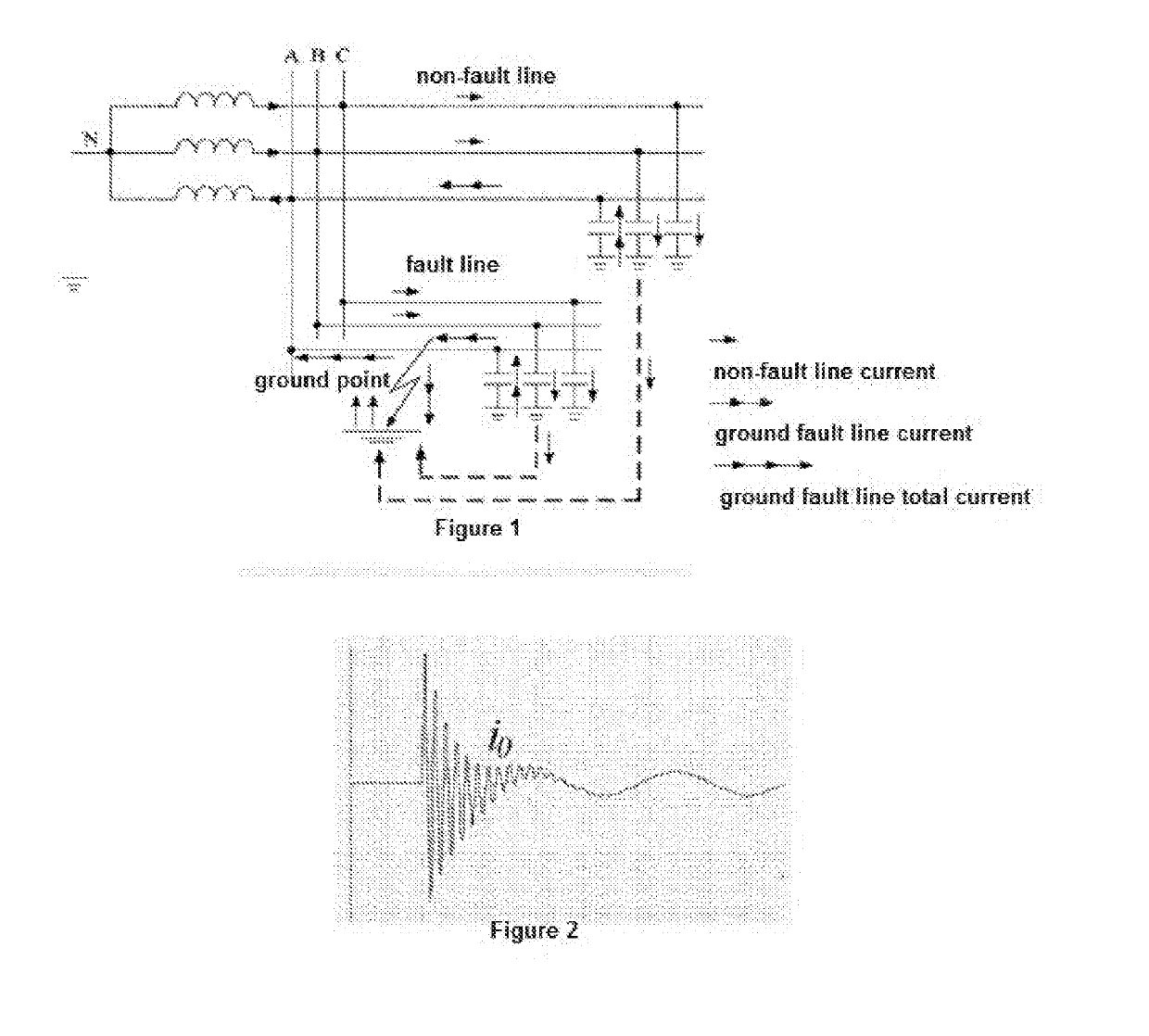
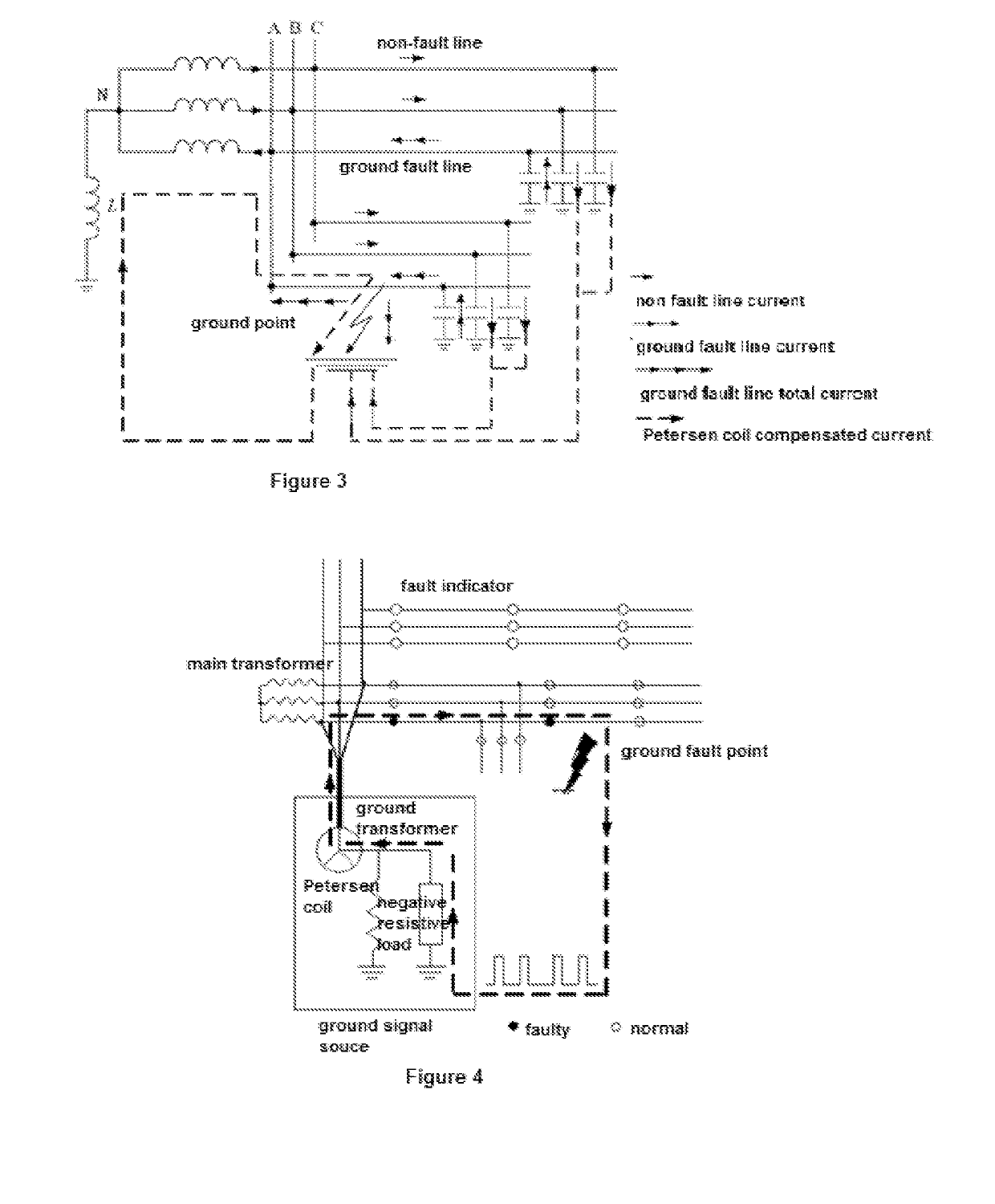
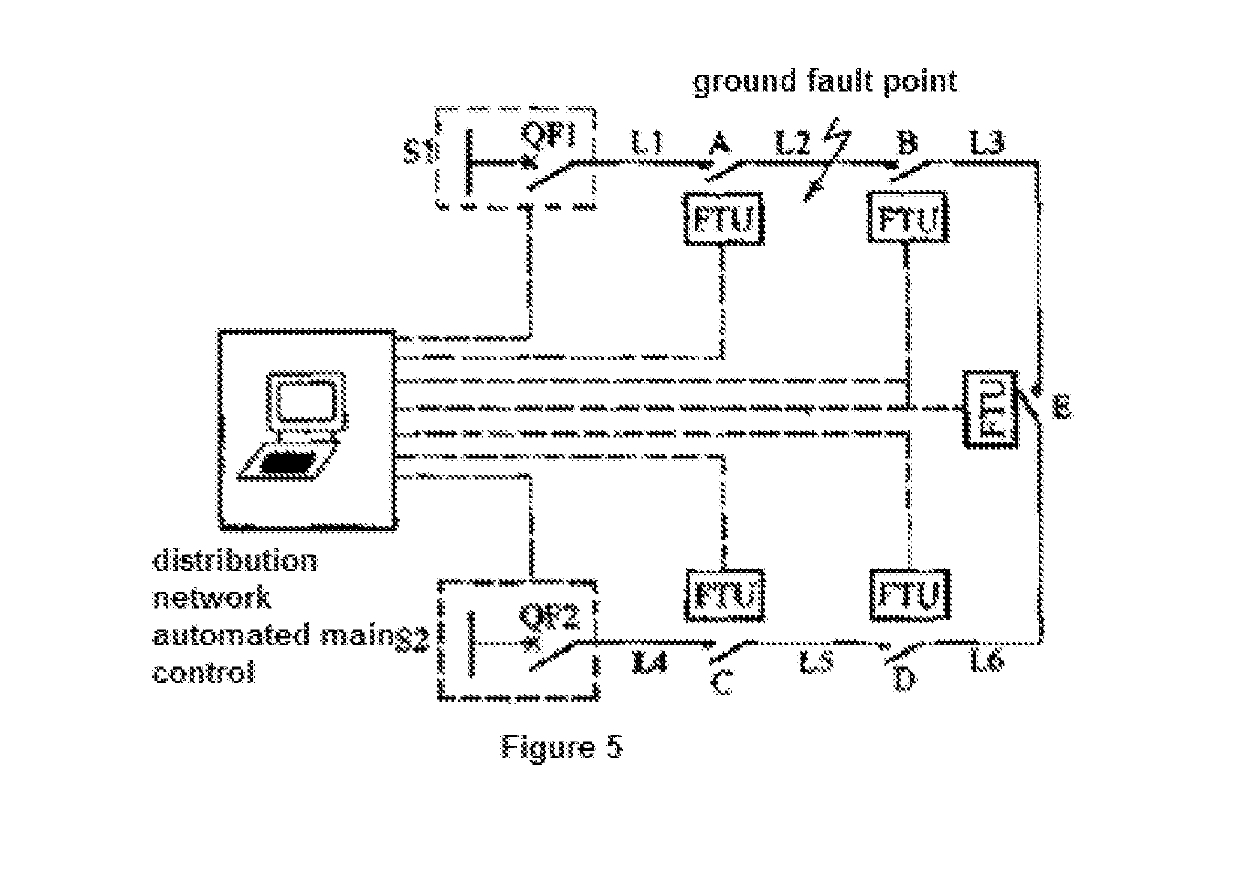
Method and system for detecting and locating single-phase ground fault on low current grounded power-distribution network
a single-phase ground fault, low-current technology, applied in the field of low-current single-phase ground fault detection and location methods and systems, can solve the problems of no effective method, large majority of failures are single-phase ground, and the main power grid is short-circuit and ground faul
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0113]Below in connection with the accompanying figures of the present invention embodiment, the present invention will be apparent in the technical implementation of the invention. The described embodiments are only part of the present invention, but not all. The described embodiments of the present invention, and all other embodiments perceived by those of ordinary skill in creativity, all belong to the scope of the present invention.
[0114]Below with references to the figures, the present invention is further described in detail.
[0115]An embodiment of the present invention is to provide a low current single-phase ground fault detection and location, as shown in FIG. 6, comprising:
[0116]At step 61, data collections were made to voltage and current signals for each of a plurality of positions in the feeder;
[0117]Specifically at set intervals, periodically the voltage and current signals on each phase feeders are collected at the plurality of positions, or they can be collected at sp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com