Method for manufacturing bonded wafer
a technology of bonded wafers and bonded layers, which is applied in the manufacturing of semiconductor/solid-state devices, electrical equipment, basic electric elements, etc., can solve the problems of remaining damage and affecting device characteristics, and achieve the effect of reducing the occurrence of concave defects, reducing surface roughness, and easy adjustmen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0069]An SOI wafer was fabricated by using the method for manufacturing a bonded wafer of the present invention.
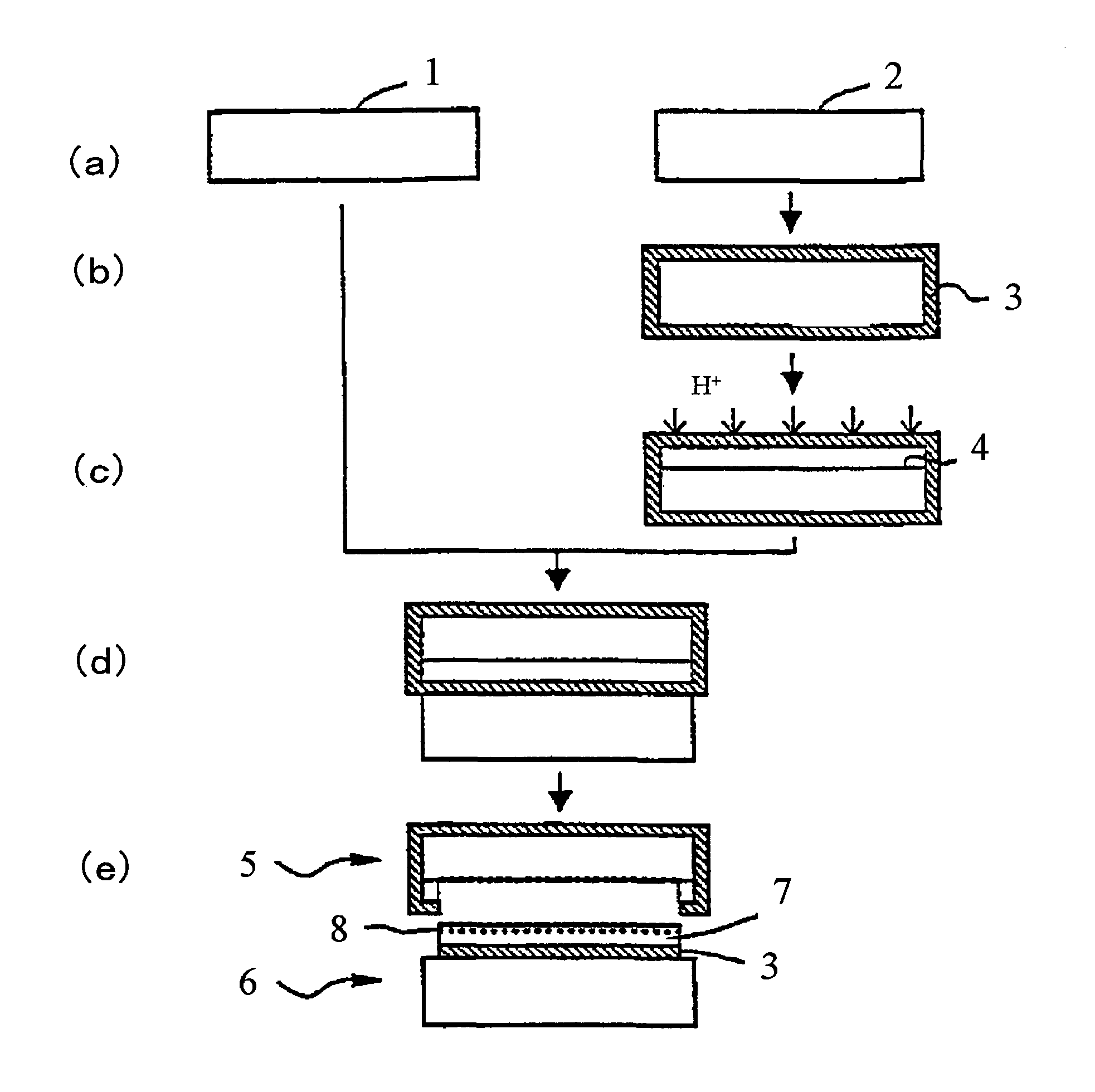
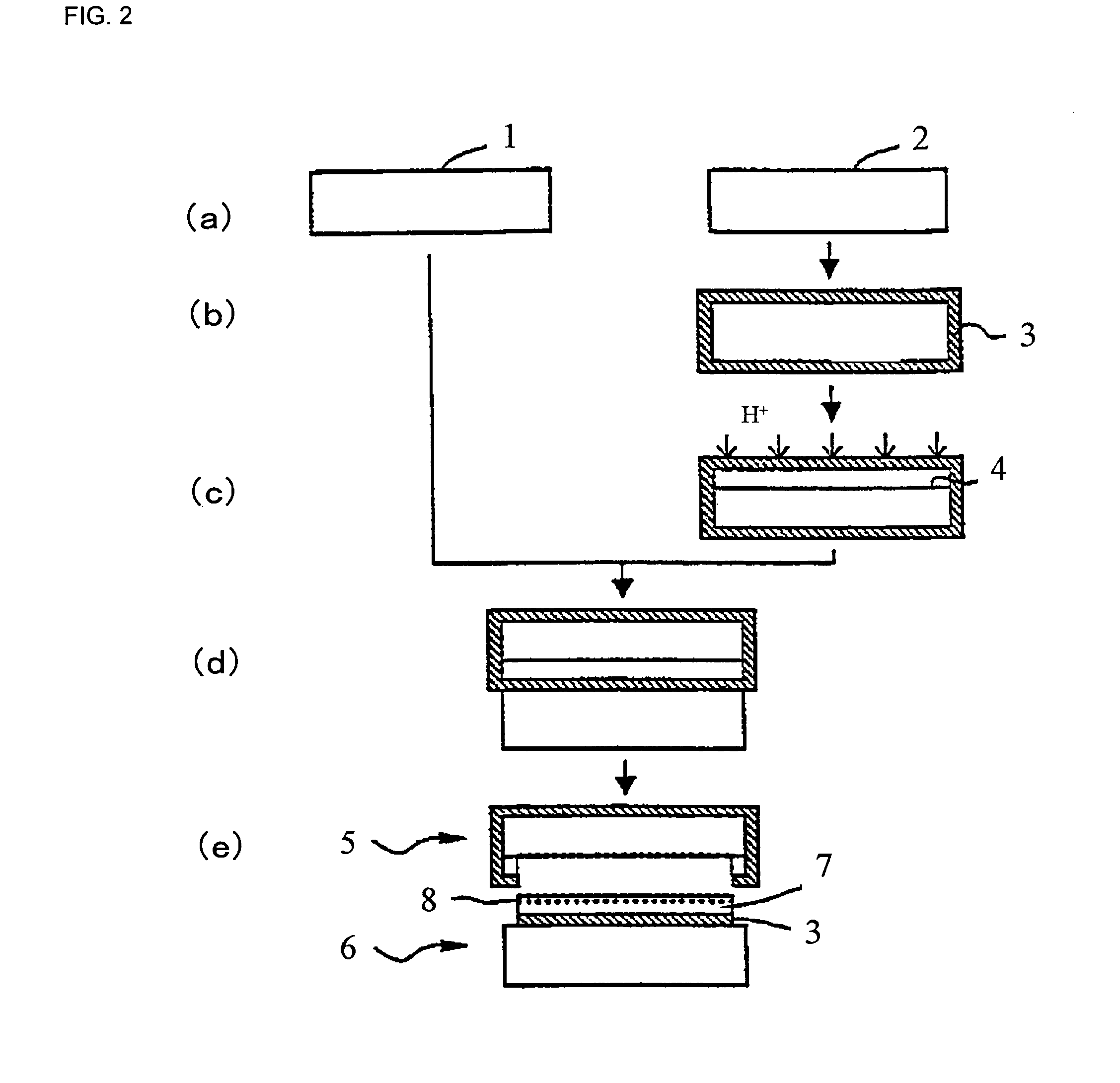
[0070]A silicon single crystal ingot produced by the Czochralski method and having a crystal orientation of , conductivity type of p-type and a resistivity of 10 Ω·cm was sliced and processed to fabricate silicon mirror surface wafers having a diameter of 300 mm. These were divided into bond wafer and base wafer, and a SOI wafer having a thin film SOI layer on a surface was obtained as a sample by the process shown in FIG. 2.
[0071]It is to be noted that a thickness of the SOI layer was 400 nm and a thickness of a buried oxide film was 150 nm. Ion implanting conditions were that implanted ions were H+ ions, implantation energy was 50 keV and dose amount was 5.0×1016 / cm2. Moreover, delaminating heat treatment was heat treatment at 500° C. for 2 hours under N2 gas atmosphere.
[0072]The SOI wafer after delaminating obtained as describe above was cleaned for 3 minutes using ozon...
example 2 , 3
Example 2, 3
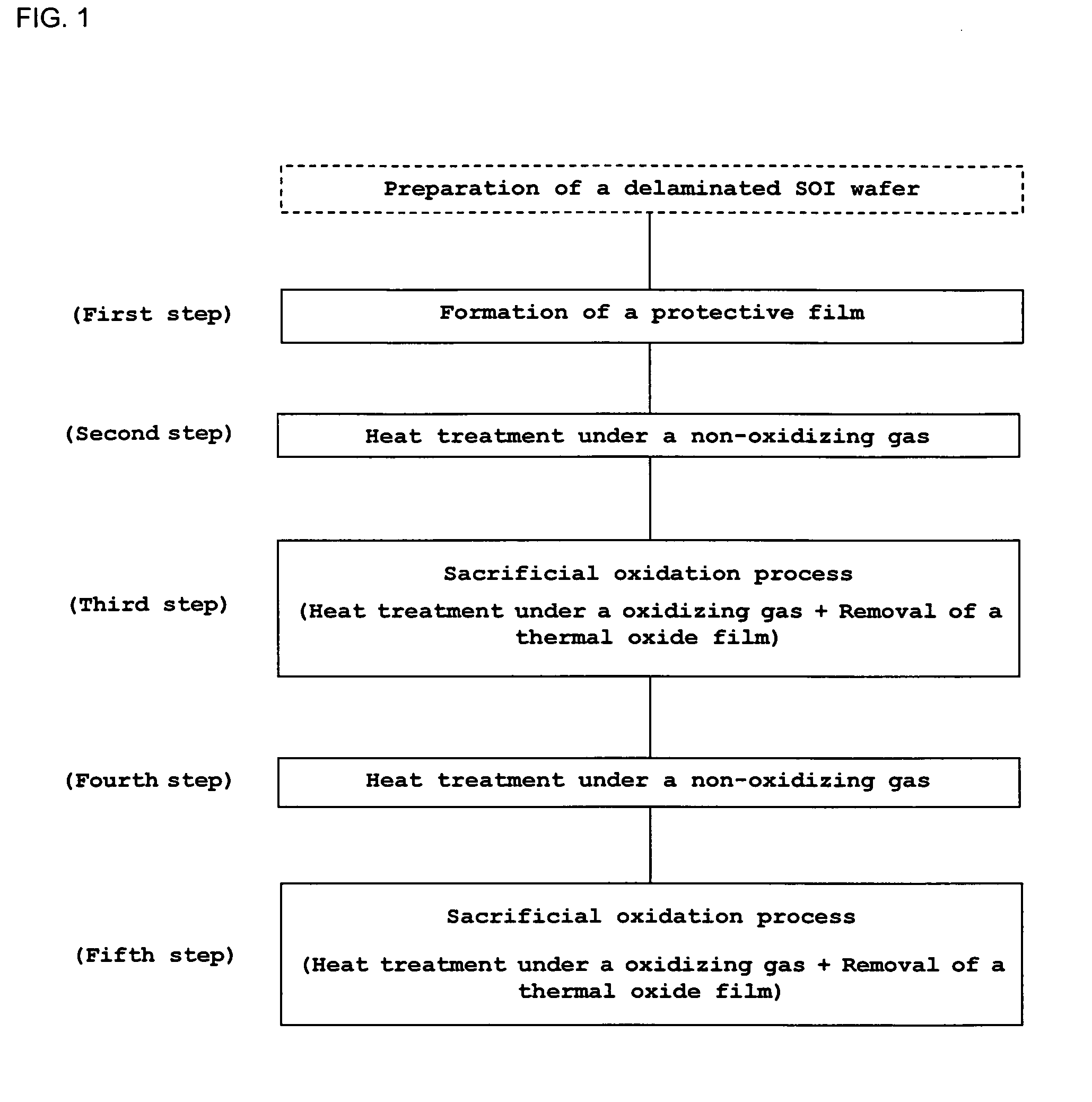
[0085]A SOI wafer was manufactured in the same conditions as Example 1 except that RTO process for forming an oxide film having a thickness of 3 nm (Example 2) and 4 nm (Example 3) on a SOI layer surface was performed in between the first step and the second step and the same evaluation as Example 1 carried out.
[0086]As a result, it is revealed that a thickness of the oxide film formed after the first step of the SOI wafer of Example 2 was 3.0 nm, pit density of the oxide film surface after the second step was 3×108 numbers / cm2, and the oxide film surface was nonuniform. Moreover, the P-V value of the wafer surface after the fifth step was 2.3 nm and the concave defect density was 3×102 numbers / cm2. From the results, it was revealed that the SOI wafer surface of Example 2 was as flat as one of Example 1 and had few concave defects.
[0087]Moreover, it is revealed that a thickness of the oxide film formed after the first step of the SOI wafer of Example 3 was 4.0 nm, pit de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com