Zinc oxide particle preparation and methods of use
a technology of zinc oxide and particle size, applied in the field of zinc oxide particle preparation and method of use, can solve the problems of low progress in the use of zinc oxide particle on a larger scale, increased surface area, and inefficient processes, so as to reduce the concentration of organic contaminants and reduce the concentration of contaminant concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanoflowers
[0107]0.2 g of zinc nitrate (Zn(NO3)2.6H2O) was weighed and transferred into a round bottomed flask with 20 mL deionized water and stirred at room temperature. This was followed by the addition of 0.2 g sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to the flask, which was then stirred for 10 minutes at room temperature. The mixture was then refluxed at 80° C. for 5 hours. The flask was cooled to room temperature and the precipitate was centrifuged, washed with deionized water, and then washed with methanol. The product was dried in an oven for 24 hours at 60° C.
example 2
Preparation of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanospheres
[0108]0.2 g of zinc nitrate (Zn(NO3)2.6H2O) was weighed and transferred into a TEFLON-lined autoclave, followed by addition of water (20 mL) and 0.2 g of sodium hydroxide (NaOH). The mixture was stirred at room temperature and then heated at 140° C. for 24 hours. The product was cooled to room temperature, and the precipitate was centrifuged, washed with deionized water, and then washed with methanol. The product was dried at 60° C. in an oven for 24 hours.
example 3
Physical Characterization
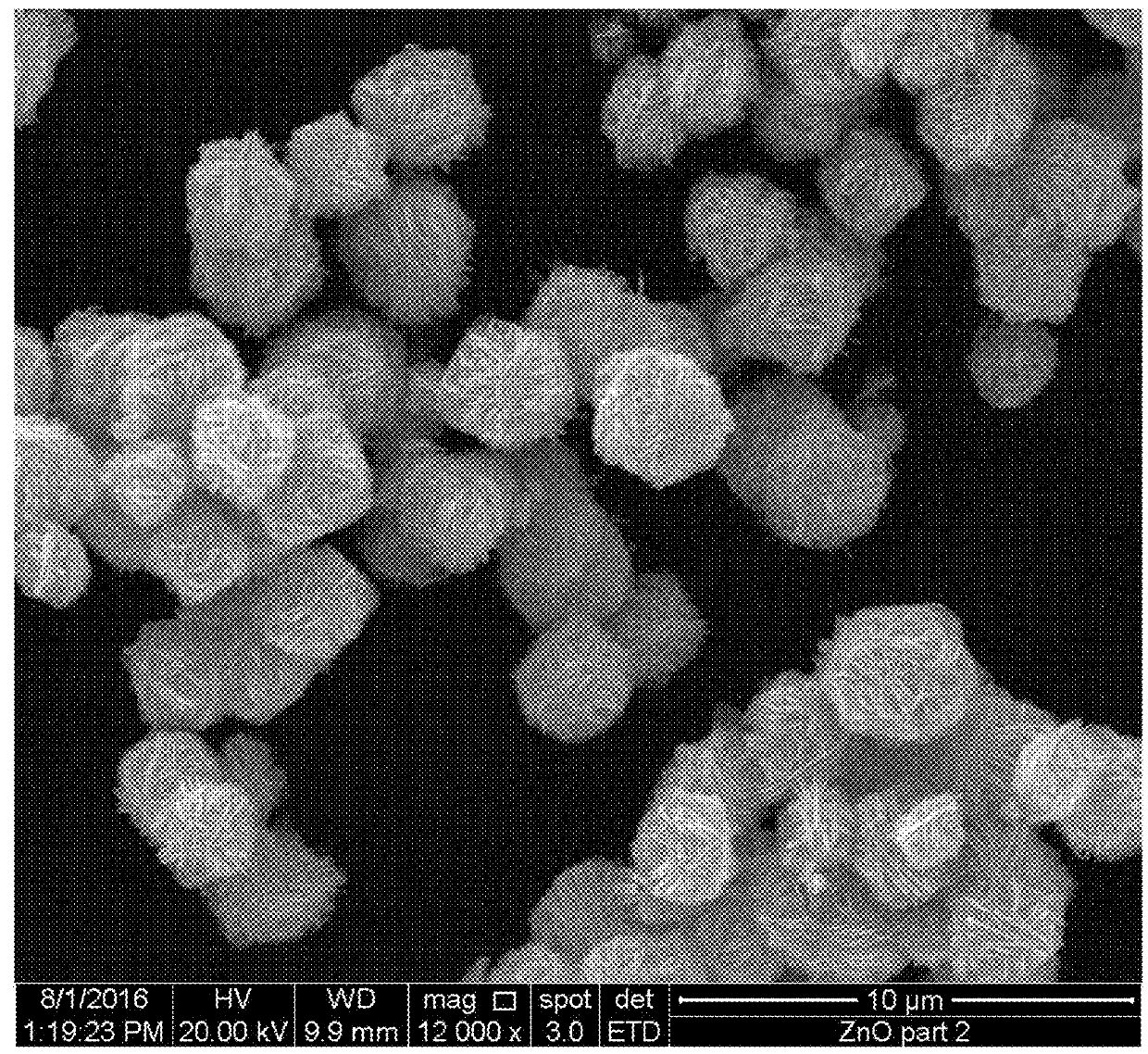
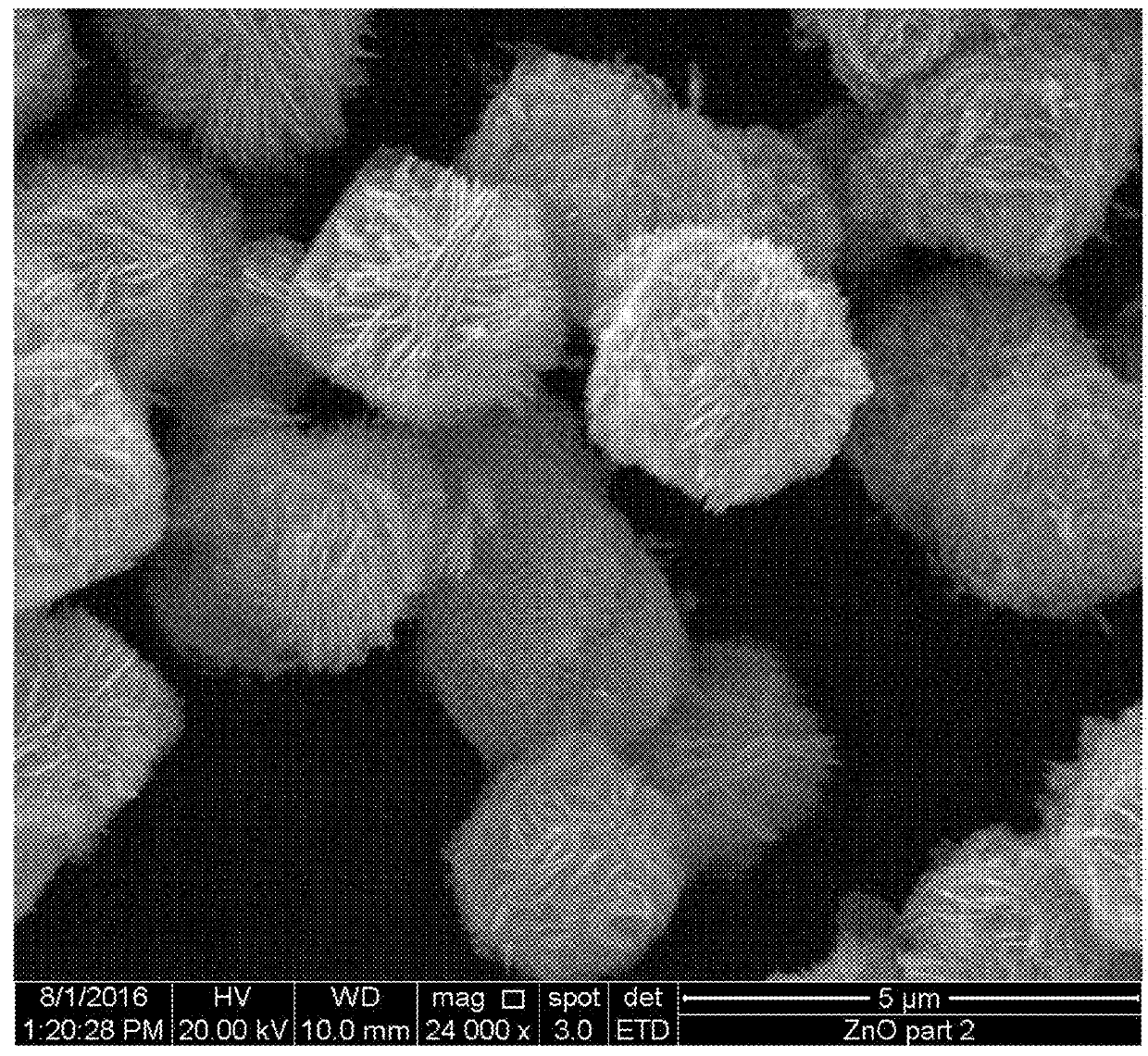
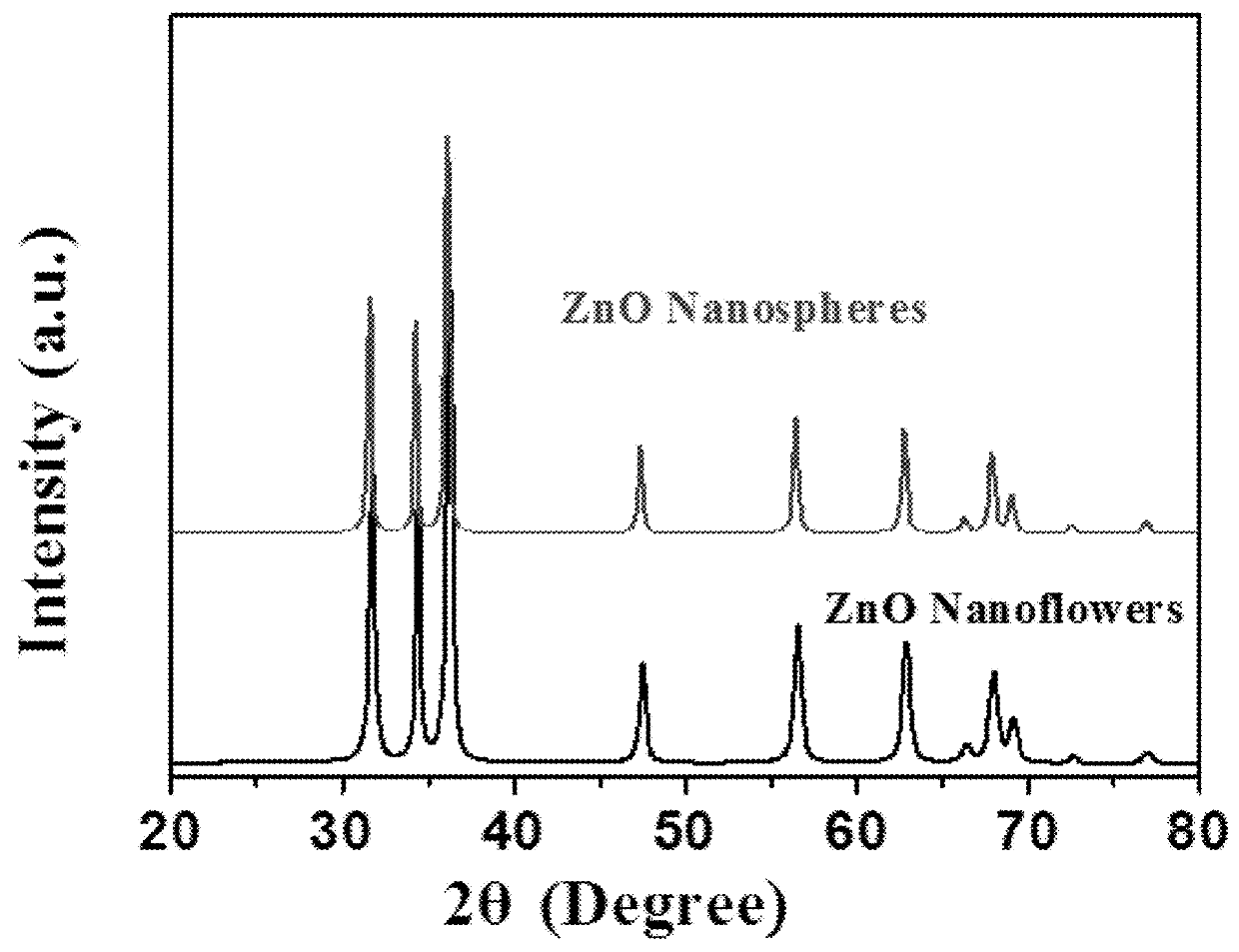
[0109]The morphologies of the zinc oxide nanoflowers and nanospheres were examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, FEI INSPECT S50), as shown in FIGS. 2A-2B and FIGS. 3A-3B, respectively. The crystallinity and crystal phases of the zinc oxide nanoflowers or nanospheres were studied by an X-ray diffractometer (XRD Rigaku, Japan) using Cu-Kα radiation (λ=1.5418 {acute over (Å)}) in the range of 10°-80° with 1° / min scanning speed. The XRD patterns for both nanoflowers and nanospheres arc shown in FIG. 1. UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra of zinc oxide nanoflowers and nanospheres, as shown in FIG. 4, were recorded on a diffuse reflectance UV-Vis spectrophotometer (JASCO V-750). Micromeritics ASAP 2020 PLUS nitrogen adsorption apparatus (USA) was employed for BET surface area determination. Before surface area analysis, samples were degassed at 180° C., and the surface area was then determined using N2 adsorption data in the relative pressure (P / P0) range ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore sizes | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com