Patents
Literature
80results about How to "Large refractive index" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
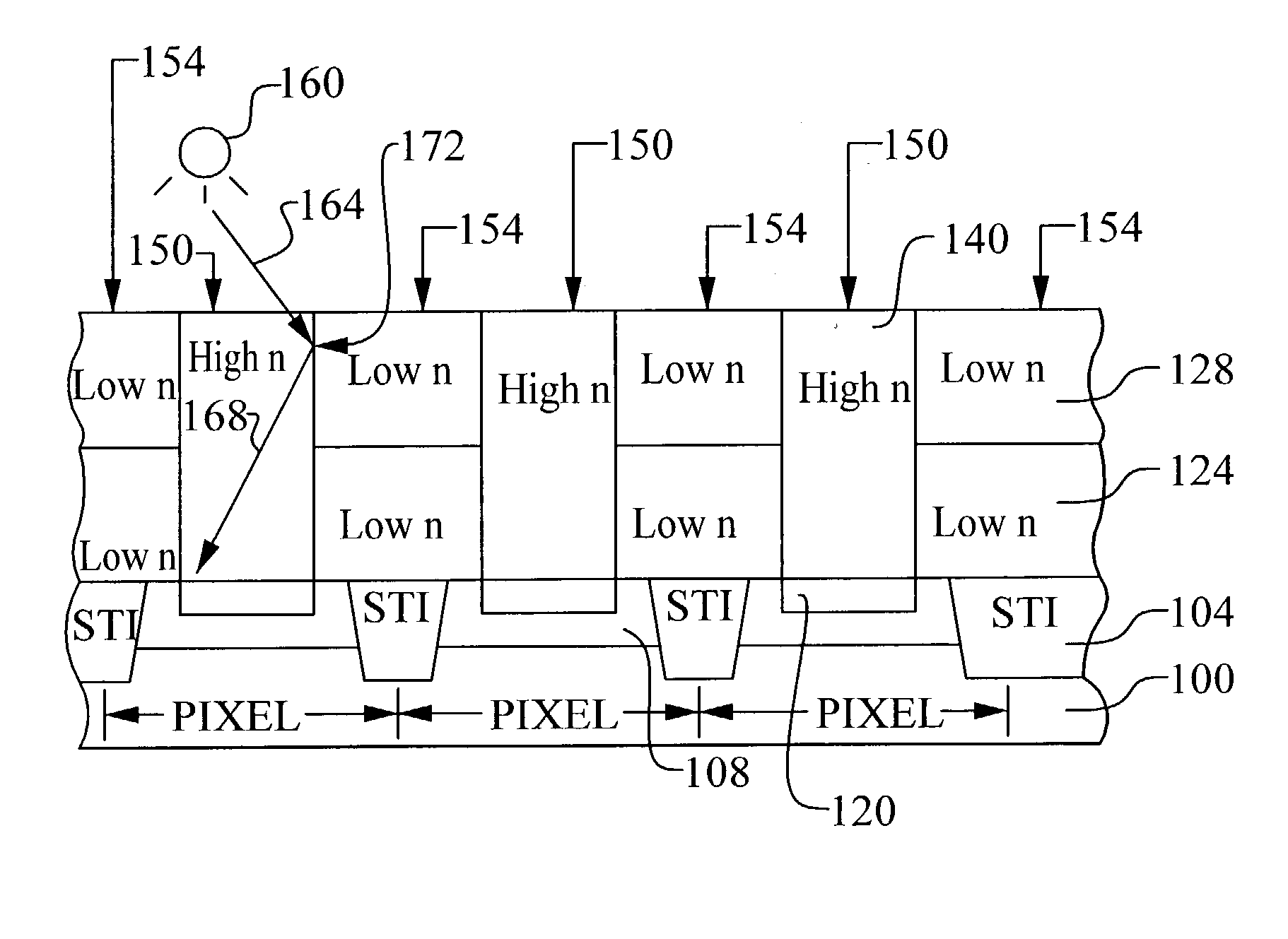
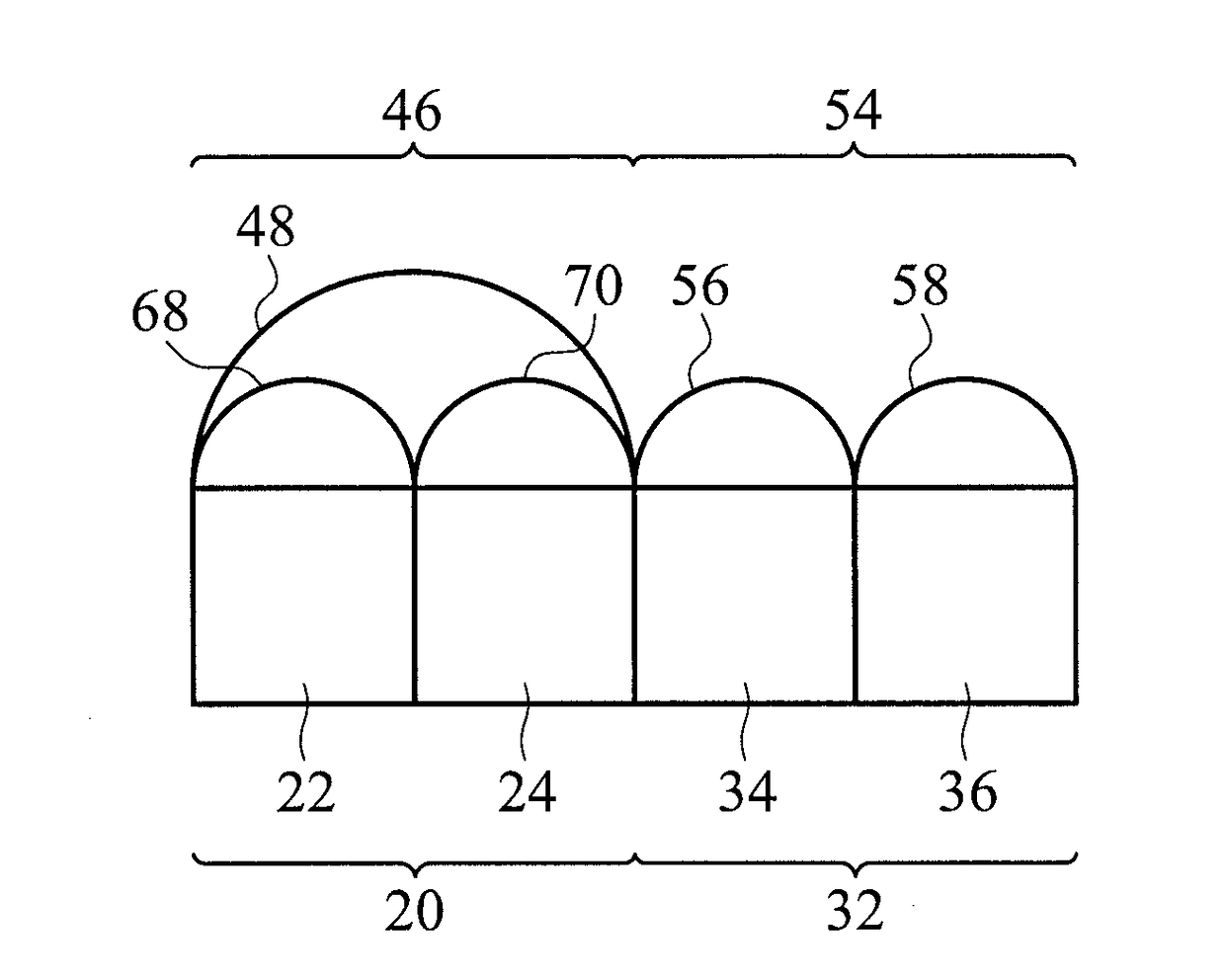
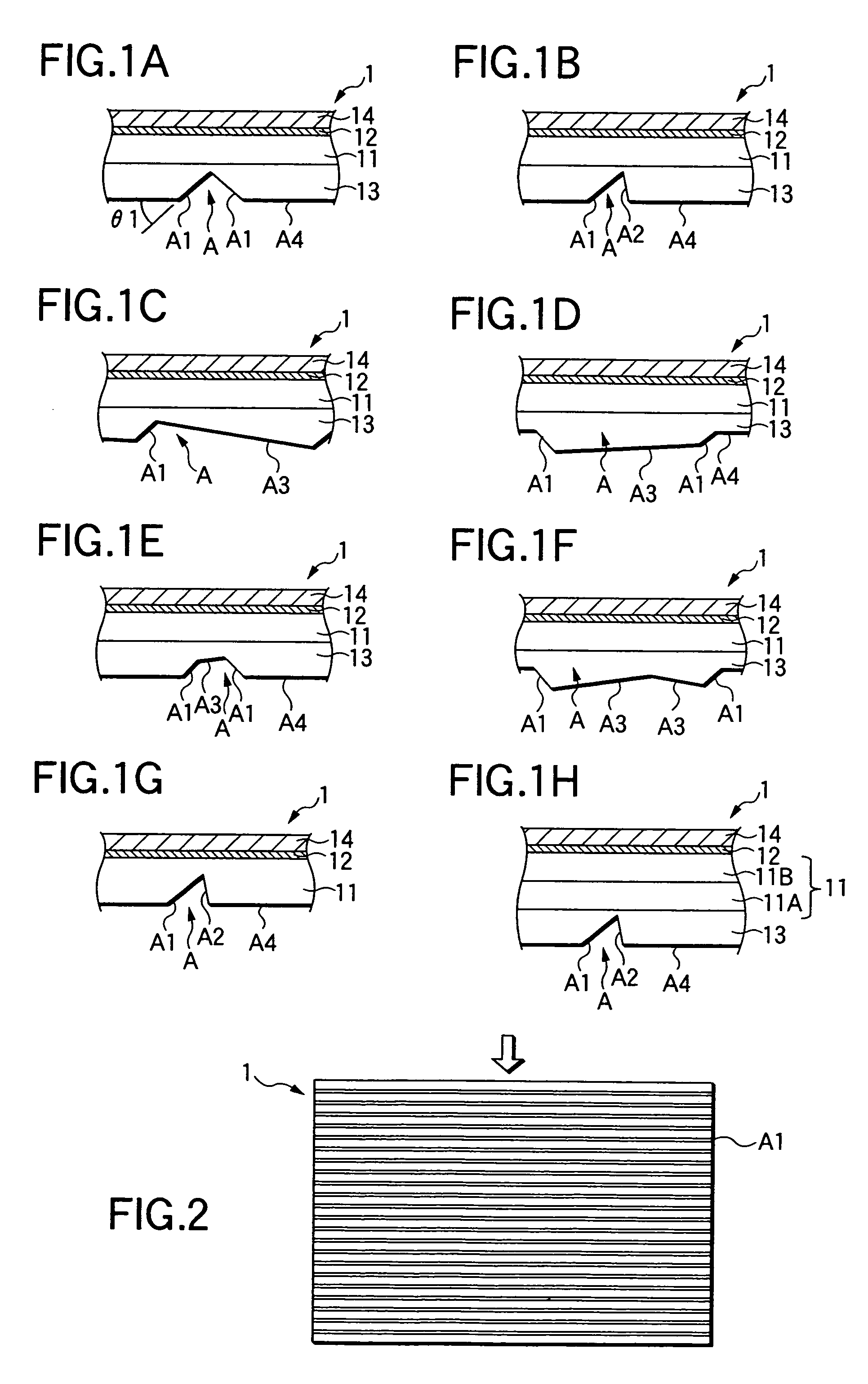
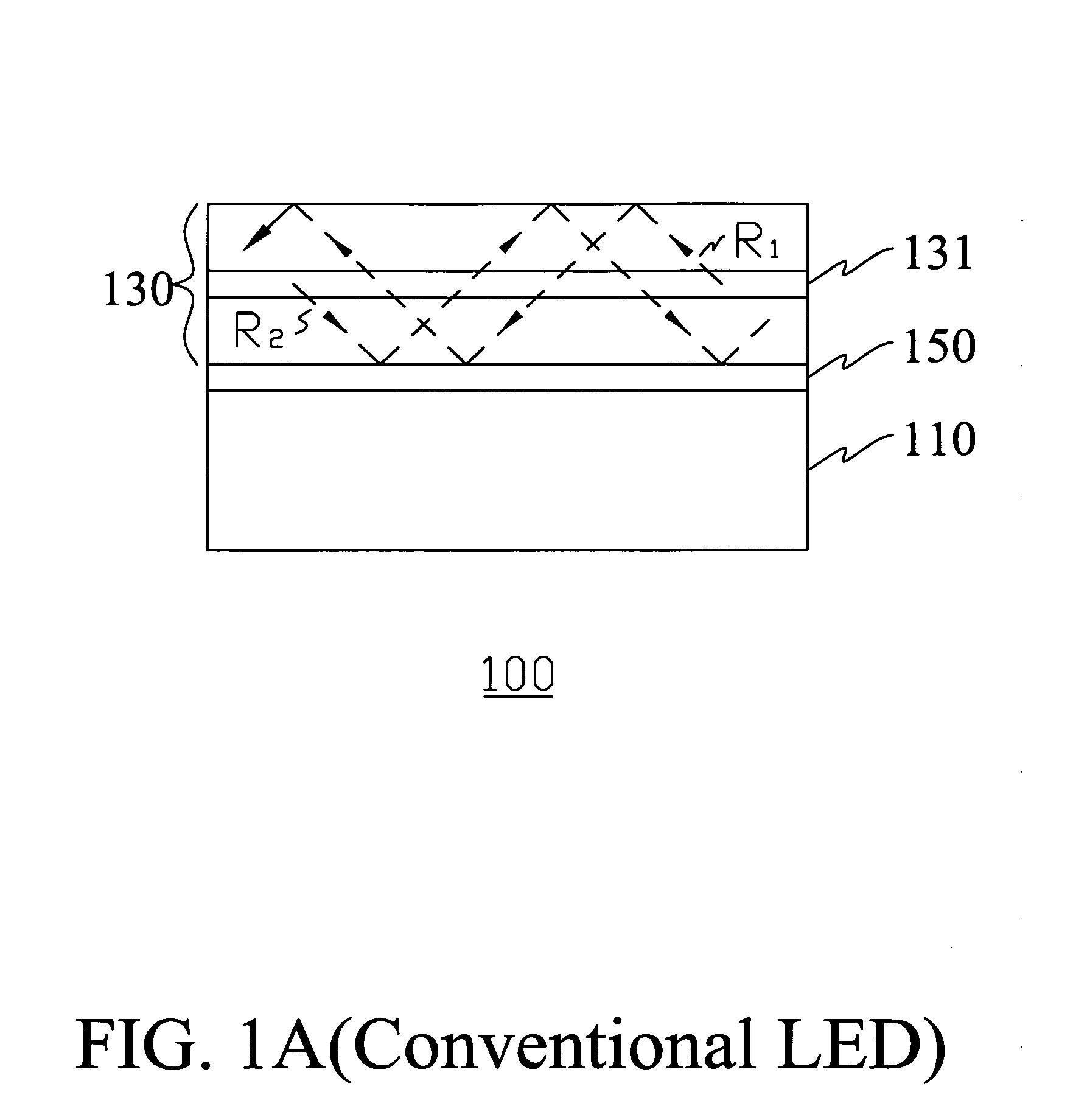
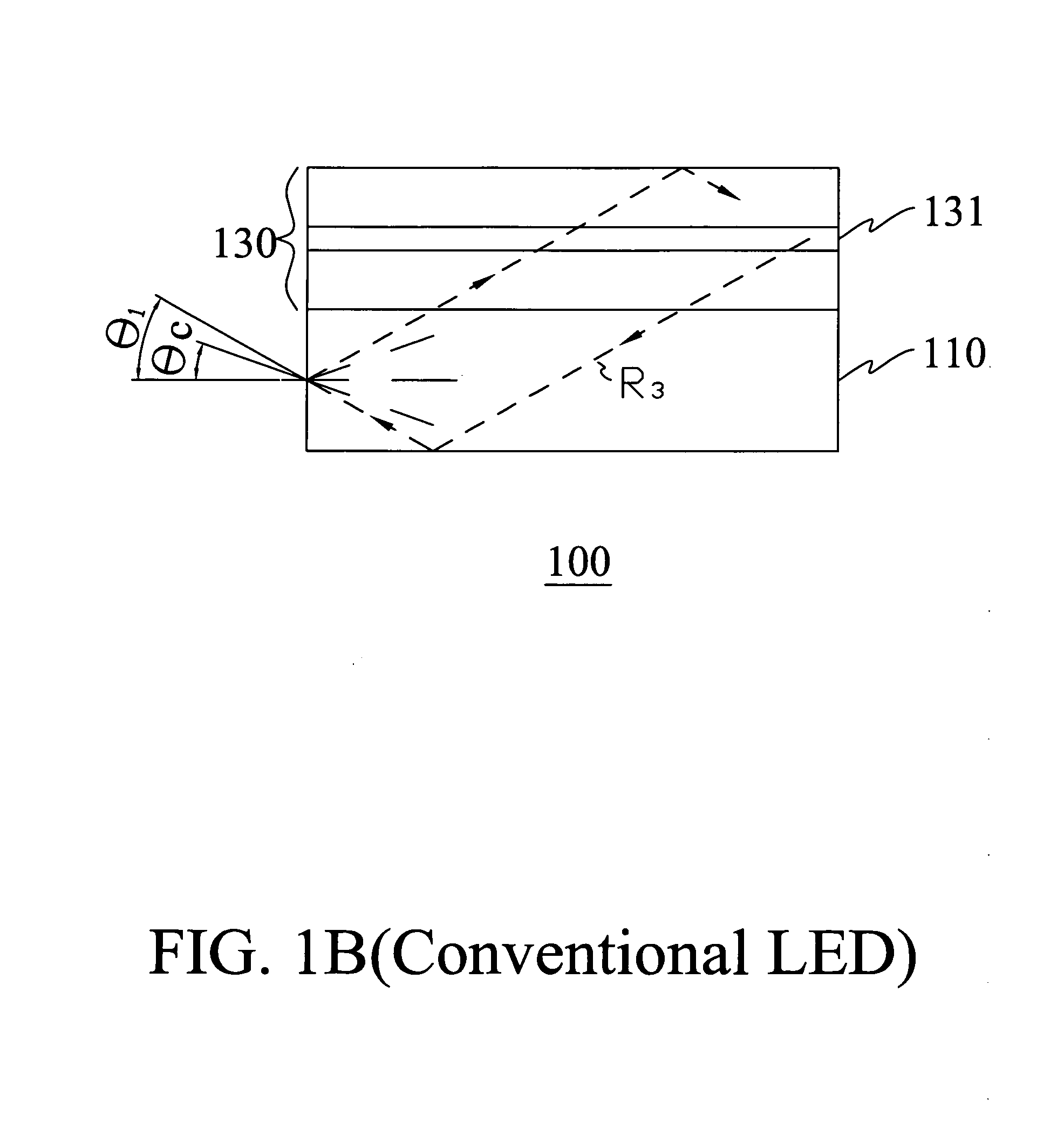
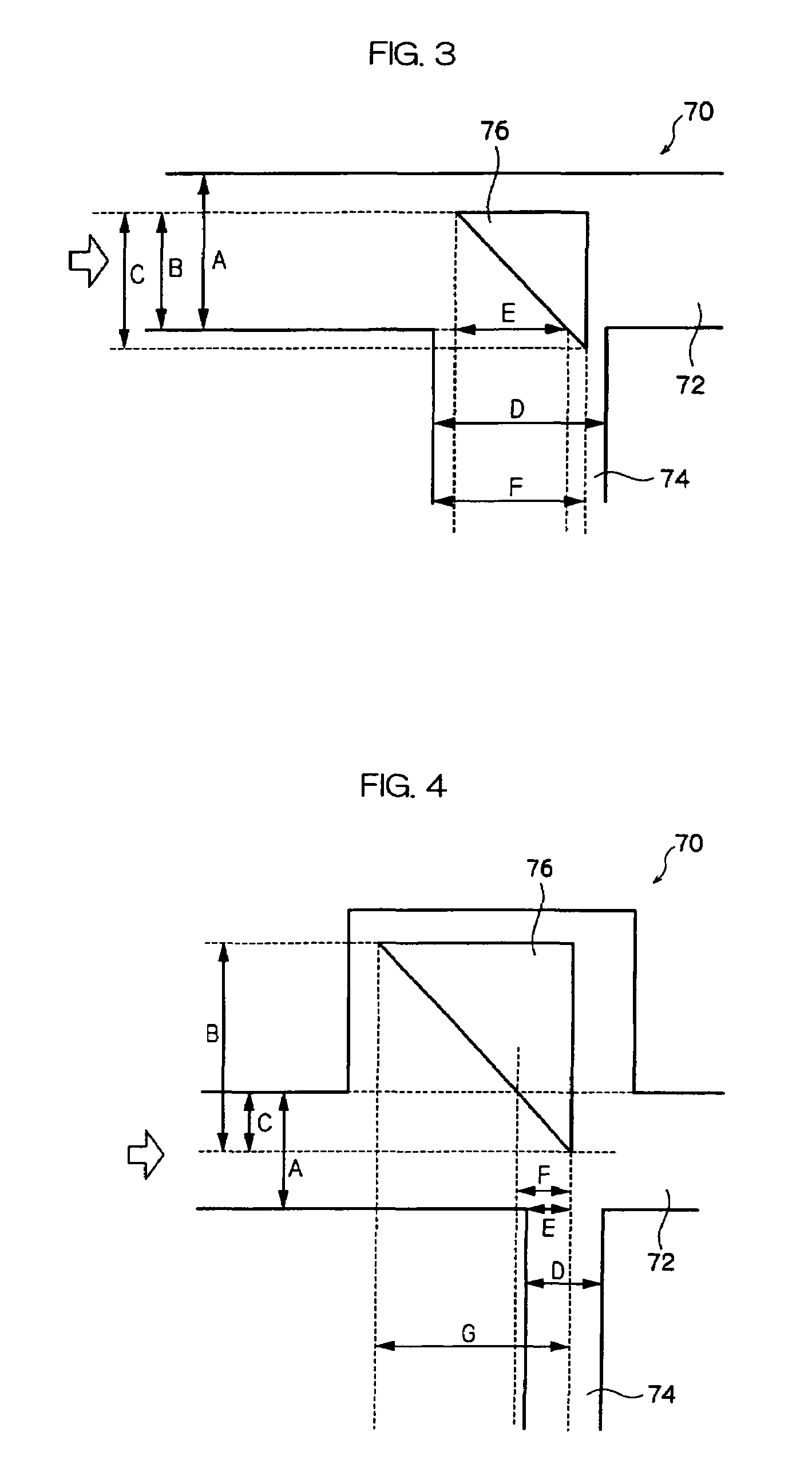
Light guide for image sensor
ActiveUS20040180461A1Avoid crosstalkImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLight guideRefractive index
A new method to form an image sensor device is achieved. The method comprises forming an image sensing array in a substrate comprising a plurality of light detecting diodes with spaces between the diodes. A first dielectric layer is formed overlying the diodes but not the spaces. The first dielectric layer has a first refractive index. A second dielectric layer is formed overlying the spaces but not the diodes. The second dielectric layer has a second refractive index that is larger than the first refractive index. A new image sensor device is disclosed.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method for producing high quality optical parts by casting
InactiveUS20060192307A1Quality improvementIncrease costOptical articlesPolymer sciencePolymer thin films
A casting method, rather than injection molding, to produce polymer optical components and systems is provided. The casting process controls shrinkage and stress, thus providing both high bulk uniformity and high quality, accurate surfaces, by incorporating polymer films into the mold. The films may remain incorporated into the part or may optionally be removed from the part after removal from the mold. In addition, the incorporation of separately produced components within the cast part is also provided, eliminating post-casting assembly manufacturing steps.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Light-scattering film and liquid crystal device using the film
InactiveUS20030117707A1Improve directivityBright enoughDiffusing elementsLayered productsAngle of incidenceLiquid-crystal display
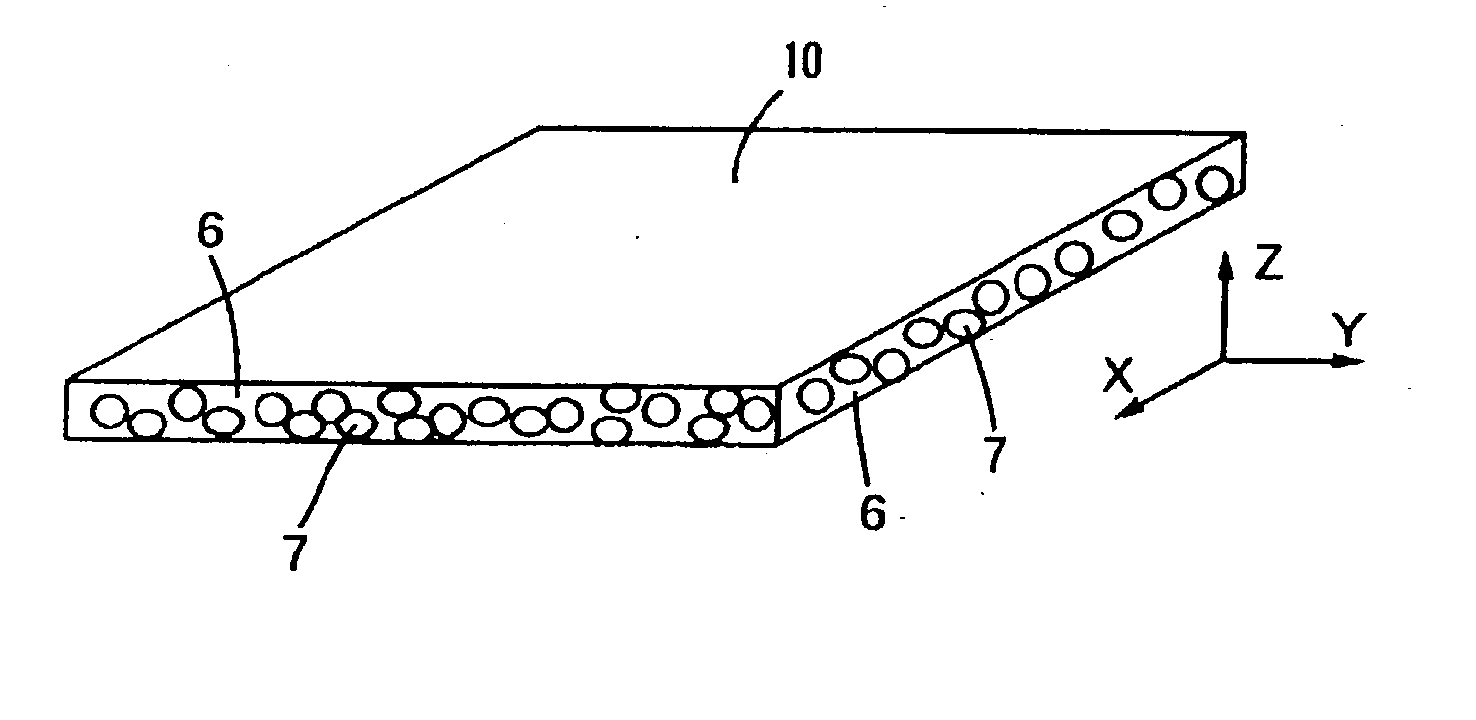
A light-scattering film 10 is obtained by subjecting a birefringent material in a resin layer to orientation treatment, in which at least one component selected from a transparent resin 6 and a scattering material 7 is the birefringent material (e.g., a birefringent resin, a liquid crystalline material). According to the light-scattering film, in the case where a linear polarized light in which a vibrating direction and a propagating direction exist in a plane containing a surface-directional axis of the film and a thickness-directional axis of the film is incident at a film surface, the rectilinear transmittance of the incident light shows maximum at an oblique incident direction to the film surface (e.g., incident angle of 20 to 89°). The rectilinear transmittance of the incident light from a direction perpendicular to the film surface is 0 to 30%, and the rectilinear transmittance of the incident light from an oblique direction having an incident angle of 40 to 70° to the film surface is 50 to 100%. Directivity in a light-scattering property of the light-scattering film is improved, and even when an incident light comes from an oblique direction, brightness of the display surface from a front direction is improved. Therefore, the film is useful for employing in combination with a polarized plate of the liquid crystal display apparatus.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD +1
Semiconductor light emitting device and semiconductor light emitting device module
InactiveUS20050201439A1Improve coupling characteristicsEffectOptical wave guidanceLaser active region structureRefractive indexOptical coupling
A semiconductor light emitting device capable of easy optical coupling to an optical fiber, etc. and excellent in high power operation characteristics is disclosed. The semiconductor light emitting device is provided by controlling the relation between the thickness and the refractive index of a clad layer and an optical guide layer.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Method and apparatus for use of beam control prisms with diode laser arrays
InactiveUS6975465B1Shorten physical lengthHigh densityPrismsLaser optical resonator constructionLaser arrayPrism
The subject invention relates to beam control prisms and the use of a beam control prism to modify the beam properties of light emitted from an edge emitting diode laser. The subject invention can utilize a beam control prism placed next to a diode laser bar. The subject beam control prism can have, for example, a curved surface and / or a high reflective coated surface for a diode laser wavelength. The curved surface can collimate the fast axis divergence and the mirror surface can change the beam direction. The subject curved surface beam control prisms can incorporate one or more features, such as parabolic reflecting surface, elliptical exit surface with flat reflecting surface, and a hyperbolic entrance surface with flat reflecting surface.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Organic electroluminescent device and display
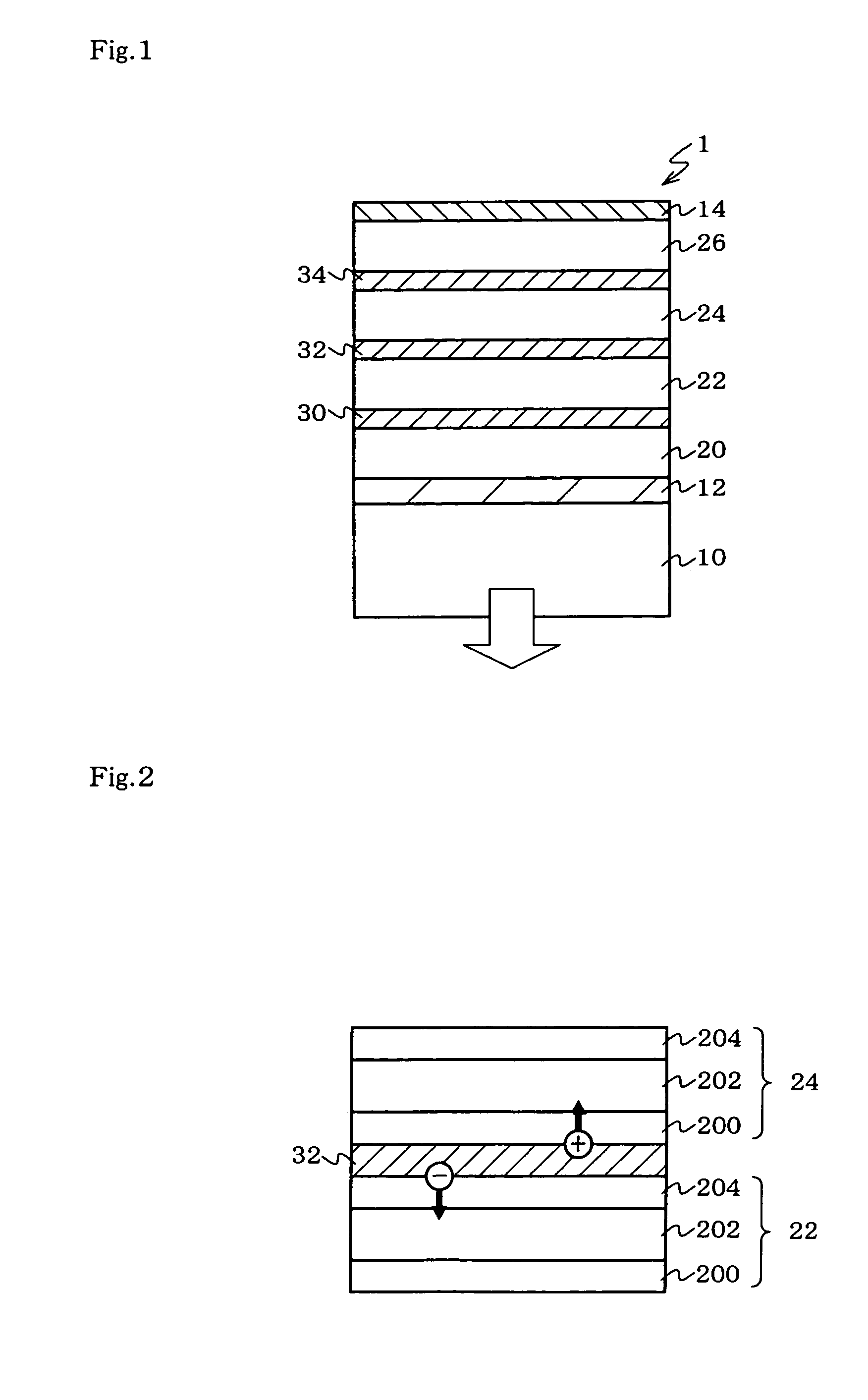
ActiveUS7358661B2Improve suppression propertiesReduced luminous efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceRefractive index
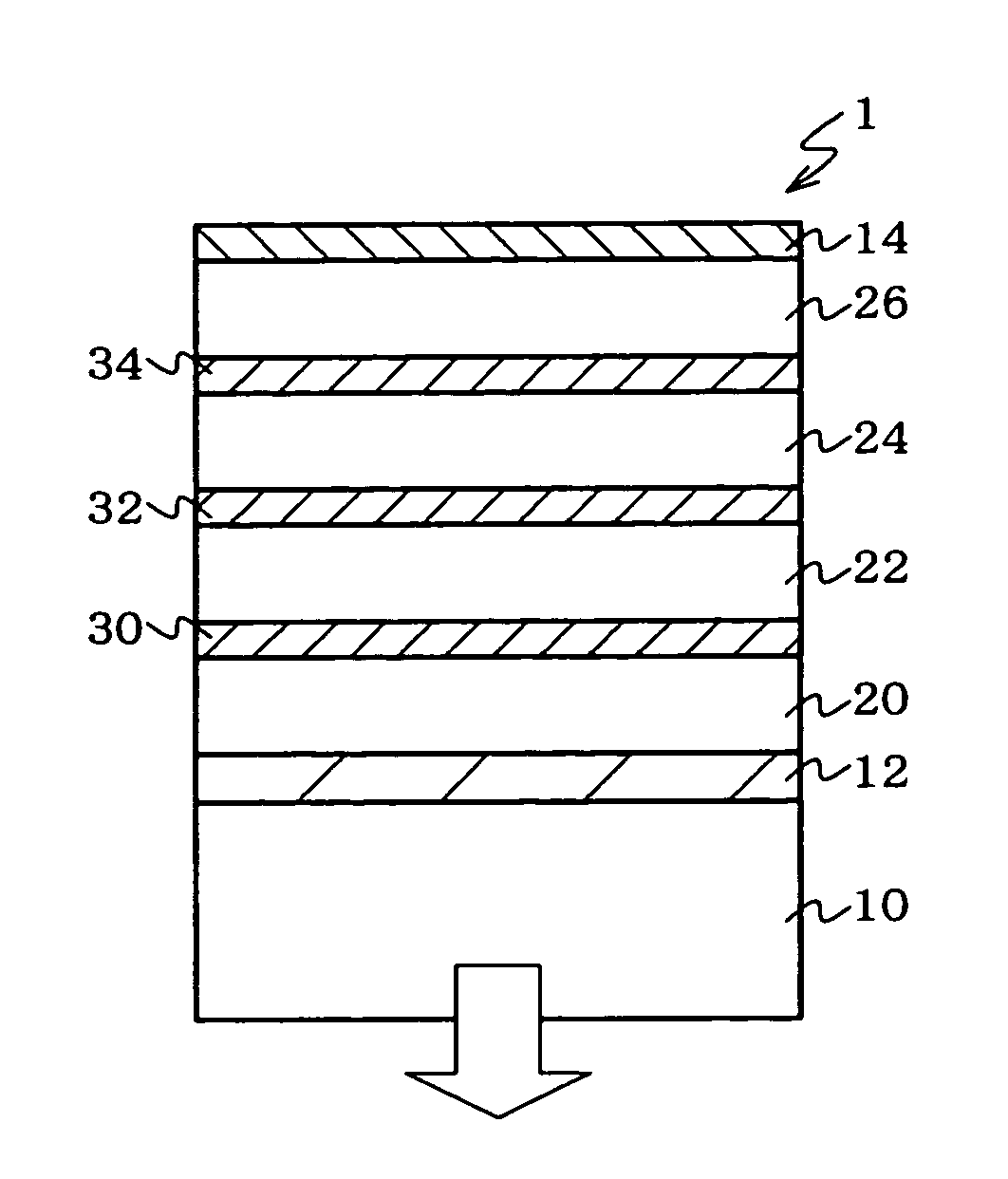
An organic EL device and a display with excellent viewing-angle properties and high efficiency are provided. An organic electroluminescent device (1) comprising: a transparent electrode (12), a counter electrode (14) arranged opposite to the transparent electrode (12), one or more intermediate conductive layers (30, 32 and 34) and one or more organic emitting layers (20, 22, 24 and 26) arranged between the transparent electrode (12) and the counter electrode (14), wherein the difference between na and nb is 0.2 or less when na is the refractive index of the intermediate conductive layer (30) and nb is the refractive index of the organic emitting layer (20).
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Radiation-emitting chip
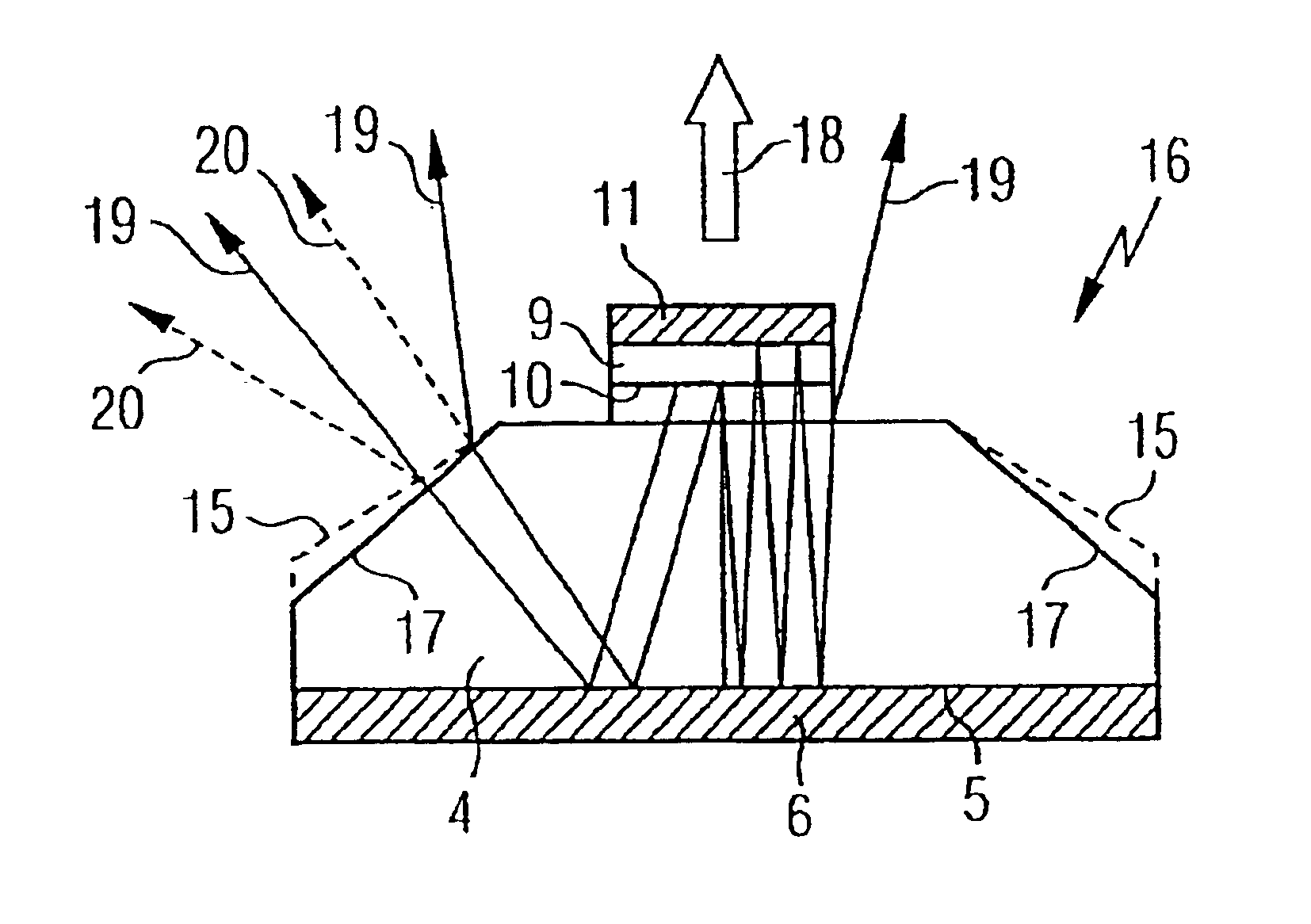
InactiveUS6897488B2Eliminate riskEasy to installSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCouplingOptoelectronics
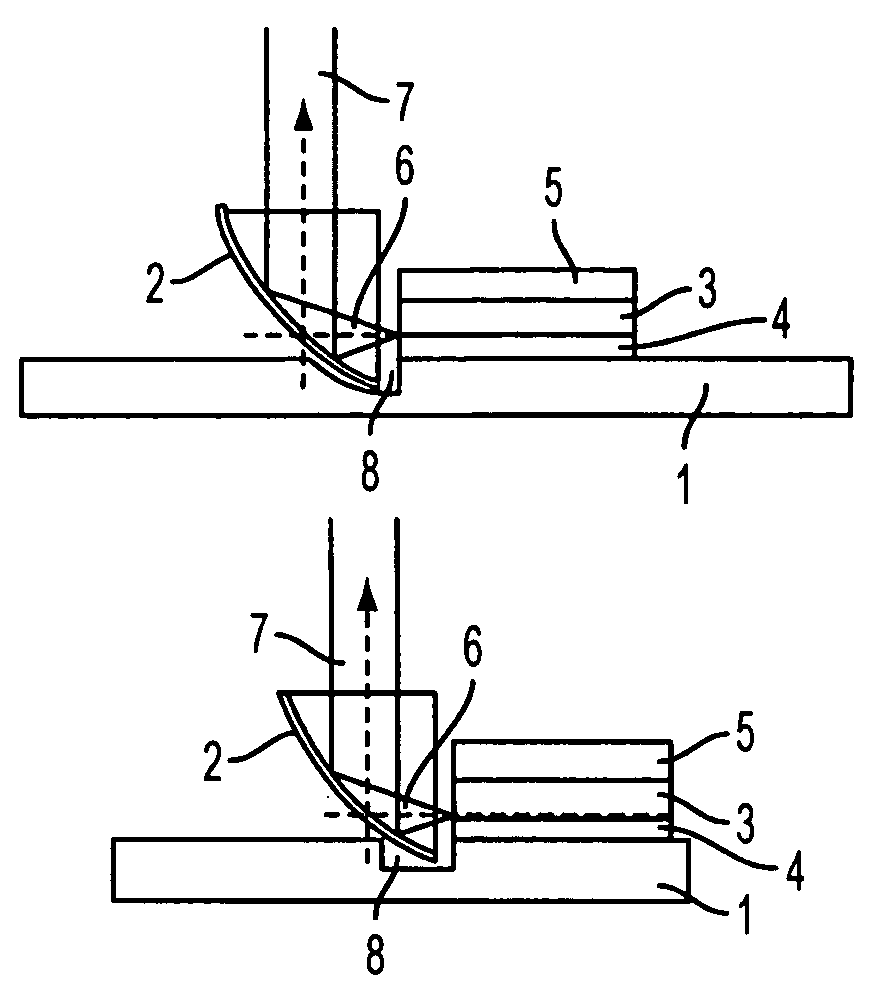
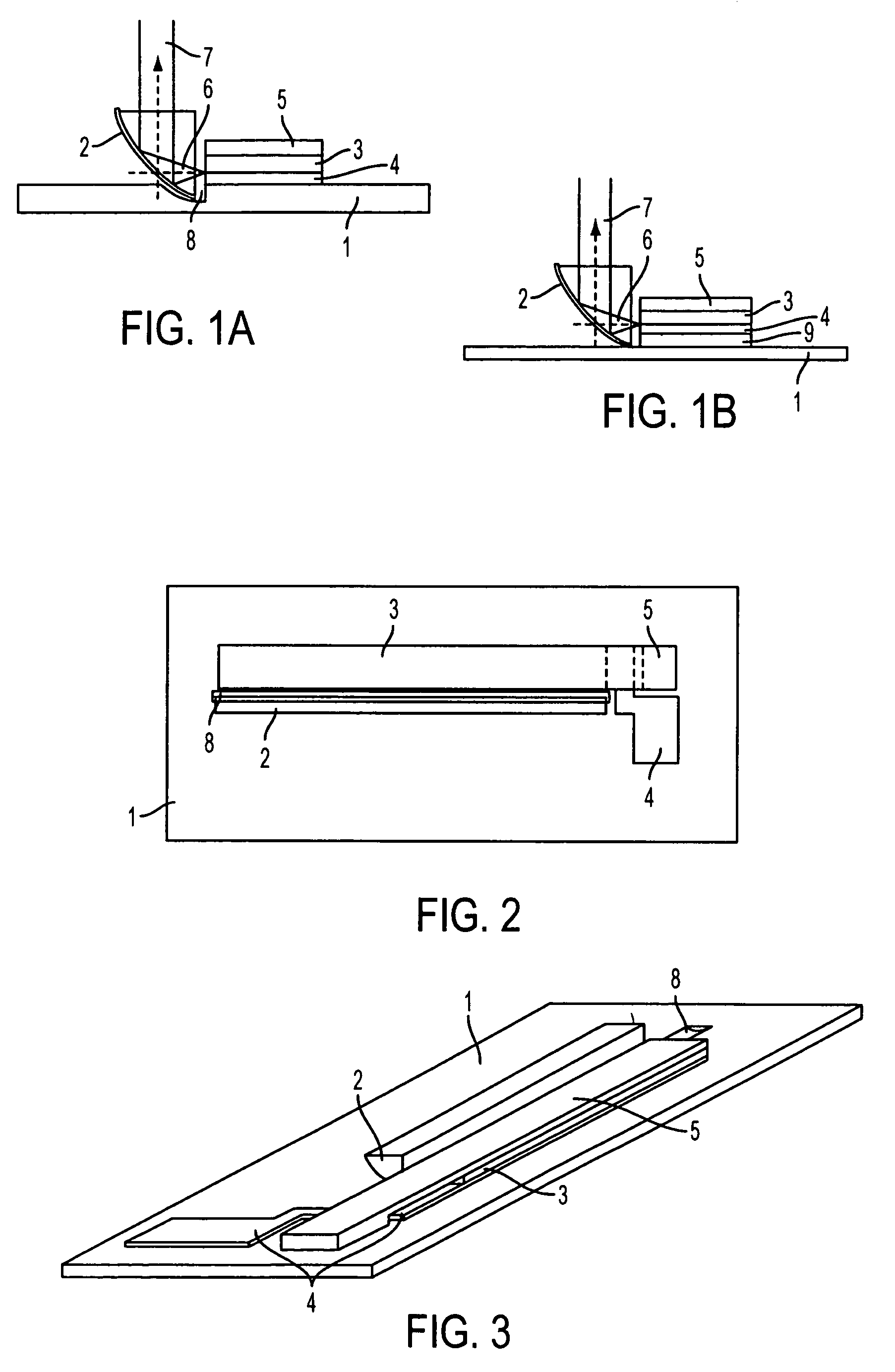
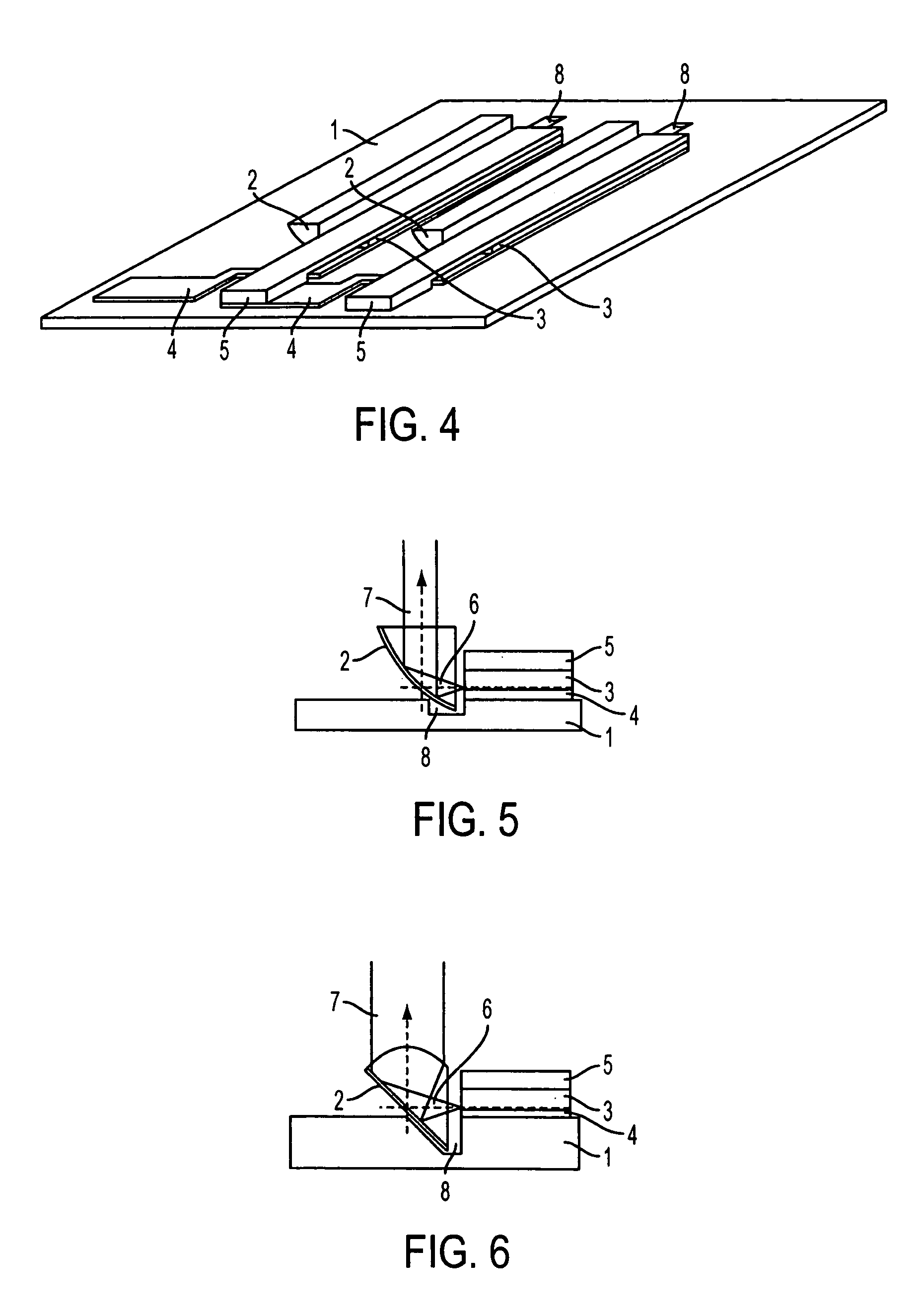
A light-emitting chip (3) has a lens-type coupling-out window (4), whose base area (5) is provided with a mirror area (6). Arranged on a coupling-out area (7) of the coupling-out window (4) is a layer sequence (9), with a photon-emitting pn junction (10). The photons emitted by the pn junction are reflected at the mirror area (6) and can leave the coupling-out window (4) through the coupling-out area (7).
Owner:OSRAM OLED
Photoirradiation device and fiber rod
ActiveUS7101072B2Low damping factorEfficient use ofMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceOptical axisLight beam
A photoirradiation device in which an optical system can be miniaturized and utilization efficiency of light can be improved in a manner that includes a first lens and a second lens, which share refraction of light to convert light beams emitted from a plurality of light sources into the light beams substantially parallel to an optical axis, and a third lens focusing the light beams from the second lens on an incident surface 20A of a lightguide 20. A fiber rod which can output uniform light beams in a manner that includes a first rod having a single fiber and a second rod having a plurality of fibers.
Owner:GC CORP
Photonic Crystal Devices Using Negative Refraction
Negative refraction in photonic crystals and diffraction grating is used to design plano-concave lenses to focus plane waves. Microwave experiments are carried out to demonstrate negative refraction and the performance of these lenses. Demonstration of negative refraction of visible light is also performed for the grism. These lenses can be used in optical circuits, astronomical applications, etc.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
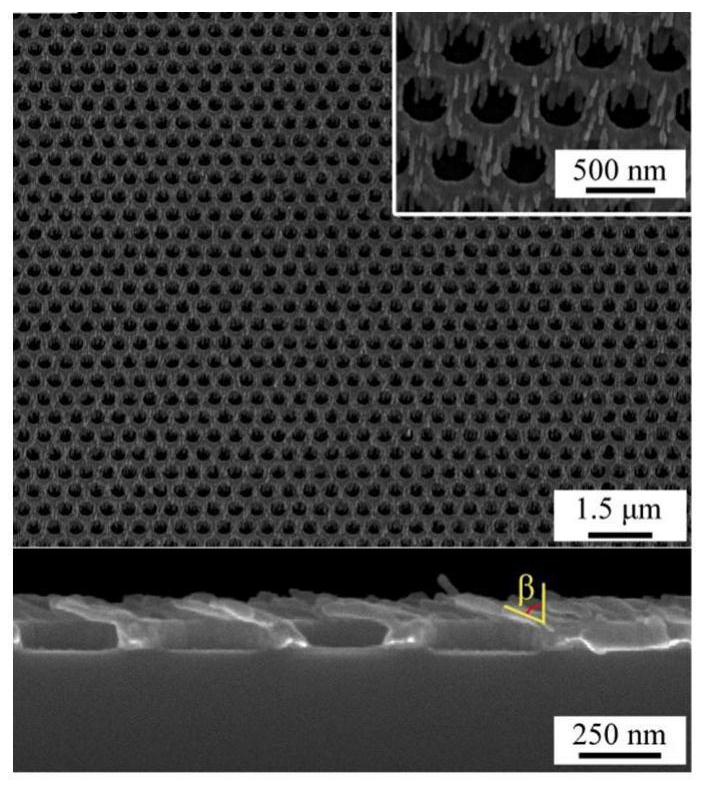
Optical waveguide and process for manufacturing the same
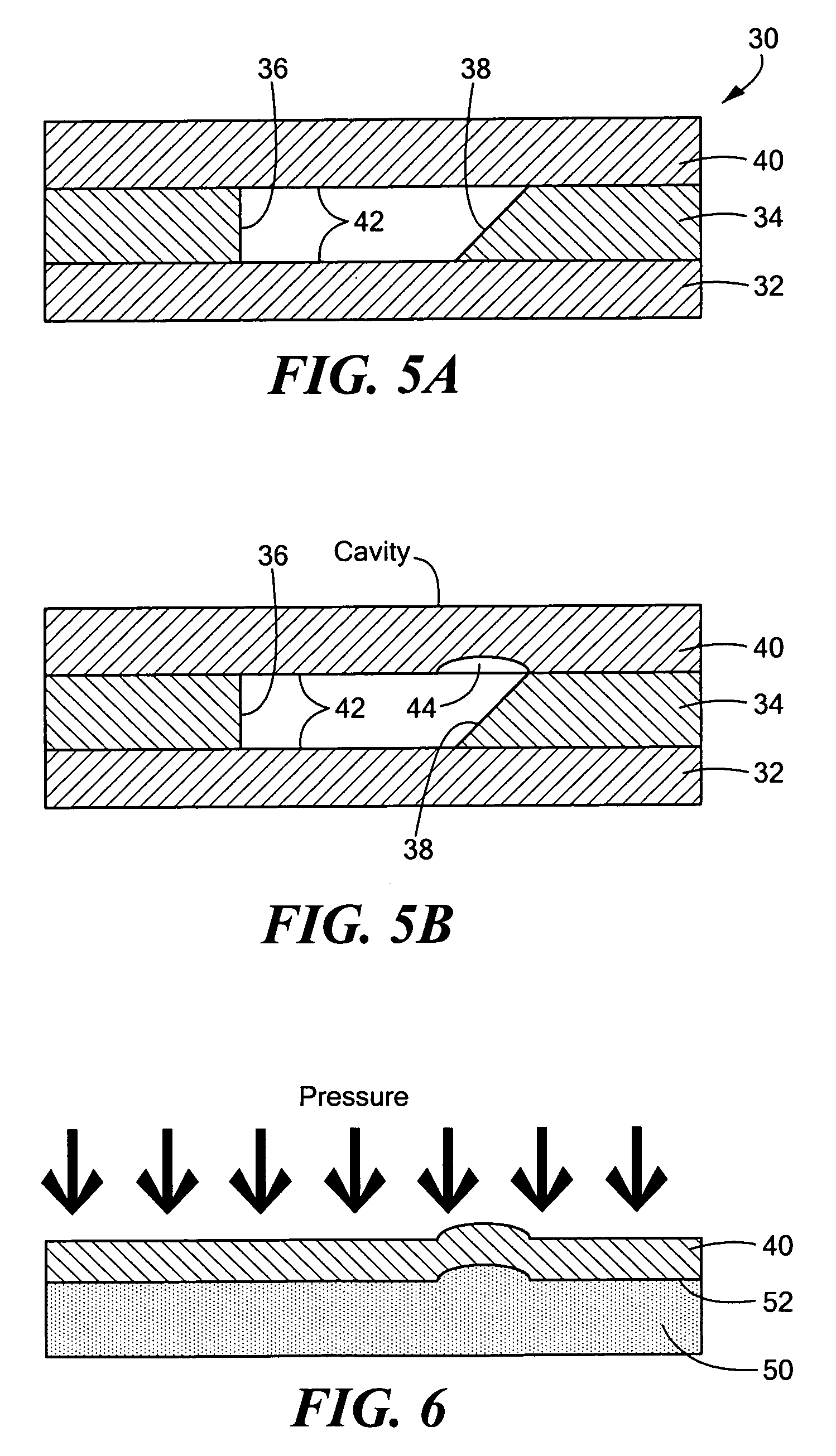
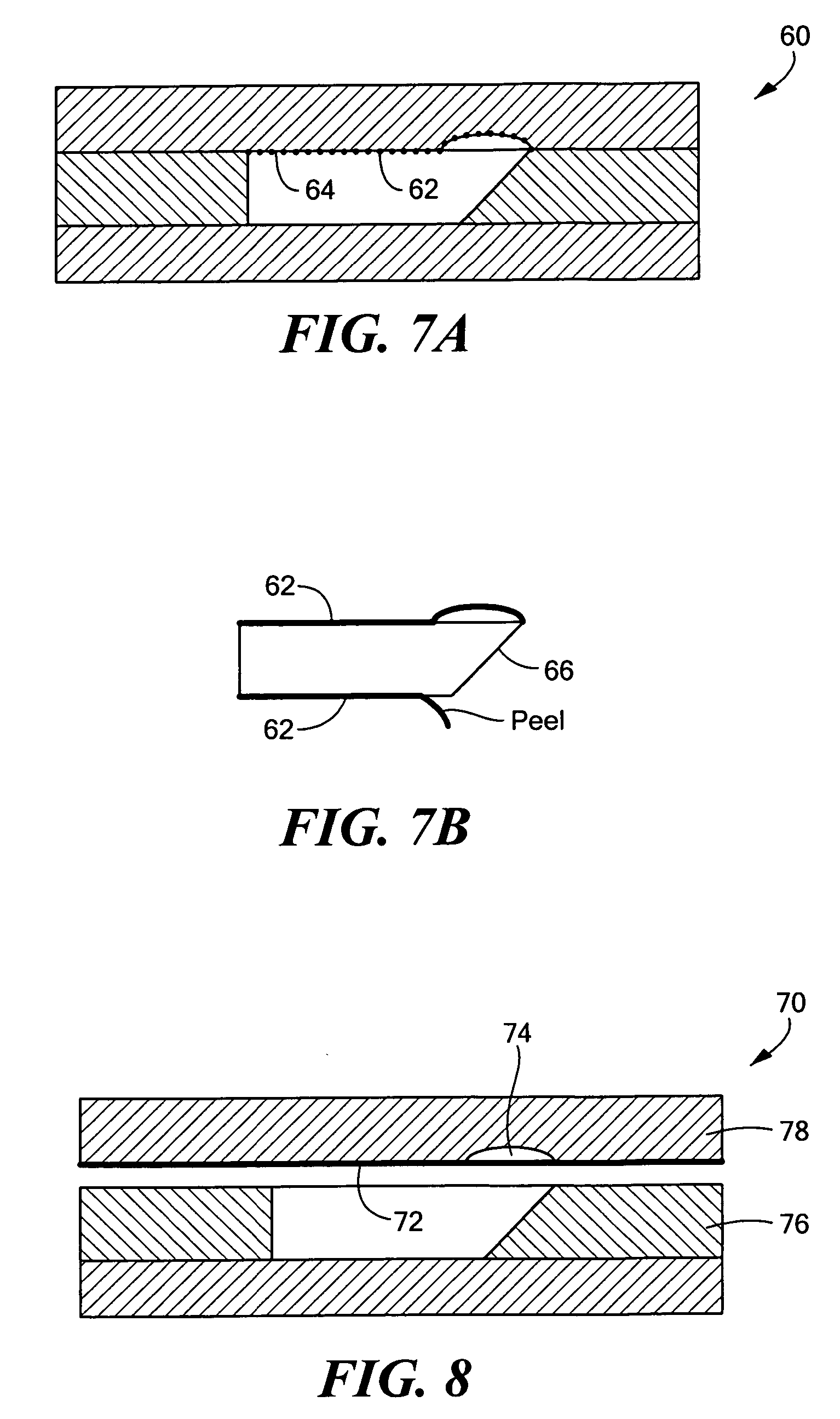
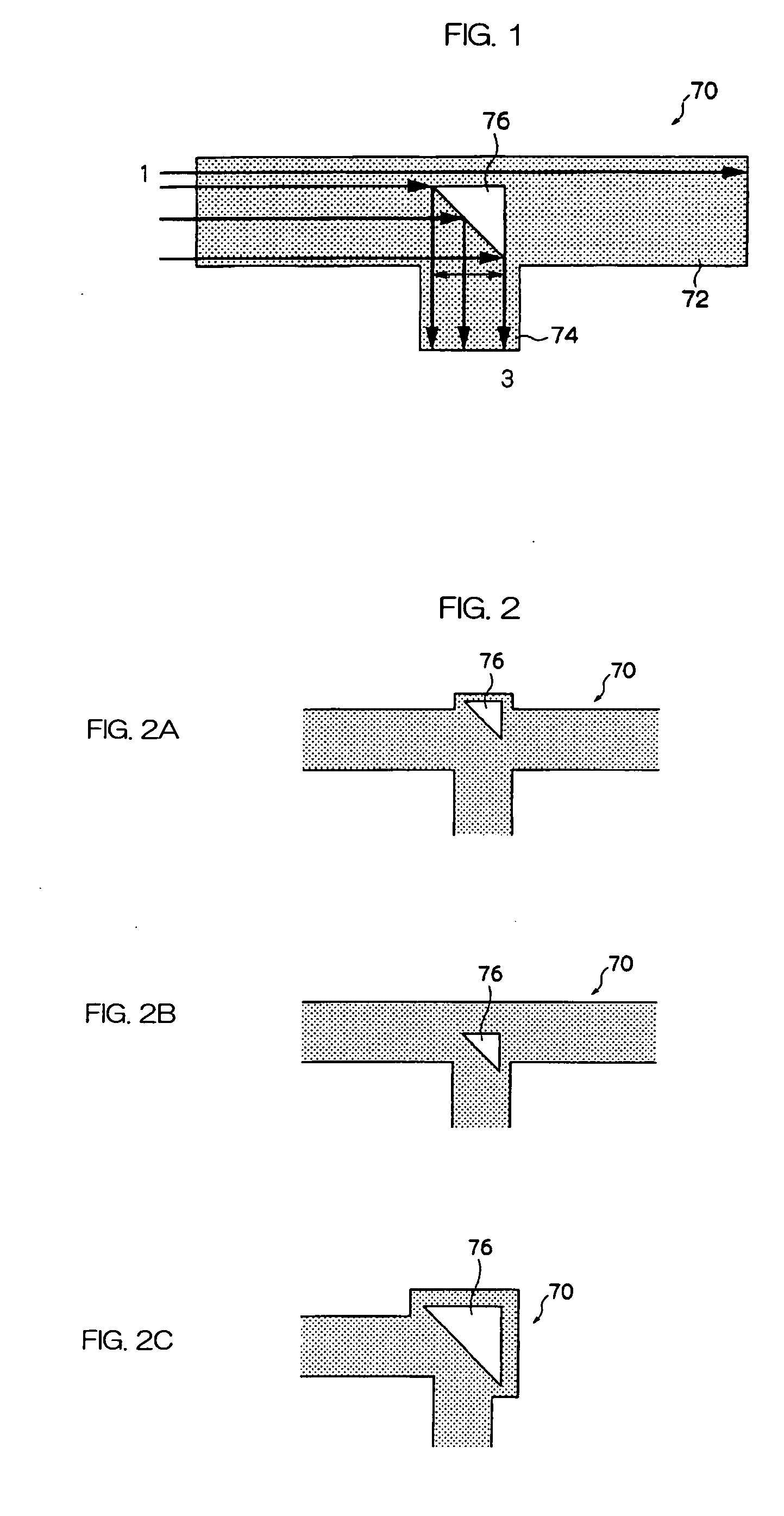
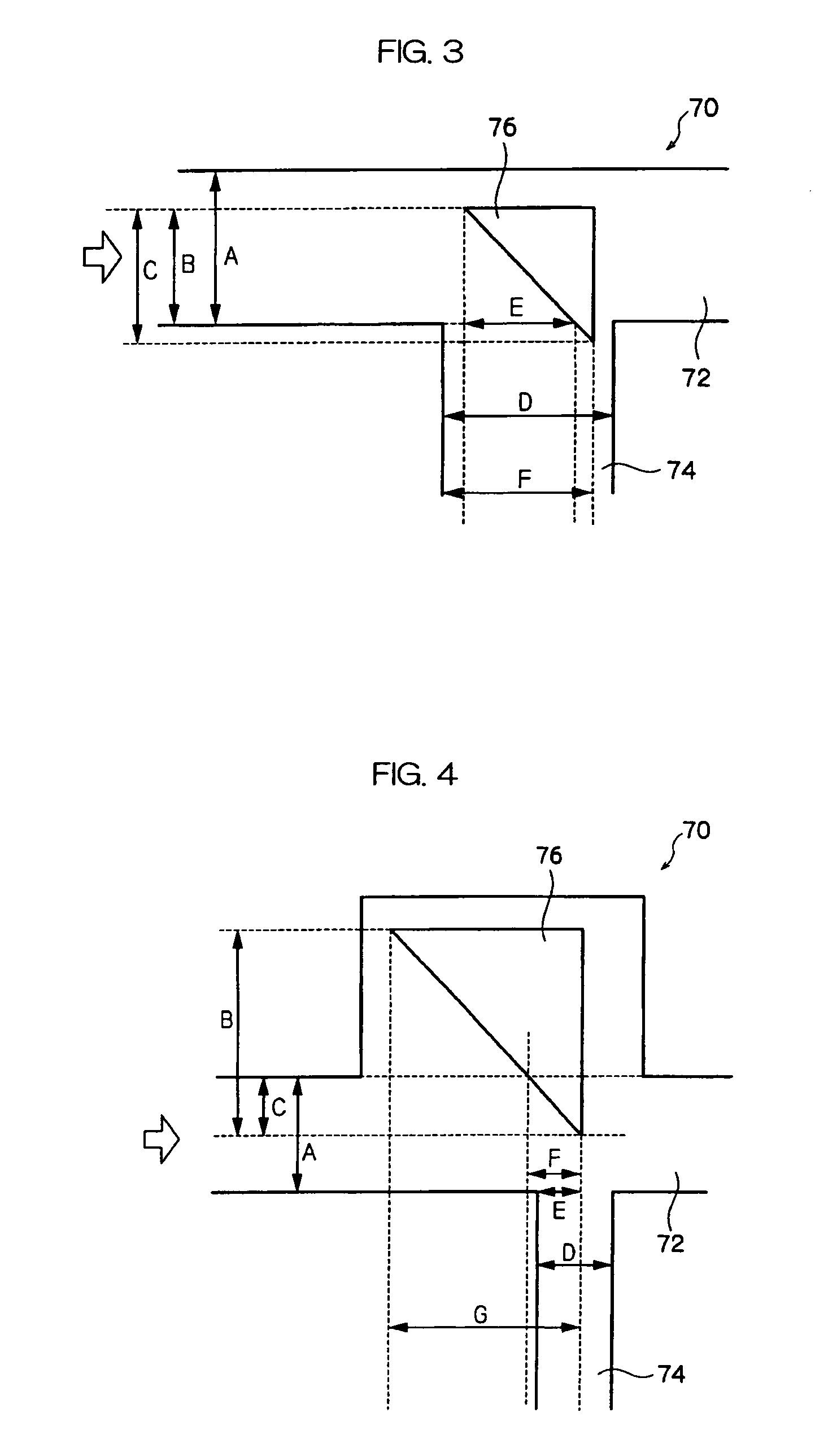
InactiveUS20060275004A1Large refractive indexLow costOptical waveguide light guideLight waveRefractive index
The present invention provides an optical waveguide, which at least includes: a waveguide core having a cavity therein; and a clad which encloses the periphery of the waveguide core and has a smaller refractive index than the waveguide core, wherein the optical waveguide changes a direction of a part or all of propagated light by using a part or all of an interface between the waveguide core and the cavity as a reflecting surface. The present invention further provides a method for manufacturing the optical waveguide, which at least includes: forming a core having a cavity therein on a substrate; applying an uncured clad material to a side surface and an upper portion of the core while maintaining the cavity which allows an atmospheric gas to be present in the cavity; and curing the clad material by heat or light to seal the gas in the cavity.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Optical compensation film, polarizing plate and liquid crystal display apparatus
ActiveUS20070132925A1Reduce contrastLarge refractive indexLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingLiquid-crystal displayFilm plane
An optical compensation film having: a retardation value Re in a film plane of the optical compensation film; and a retardation value Rth in a thickness direction of the optical compensation film, the retardation value Re and Rth being reduced by an elongation, satisfying the formulae (1) and (2) without the elongation, and satisfying the formulae (3) to (6) after the elongation: Re=0 to 30 nm (1) Rth=−50 to 50 nm (2) Re(n)=−500 to 0 nm (3) Rth(n)=−800 to 0 nm (4) Re(n)−Re(0)<0 (5) Rth(n)−Rth(0)<0 (6)
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Optical film and liquid-crystal display device
InactiveUS6917473B2Small thicknessLight weightPrismsMechanical apparatusIn planeLiquid-crystal display
An optical film has a transparent film, an adhesive layer provided on one surface of the transparent film, the adhesive layer having a refractive index different by 0.1 or less from that of a layer of the one surface of the transparent film, and a repetitive prismatic structure provided on the other surface of the transparent film, the repetitive prismatic structure having optical path changing slopes aligned in a substantially constant direction at an inclination angle in a range of from 35 to 48 degrees with respect to a plane of the transparent film. Another optical film has a transparent film having an average in-plane retardation of not larger than 30 nm, an adhesive layer provided on one surface of the transparent film, the adhesive layer having a refractive index different by 0.12 or less from that of a layer of the one surface of the transparent film, and the repetitive prismatic structure provided on the other surface of the transparent film. Still another optical film has a transparent film having a refractive index of not lower than 1.49, a transparent adhesive layer provided on one surface of the transparent film, the transparent adhesive means having a refractive index of not lower than 1.49, and the repetitive prismatic structure provided on the other surface of the transparent film.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
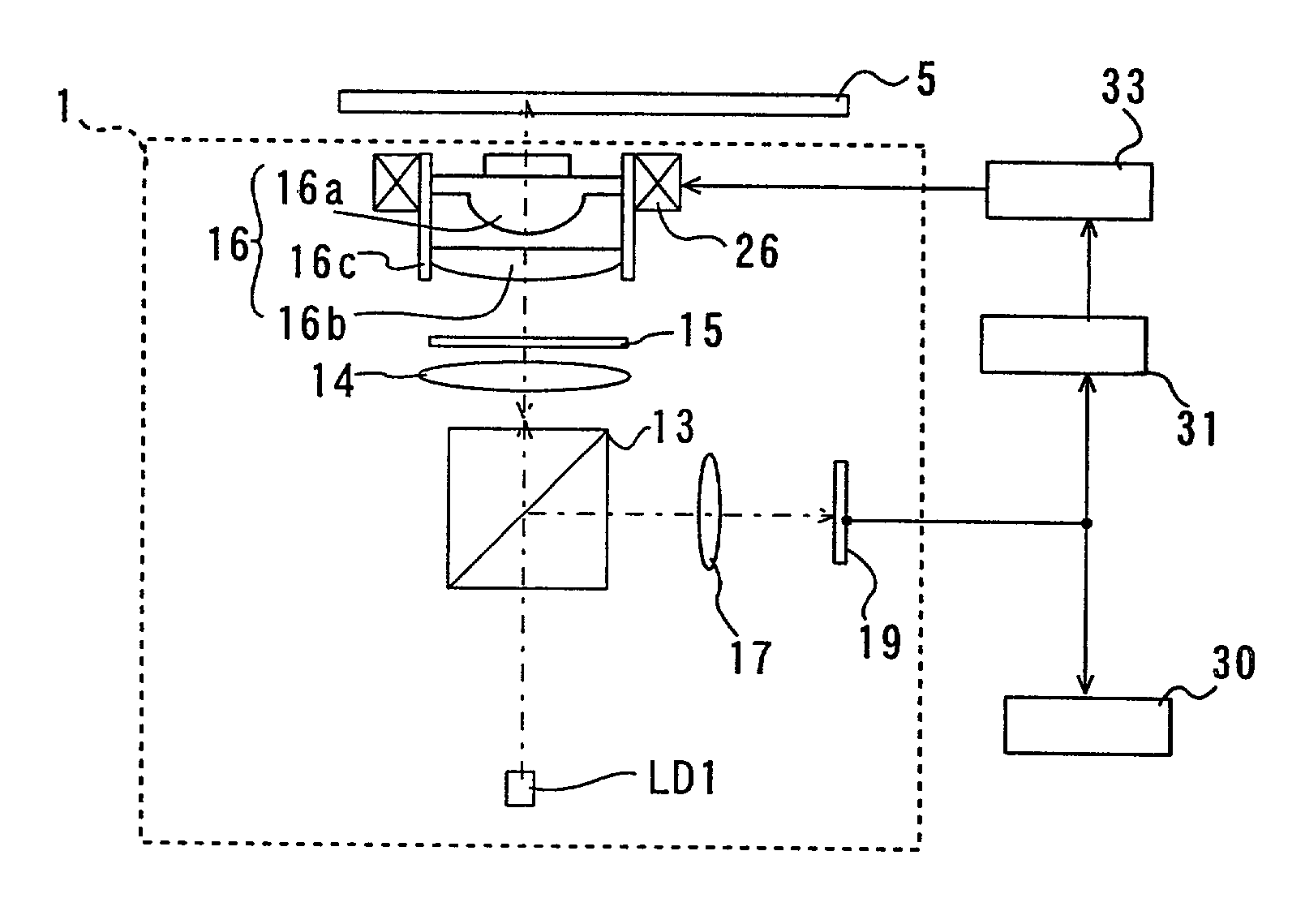
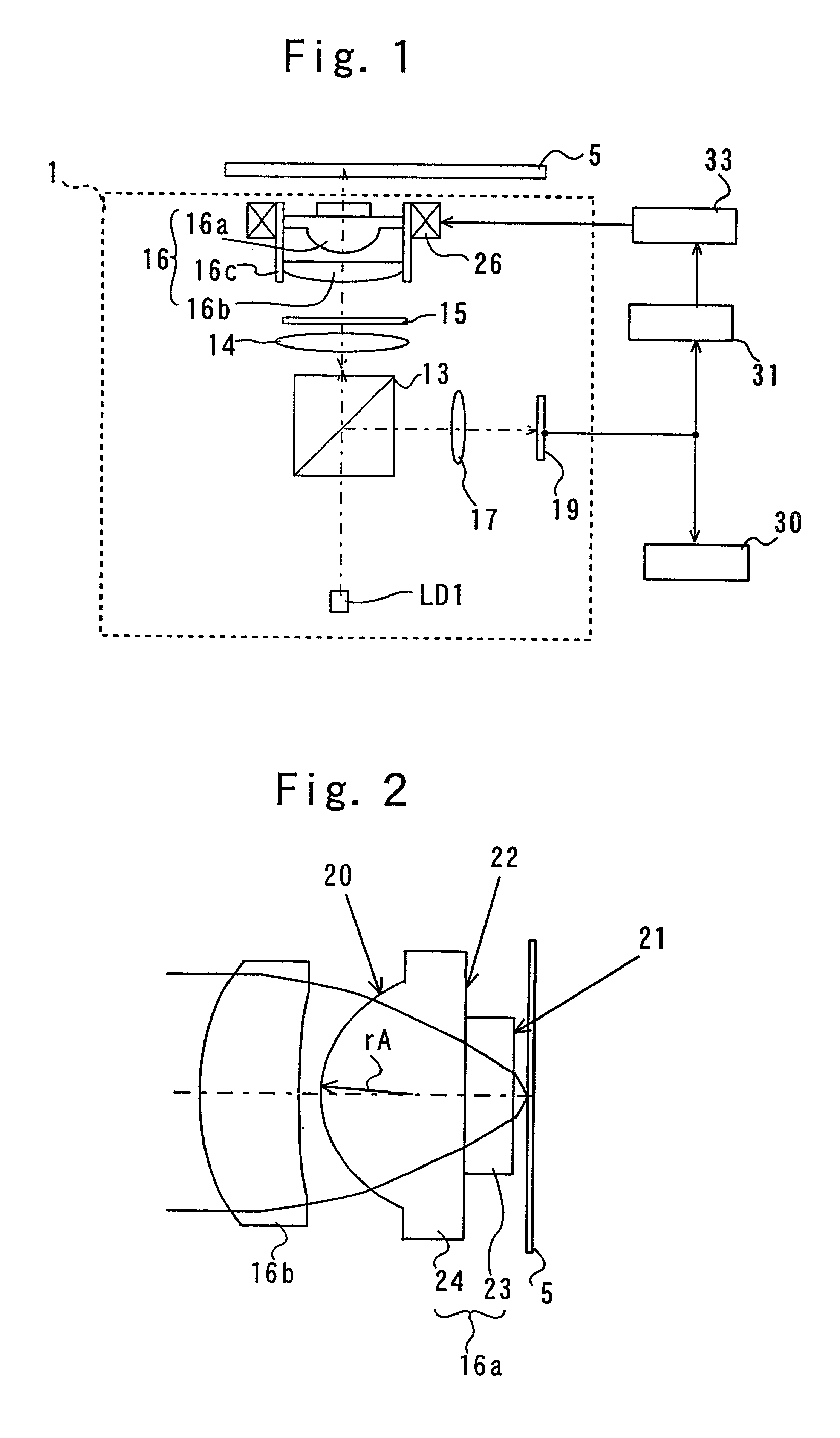
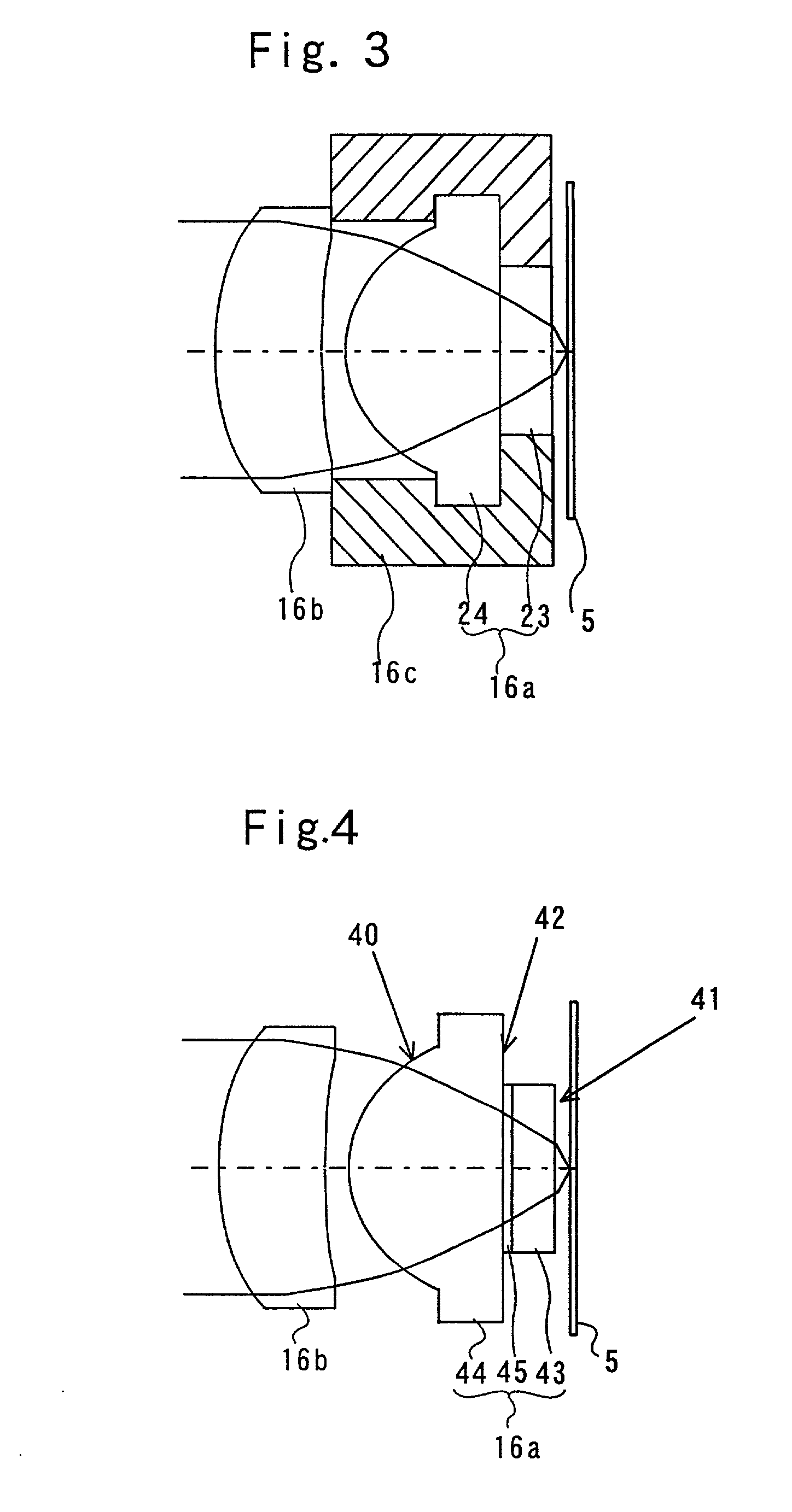
Complex objective lens and method for manufacturing the same and optical pickup device and optical recording/reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20020027863A1Large refractive indexImprove toleranceRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansOptical pickupLight beam
A complex objective lens includes a first optical element having a first surface including a convex aspherical surface shape and an opposite side surface opposing to the first surface; and a second optical element having an exit surface through which an optical beam passing and an entry surface opposing to the exit surface. The opposite side surface opposing to the first surface of the first optical element and the entry surface opposing to the exit surface of the second optical element are directly contacted to each other.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
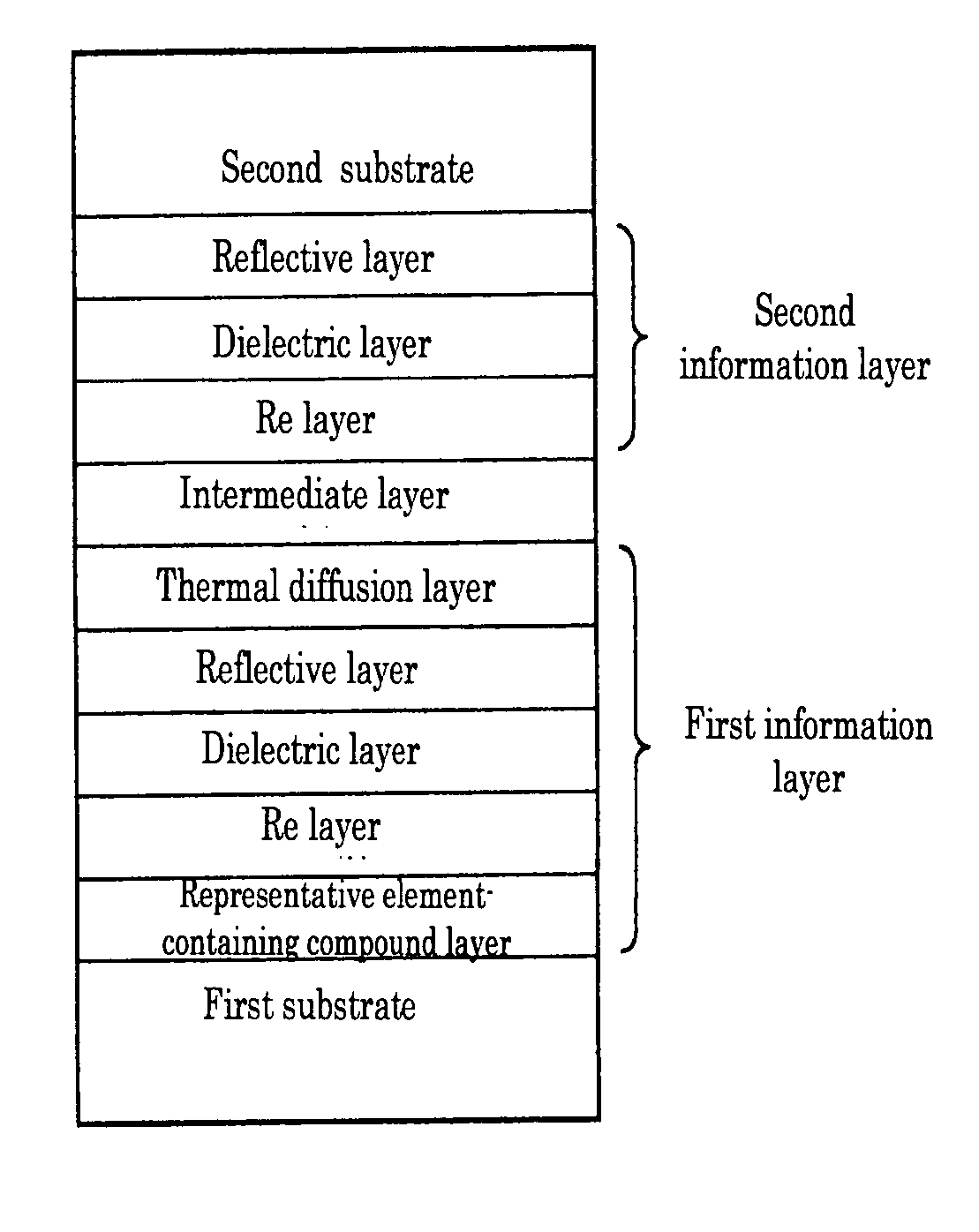
Dual-layer recordable optical recording medium
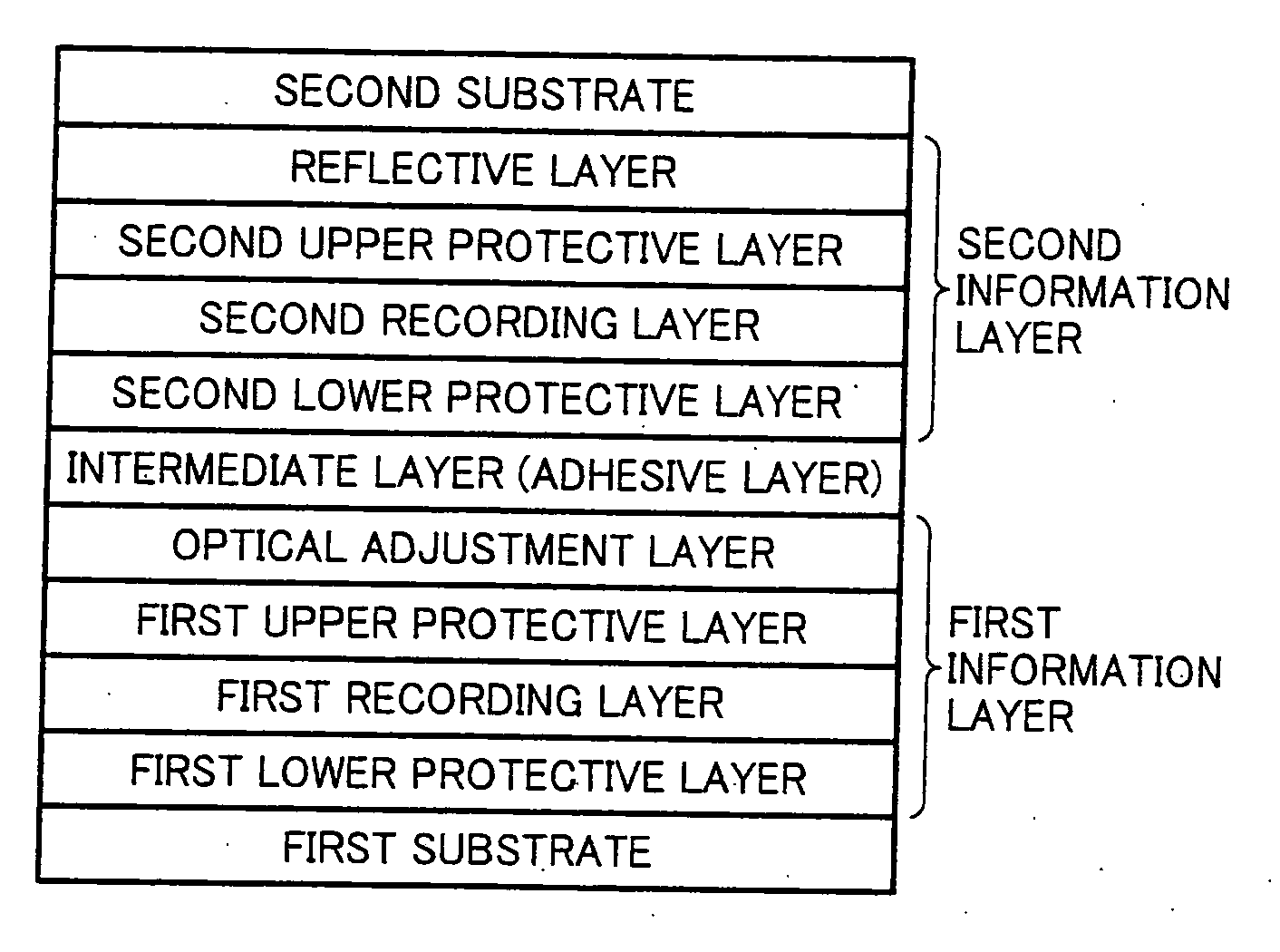
InactiveUS20070237064A1Improve recording characteristicImprove reflectivityMechanical record carriersRecord information storageInformation layerAdditive ingredient
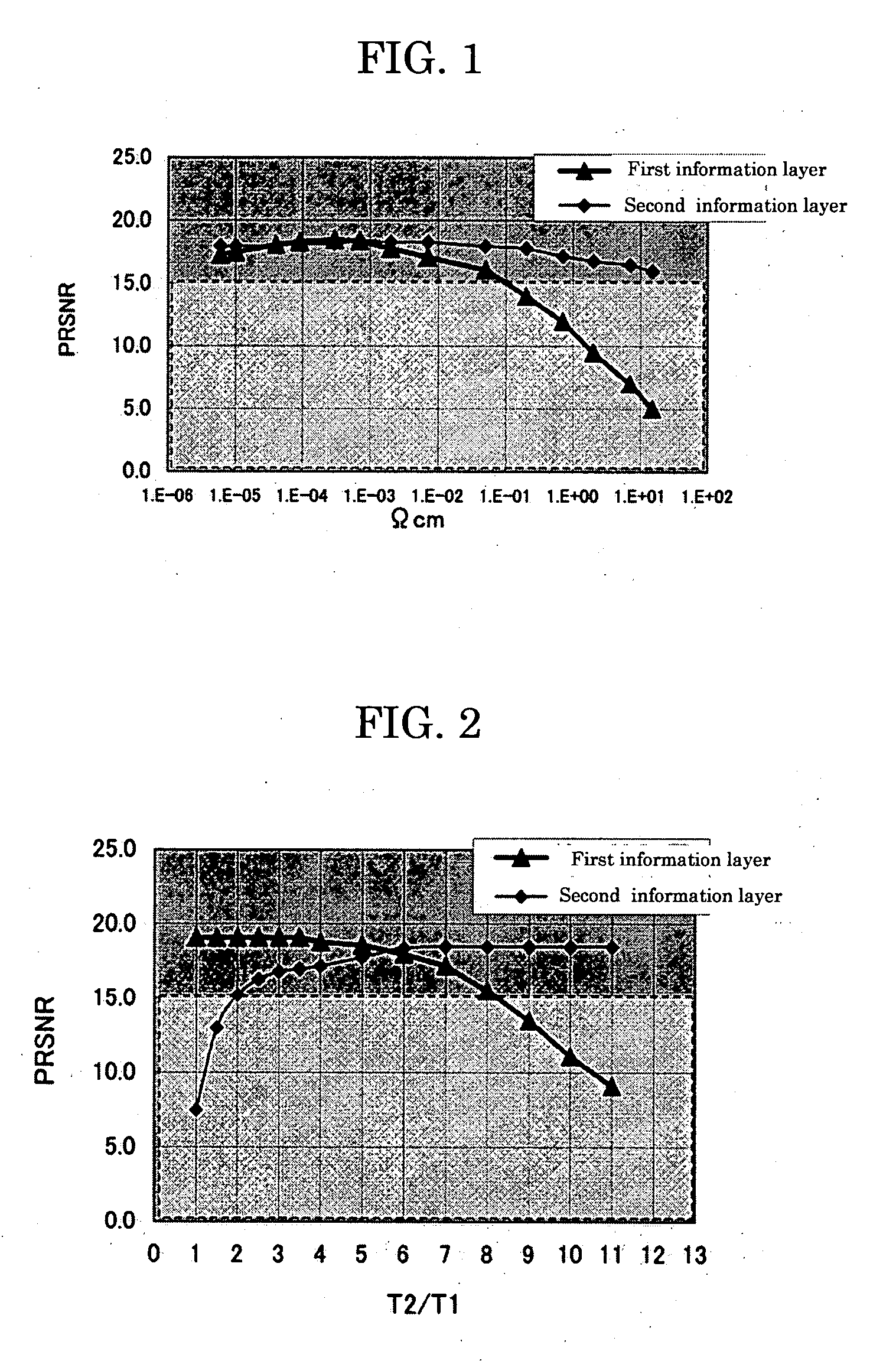
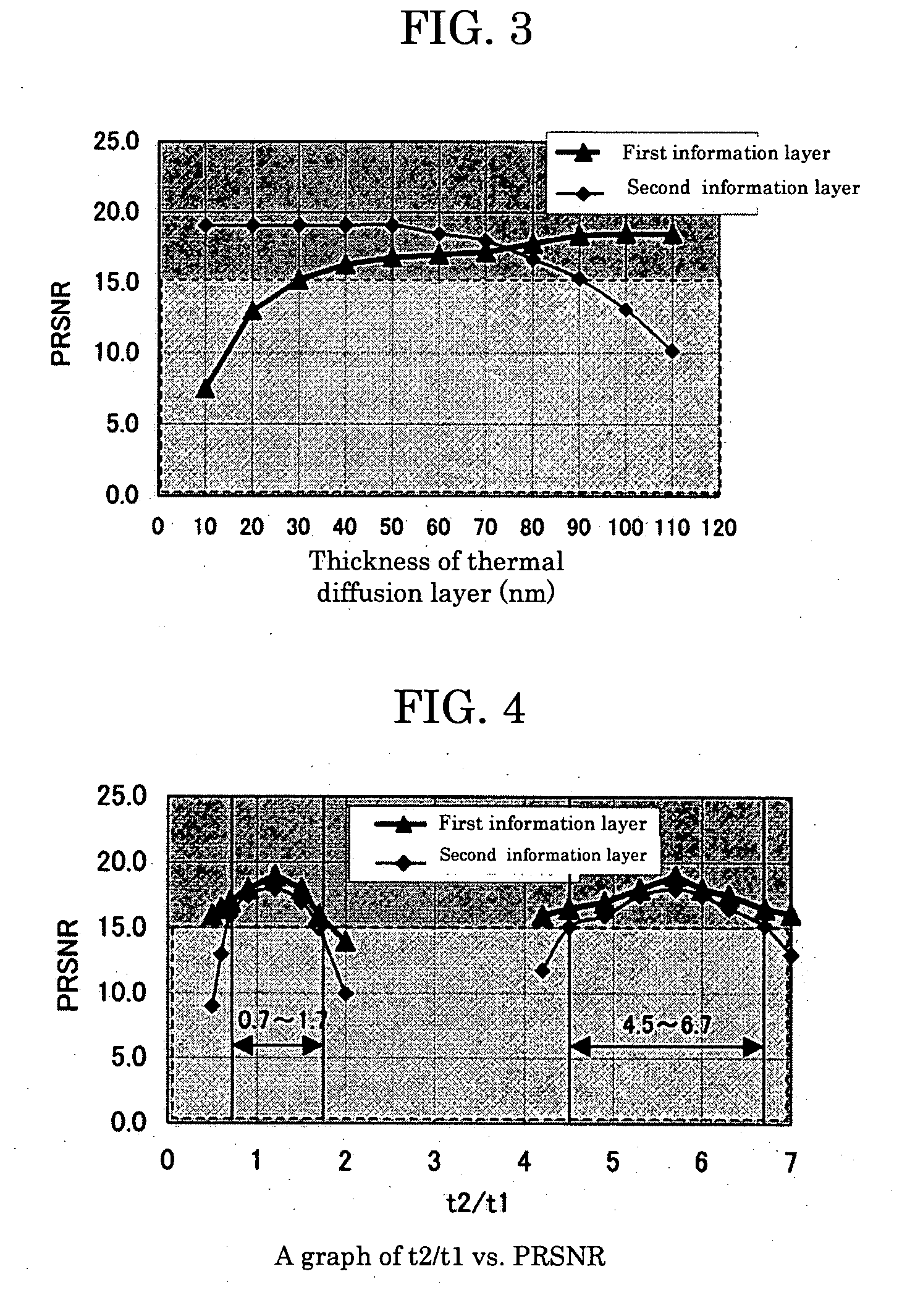
To provide a dual-layer recordable optical recording medium, including: a first information layer; intermediate layer disposed over the first information layer; and second information layer disposed over the intermediate layer, the first information layer, intermediate layer, and second information layer being sequentially deposited from a laser irradiation side, wherein the first information layer comprises, from the laser irradiation side, at least a thin film containing Bi as a main ingredient, dielectric layer, reflective layer and thermal diffusion layer, and the second information layer comprises, from the laser irradiation side, at least a thin film containing Bi as a main ingredient, dielectric layer and reflective layer, and wherein the ratio of the thickness of the dielectric layer of the second information layer (t2) to the thickness of the dielectric layer of the first information layer (t1), t2 / t1, is in a range of 0.7 to 1.5 or 4.5 to 6.0.
Owner:RICOH KK
Exposure system, exposure method and method for fabricating semiconductor device
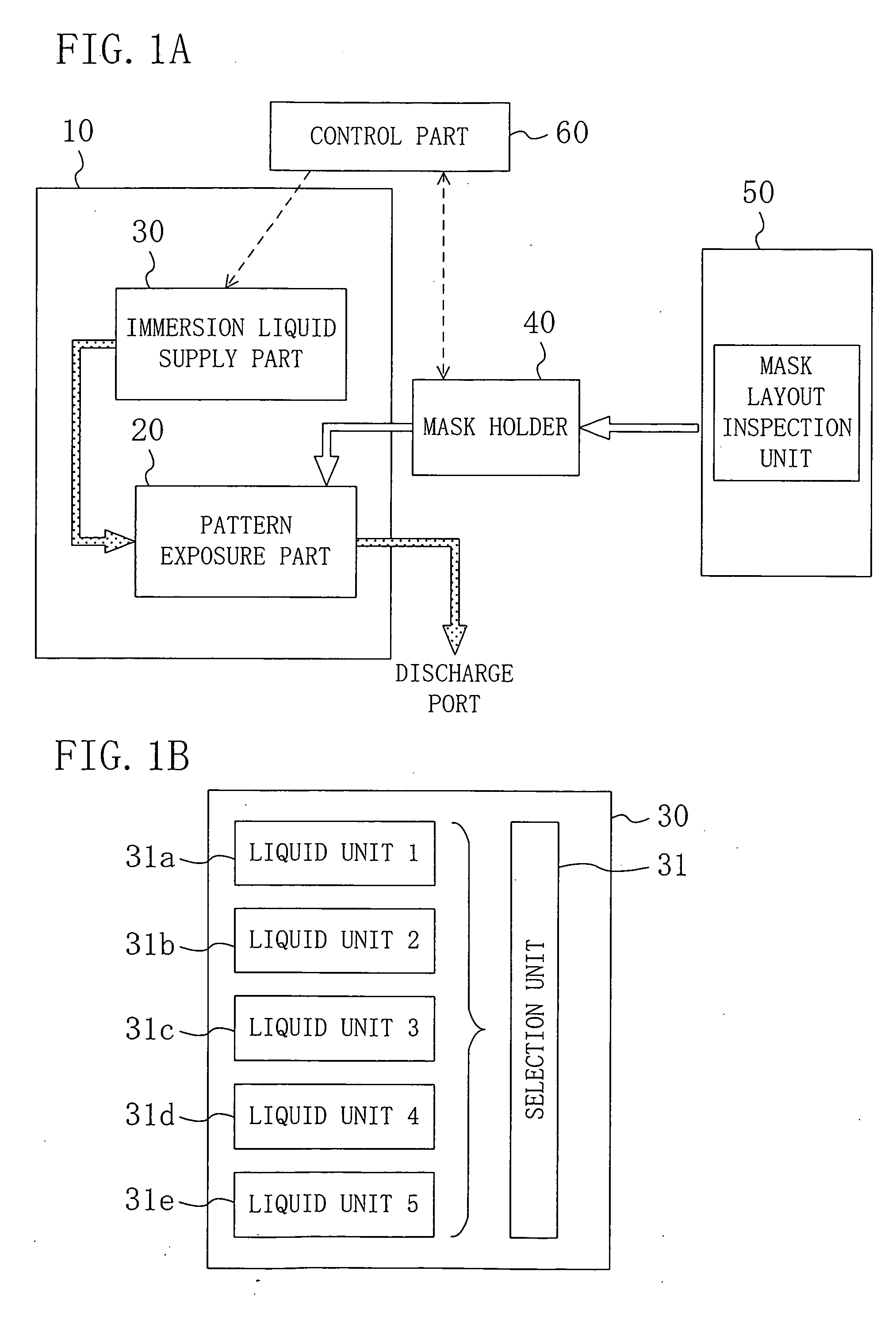
InactiveUS20060019204A1High resolutionIncrease valuePhotoprinting processesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusResistDevice material
An exposure system includes an exposure part for irradiating a resist film formed on a substrate with exposing light through a mask with a liquid provided on the resist film; and a liquid supply part for supplying the liquid to the exposure part. The liquid supplying part includes a plurality of liquid units respectively containing a plurality of liquids having different refractive indexes, and a selection unit for selecting one liquid unit from the plural liquid units and supplying a liquid contained in the selected liquid unit to the exposure part.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Methods for fabricating lenses at the end of optical fibers in the far field of the fiber aperture
InactiveUS7128943B1High transparencyLow shrinkageCladded optical fibrePretreated surfacesChemical treatmentMicrosphere
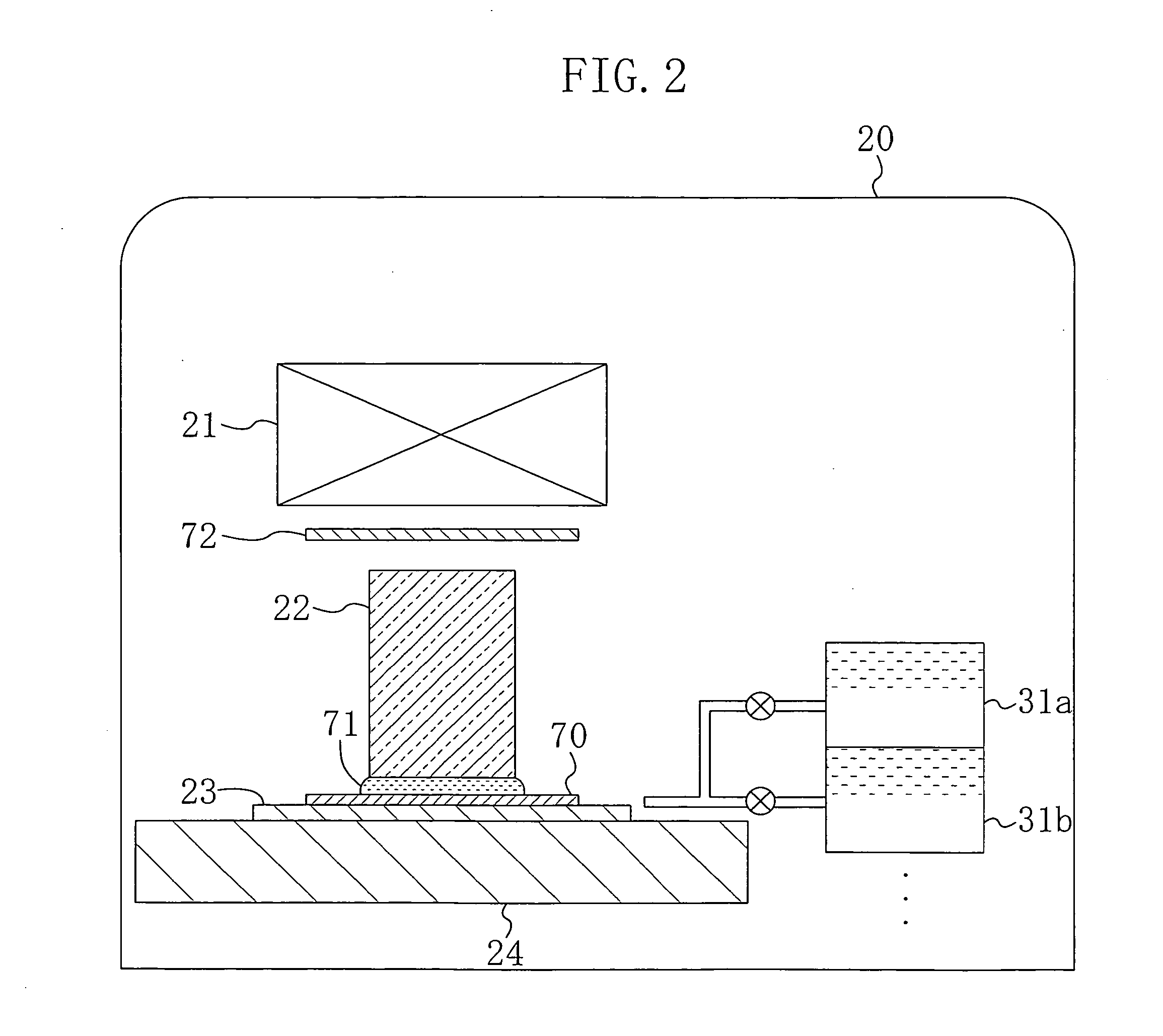
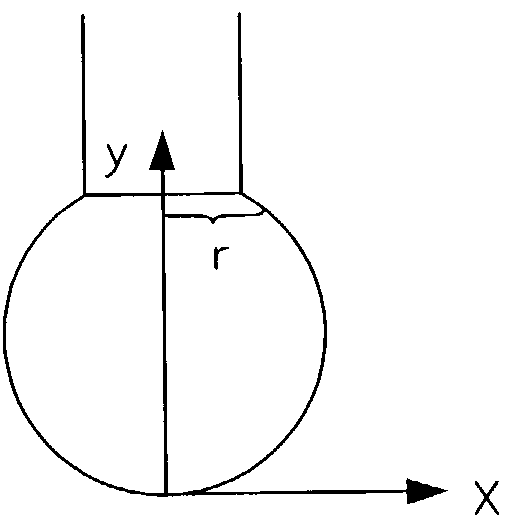
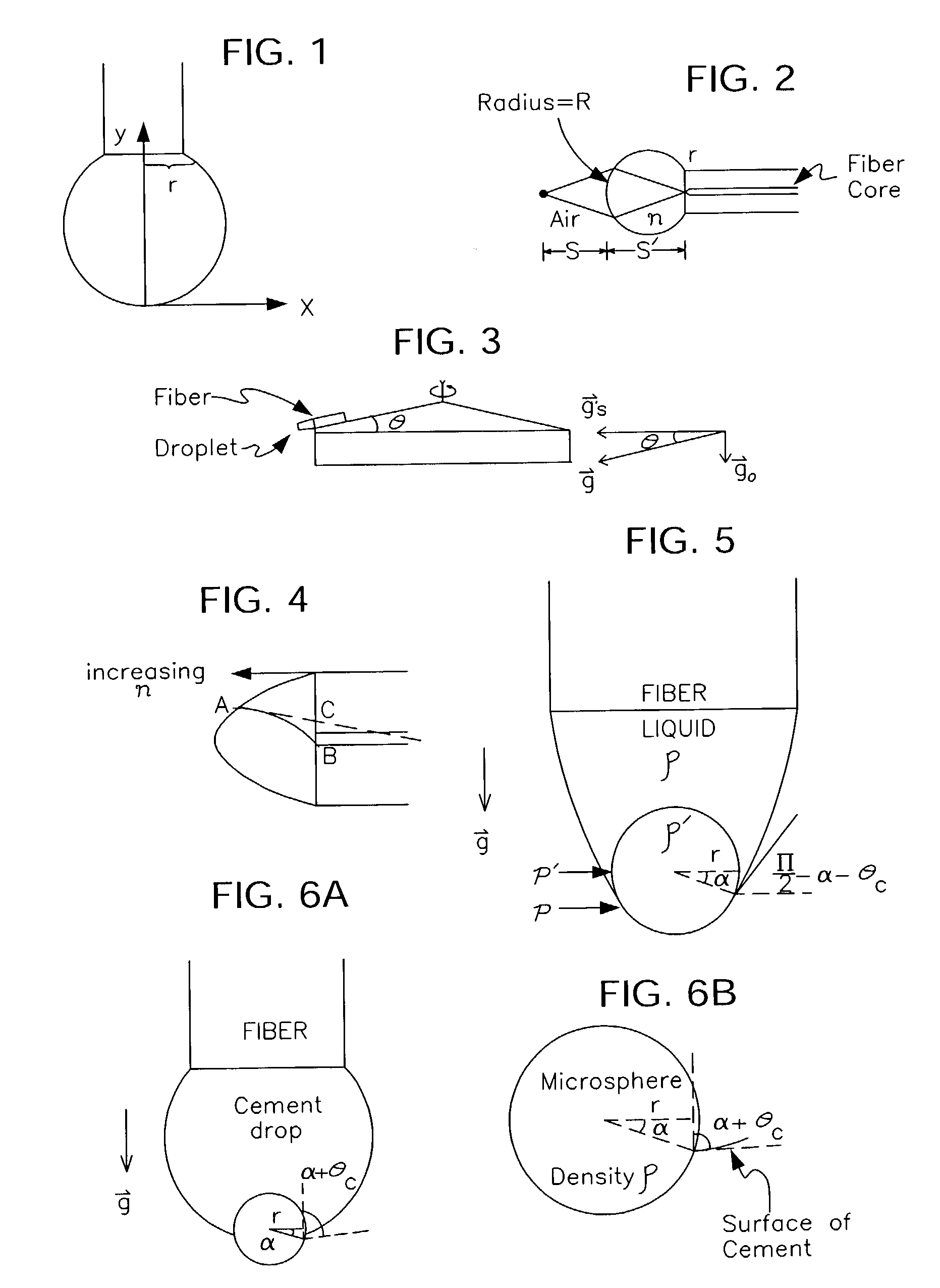
A microlens is affixed in the far field of an optical fiber to spatially transform a beam either entering or exiting the fiber. In a first embodiment, a droplet of photo polymer is placed on the end of an optical fiber and the fiber is spun to create an artificial gravity. The droplet is cured by UV radiation during the spinning. In a second embodiment, nanoparticles are mixed into the droplet to increase the refractive index of the photo polymer. A third embodiment employs artificial gravity to attach a microsphere to the end of the optical fiber. A fourth embodiment chemically treats the surface of the microsphere so that the requirement of artificial gravity is either reduced or eliminated. In a fifth embodiment the droplet is cured under equlibrium or nonequilibrium conditions to obtain different final shapes for the lenslet. A sixth embodiment discloses fabrication of microlens arrays.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
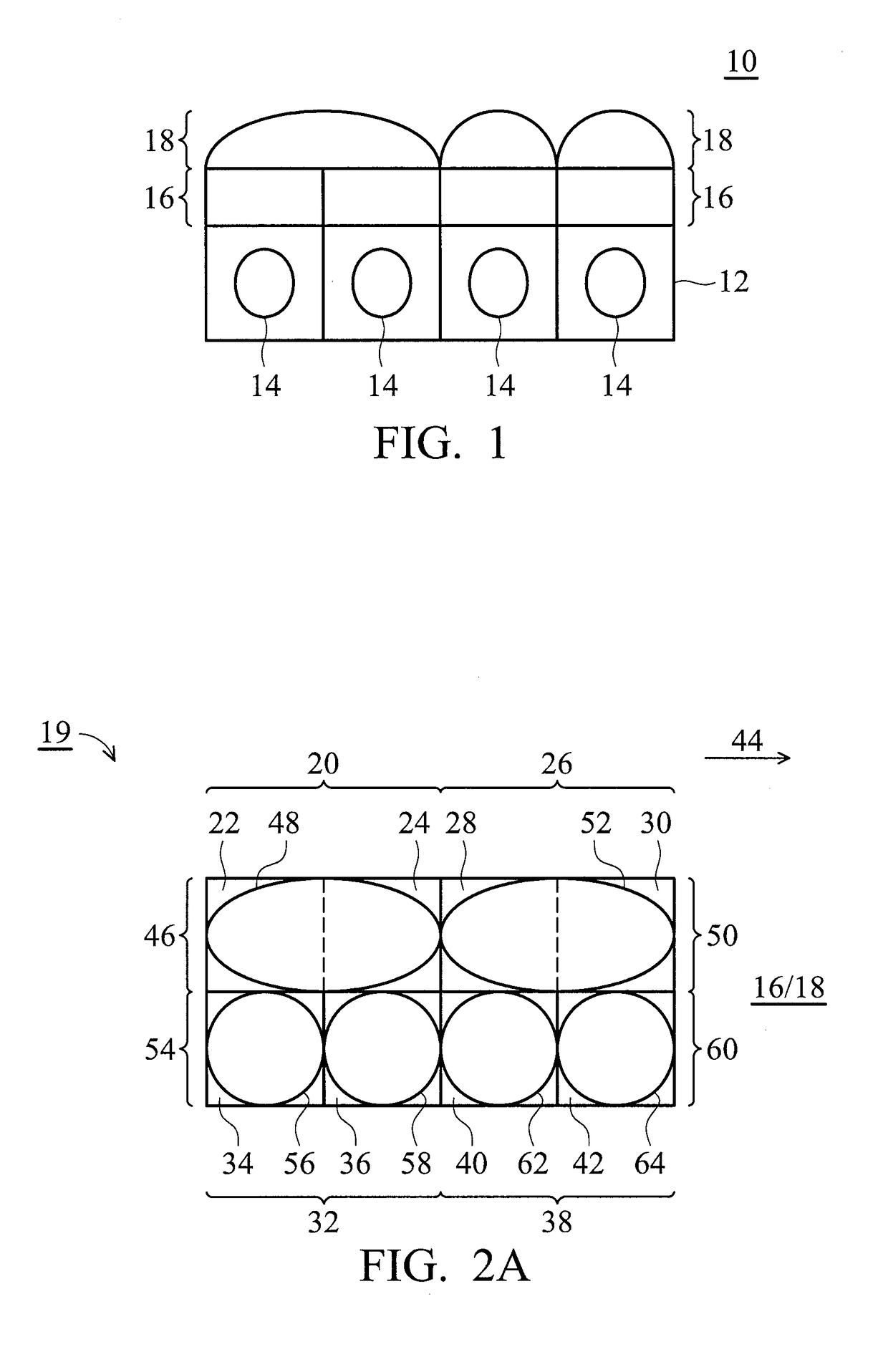
Image-sensor structures
An image-sensor structure is provided. The image-sensor structure includes a plurality of color filter patterns divided into a first unit including one green filter, a second unit including one green filter, a third unit including one blue filter, and a fourth unit including one red filter, wherein the first unit is adjacent to the second unit; and a plurality of microlenses formed above the color filter patterns, wherein the microlenses are divided into a first microlens unit having one microlens above the one green filter of the first unit and the one green filter of the second unit, a second microlens unit above the one blue filter of the third unit, and a third microlens unit above the one red filter of the fourth unit.
Owner:VISERA TECH CO LTD
Sensitized optical fiber method and article
InactiveUS6941052B2Improve writing efficiencyImprovement in maximum achievable refractive index changeGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreGratingRefractive index
A refractive index grating comprising an optical fiber having at least one radiation-sensitized portion, in a longitudinal section of the optical fiber, containing a periodic variation of refractive index. The refractive index grating has an initial magnitude that changes no more than two percent after conditioning at a temperature of 300° C. for a time of ten minutes.
Owner:PROXIMON FIBER SYST
Optical film and liquid-crystal display device
InactiveUS7227685B2Small thicknessLight weightPrismsMechanical apparatusIn planeLiquid-crystal display
An optical film has a transparent film and an adhesive layer provided on one surface of the transparent film. The adhesive layer has a refractive index different by 0.12 or less from that of a layer of the one surface of the transparent film. The transparent film has an average in-plane retardation of not larger than 30 nm. A repetitive prismatic structure is provided on the other surface of the transparent film, the repetitive prismatic structure having optical path changing slopes aligned in a substantially constant direction at an inclination angle in a range from 35 to 48 degrees with respect to a plane of the transparent film.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Photonic crystal devices using negative refraction
InactiveUS7808716B2Large refractive indexMinimum aberrationNanoopticsDiffraction gratingsCamera lensGrism
Negative refraction in photonic crystals and diffraction grating is used to design plano-concave lenses to focus plane waves. Microwave experiments are carried out to demonstrate negative refraction and the performance of these lenses. Demonstration of negative refraction of visible light is also performed for the grism. These lenses can be used in optical circuits, astronomical applications, etc.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
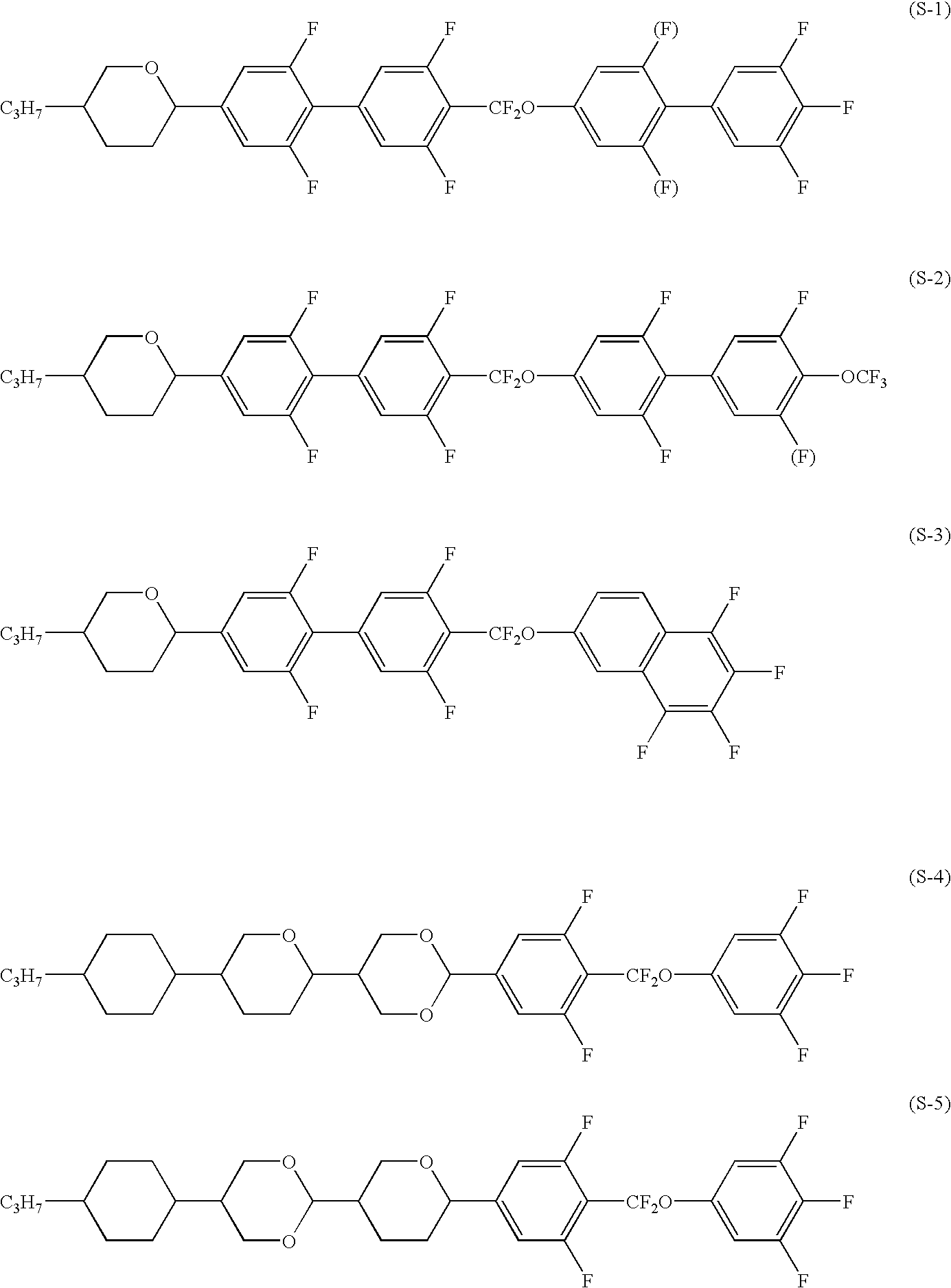
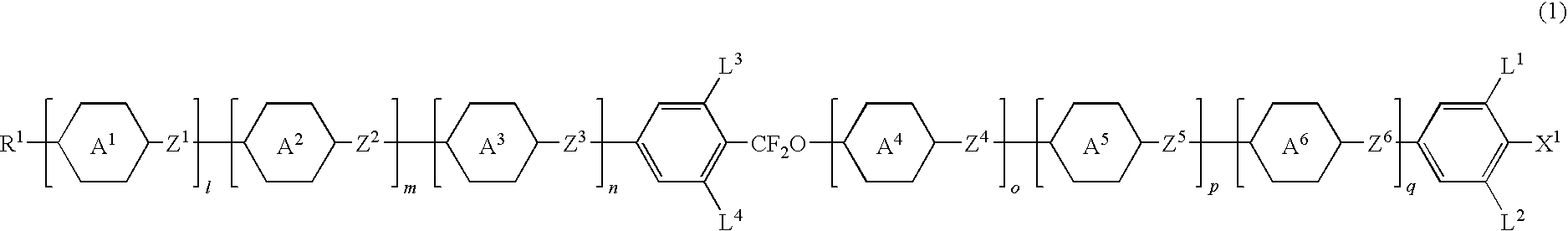
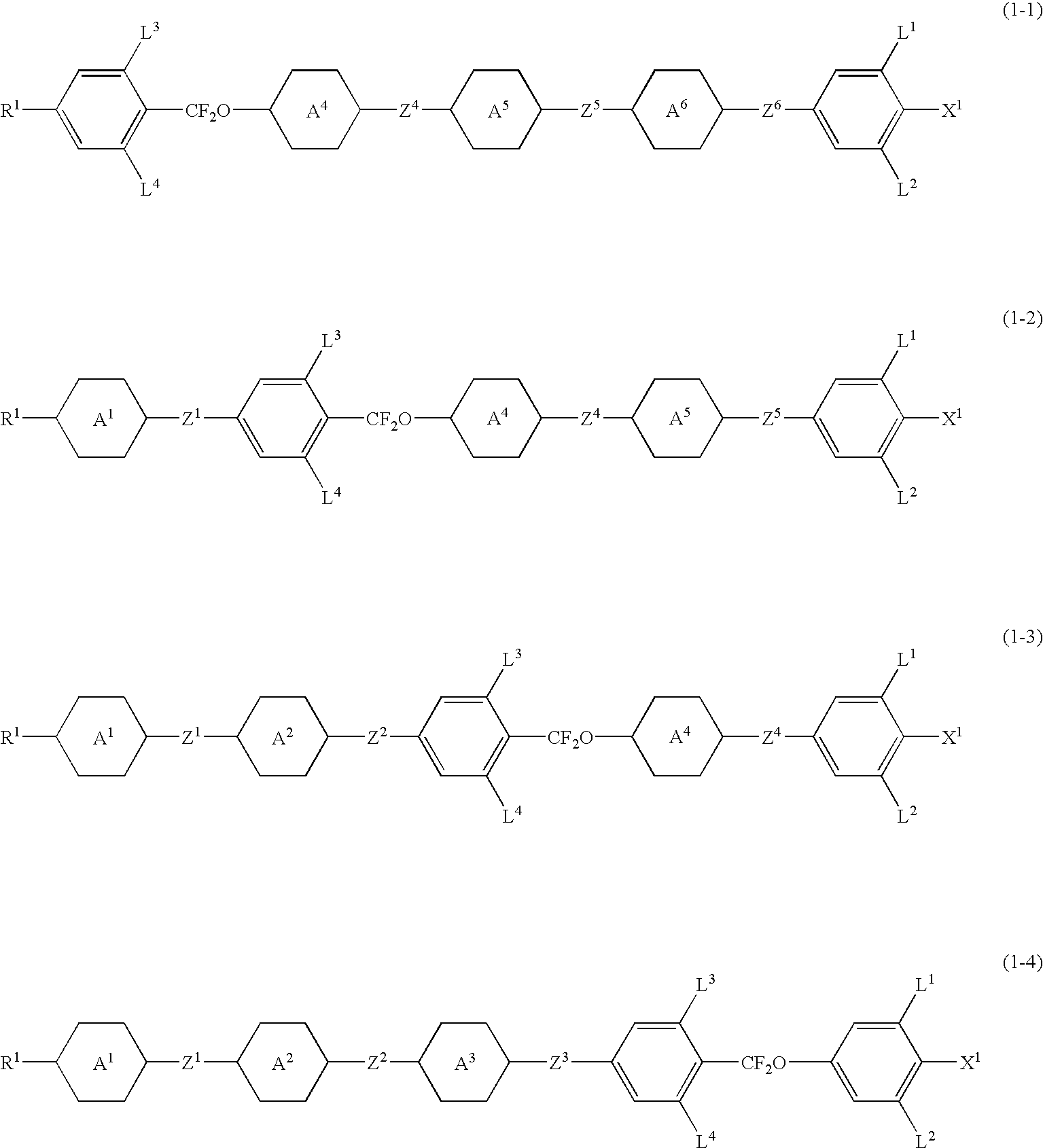
Five-ring liquid crystal compound having CF2O bonding group, liquid crystal composition, and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS7951433B2Increase temperatureWide temperature range usableLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic compound preparationDielectric anisotropyRefractive index
The invention provides a five-ring liquid crystal compound having a CF2O bonding group as a new compound having a general physical properties necessary for compounds, stability to heat, light and so forth, a wide temperature range of liquid crystal phases, a high clearing point, a good compatibility with other compounds, a large dielectric anisotropy and refractive index anisotropy, and an especially high clearing point and an especially large refractive index anisotropy, and provides a liquid crystal composition and a liquid crystal display device.
Owner:JNC PETROCHEM CORP +1
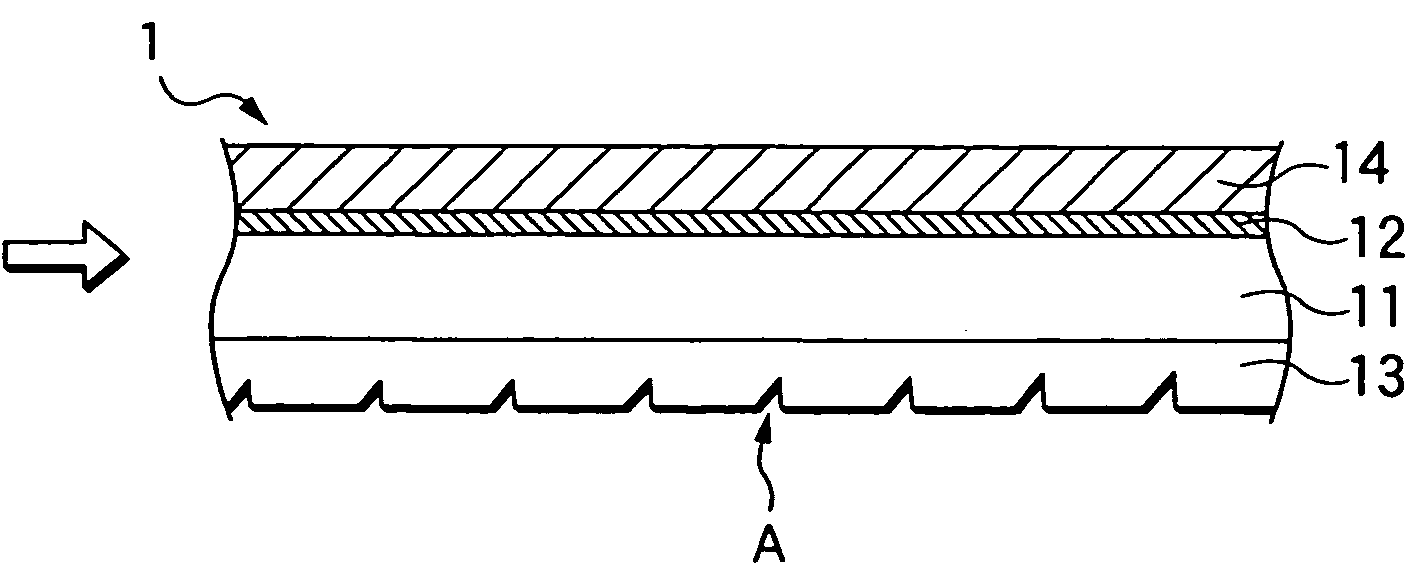
Optical device having optical waveguide and method for manufacturing the same
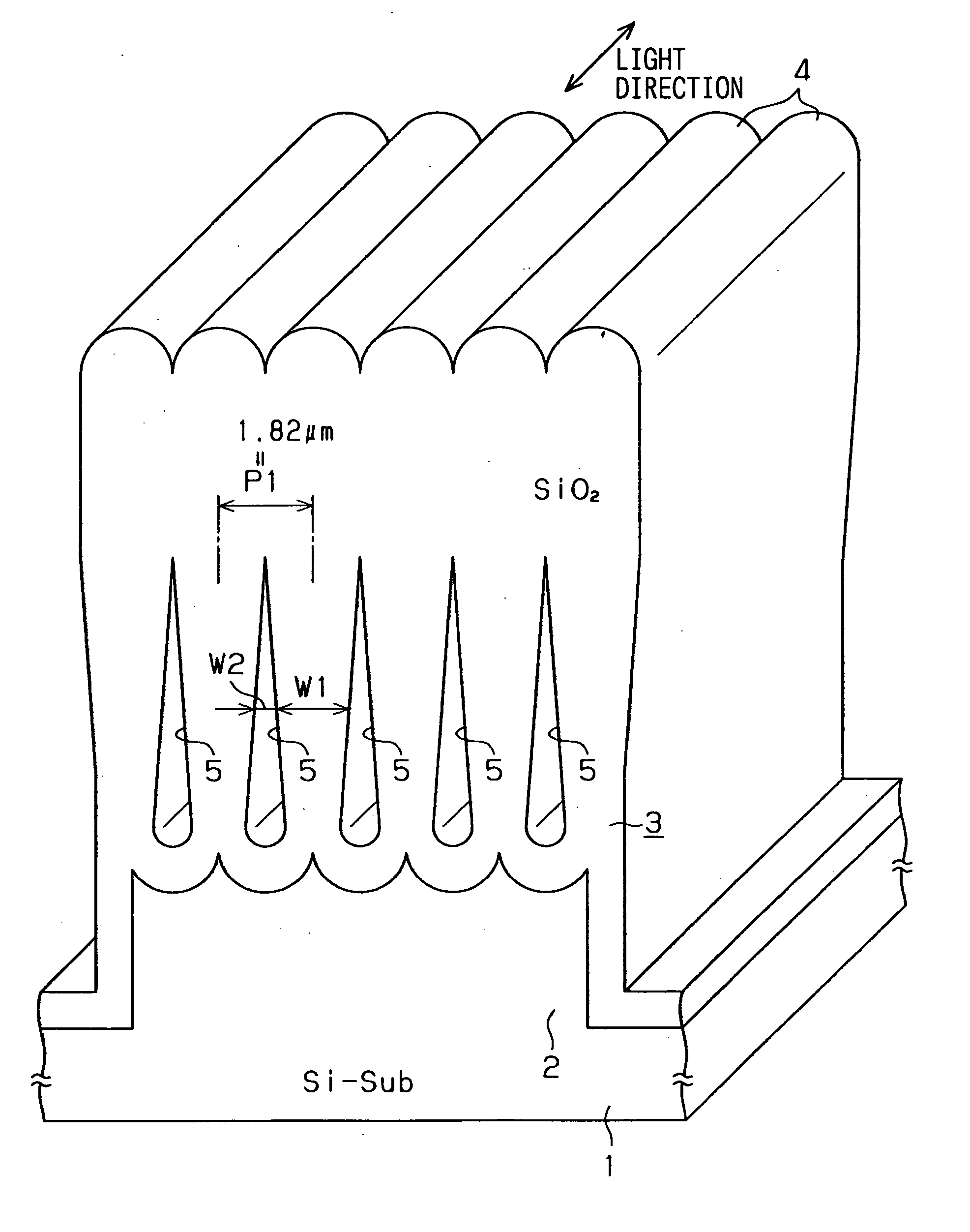
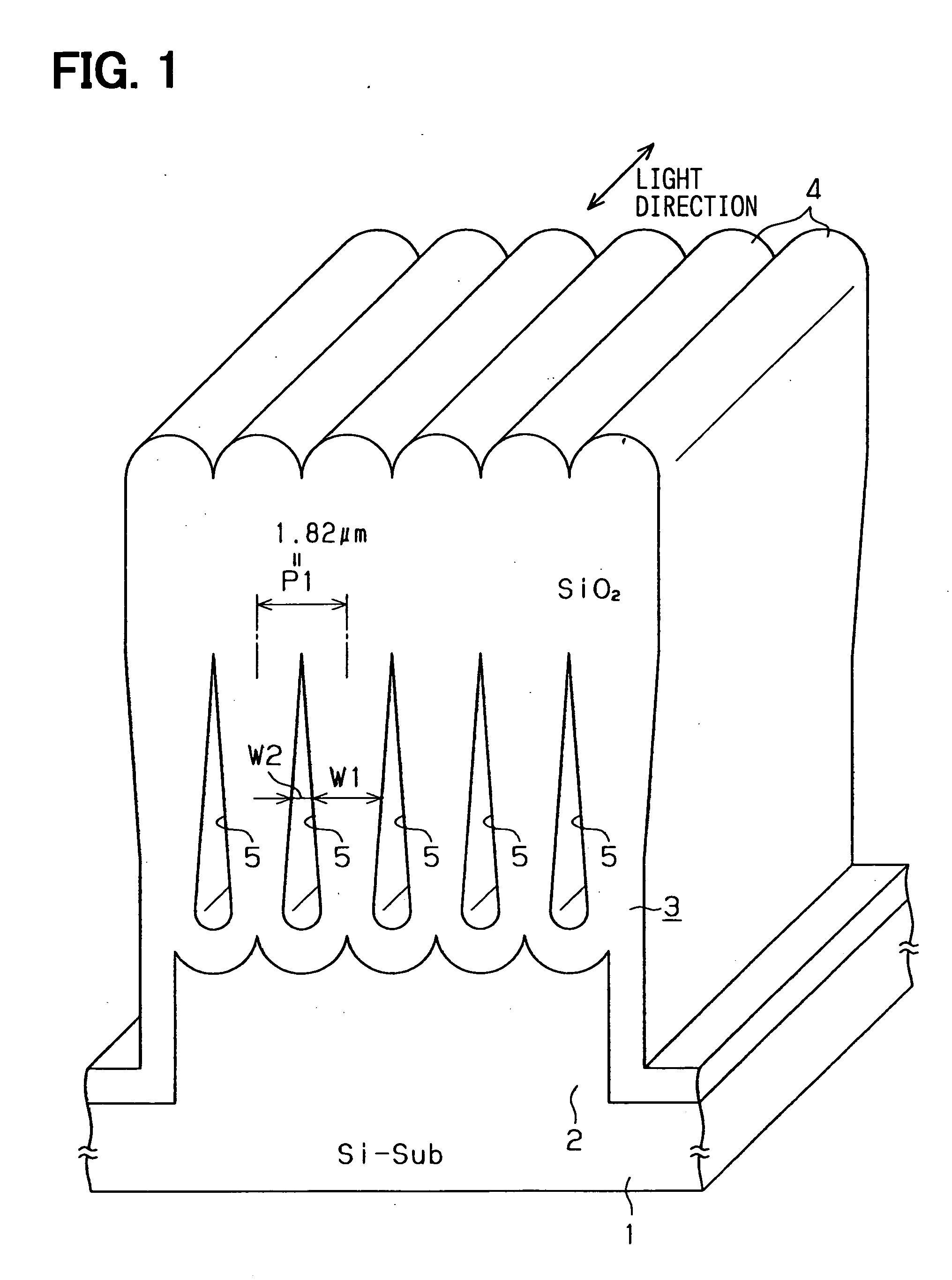
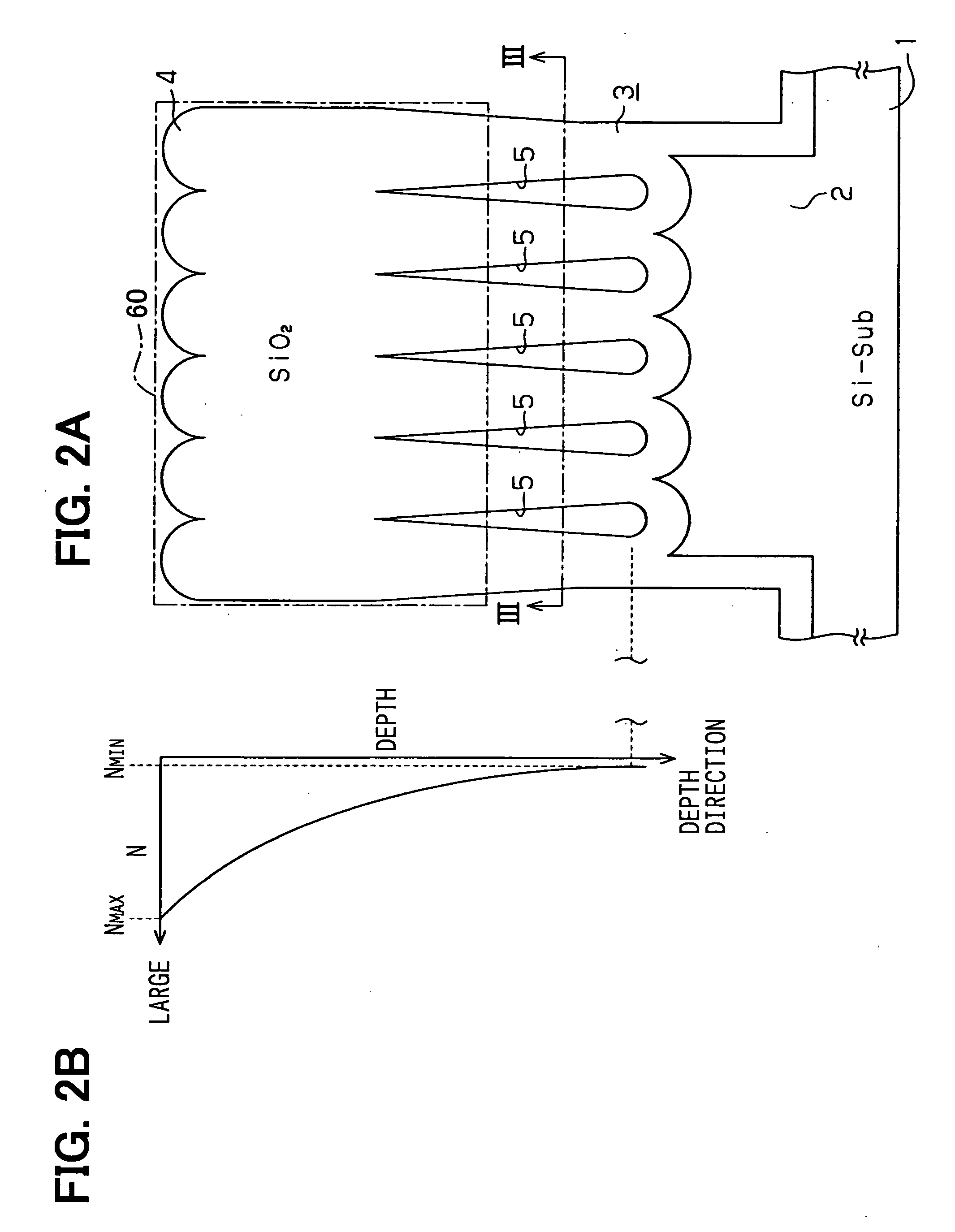
ActiveUS20050265662A1Reduce connection lossLarge refractive indexSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoupling light guidesSilicon oxideWaveguide
An optical device includes: a silicon substrate; a plurality of silicon oxide columns having a rectangular plan shape; and a cavity disposed between the columns. Each column has a lower portion disposed on the substrate. Each column has a width defined as W1. The cavity has a width defined as W2. A ratio of W1 / W2 becomes smaller as it goes to the lower portion of the column. A core layer provided by the columns and the cavity can have the thickness equal to or larger than a few dozen μm easily. Therefore, connection loss between a light source and the device is reduced.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Semiconductor light emitting device
ActiveUS20080303048A1Reduce light absorptionLight extraction efficiency can be improvedSemiconductor devicesRefractive indexLight emitting device
This invention discloses a light emitting semiconductor device including a light-emitting structure and an external optical element. The optical element couples to the light-emitting structure circumferentially. In addition, the refractive index of the external optical element is greater than or about the same as that of a transparent substrate of the light-emitting structure, or in-between that of the transparent substrate and the encapsulant material.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Inkjet ink composition
InactiveUS7901501B2High levelHigh of property propertyMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentVolume averagePigment
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Linear wave guide type surface plasmon resonance microsensor
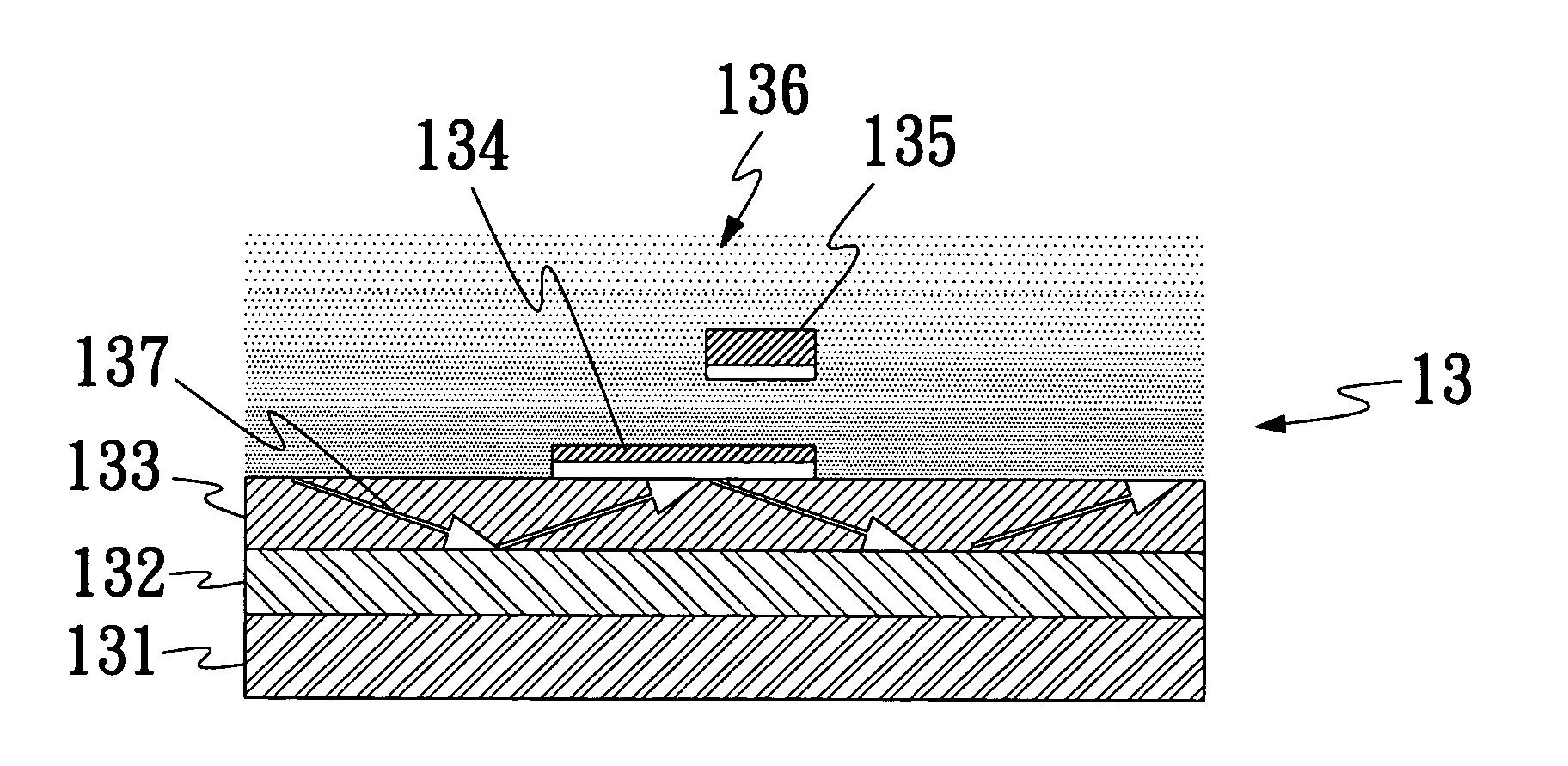
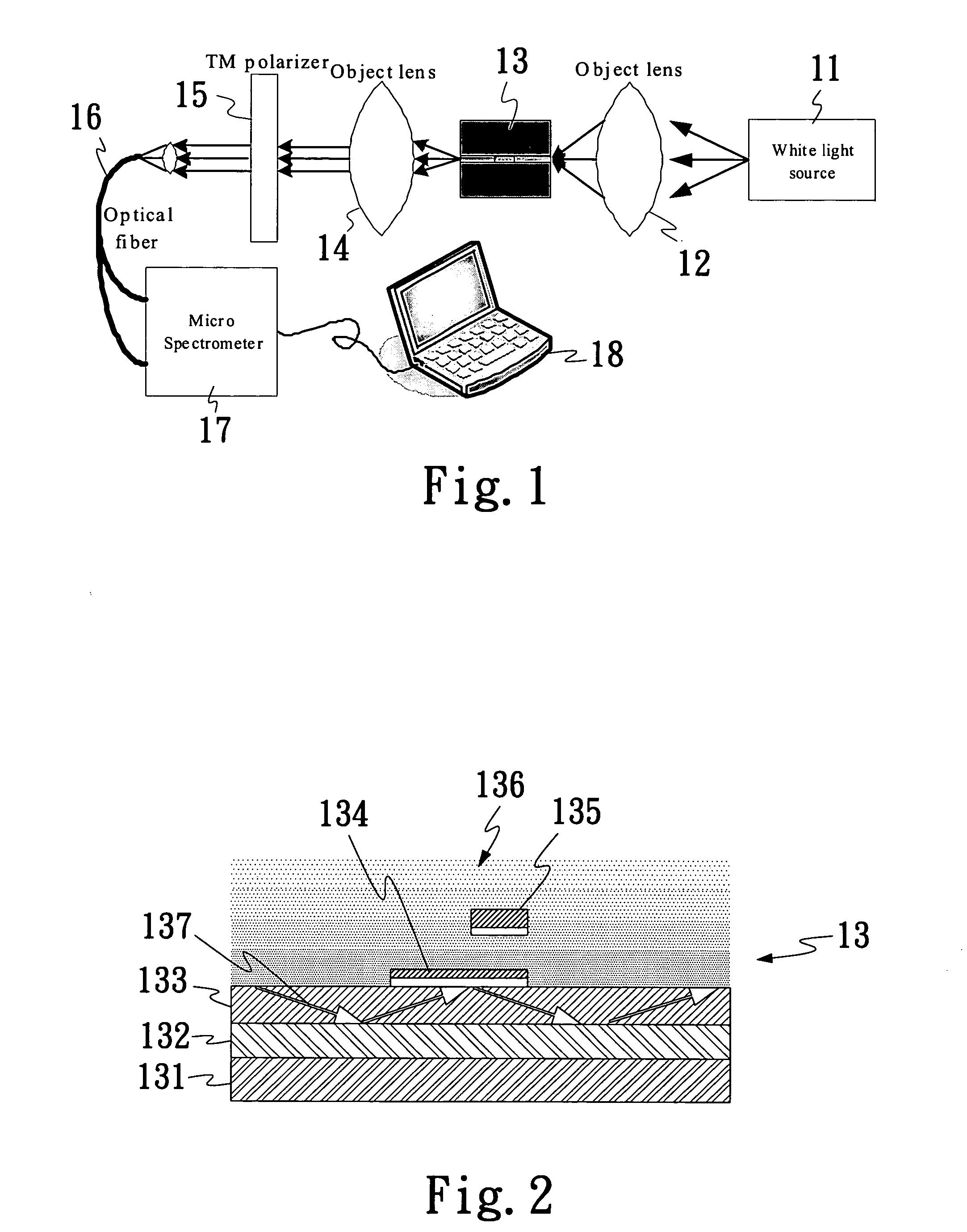
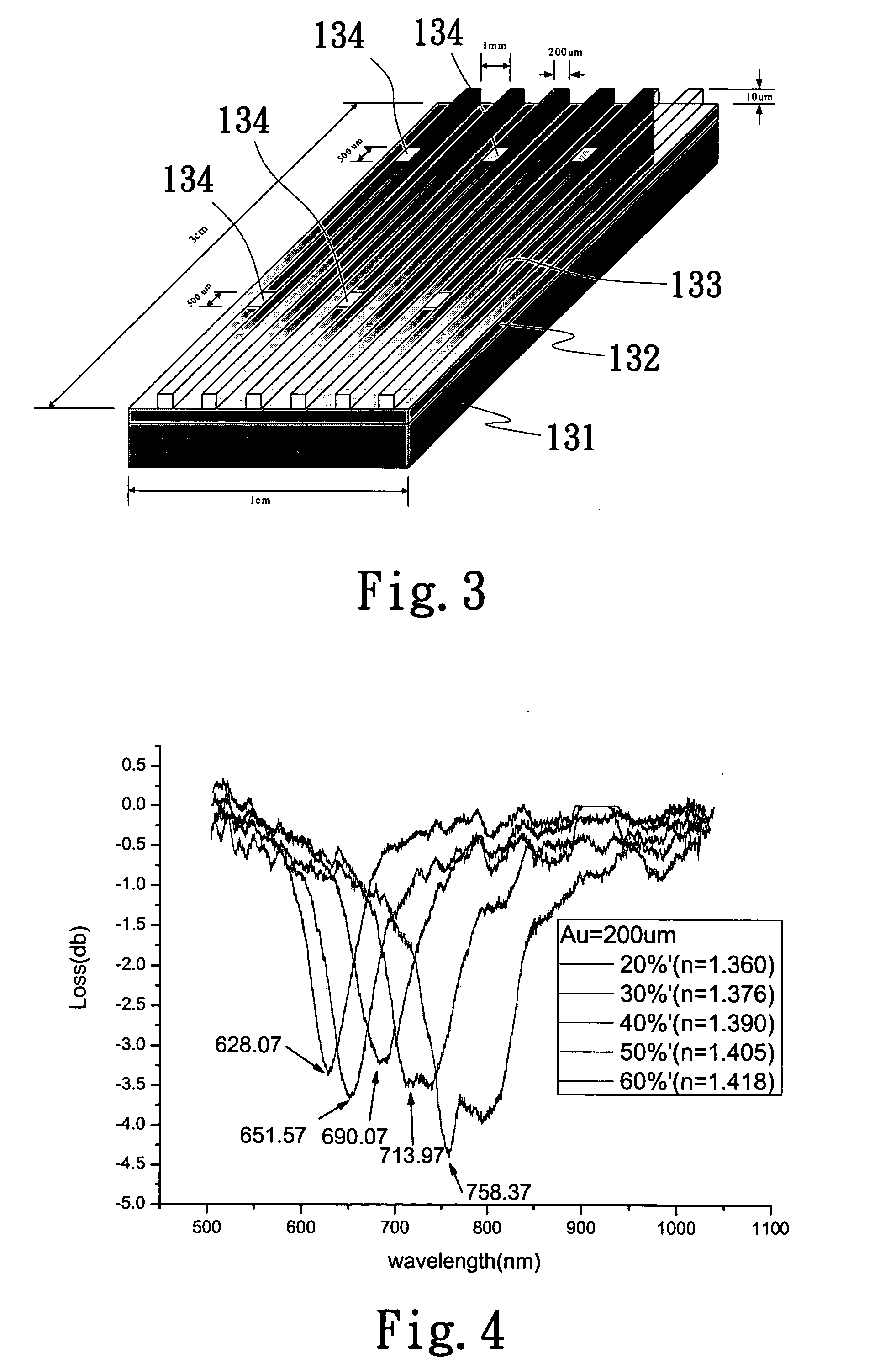
InactiveUS20060146332A1Improve performanceEasy to measureScattering properties measurementsHigh fluxAqueous solution
An improved linear wave guide type surface plasmon resonance (SPR) microsensor, particularly a microsensor employing a dual-opening multi-channel design, adopts a cross differential comparison to enhance the performance of the microsensor and uses a surface plated metal thin film to provide a wavelength absorption according to a SPR characteristic and match with an appropriate sized micro-channel to give a highly sensitive high-flux measurement. The invention applied in a water solution sample comprises: a substrate; a bottom layer contacting a surface of the substrate; at least one wave guide layer contacting the bottom layer and the other surface of the substrate; at least two SPR sensing areas on a surface opposite to the contact surface of the wave guide layer and the bottom layer; at least two SPR sensing film layers on a surface opposite to the contact surface of the two PRS sensing areas and the wave guide layer.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Optical recording medium
InactiveUS20090022932A1Improves light absorption index kImproves absorption index kLayered productsRecord information storageLaser beamsAbsorption index
An optical recording medium including a first substrate, multiple information layers in which each of the multiple information layers except for an information layer located at a furthermost back relative to the side of laser beam irradiation includes a recording layer, an upper protective layer and an optical adjustment layer having an absorption index k of from 0.05 to 0.20 to a light having a wavelength of 405 nm arranged in this order from the side of laser beam irradiation; andintermediate layers provided between the multiple information layers.
Owner:RICOH KK
SERS-SPR dual-mode sensor as well as preparation method and application thereof
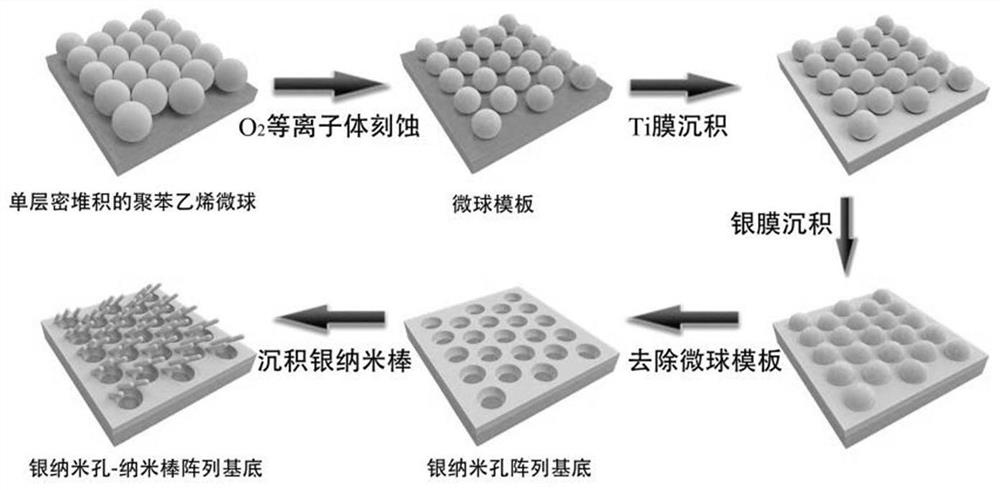
ActiveCN111812075AStrong resonance enhancement effectExcellent optical propertiesRaman scatteringNucleic acid detectionA-DNA
The invention discloses an SERS-SPR dual-mode sensor for nucleic acid detection. The SERS-SPR dual-mode sensor comprises a detection chip and a DNA probe, wherein the detection chip is a silver nanopore-nanorod array substrate of which the surface is modified with tetrahedral DNA. The invention further discloses a preparation method and a detection method of the SERS-SPR dual-mode sensor. The detection method comprises the following steps of: sequentially mixing the detection chip with a to-be-detected liquid sample and a DNA probe solution; forming a 'detection chip-target DNA-DNA probe' compound through complementary pairing; and then sequentially carrying out a transmission spectrum test and an SERS test. According to the detection method, high-sensitivity and specific dual-mode sensingdetection on nucleic acid in serum is realized through wavelength change of characteristic valleys of a transmission spectrum, an SERS spectrum and characteristic signal intensity values of the SERSspectrum, the detection limits of the SERS sensing mode and the SPR sensing mode reach the sub-femtomole per liter magnitude and the sub-picomole per liter magnitude respectively, and the nucleic acidmarker can be detected in complex environments such as serum.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Optical waveguide and process for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7308180B2Large refractive indexLow costOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexWaveguide
The present invention provides an optical waveguide, which at least includes: a waveguide core having a cavity therein; and a clad which encloses the periphery of the waveguide core and has a smaller refractive index than the waveguide core, wherein the optical waveguide changes a direction of a part or all of propagated light by using a part or all of an interface between the waveguide core and the cavity as a reflecting surface. The present invention further provides a method for manufacturing the optical waveguide, which at least includes: forming a core having a cavity therein on a substrate; applying an uncured clad material to a side surface and an upper portion of the core while maintaining the cavity which allows an atmospheric gas to be present in the cavity; and curing the clad material by heat or light to seal the gas in the cavity.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Two-photon absorption recording material containing dye having polymerizable group
InactiveUS20090088490A1Significant differenceLarge refractive indexMonoazo dyesOrganic chemistryPhotochemistryTwo-photon absorption
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Package material for packaging photoelectric device and package
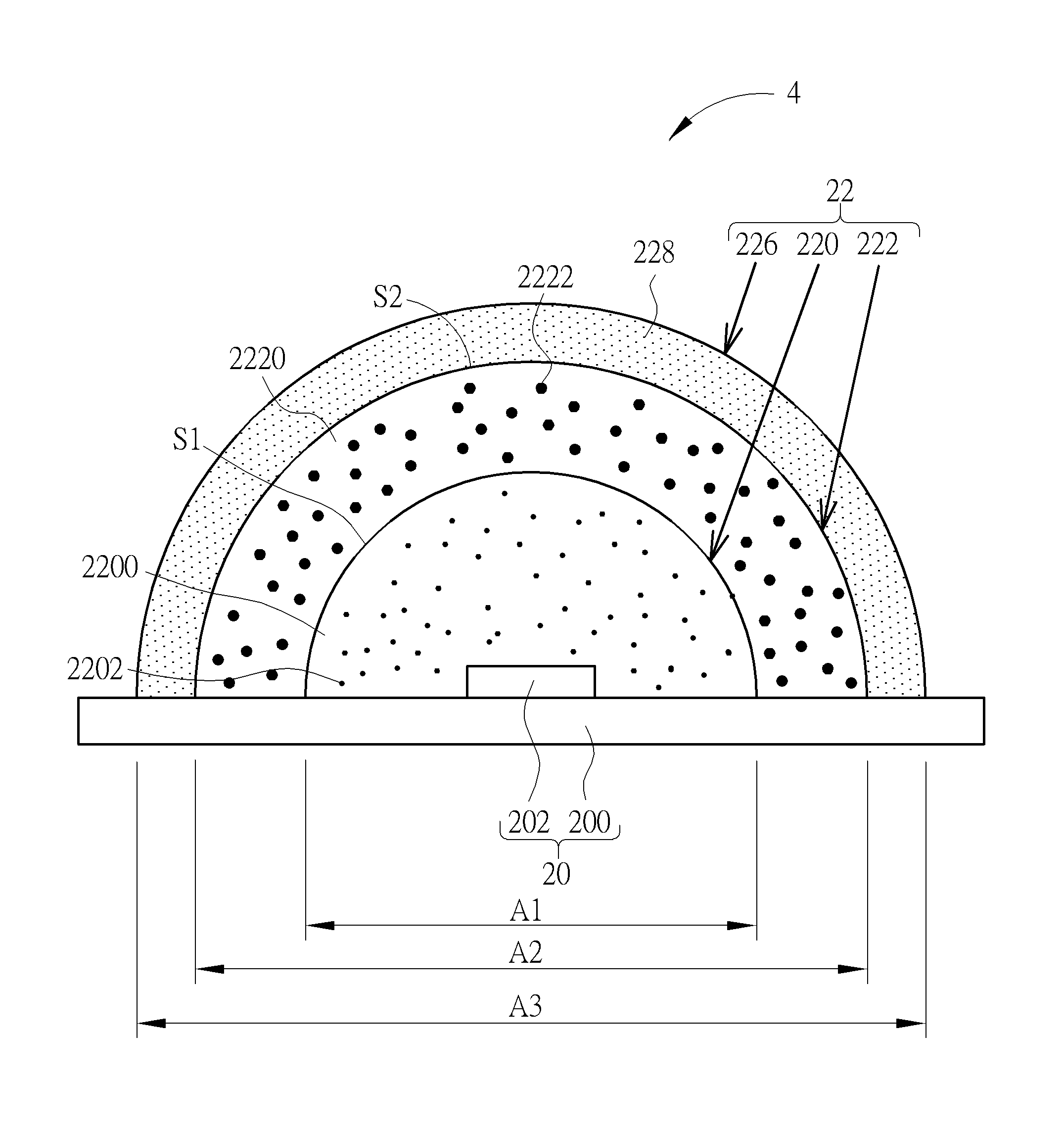
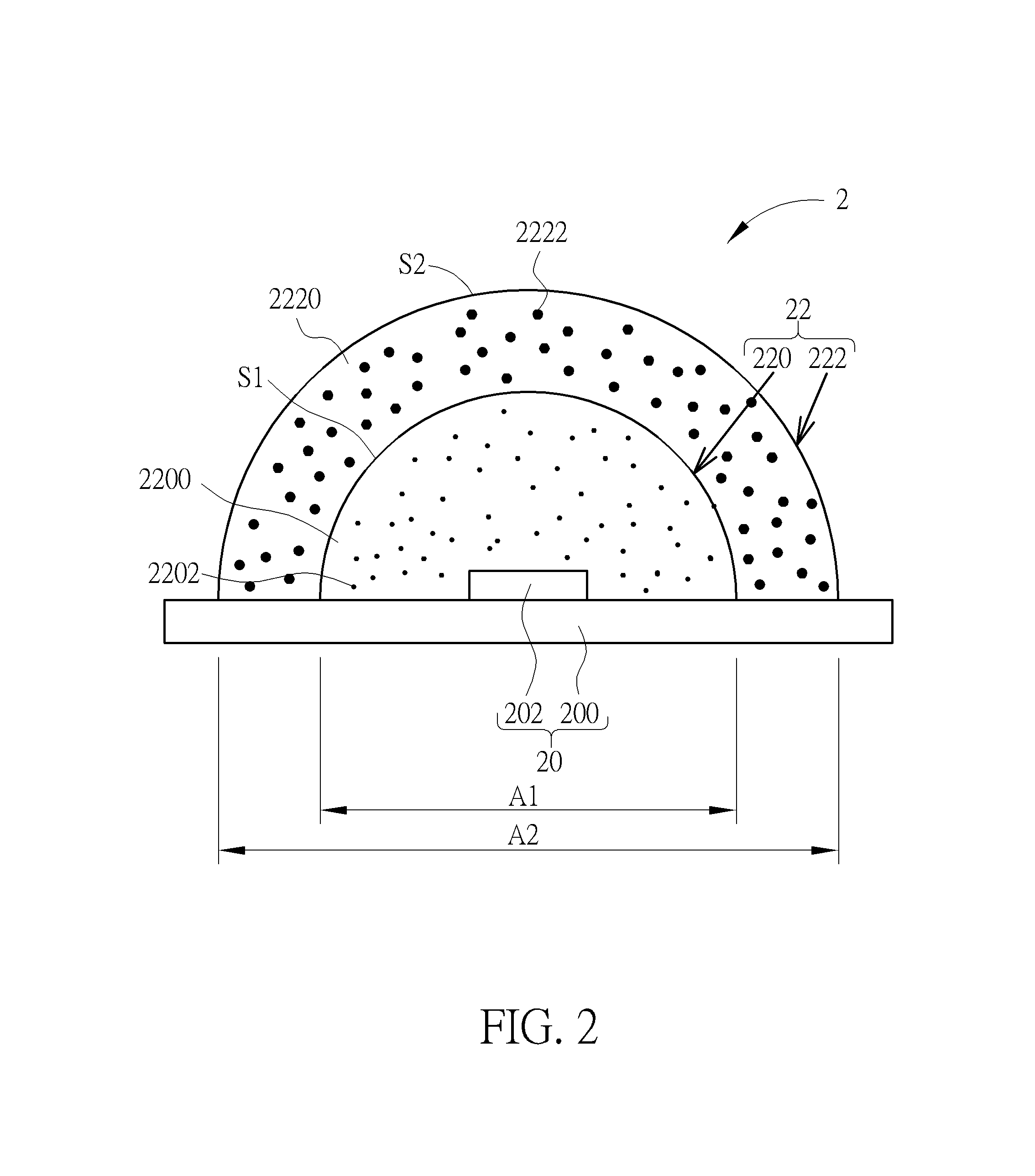
InactiveUS20150287893A1Increase the number ofLow color requirementSemiconductor devicesRefractive indexSubmicron scale
A package material for packaging a photoelectric device includes a first molding portion and a second molding portion. The first molding portion is disposed on the photoelectric device. The first molding portion includes a first molding compound and a plurality of nano-scale metal oxide particles, wherein the nano-scale metal oxide particles are doped in the first molding compound. The second molding portion is disposed on the first molding portion and away from the photoelectric device. The second molding portion includes a second molding compound and a plurality of submicron-scale metal oxide particles, wherein the submicron-scale metal oxide particles are doped in the second molding compound. A whole refractive index of the first molding portion is larger than a whole refractive index of the second molding portion.
Owner:GENESIS PHOTONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com