Optical waveguide and process for manufacturing the same
a technology of optical waveguides and manufacturing processes, applied in the field of optical waveguides, can solve the problems of inability to complete total reflection, large change in direction, inability to avoid loss, etc., and achieve the effect of significant change in the direction of light propagation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
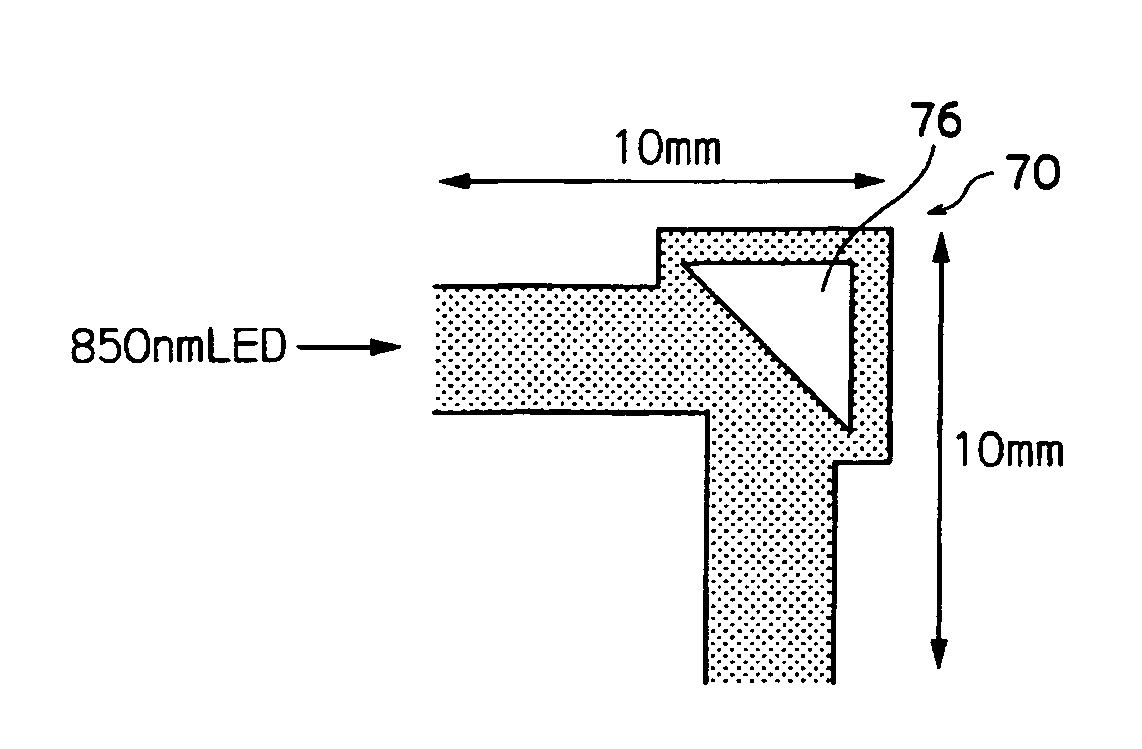
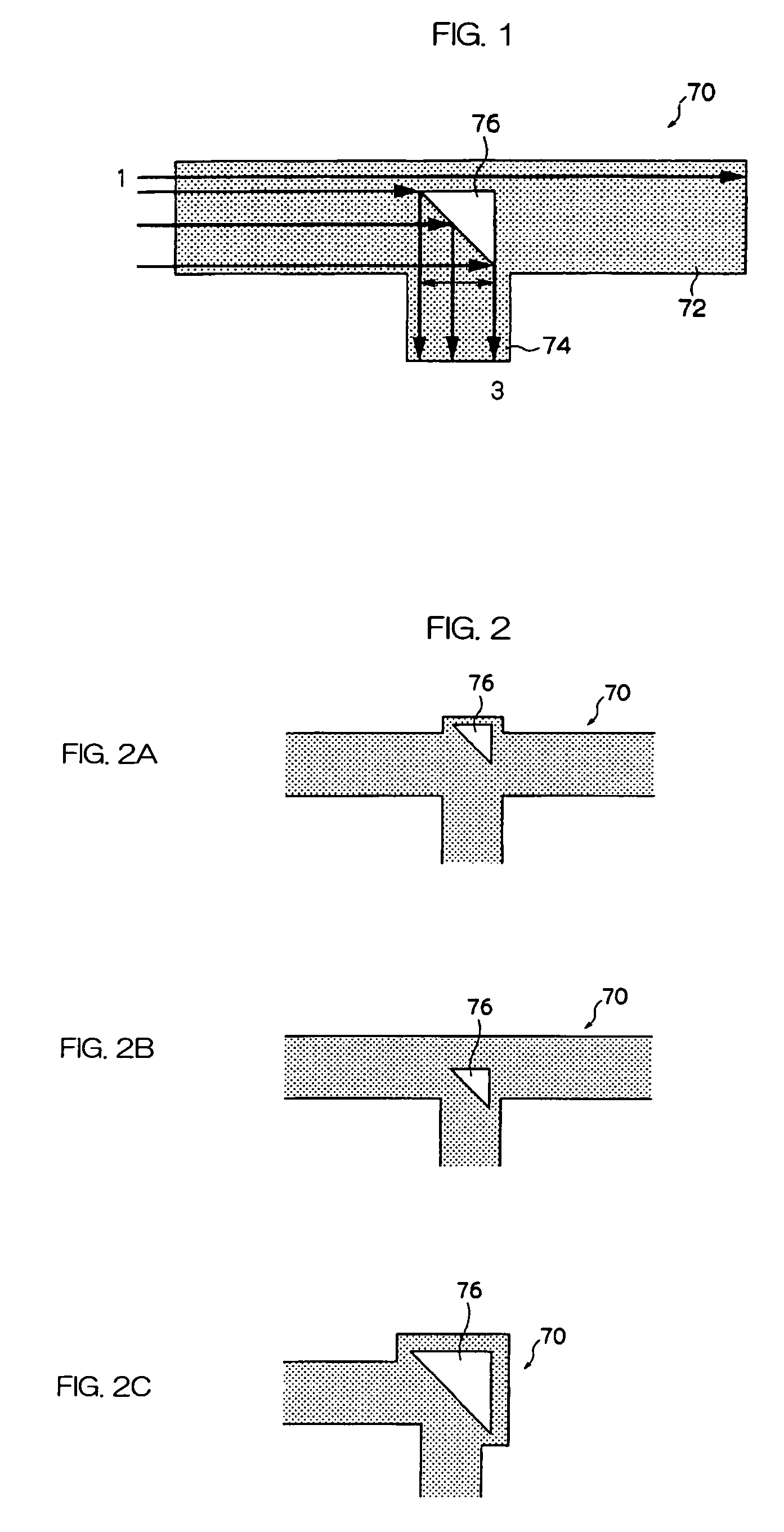
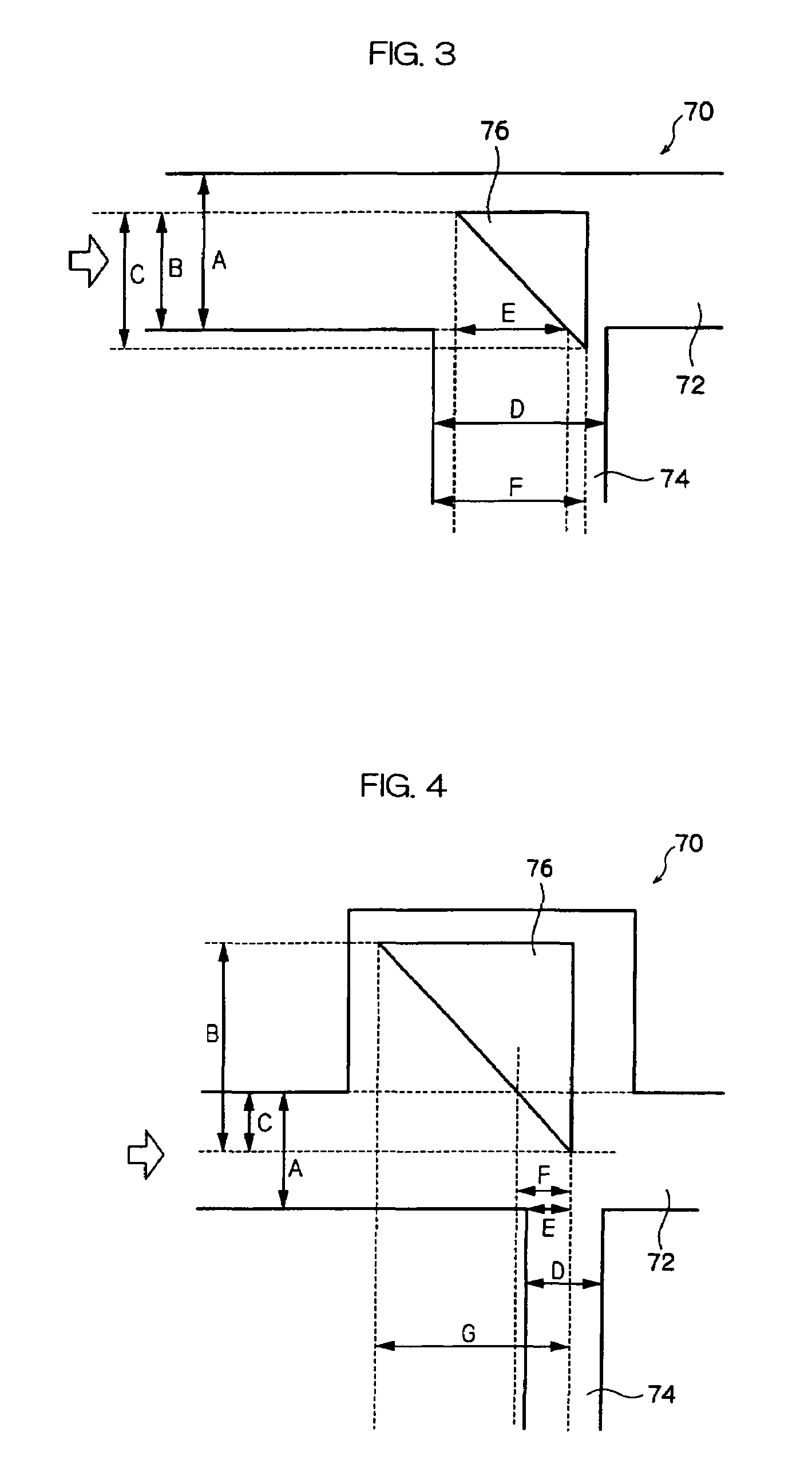
[0134]As shown in FIG. 7, a main waveguide is 100 μm by 100 μm and has a length of 20 mm, a gas cavity constituted of air has a configuration which is an isosceles triangle structure in which the sides forming a right angle are each 50 μm in length and has a plane inclined at an angle of 45° in the direction of light propagation in the main waveguide and disposed at the center of the main waveguide and a branched waveguide which is 100 μm by 100 μm and has a length of 5 mm. A ultraviolet ray-curable polymer having a refractive index of 1.54 is used for a core, a ultraviolet ray-curable polymer having a refractive index of 1.51 is used as a clad and ARTON FILM® (manufactured by JSR Corporation) is used as a bottom substrate. An LED having a wavelength of 850 nm is disposed on the incident side through a φ62.51 μm GI fiber and the light receptor side of each end part of the main waveguide, and a branched waveguide is connected to a light intensity measurer through a φ200 μm HPCF-GI fi...
example 2
[0138]As shown in FIG. 8, a main waveguide is 50 μm by 50 μm and has a length of 10 mm, a gas cavity constituted of air has a configuration which is an isosceles triangle structure in which the sides forming a right angle are each 50 μm in length has a plane inclined at an angle of 45° in the direction of light propagation in the main waveguide and disposed at the center of the main waveguide and the main waveguide which extends 10 mm in the direction at an angle of 90° in the direction of the main waveguide from the border of the air part. An ultraviolet ray-curable polymer having a refractive index of 1.54 is used for a core, an ultraviolet ray-curable polymer having a refractive index of 1.51 is used as a clad and ARTON FILM® (described above) is used as a top and a bottom substrate. An LED having a wavelength of 850 nm is disposed on the incident side through a φ62.5 μm GI fiber, and the main waveguide end is connected to a light intensity measurer through a φ200 μm HPCF-GI fibe...
example 3
Production of a Master Plate
[0140]As shown in FIG. 9A, a thick film resist is applied to a Si substrate 80 by a spin coating method, then pre-baked at 80° C., subjected to exposure through a photomask, and then developed to form waveguide core convex portions 82 and 84 for changing the direction of light propagation and a concave portion 86 for a cavity in a core (core width: 100 μm, cavity width: 50 cm). The substrate is post-baked at 120° C. to produce a master plate for manufacturing an optical waveguide core and a cavity in the core.
Production of a Mold
[0141]Next, after a releasing agent is applied to the master plate, a heat-curable dimethylsiloxane resin (trade name: SYLGARD184, manufactured by Dow Coning Asia Ltd.) is poured into the master plate, allowed to stand for a fixed time, then subjected to defoaming under a vacuum for 10 minutes, and heated at 120° C. for 30 minutes to solidify the resin. The solidified resin is then released to produce a mold 80A having a concave p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com