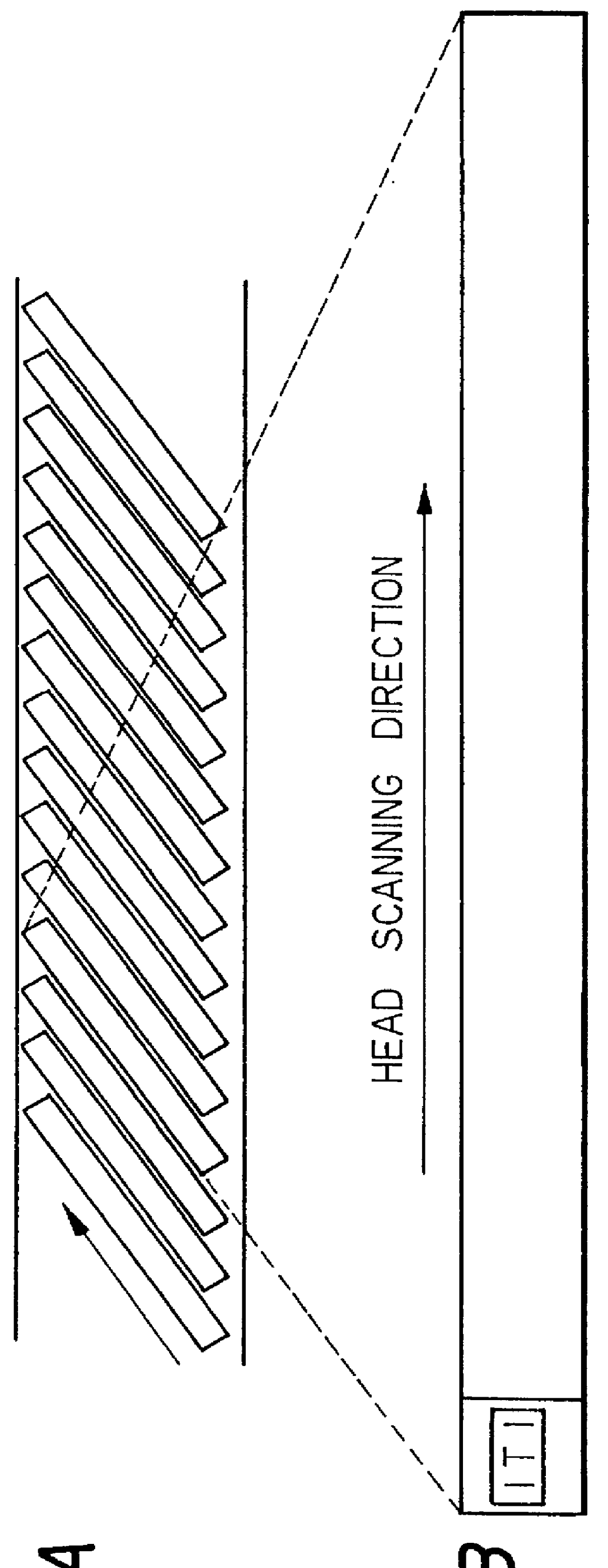
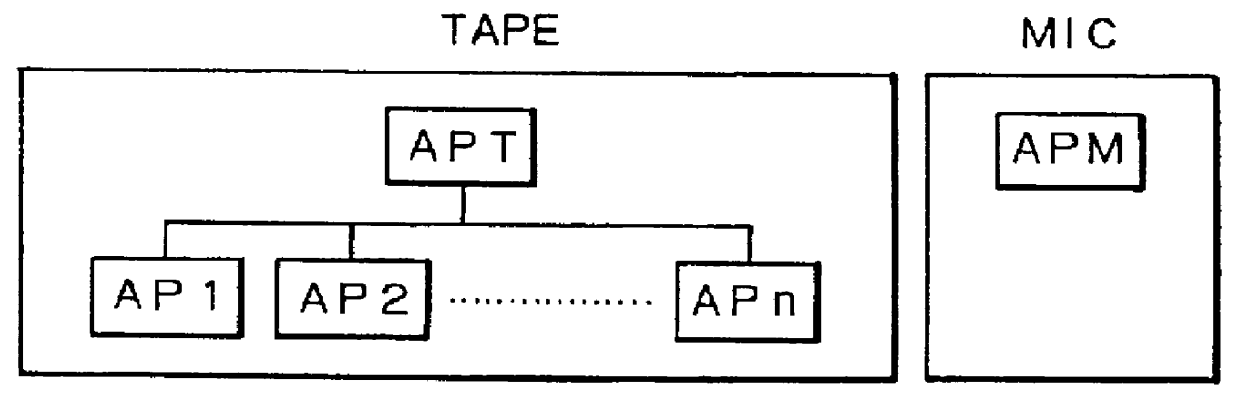
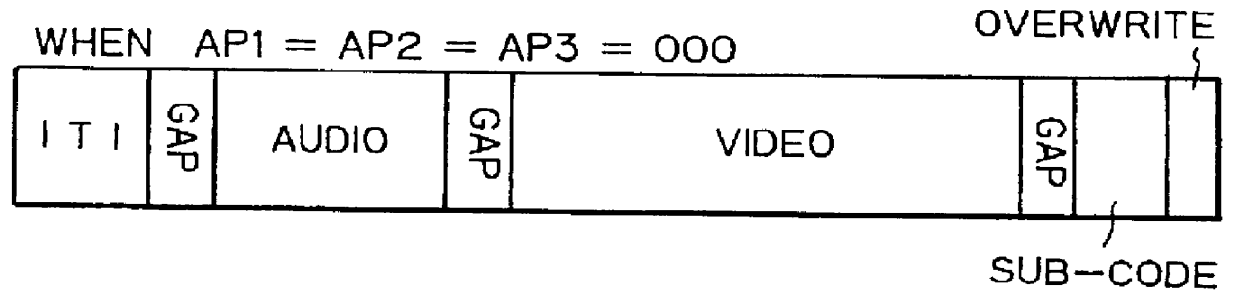
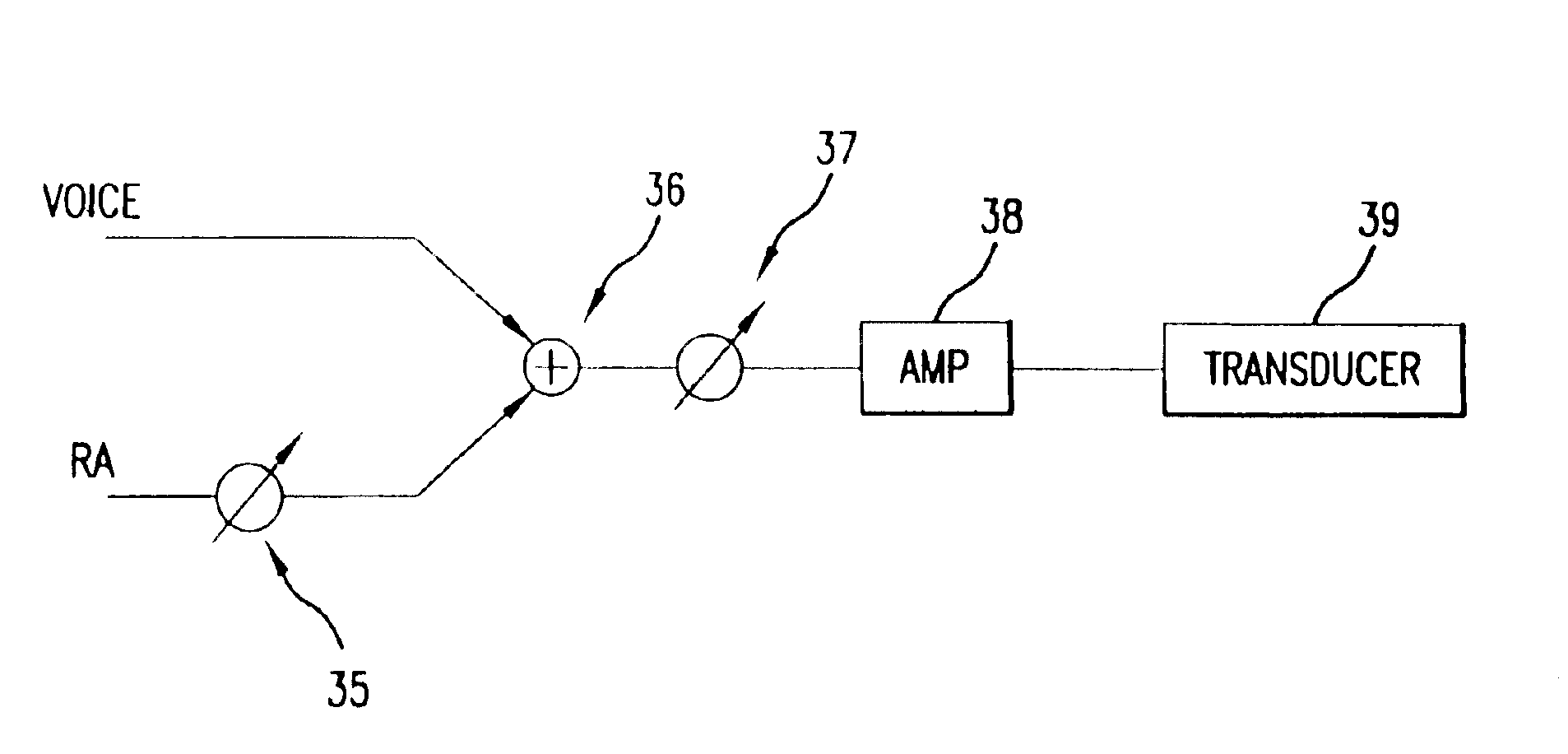
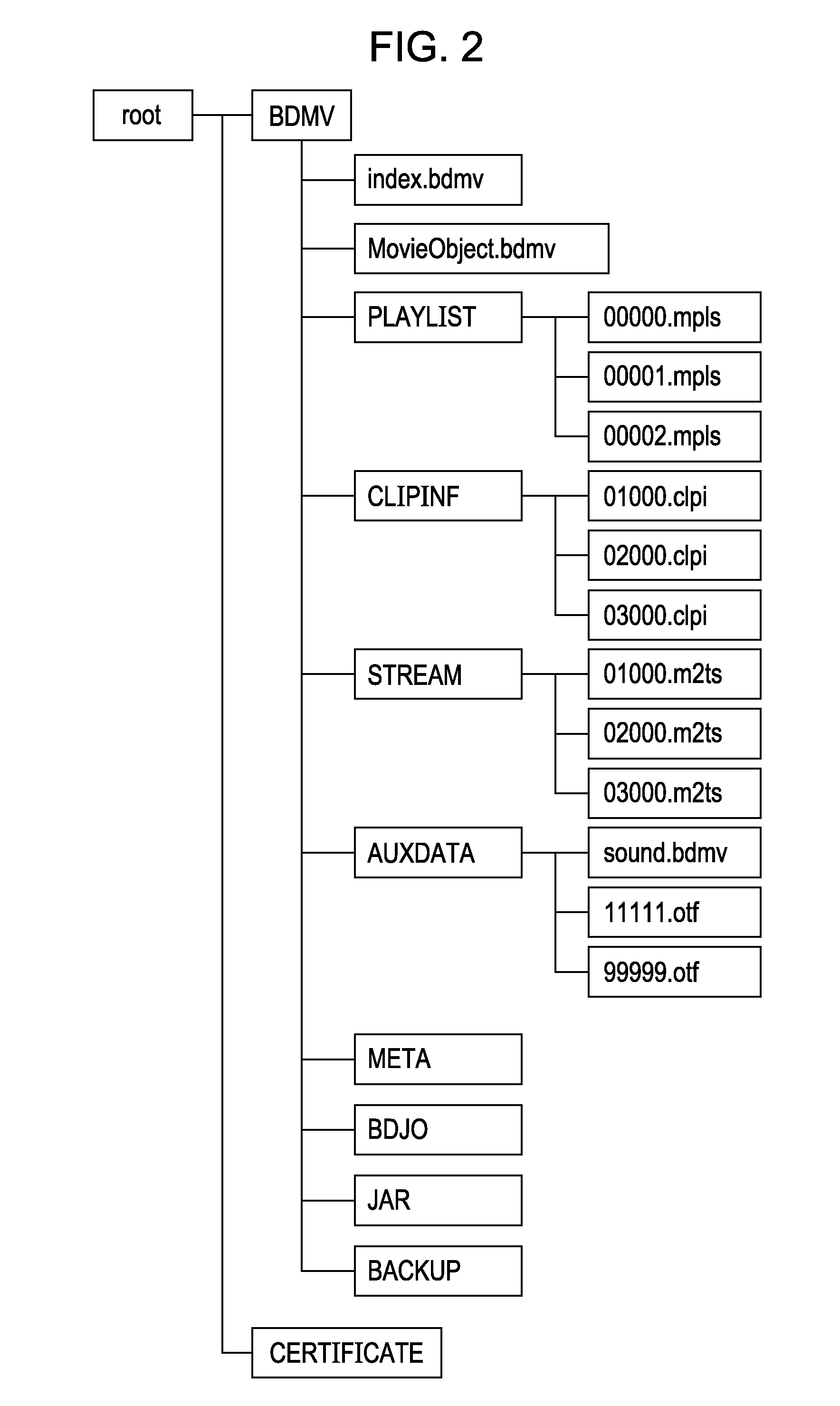
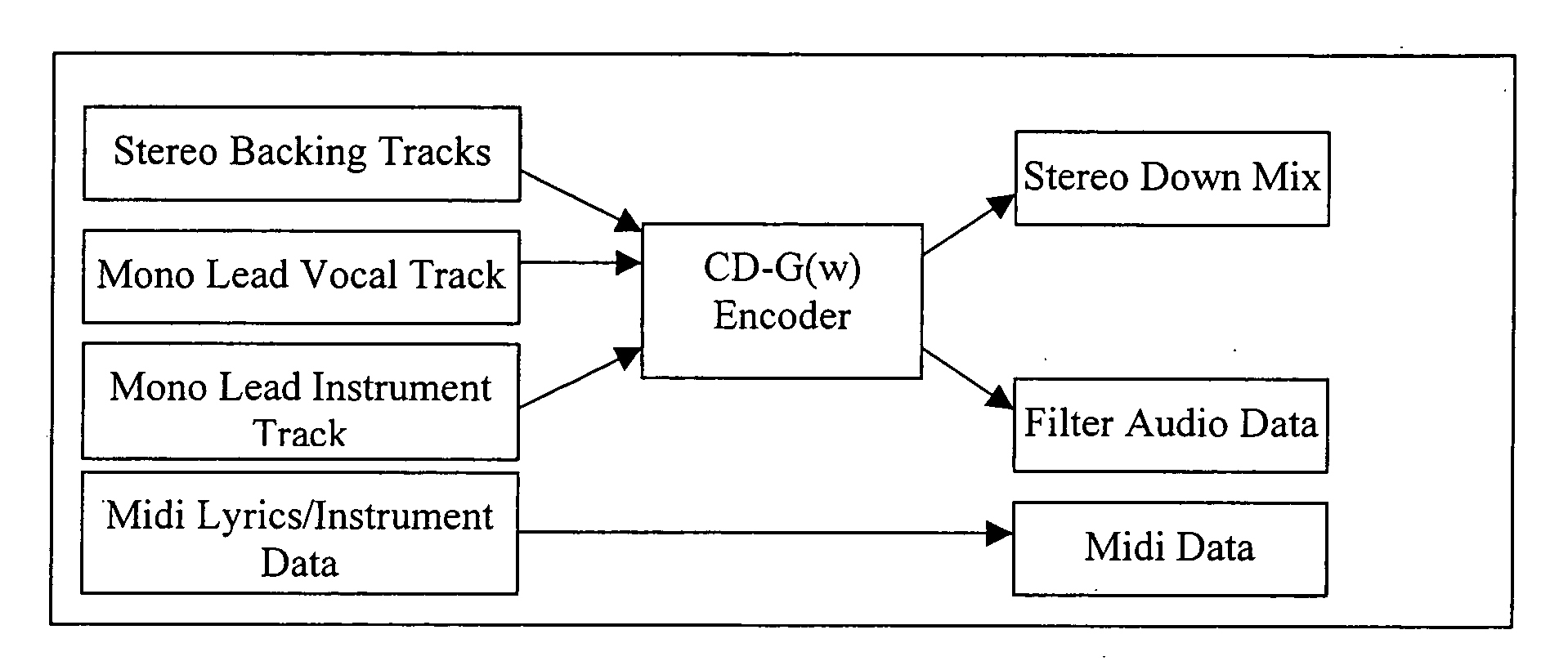
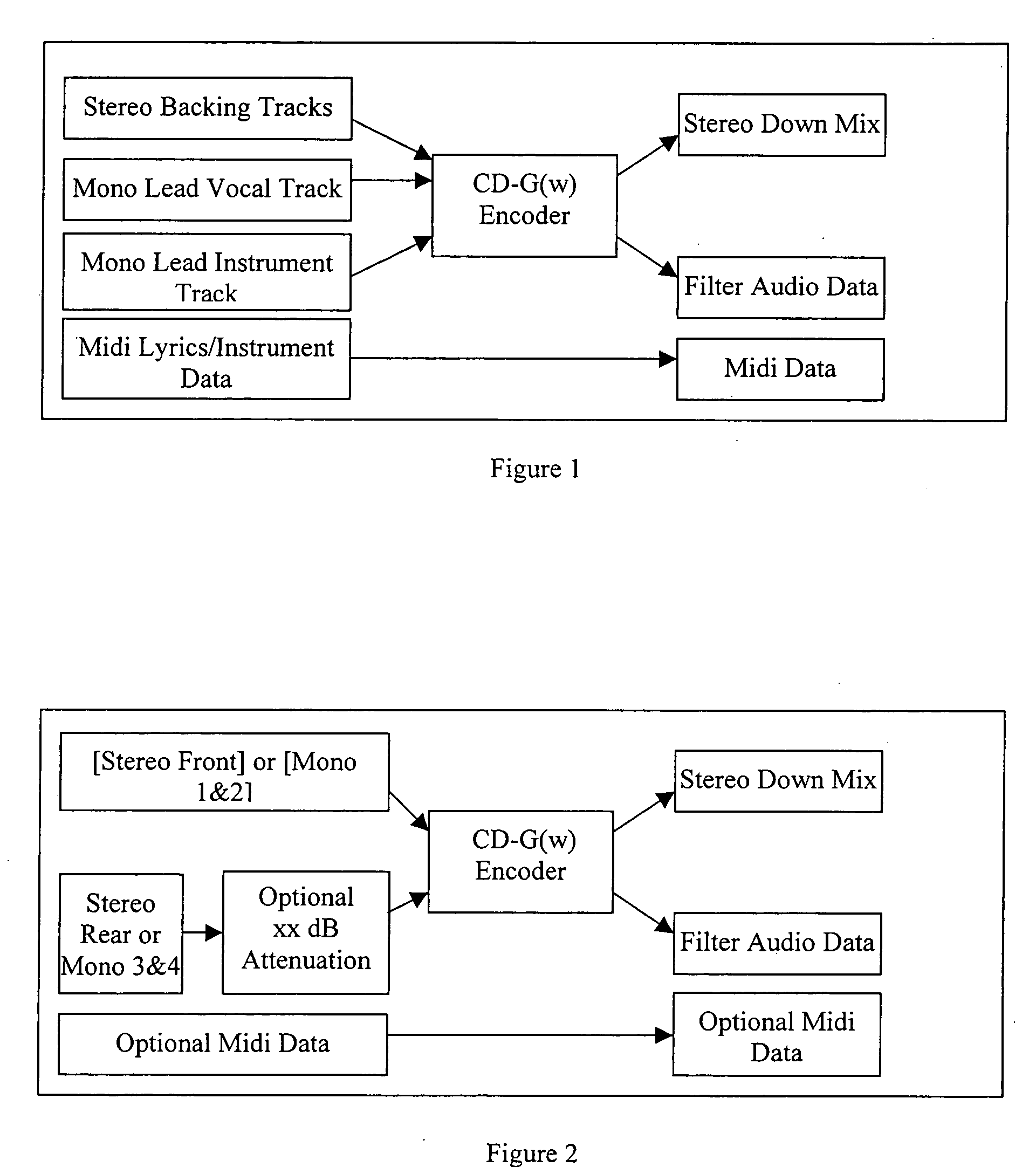
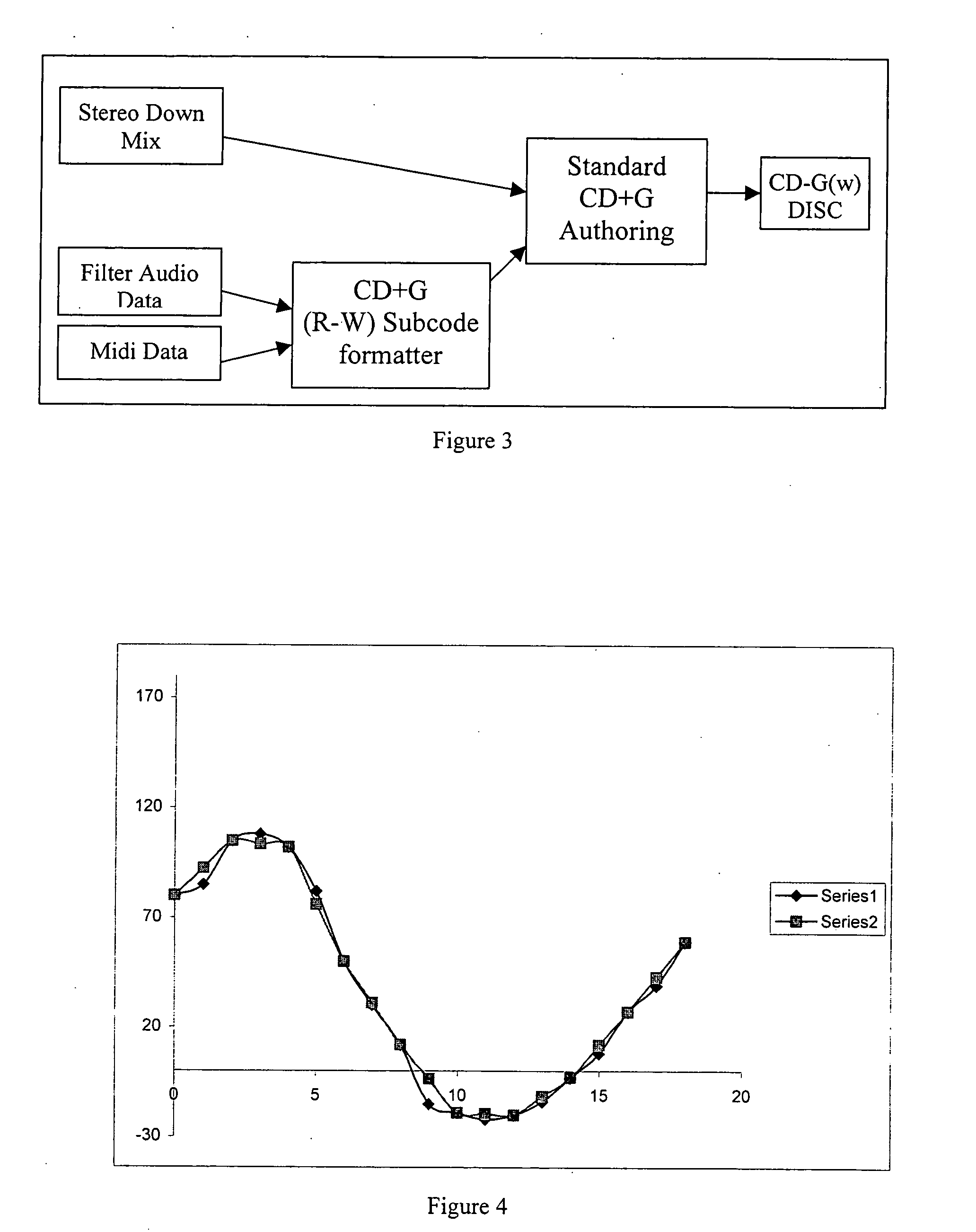
Patents
Literature
55results about "Stereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
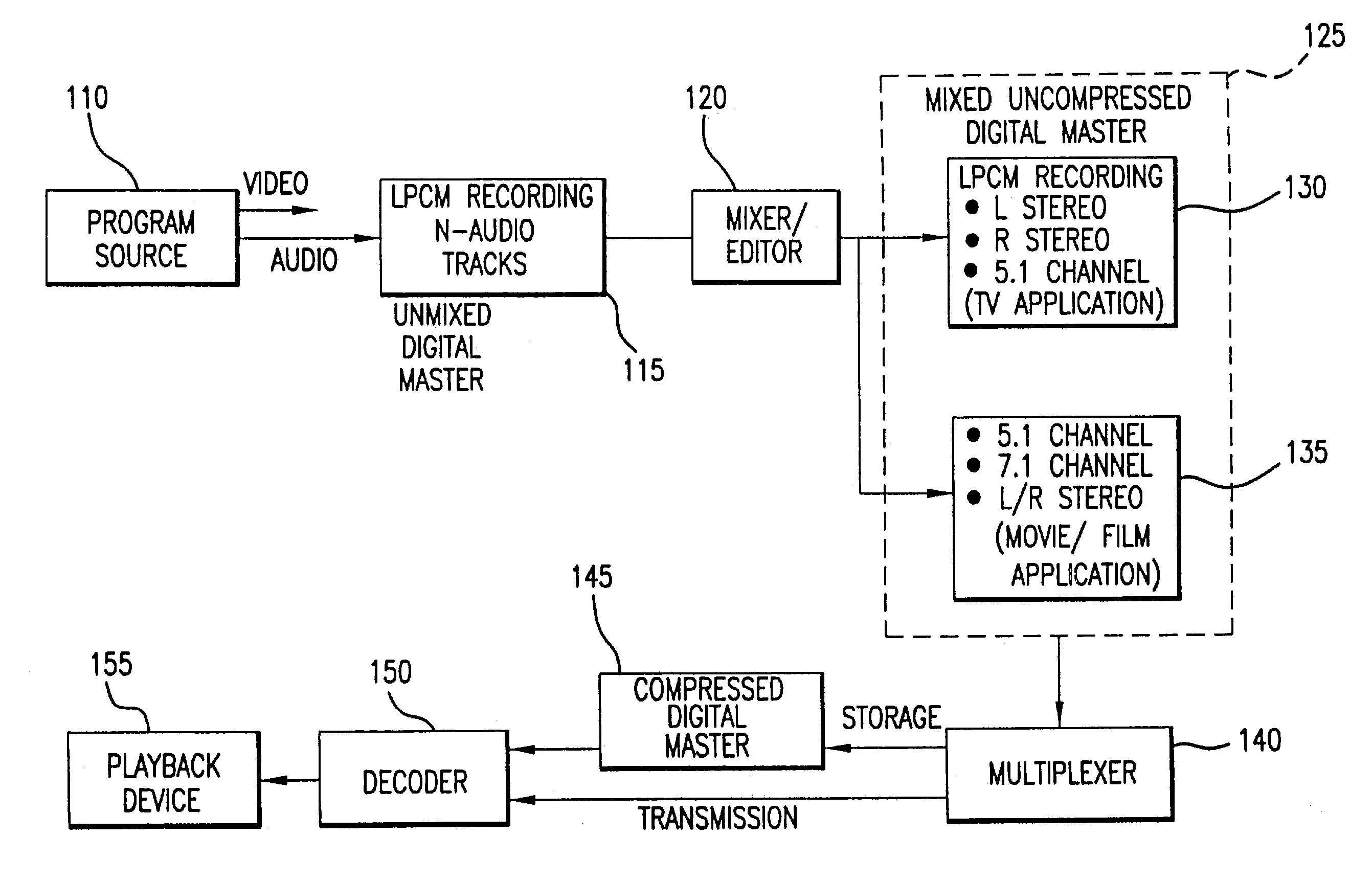
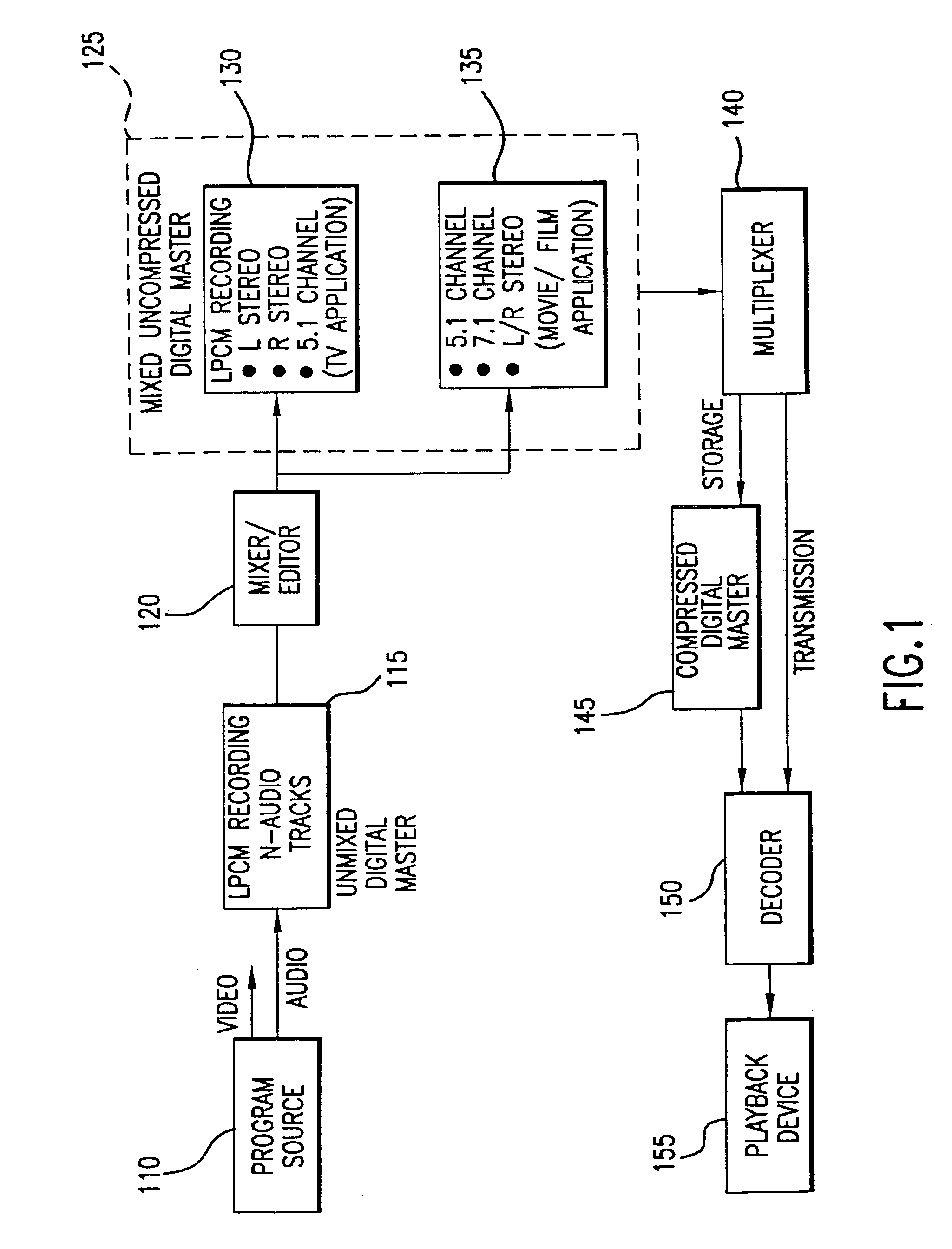
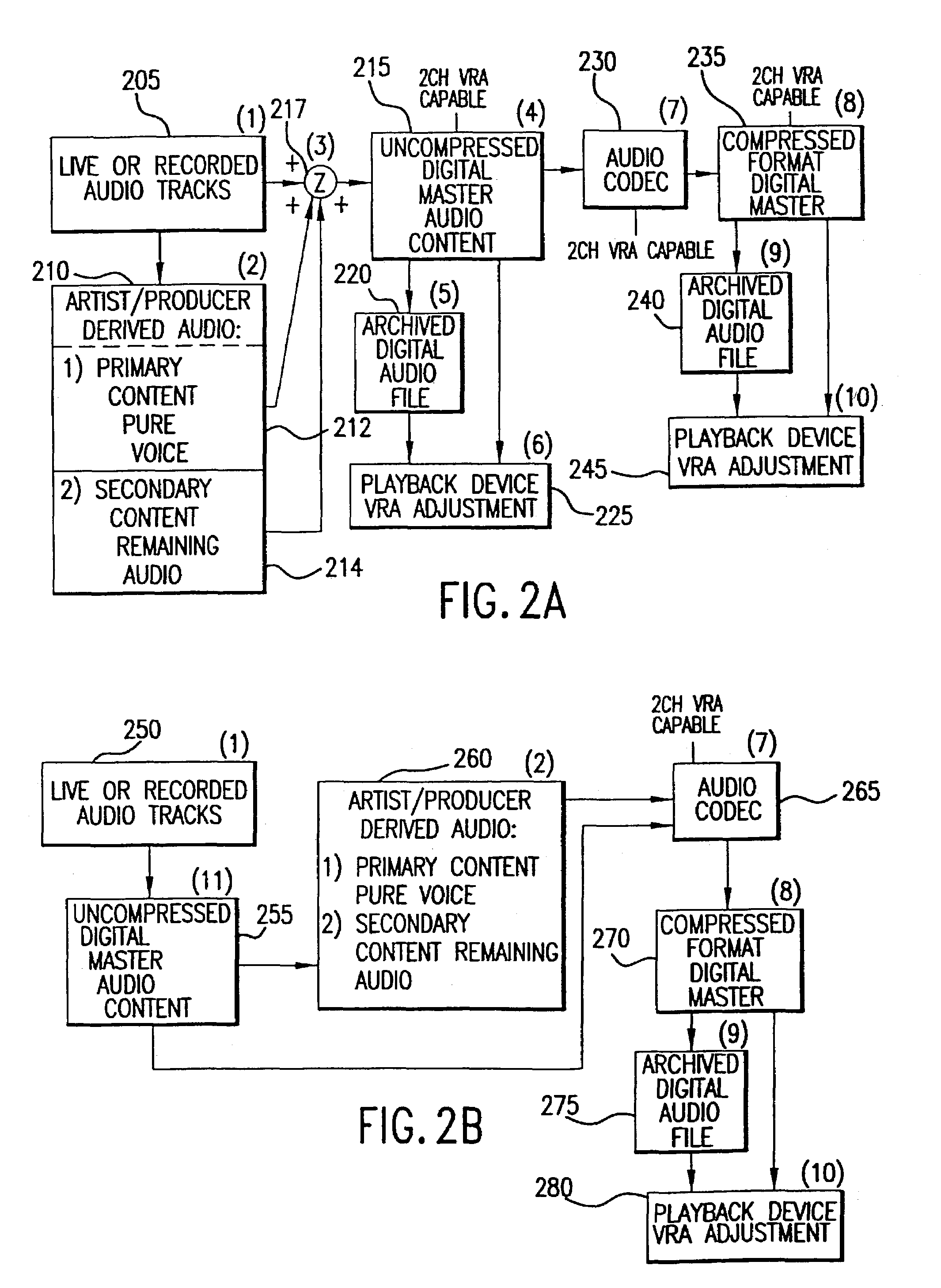
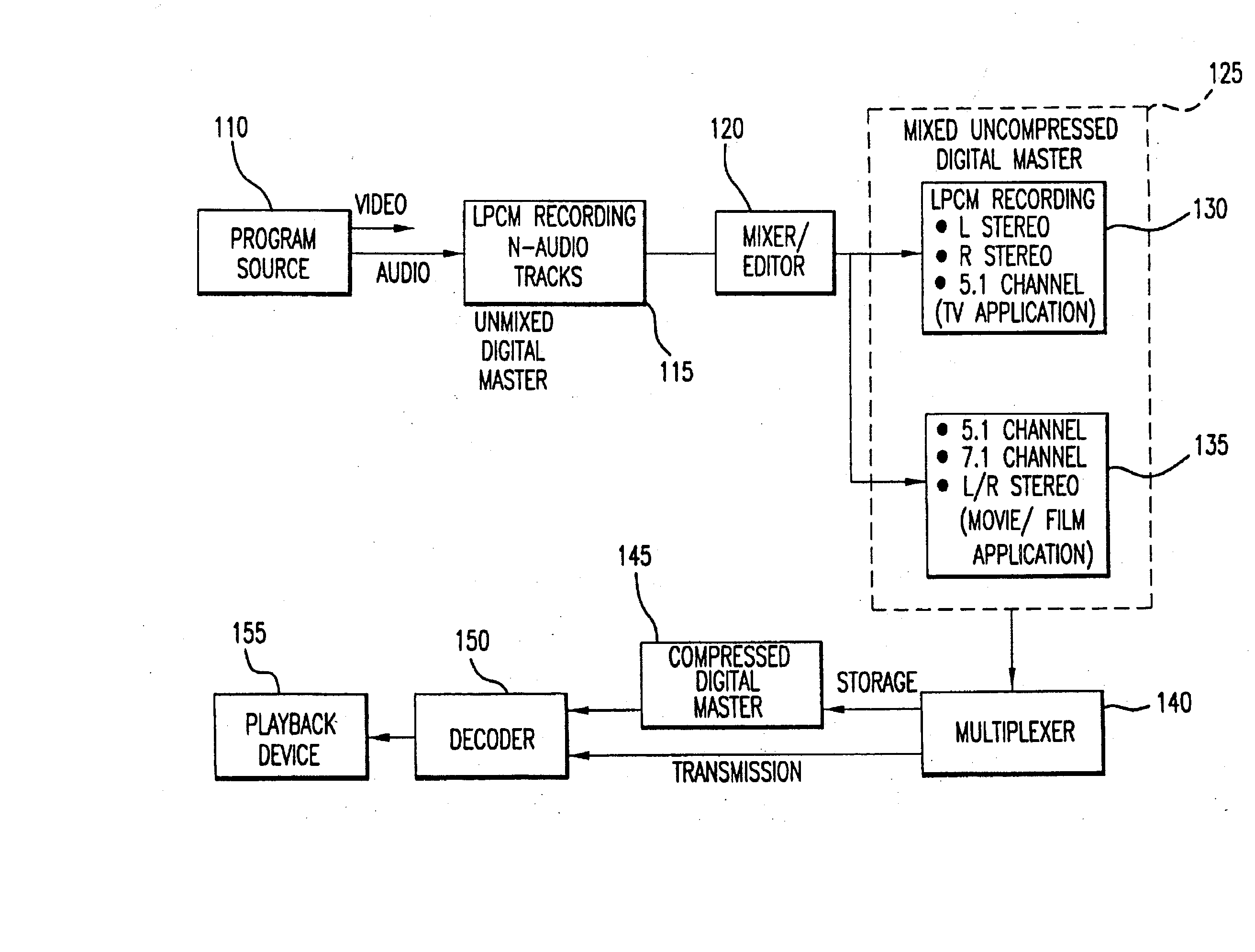
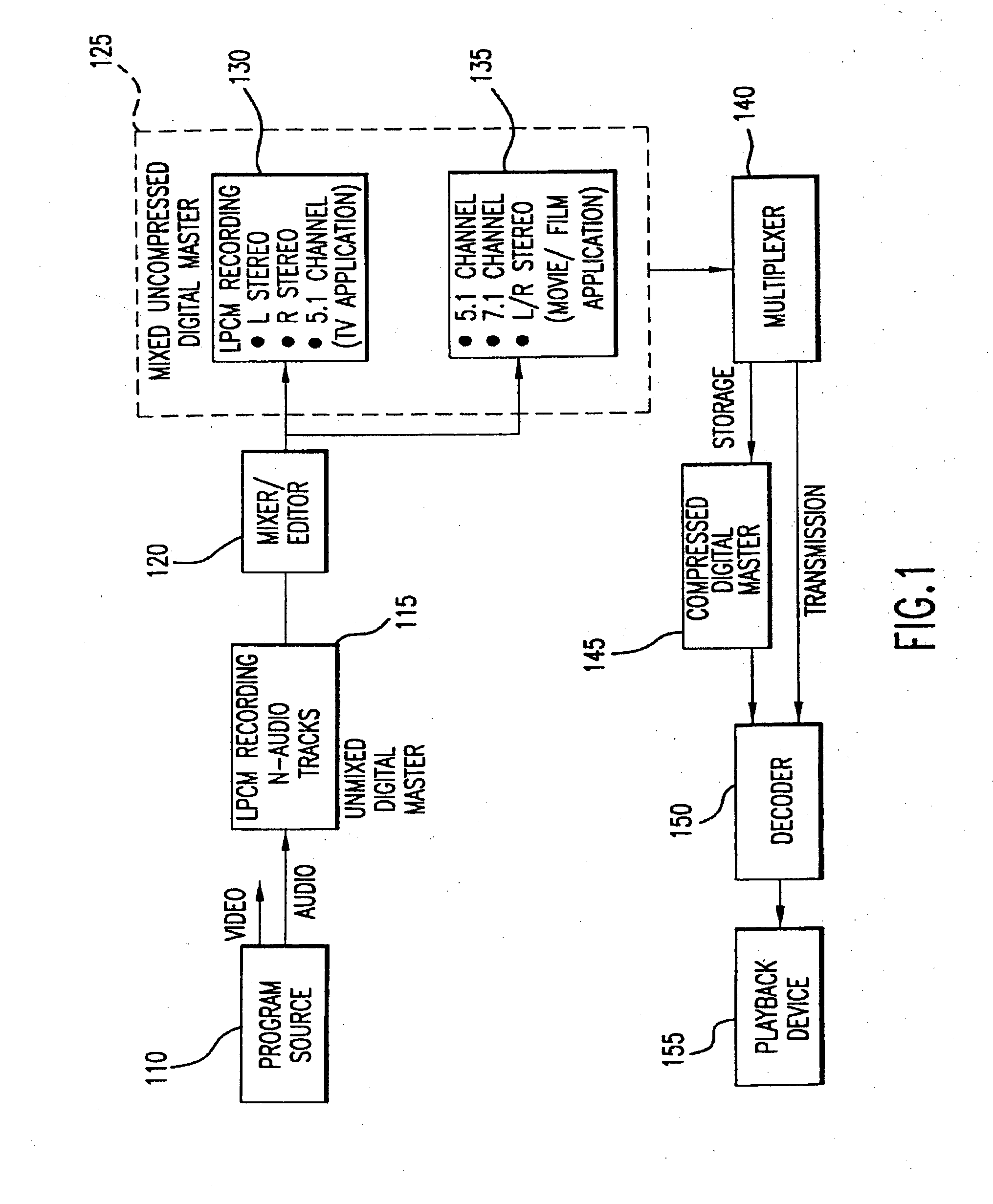
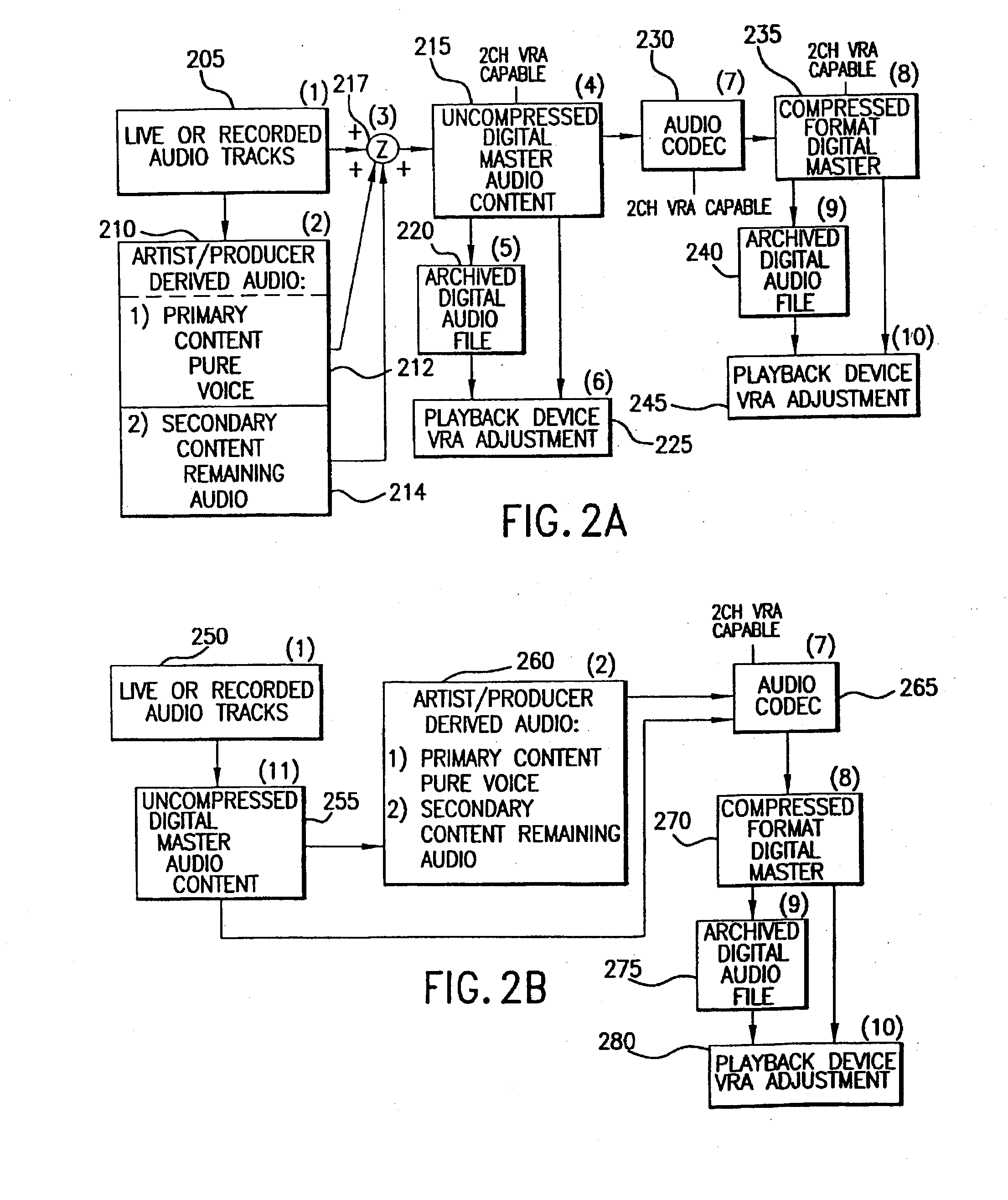
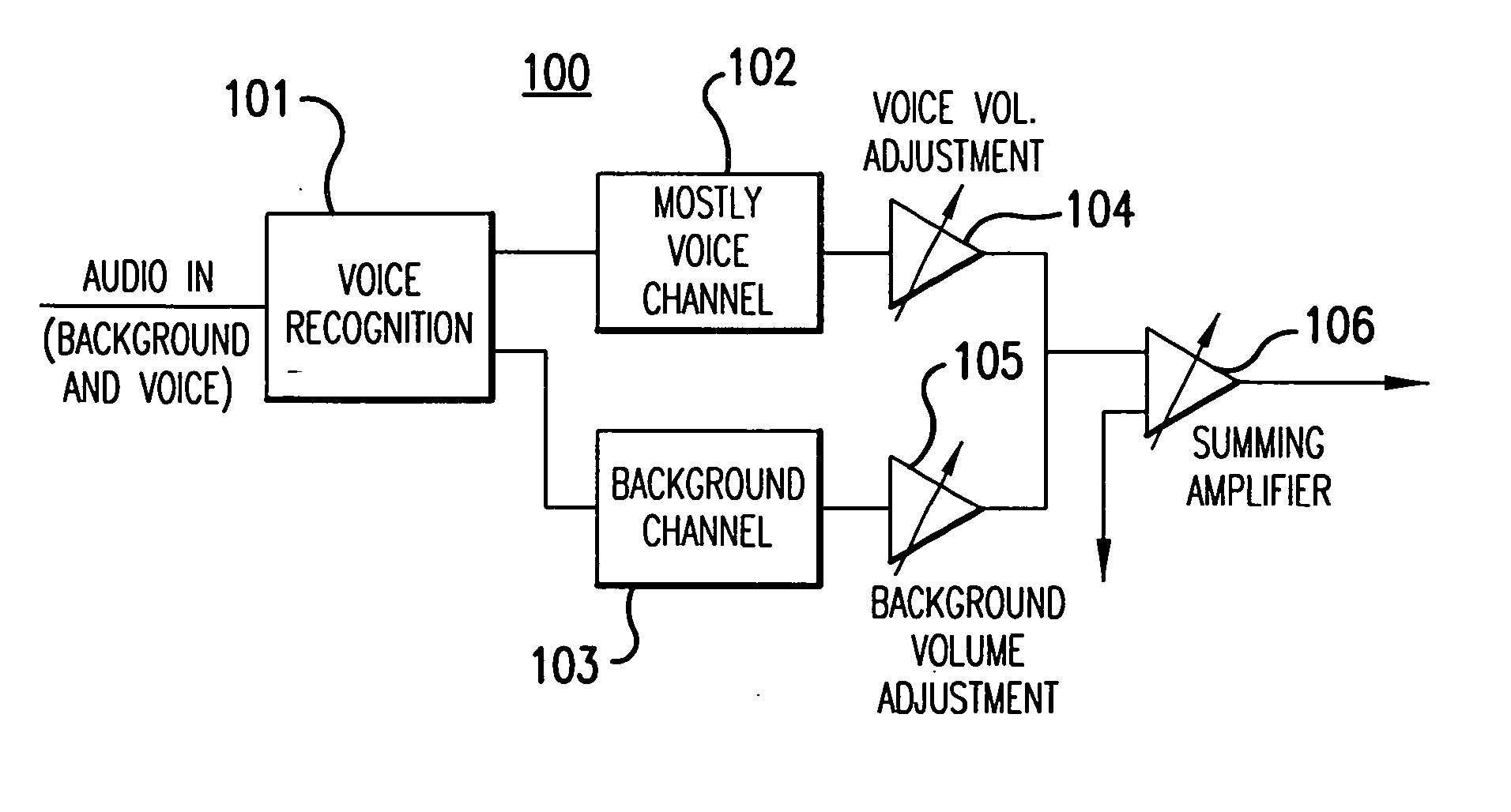
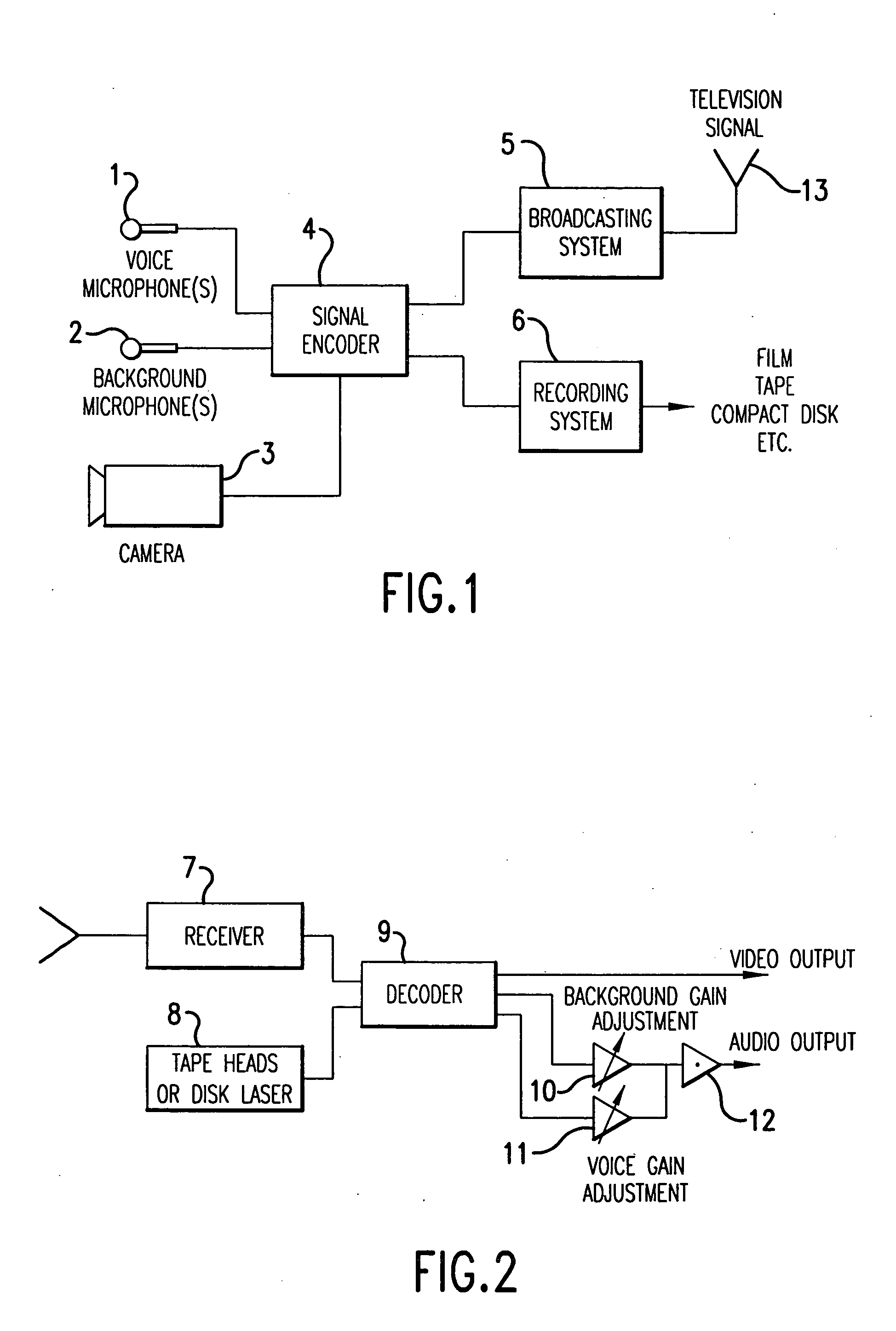
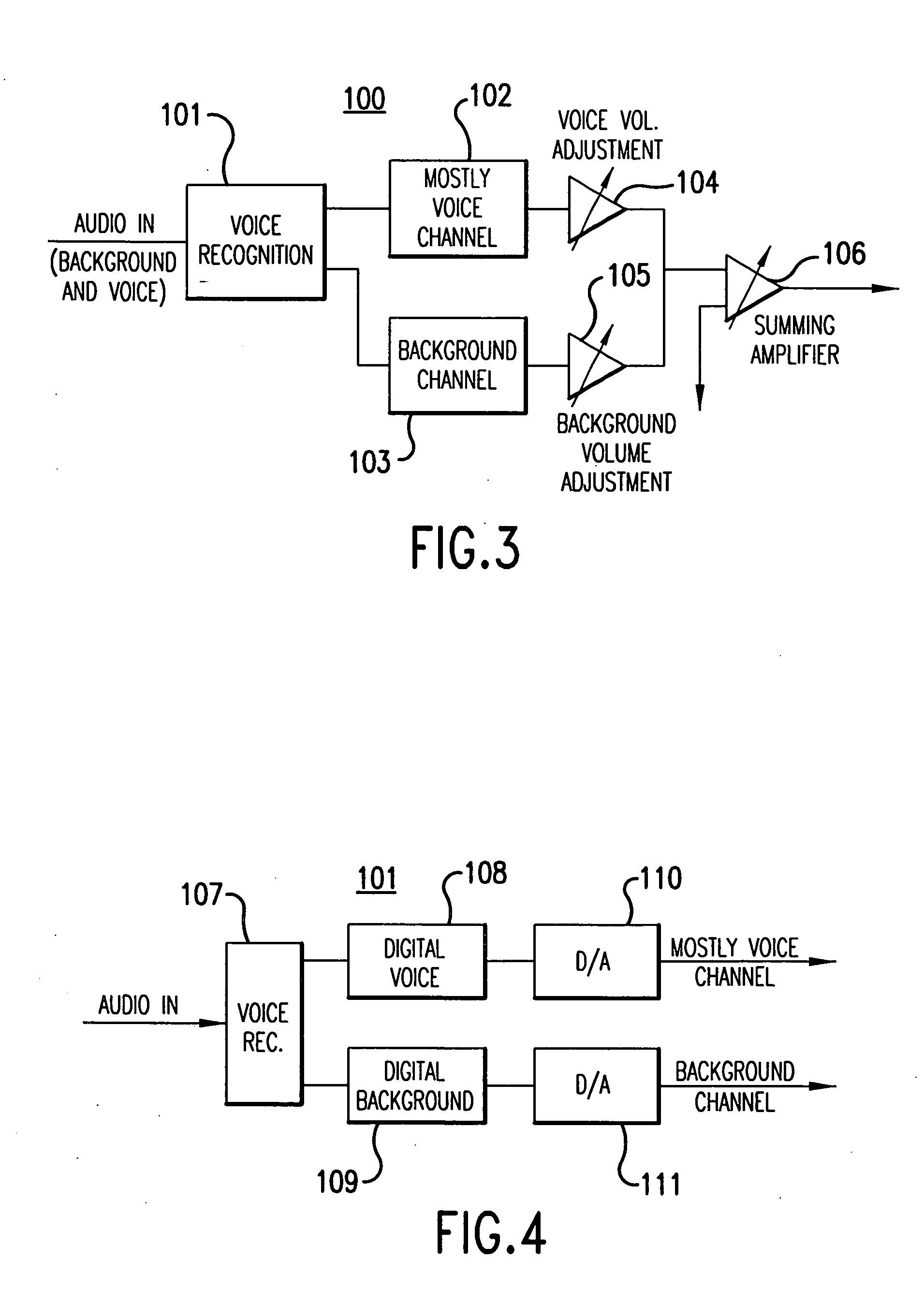
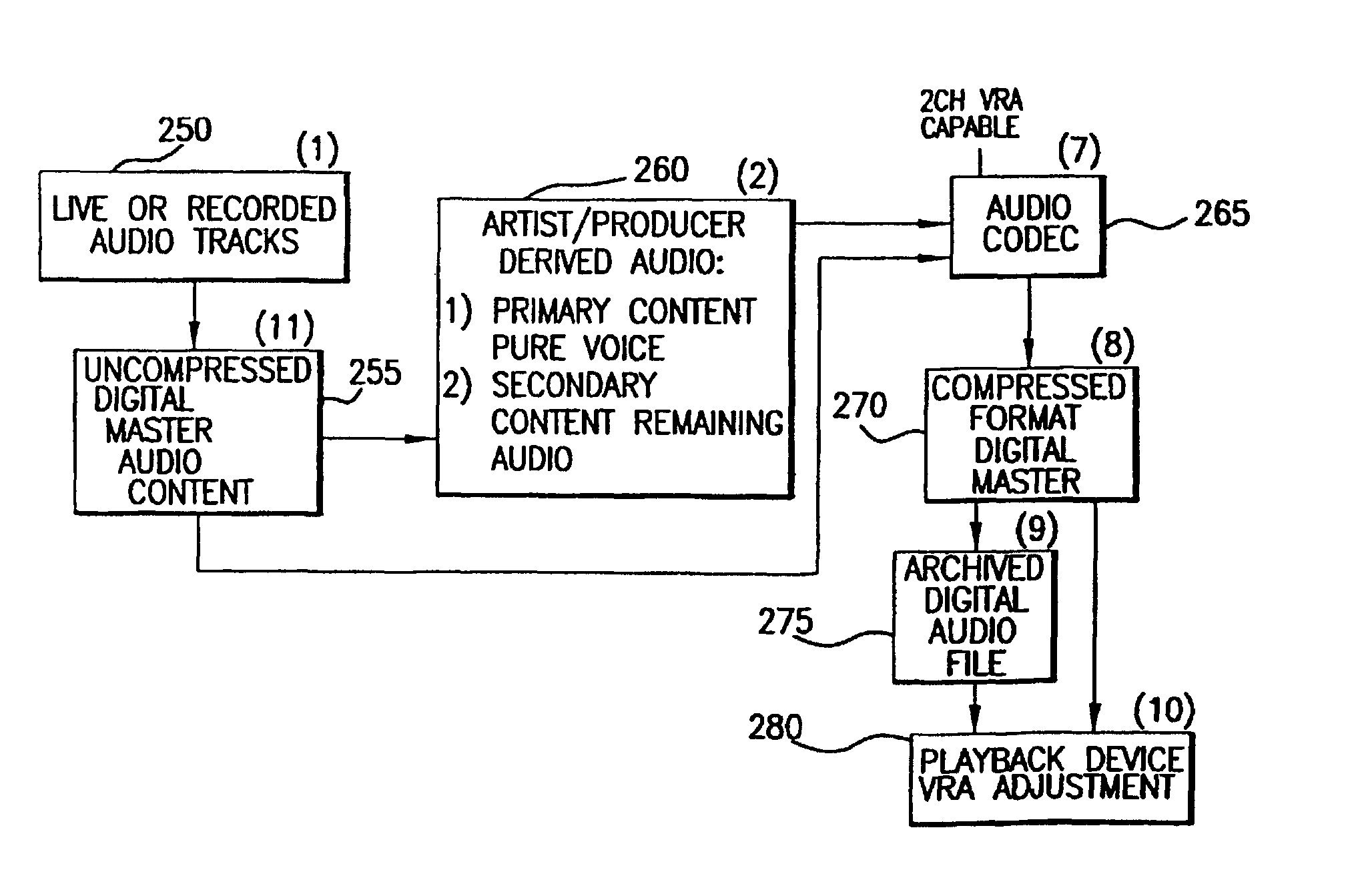
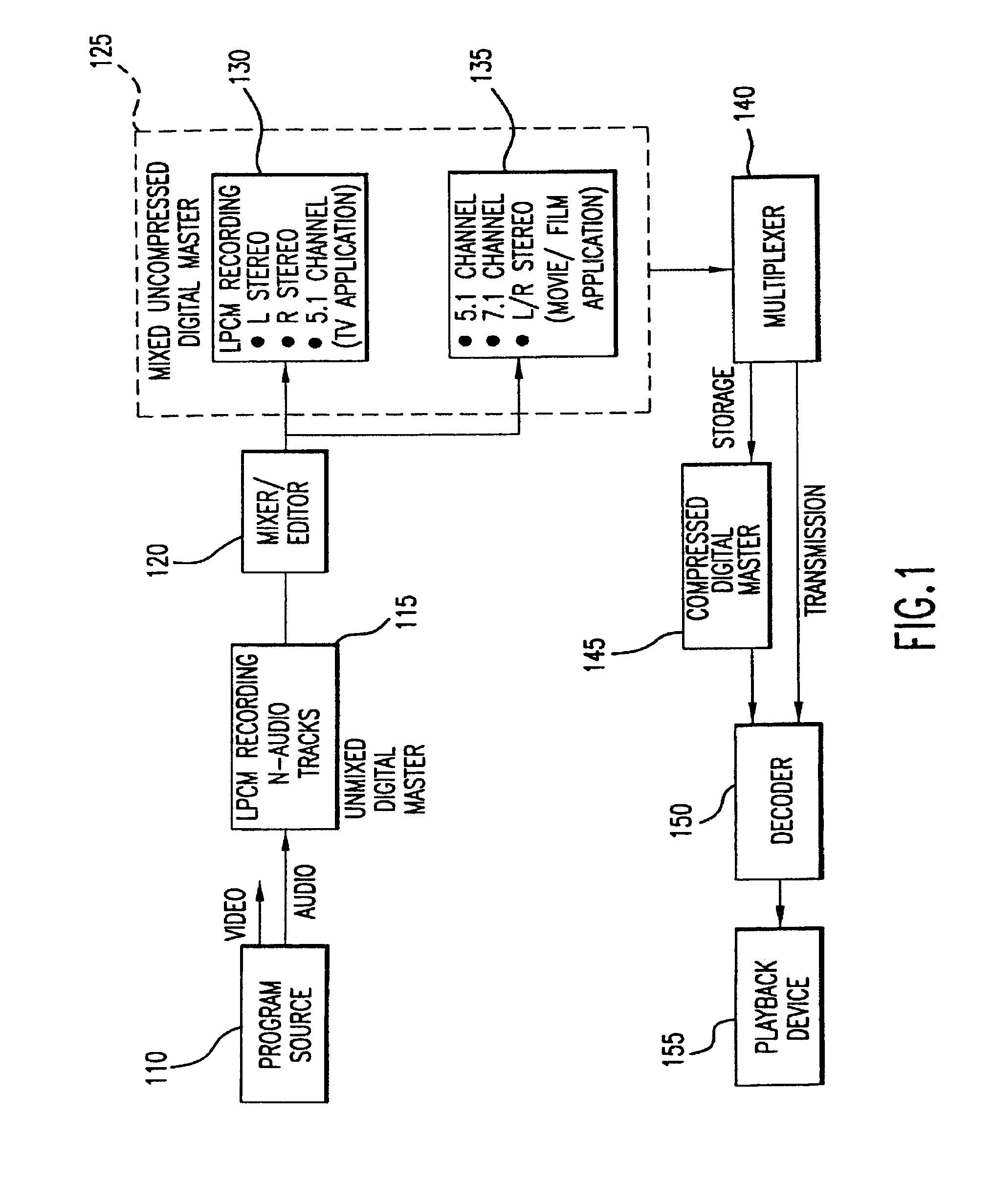
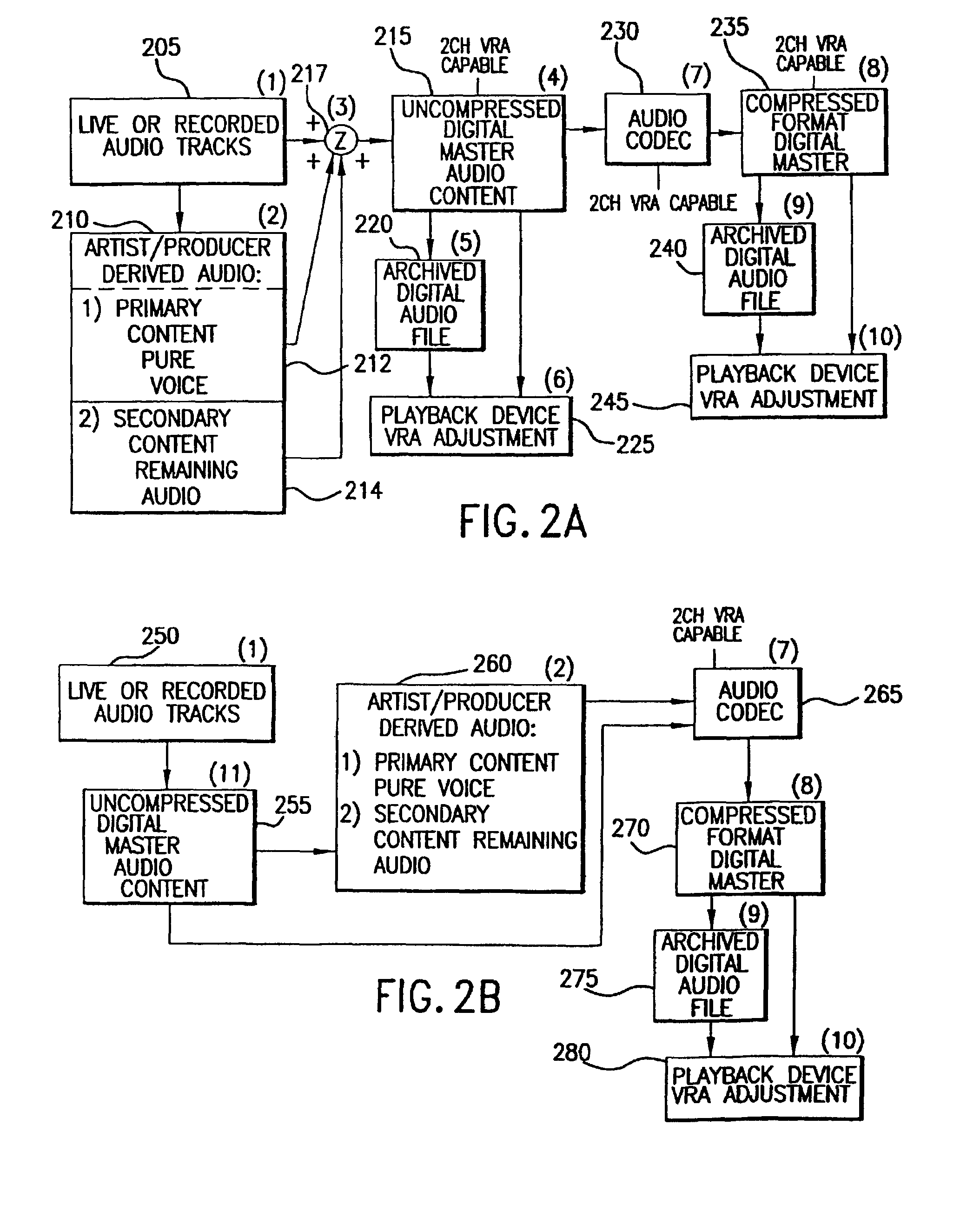
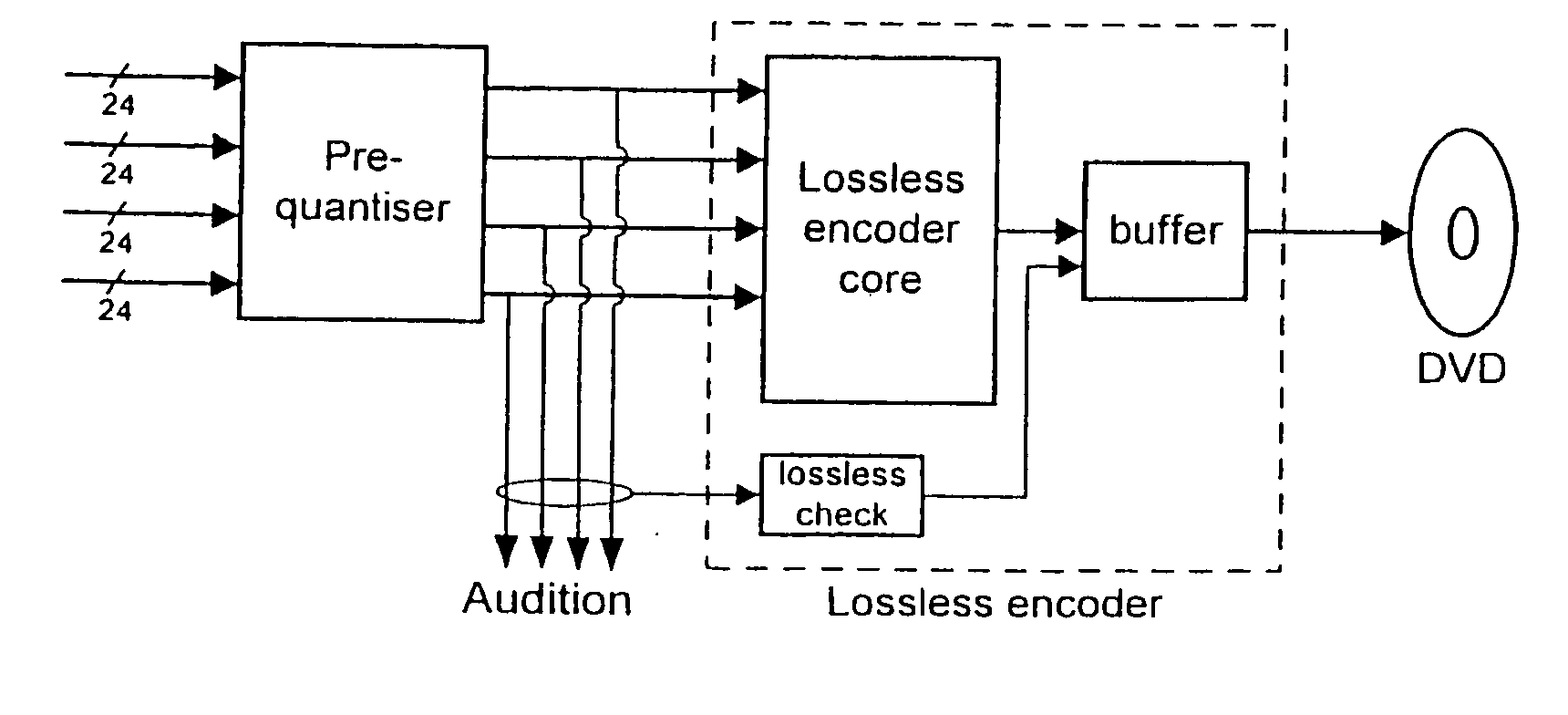
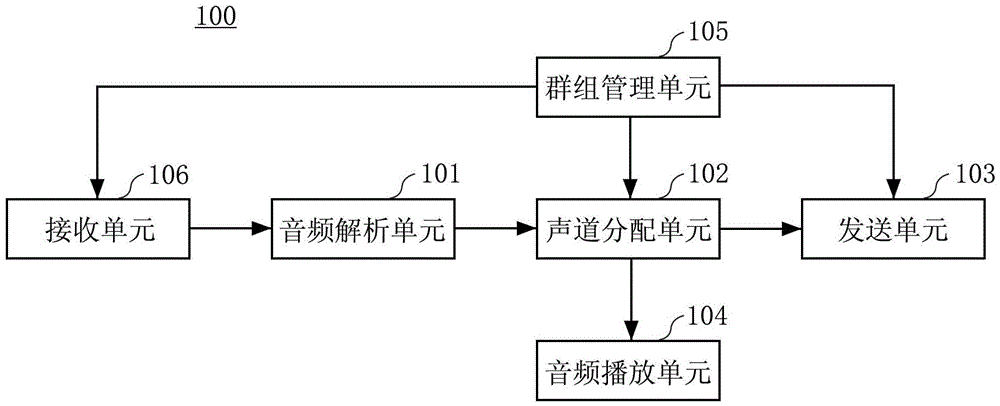
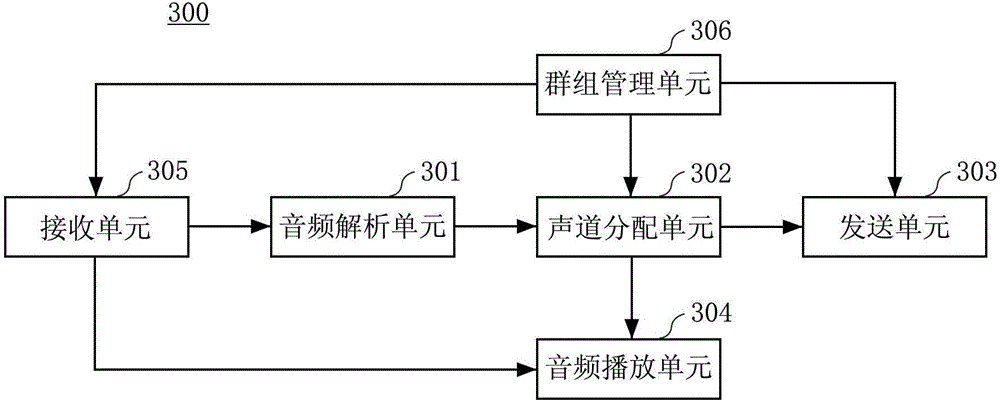
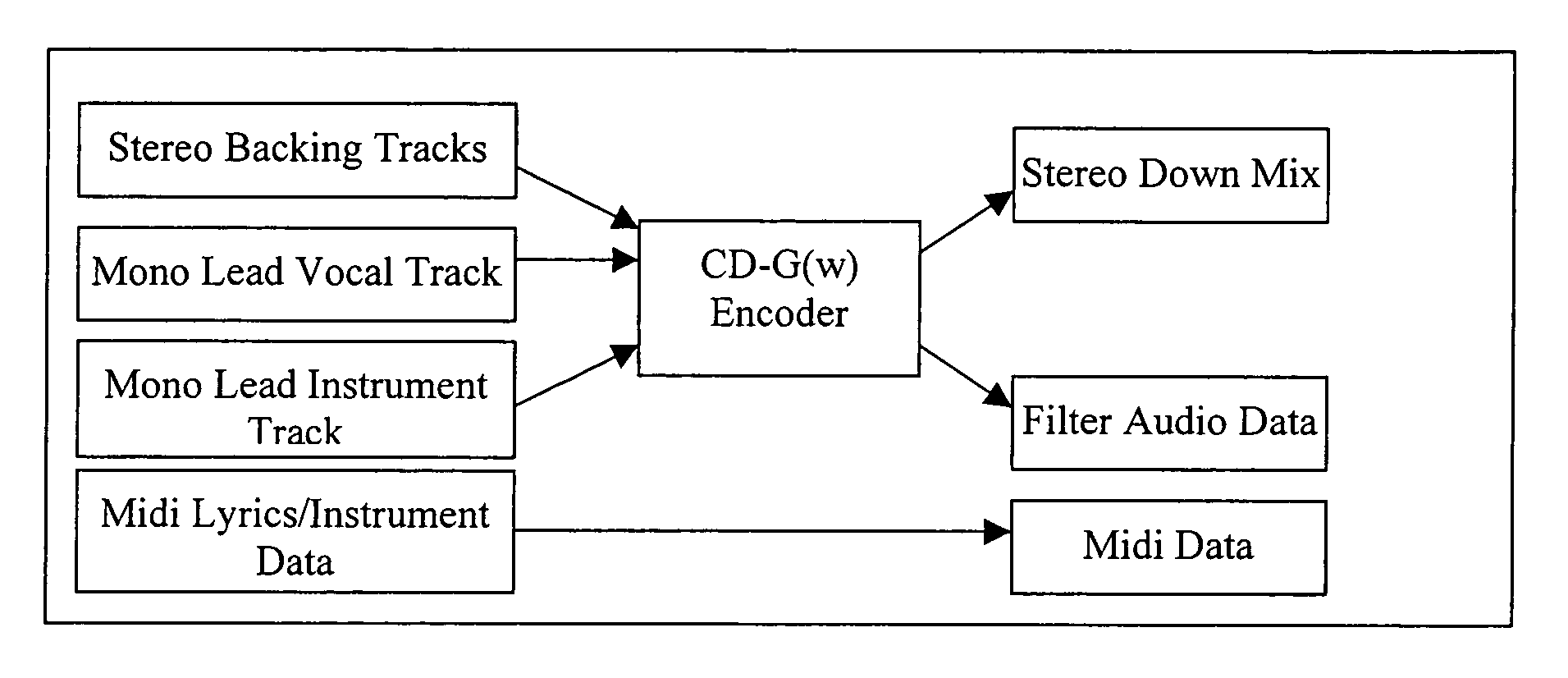
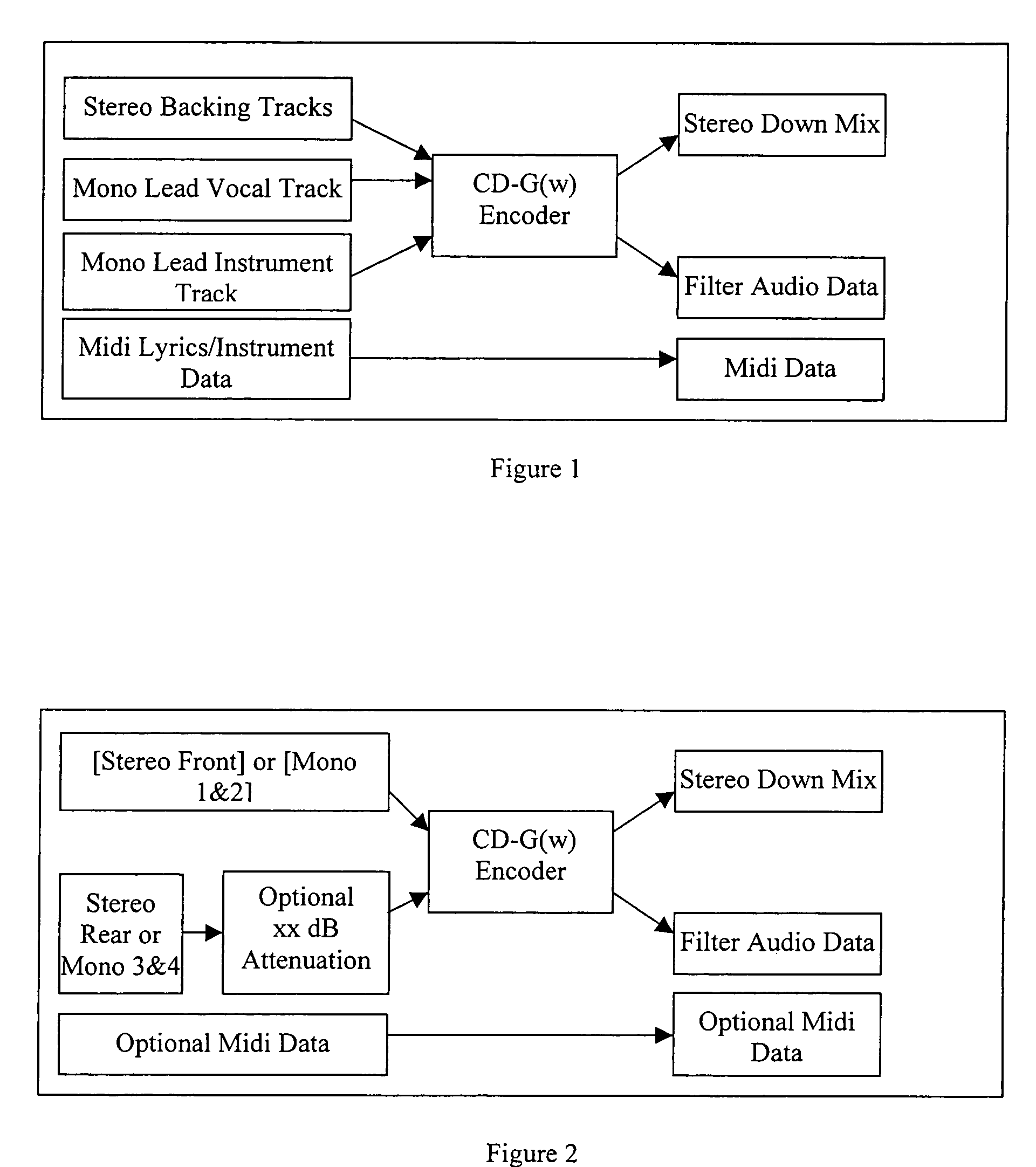
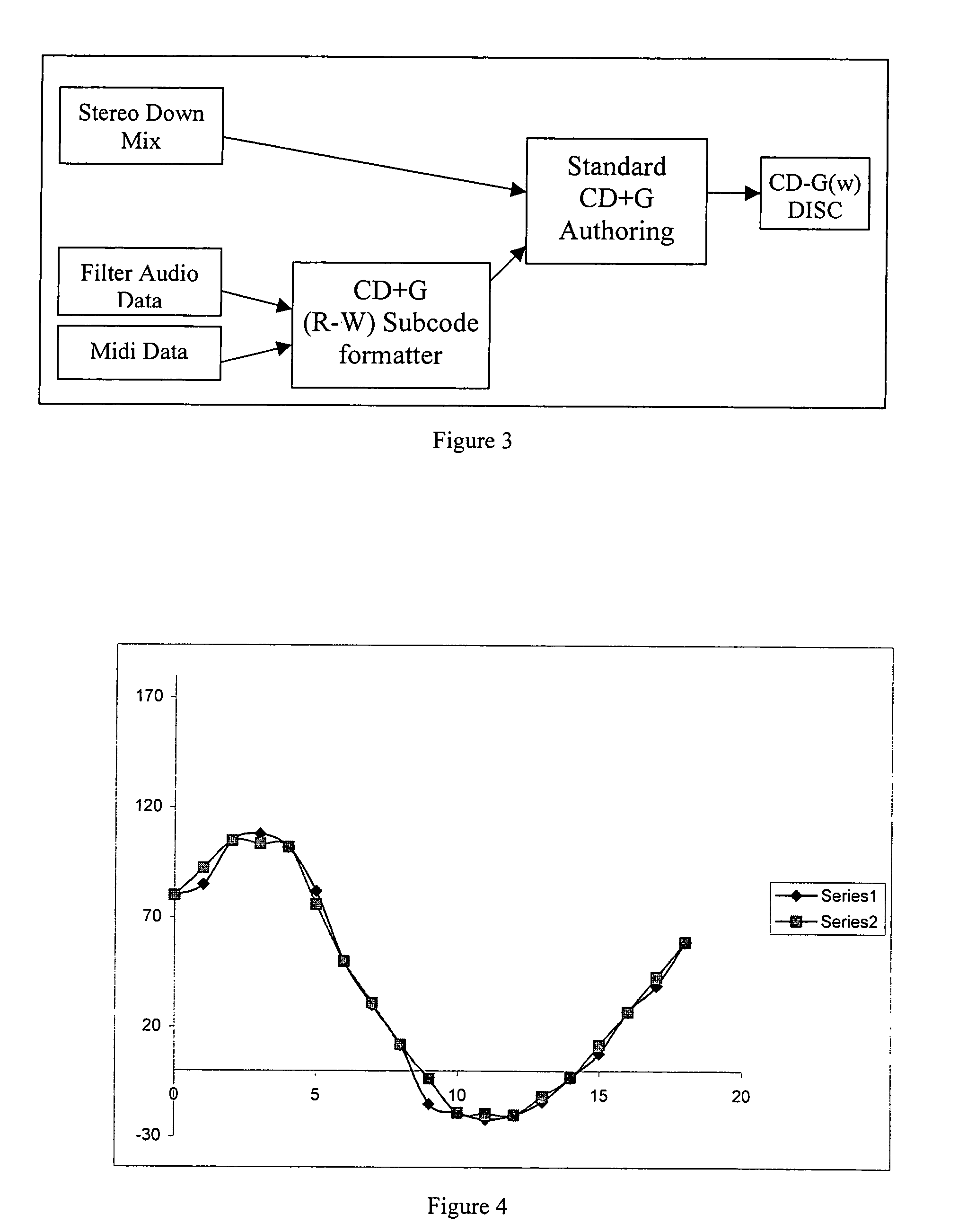
Method and apparatus for accommodating primary content audio and secondary content remaining audio capability in the digital audio production process
InactiveUS7266501B2Reduce lossesAudio/video recordingStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsComputer hardwareOptical storage
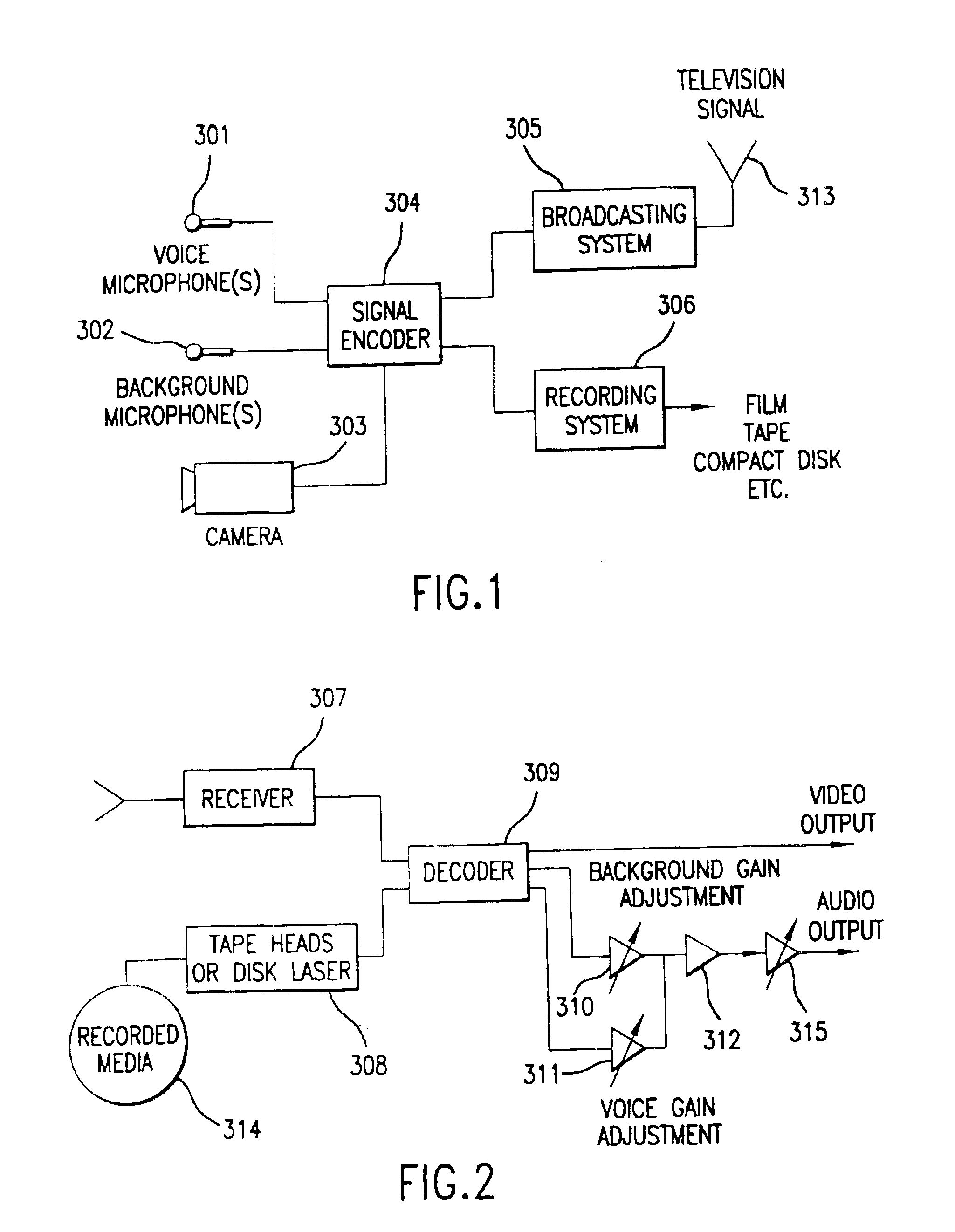
The invention enables the inclusion of voice and remaining audio information at different parts of the audio production process. In particular, the invention embodies special techniques for VRA-capable digital mastering, accommodation of PCPV / PCA and / or SCRA signals in audio CODECs, VRA-capable encoders and decoders, and VRA in DVD and other digital audio file formats. The invention facilitates an end-listener's voice-to-remaining audio (VRA) adjustment upon the playback of digital audio media formats by focusing on new configurations of multiple parts of the entire digital audio system, thereby enabling a new technique intended to benefit audio end-users (end-listeners) who wish to control the ratio of the primary vocal / dialog content of an audio program relative to the remaining portion of the audio content in that program. The invention facilitates storage of VRA audio programs on optical storage media, authoring systems for VRA-capable DVDs, playback hardware integrated into VRA-capable optical disc apparatus, and VRA playback hardware for use with non-VRA capable optical disc playback apparatus.
Owner:BENHOV GMBH LLC
Techniques for accommodating primary content (pure voice) audio and secondary content remaining audio capability in the digital audio production process
InactiveUS20080059160A1Audio/video recordingStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsComputer hardwareOptical storage
The invention enables the inclusion of voice and remaining audio information at different parts of the audio production process. In particular, the invention embodies special techniques for VRA-capable digital mastering, accommodation of PCPV / PCA and / or SCRA signals in audio CODECs, VRA-capable encoders and decoders, and VRA in DVD and other digital audio file formats. The invention facilitates an end-listener's voice-to-remaining audio (VRA) adjustment upon the playback of digital audio media formats by focusing on new configurations of multiple parts of the entire digital audio system, thereby enabling a new technique intended to benefit audio end-users (end-listeners) who wish to control the ratio of the primary vocal / dialog content of an audio program relative to the remaining portion of the audio content in that program. The invention facilitates storage of VRA audio programs on optical storage media, authoring systems for VRA-capable DVDs, playback hardware integrated into VRA-capable optical disc apparatus, and VRA playback hardware for use with non-VRA capable optical disc playback apparatus.
Owner:BENHOV GMBH LLC
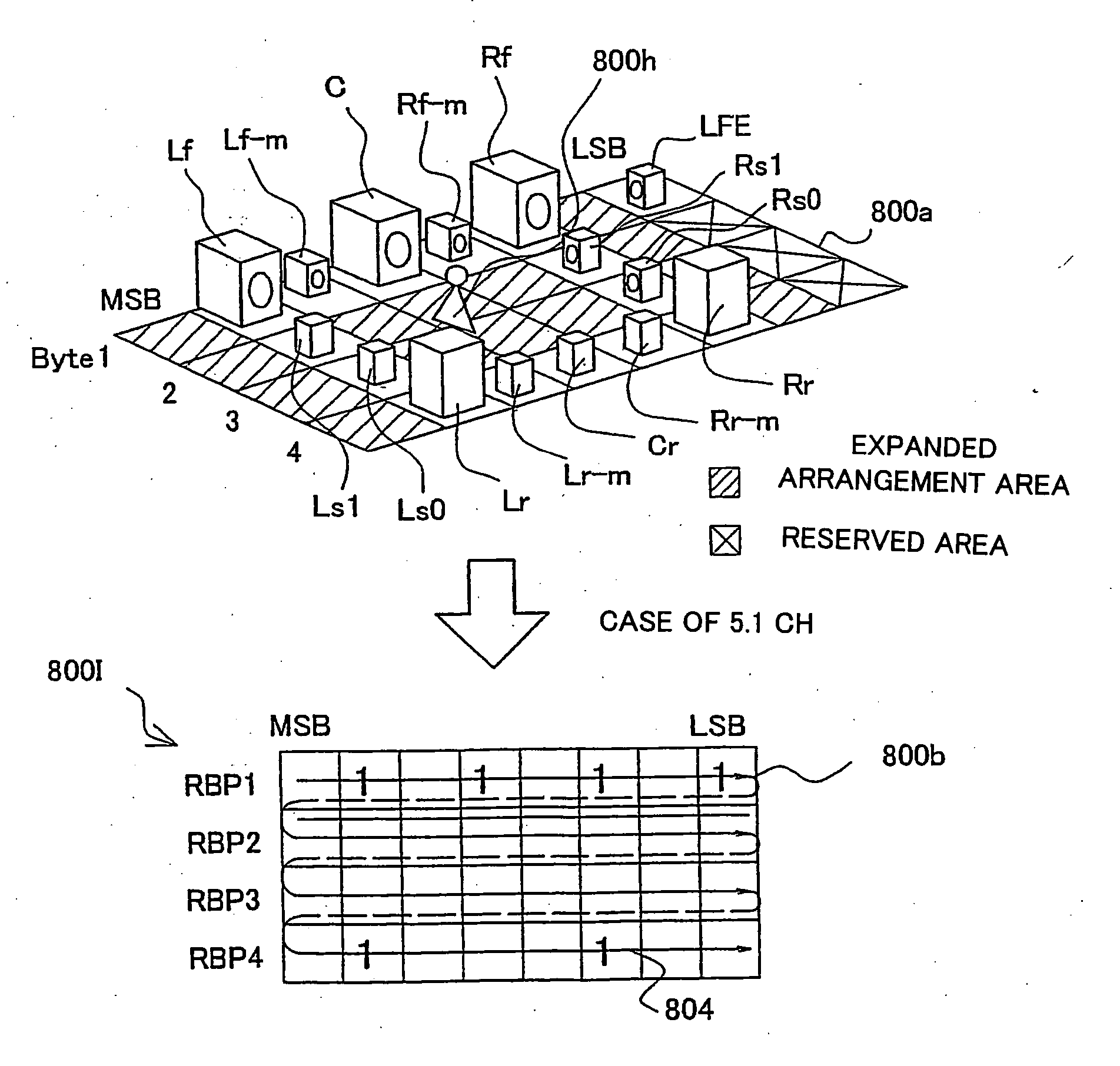
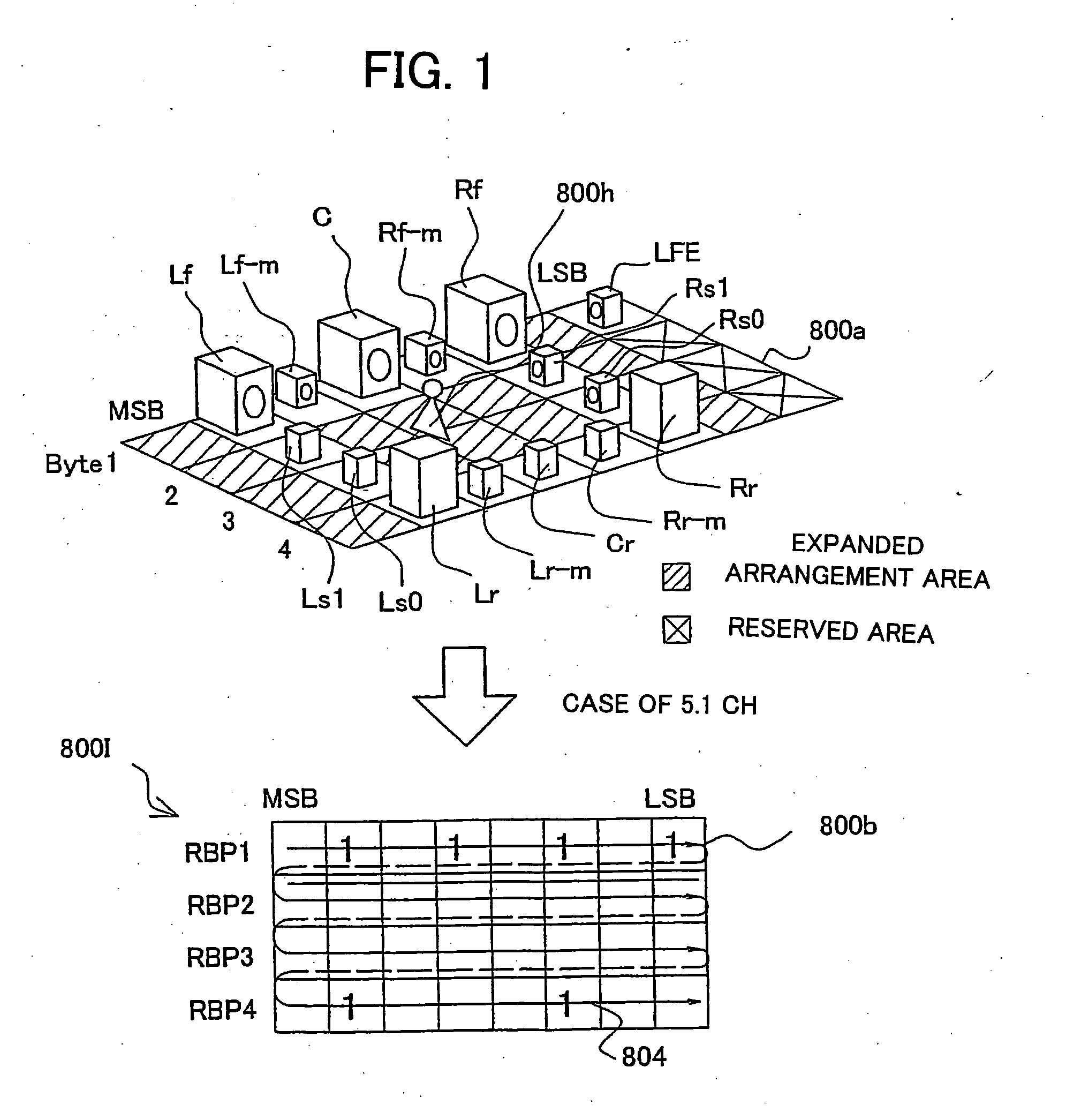
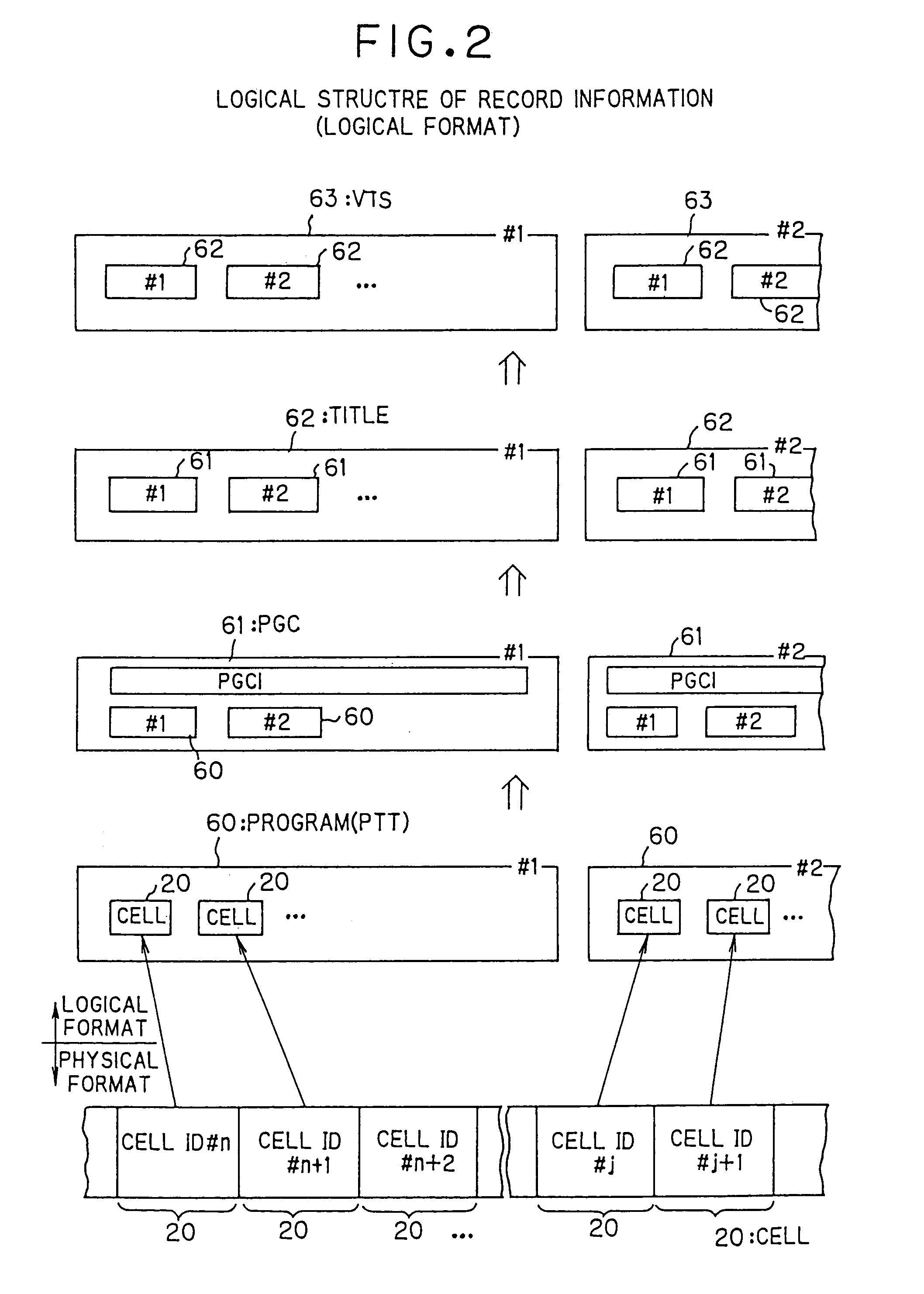
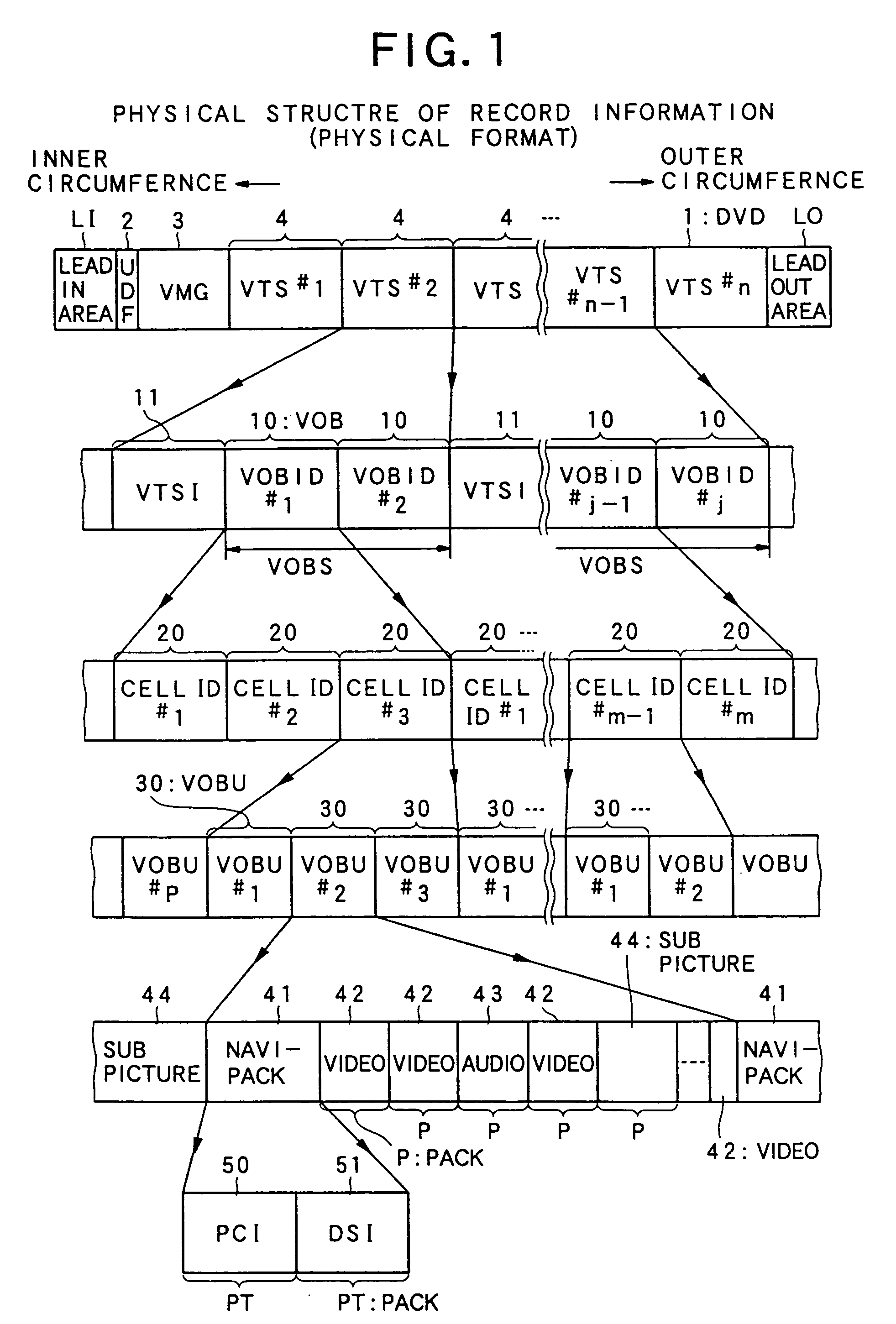
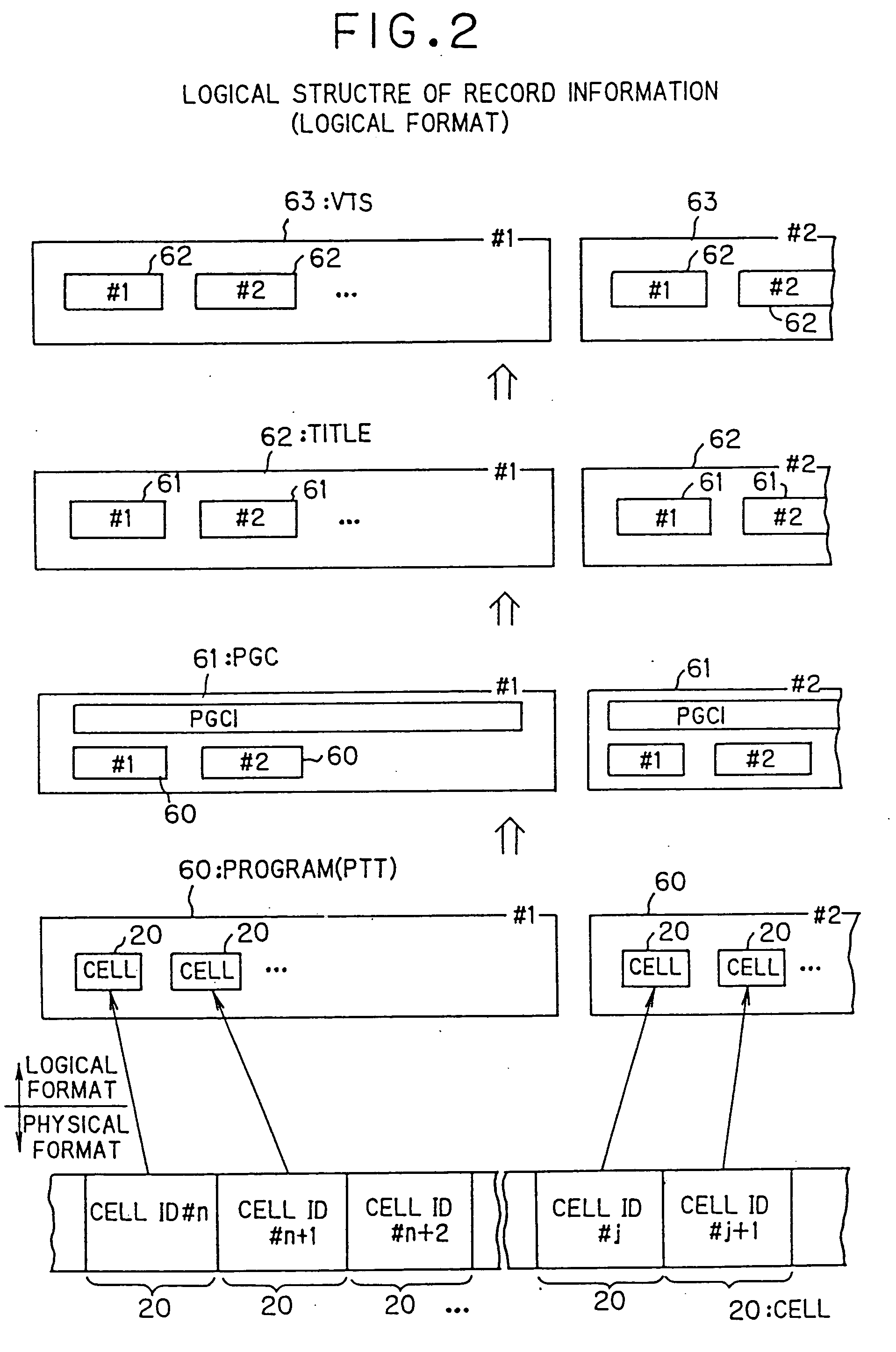
Information recording medium, information recording device and method, information reproduction device and method, information recording/reproduction device and method, computer program, and data structure
InactiveUS20050254281A1Good flexibilityAudio/video recordingStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsComputer hardwareLoudspeaker
Owner:PIONEER CORP
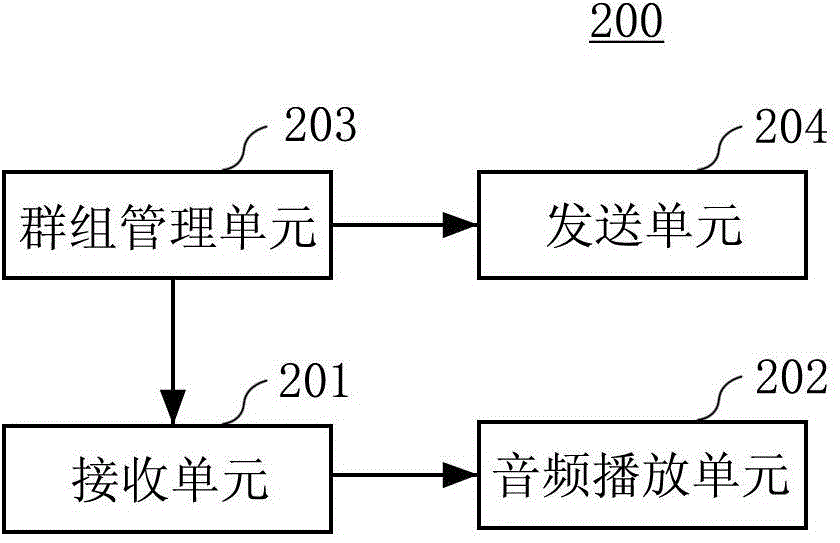
Use of voice-to-remaining audio (VRA) in consumer applications
InactiveUS20050232445A1Stereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsBroadcast information characterisationTransducerSpeech sound
Systems provide an audio / visual output to each of a plurality of listeners in a manner that permits individualized audio adjustment, wherein audio comprises a first signal that is substantially voice and a second signal that is substantially other than voice. The systems may include a video device, a storage medium, and a transmitter that transmits the first and second signals to a plurality of personal listening devices. Each of the plurality of personal listening devices may include first and second receivers, first and second adjustment devices, an audio signal combining device, and one or more transducers, wherein the systems permit each of the plurality of listeners to adjust the first and second signals independently of other ones of the plurality of listeners in an audience.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
Digital audio signal transmission apparatus with data blocks of varying sizes
InactiveUS6097558AEasy loadingEasy to synthesizeTelevision system detailsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsComputer hardwareData segment
Digital audio signal transmission is provided for digitally processing, for transmission in a digital VCR format, audio signals from a plurality of channels into a digitized audio data segmented into blocks having a data size, each block reserved for audio data digitized from one of the channels. The audio data is converted from the channels into the blocks of digitized audio data by varying the data size of the blocks. The audio data is composed by scaling the audio data in at least one of the blocks and combining the scaled audio data with the audio data of another of the blocks into a block reserved for composite audio data.
Owner:SONY CORP
Use of voice-to-remaining audio (VRA) in consumer applications
InactiveUS6912501B2Stereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsBroadcast information characterisationSpeech soundAudio frequency
A method for providing multiple users with voice-to-remaining audio (VRA) adjustment capability includes receiving at a first decoder a voice signal and a remaining audio signal and simultaneously receiving at a second decoder, the voice signal and the remaining audio signal, wherein the voice signal and the remaining audio signal are received separately; and separately adjusting by each of the decoders, the separately received voice and remaining audio signals.
Owner:AKIBA ELECTRONICS INST LLC +1
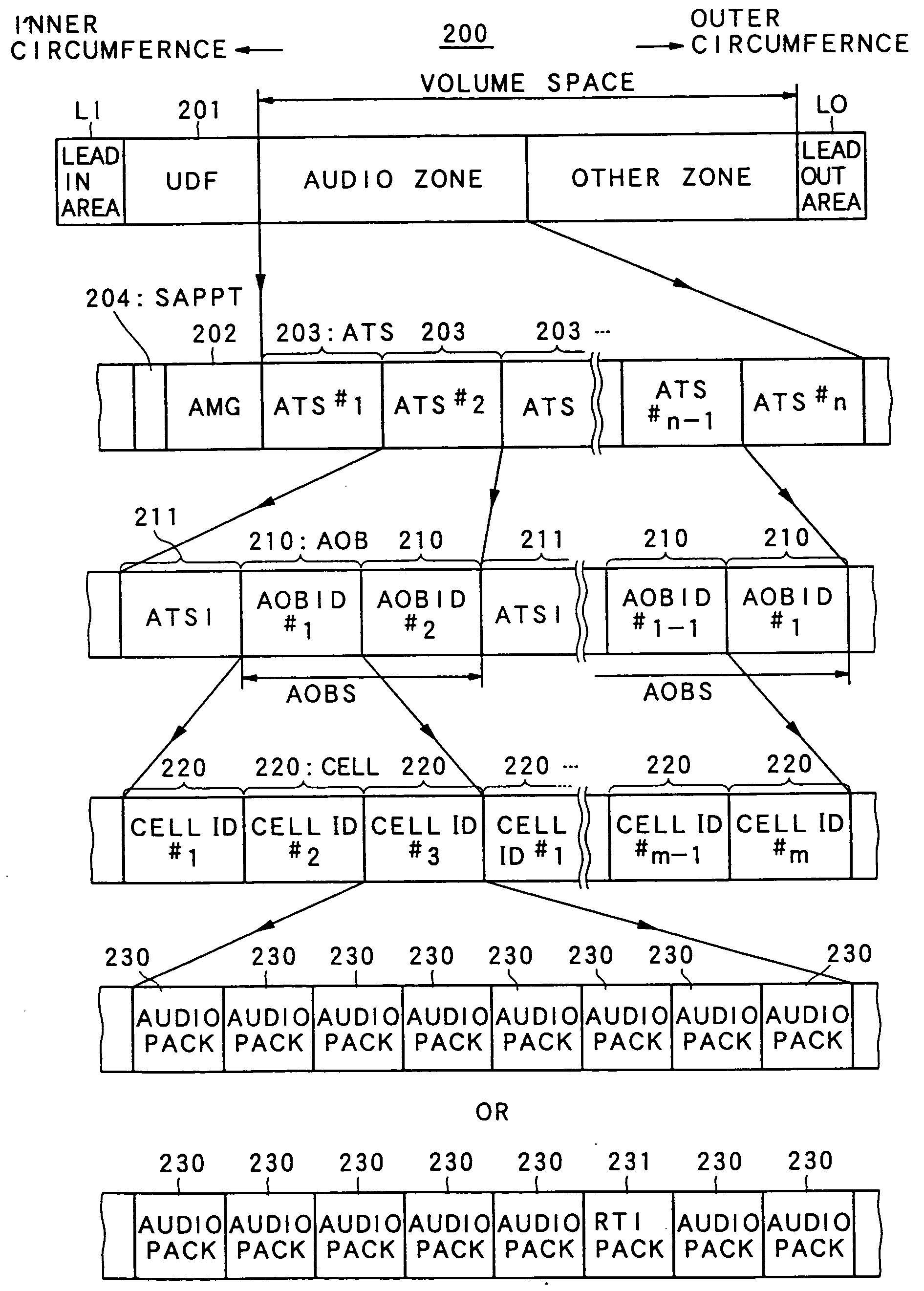
Information record medium and apparatus for reproducing the same
InactiveUS6965727B1Exact reproductionTelevision system detailsAudio/video recordingComputer hardwareAudio frequency
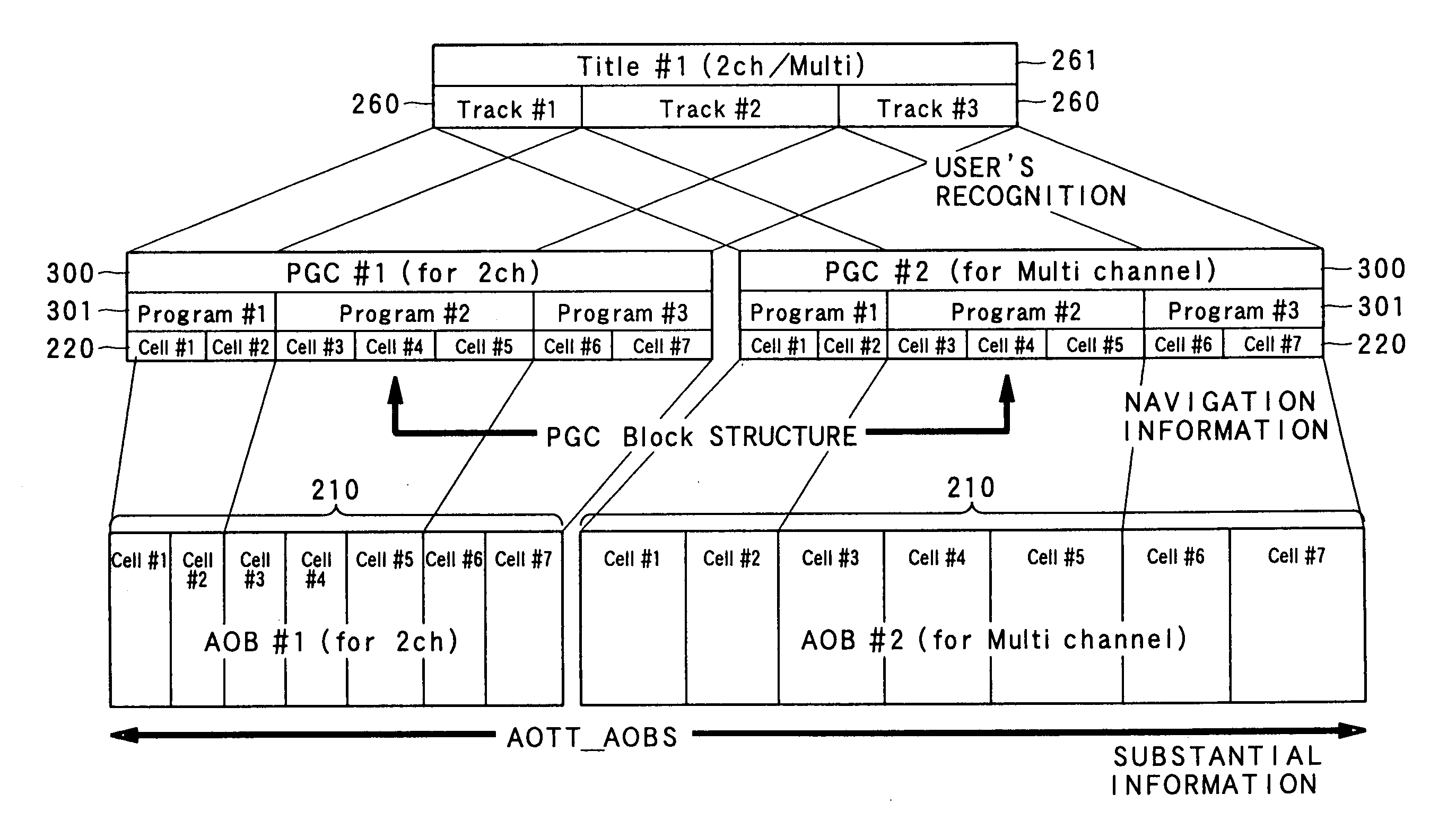
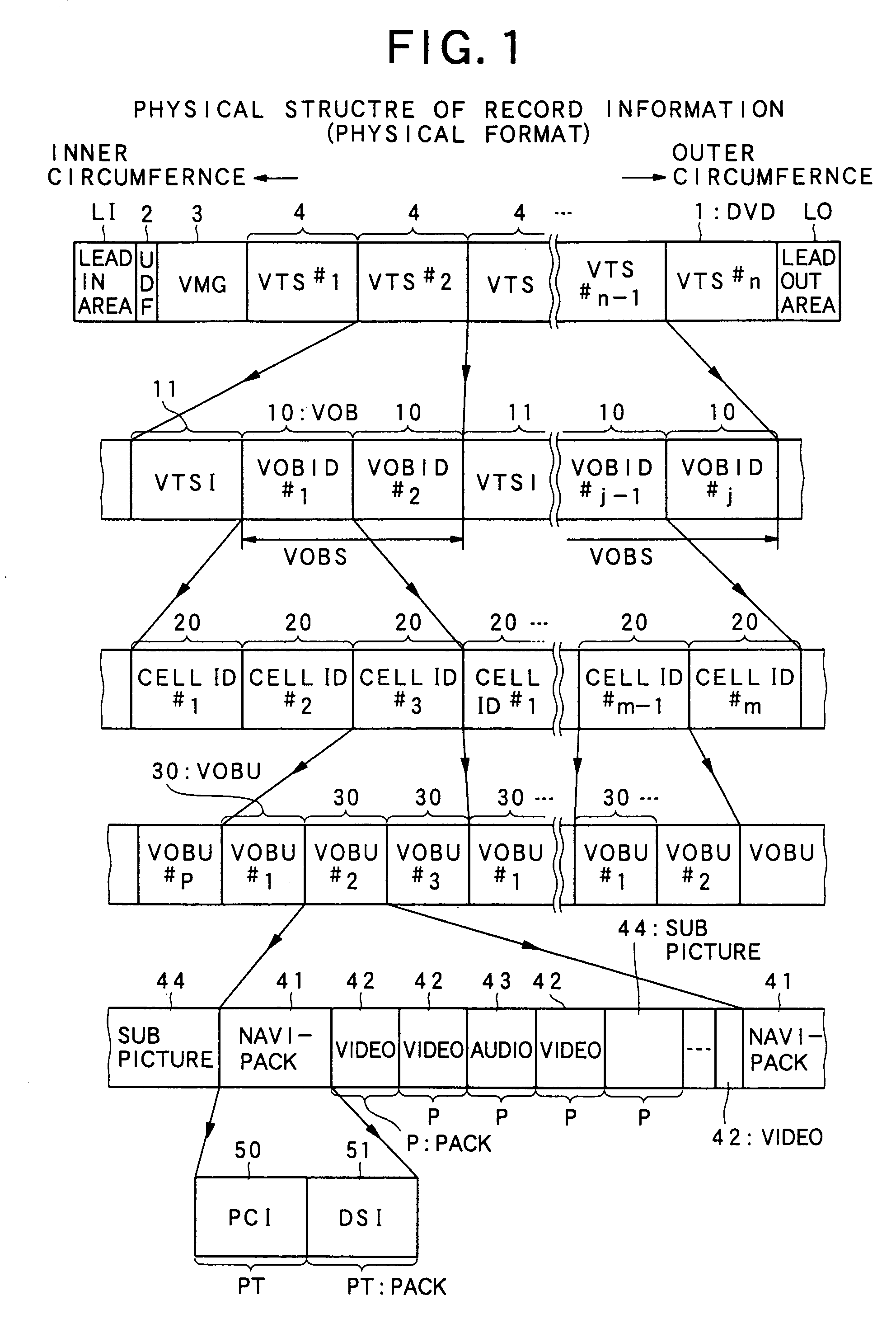
An information record medium (1) is provided with: an audio information recording area on which a plurality of audio information (210) which are different in recording method are recorded; and a control information recording area on which control information (211) required to reproduce the plurality of audio information recorded on the audio information recording area is recorded. The control information recorded on the control information recording area includes a plurality of first division information for identifying first division units (260) respectively so as to divide each of the plurality of audio information recorded on the audio information recording area by the first division units respectively. The first division information, which indicates that the audio information divided by the first division units belongs to a same first division unit, is provided for each of the plurality of audio information same in content and different in recording method. The plurality of audio information same in content and different in recording method, which are identified by the first division information, are recorded on recording positions different from each other in the audio information recording area.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Information record medium and apparatus for reproducing the same
InactiveUS20050232111A1Exact reproductionTelevision system detailsAudio/video recordingComputer hardwareAudio frequency
An information record medium (1) is provided with: an audio information recording area on which a plurality of audio information (210) which are different in recording method are recorded; and a control information recording area on which control information (211) required to reproduce the plurality of audio information recorded on the audio information recording area is recorded. The control information recorded on the control information recording area includes a plurality of first division information for identifying first division units (260) respectively so as to divide each of the plurality of audio information recorded on the audio information recording area by the first division units respectively. The first division information, which indicates that the audio information divided by the first division units belongs to a same first division unit, is provided for each of the plurality of audio information same in content and different in recording method. The plurality of audio information same in content and different in recording method, which are identified by the first division information, are recorded on recording positions different from each other in the audio information recording area.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Techniques for accommodating primary content (pure voice) audio and secondary content remaining audio capability in the digital audio production process
InactiveUS8108220B2Audio/video recordingStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsComputer hardwareDigital master
The invention enables the inclusion of voice and remaining audio information at different parts of the audio production process. In particular, the invention embodies special techniques for VRA-capable digital mastering, accommodation of PCPV / PCA and / or SCRA signals in audio CODECs, VRA-capable encoders and decoders, and VRA in DVD and other digital audio file formats. The invention facilitates an end-listener's voice-to-remaining audio (VRA) adjustment upon the playback of digital audio media formats by focusing on new configurations of multiple parts of the entire digital audio system, thereby enabling a new technique intended to benefit audio end-users (end-listeners) who wish to control the ratio of the primary vocal / dialog content of an audio program relative to the remaining portion of the audio content in that program. The invention facilitates storage of VRA audio programs on optical storage media, authoring systems for VRA-capable DVDs, playback hardware integrated into VRA-capable optical disc apparatus, and VRA playback hardware for use with non-VRA capable optical disc playback apparatus.
Owner:BENHOV GMBH LLC
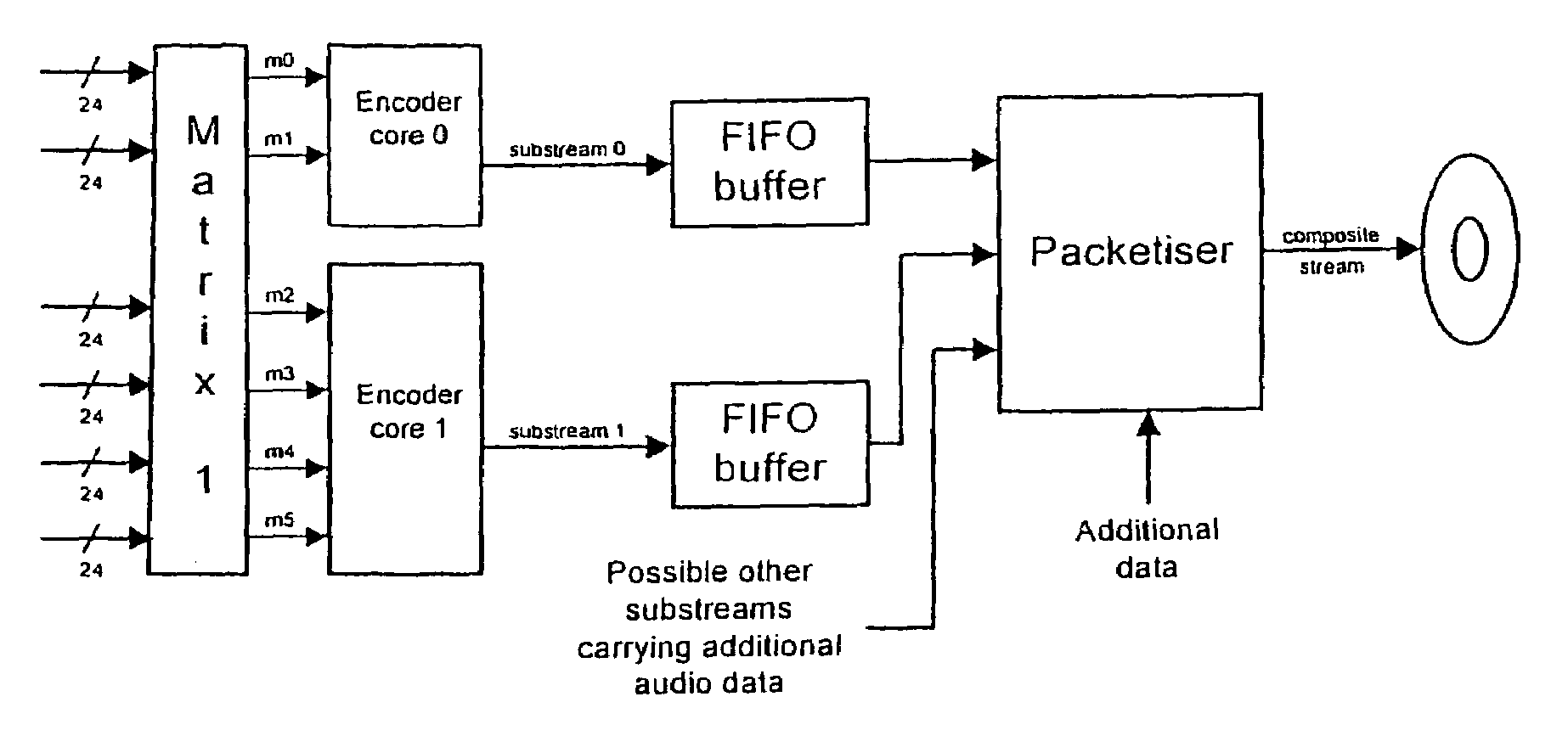
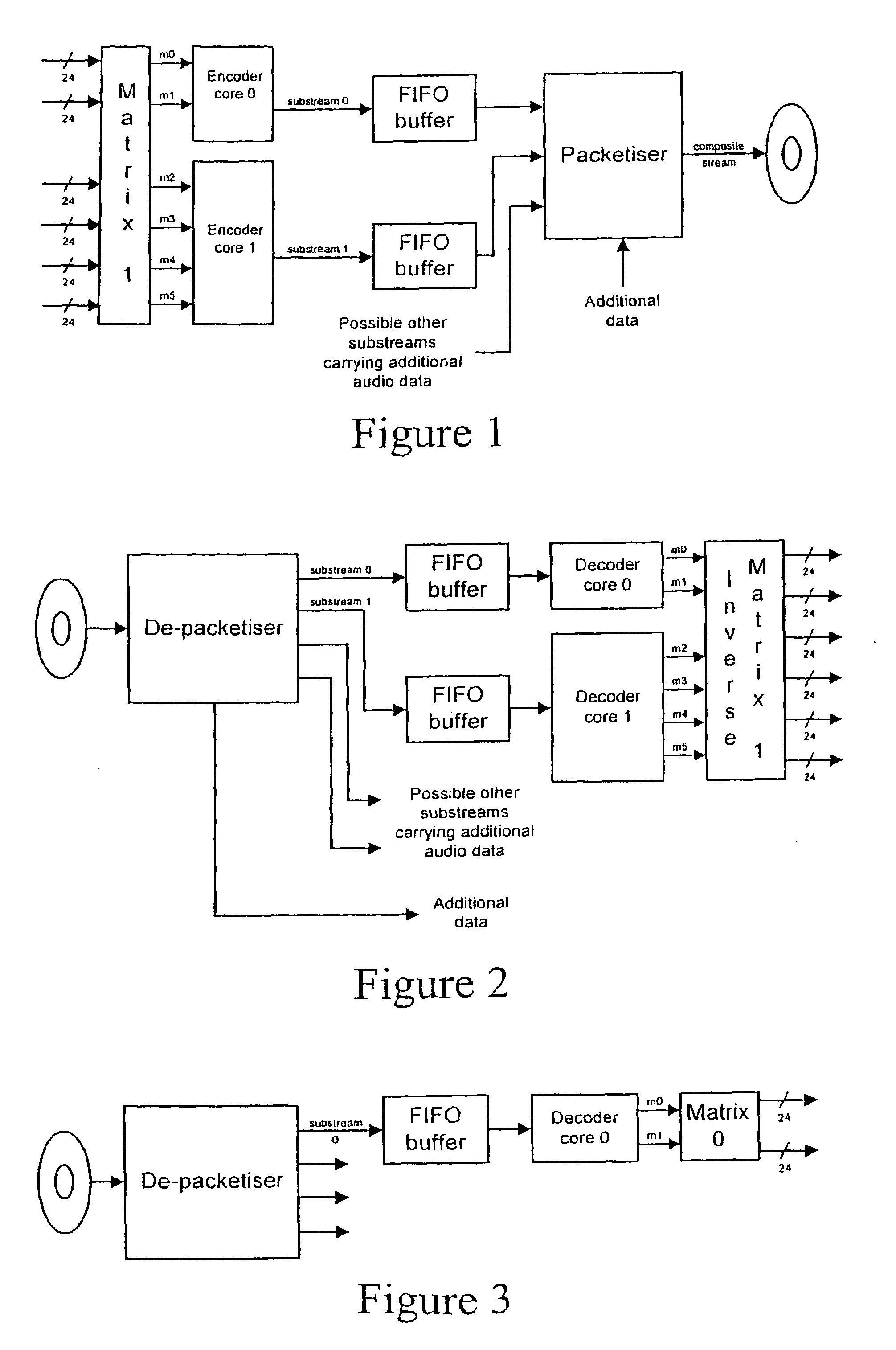
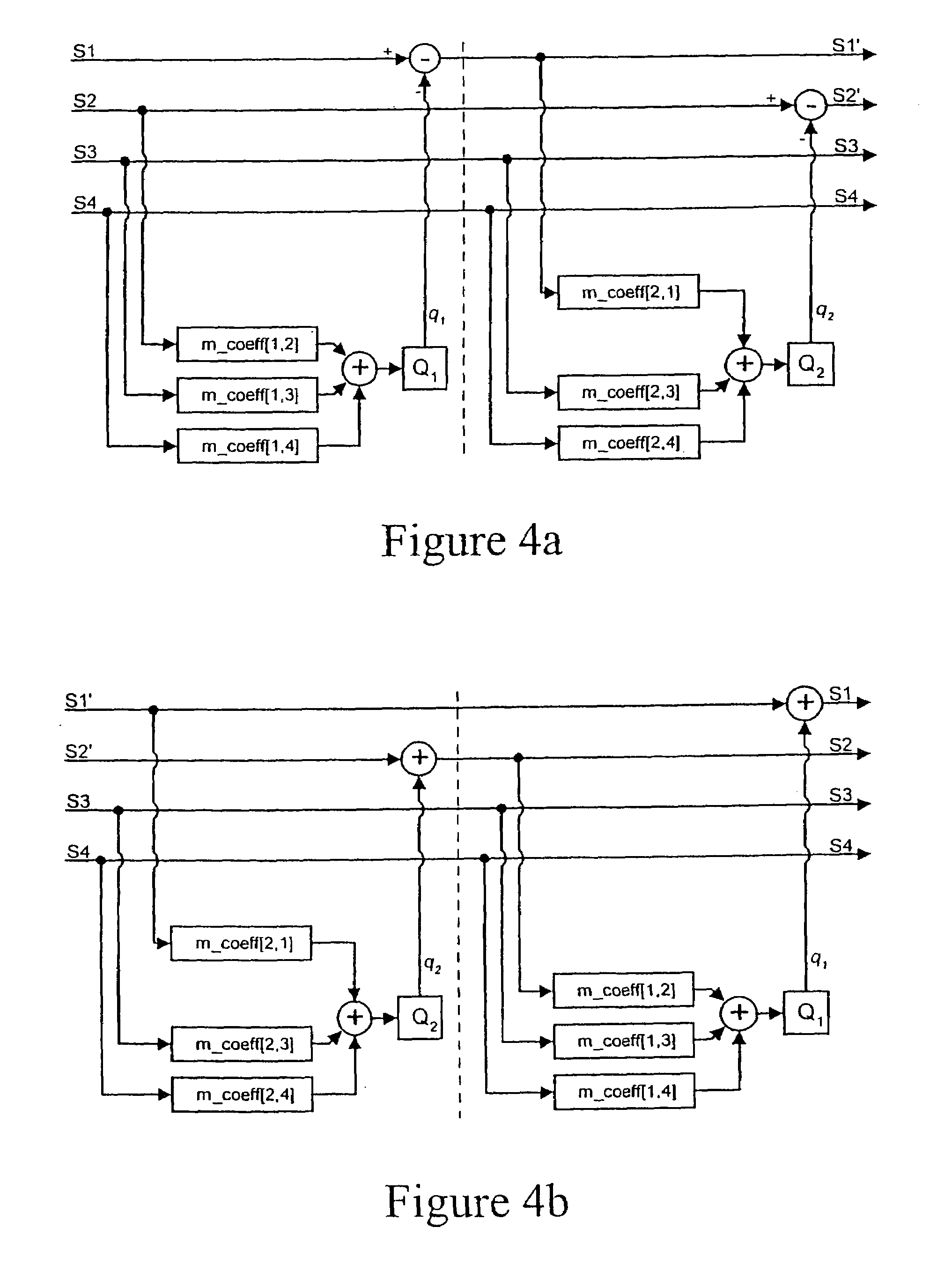
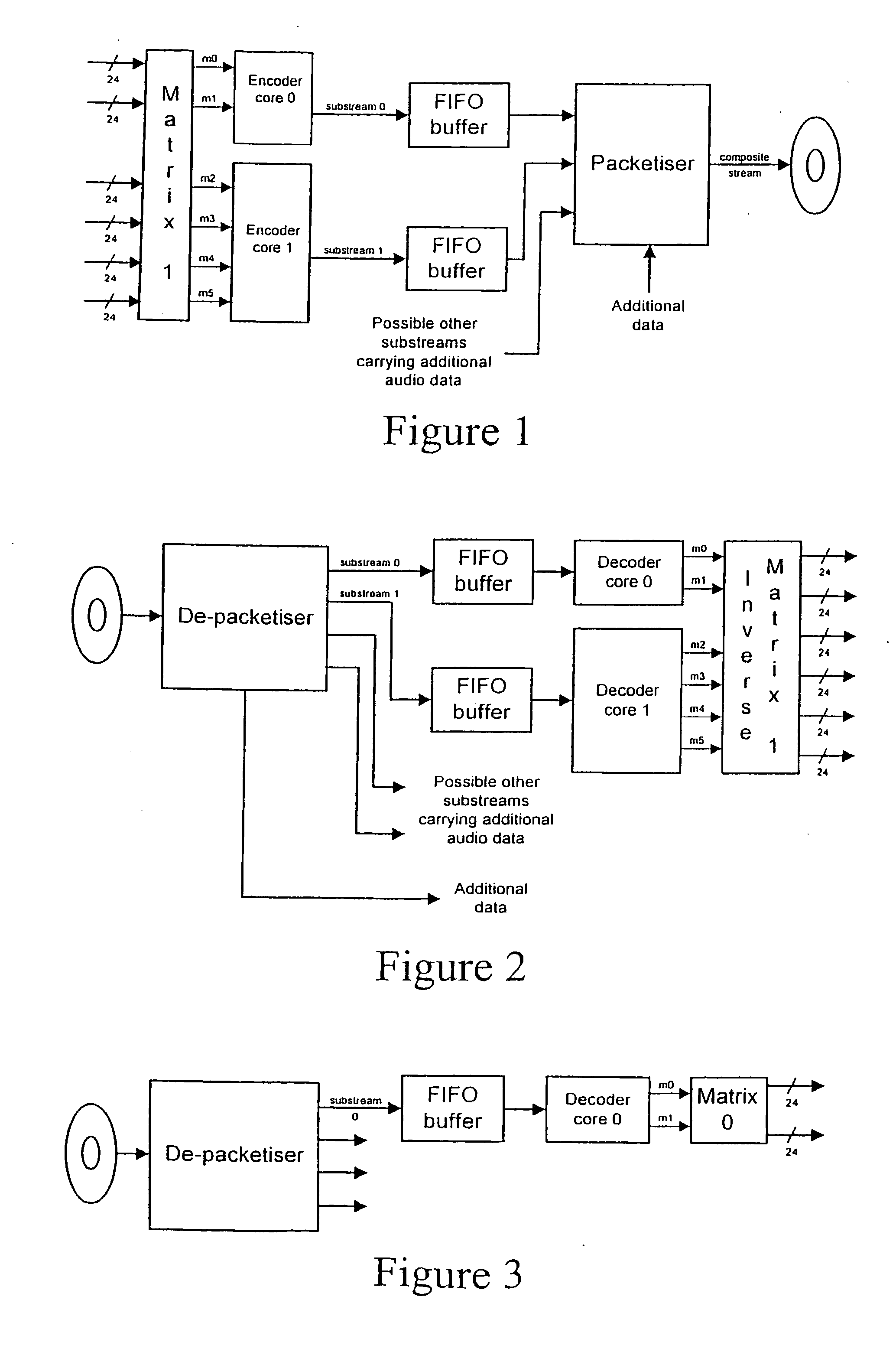
Matrix improvements to lossless encoding and decoding
InactiveUS7193538B2Signal can be recoveredPrevent overloadTelevision system detailsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsLossless coding24-bit
A lossless encoder and decoder are provided for transmitting a multichannel signal on a medium such as DVD-Audio. The encoder accepts additionally a downmix specification and splits the encoded stream into two substreams, such that a two-channel decoder of meagre computational power can implement the downmix specification by decoding one substream, while a multichannel decoder can decode the original multichannel signal losslessly using both substreams. Further features provide for efficient implementation on 24-bit processors, for confirmation of lossless reproduction to the user, and for benign behaviour in the case of downmix specifications that result in overload. The principle is also extended to mixed-rate signals, where for example some input channels are sampled at 48 kHz and some are sampled at 96 kHz.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Matrix improvements to lossless encoding and decoding
InactiveUS20050007262A1Prevent overloadSignal can be recoveredTelevision system detailsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsLossless coding24-bit
A lossless encoder and decoder are provided for transmitting a multichannel signal on a medium such as DVD-Audio. The encoder accepts additionally a downmix specification and splits the encoded stream into two substreams, such that a two-channel decoder of meagre computational power can implement the downmix specification by decoding one substream, while a multichannel decoder can decode the original multichannel signal losslessly using both substreams. Further features provide for efficient implementation on 24-bit processors, for confirmation of lossless reproduction to the user, and for benign behaviour in the case of downmix specifications that result in overload. The principle is also extended to mixed-rate signals, where for example some input channels are sampled at 48 kHz and some are sampled at 96 kHz
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
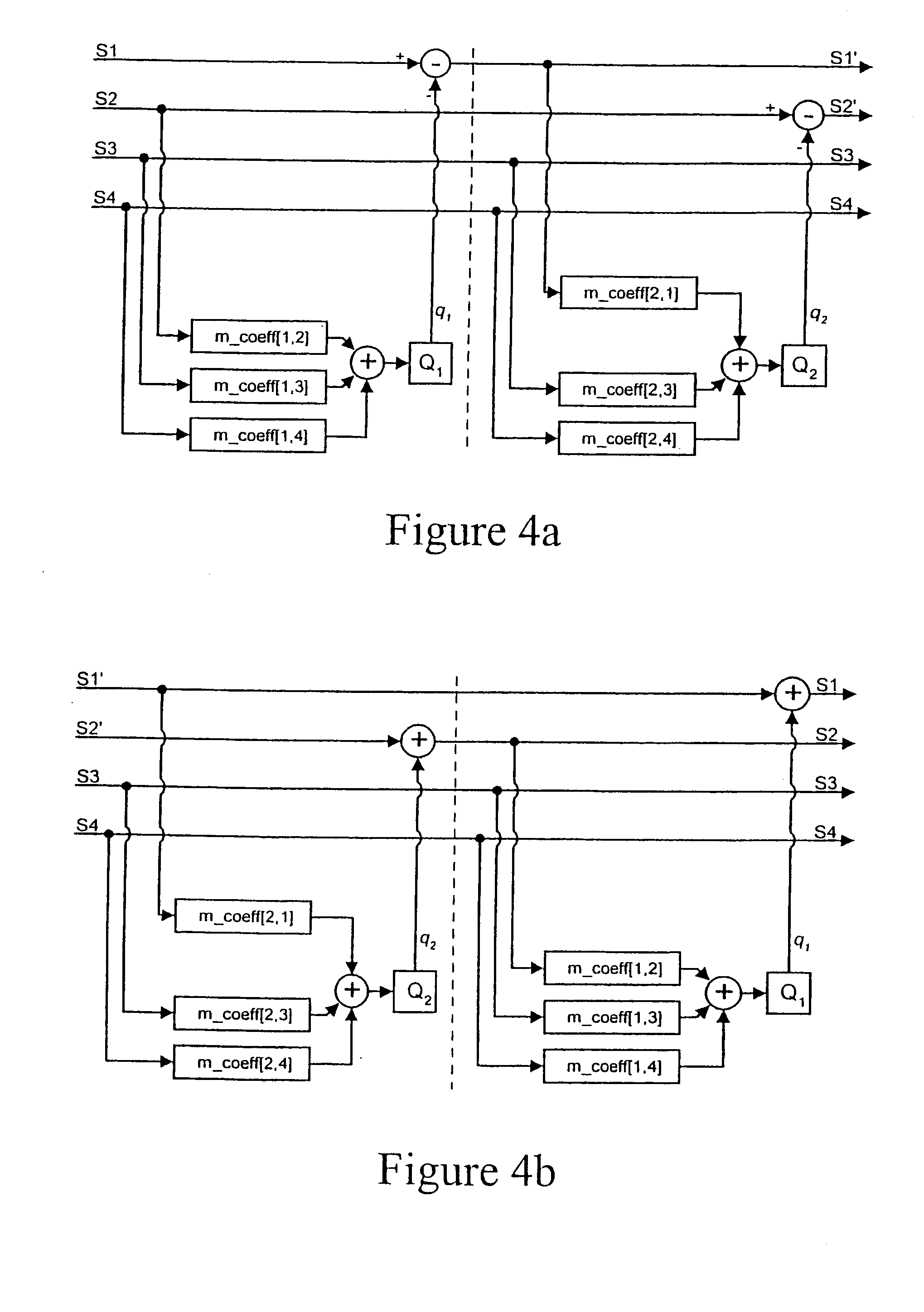
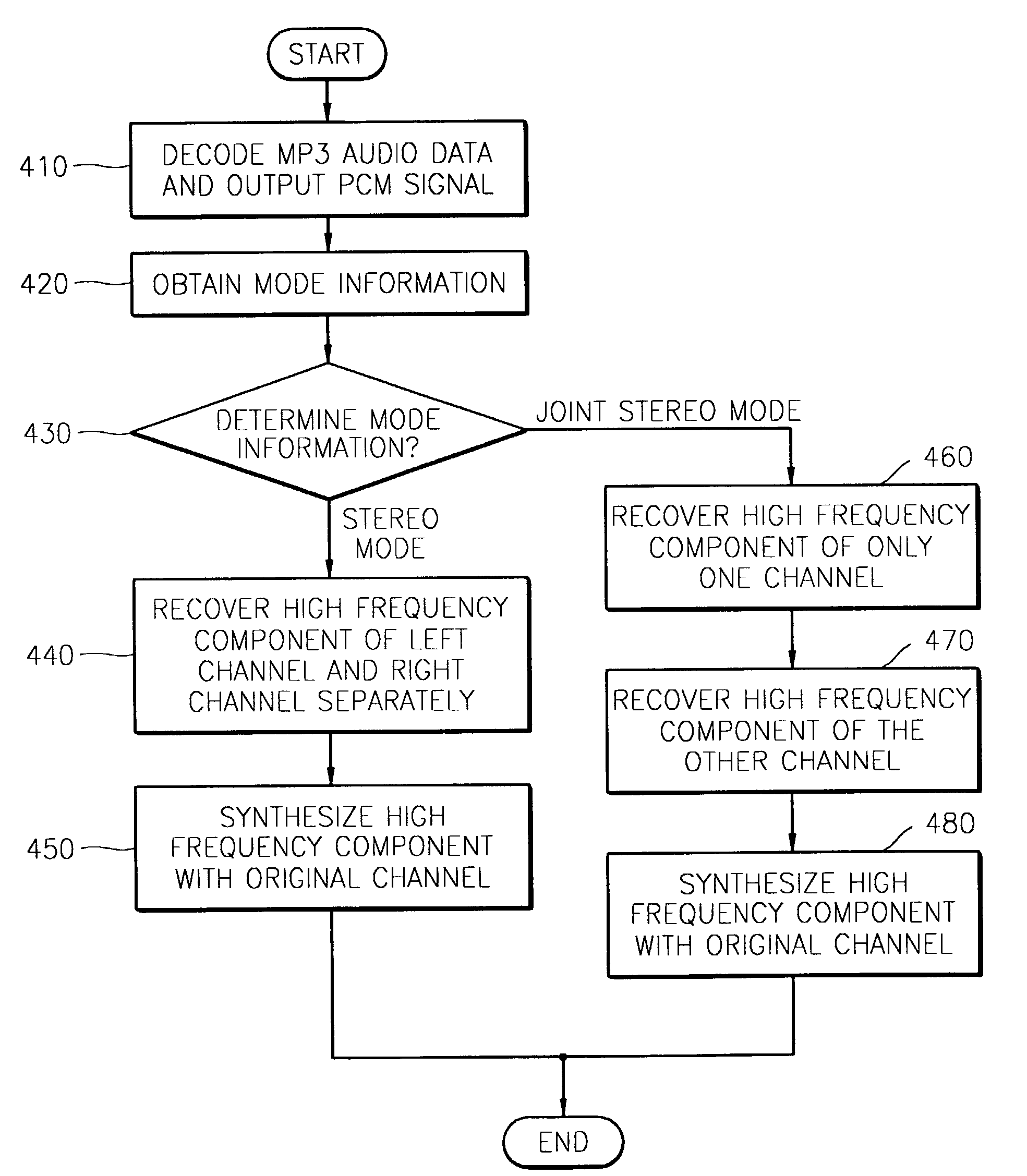
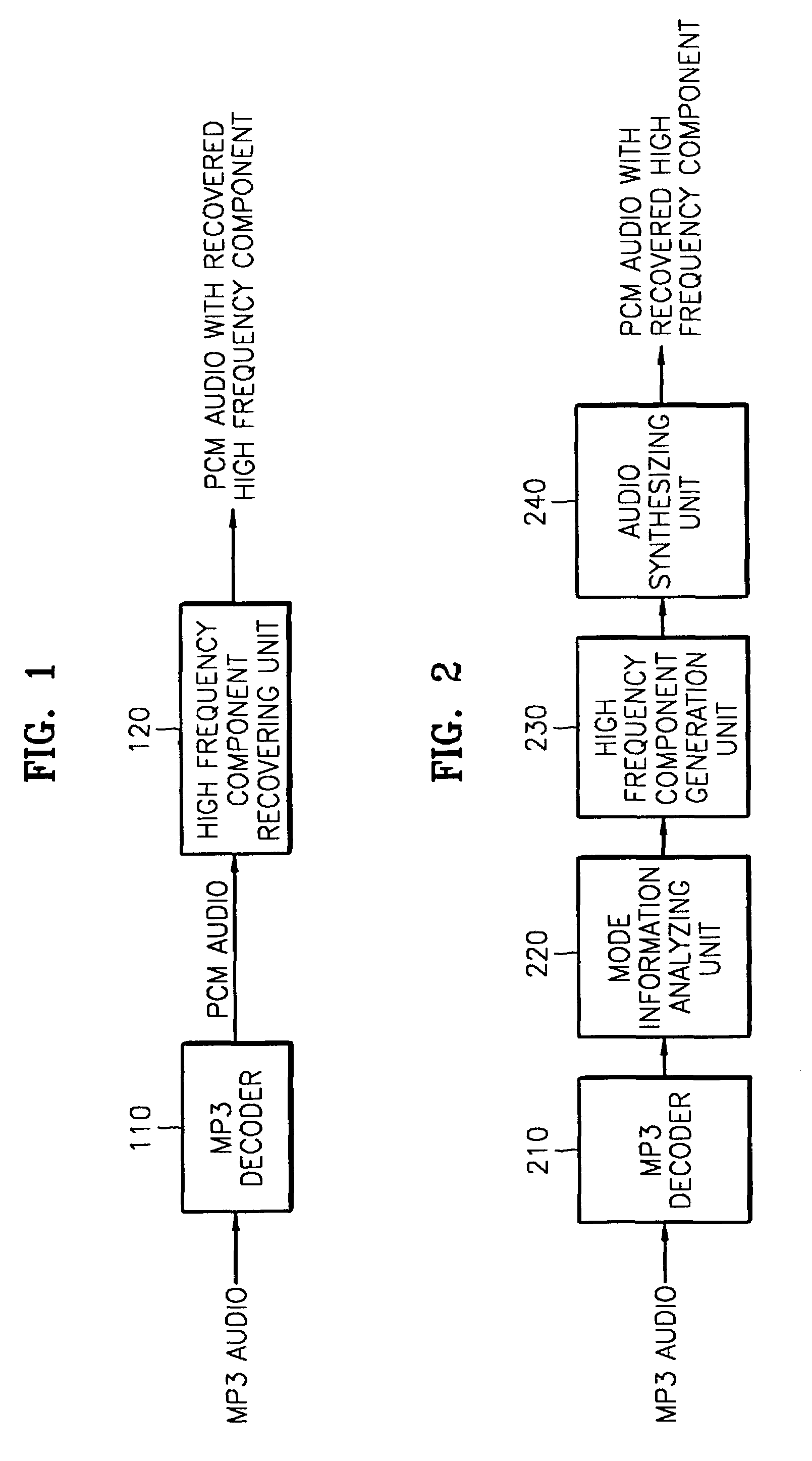
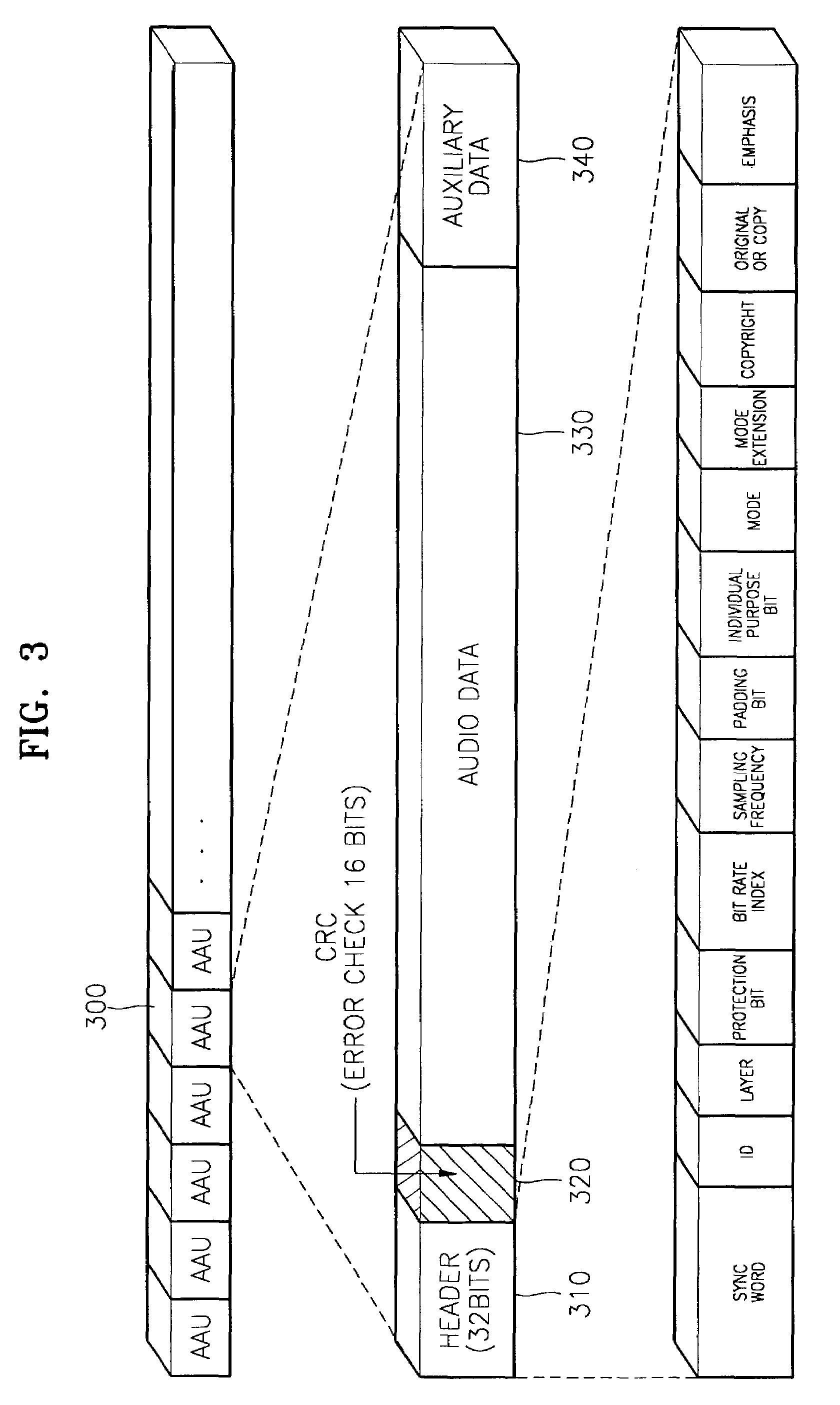
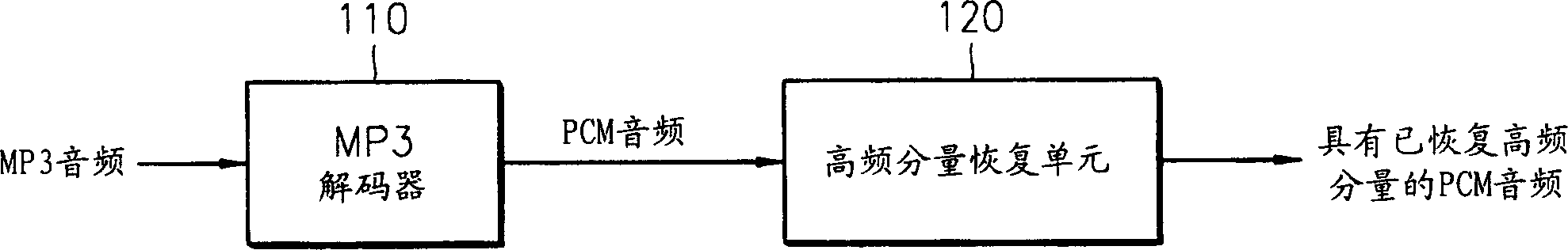
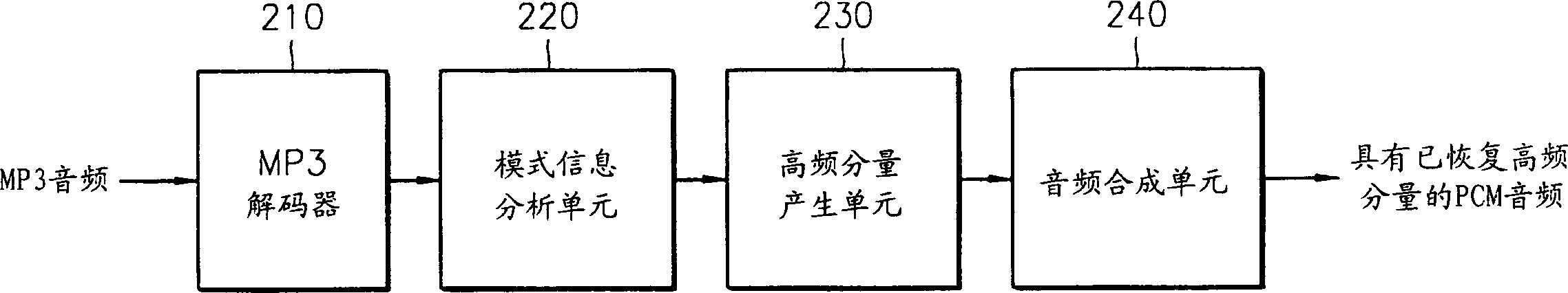
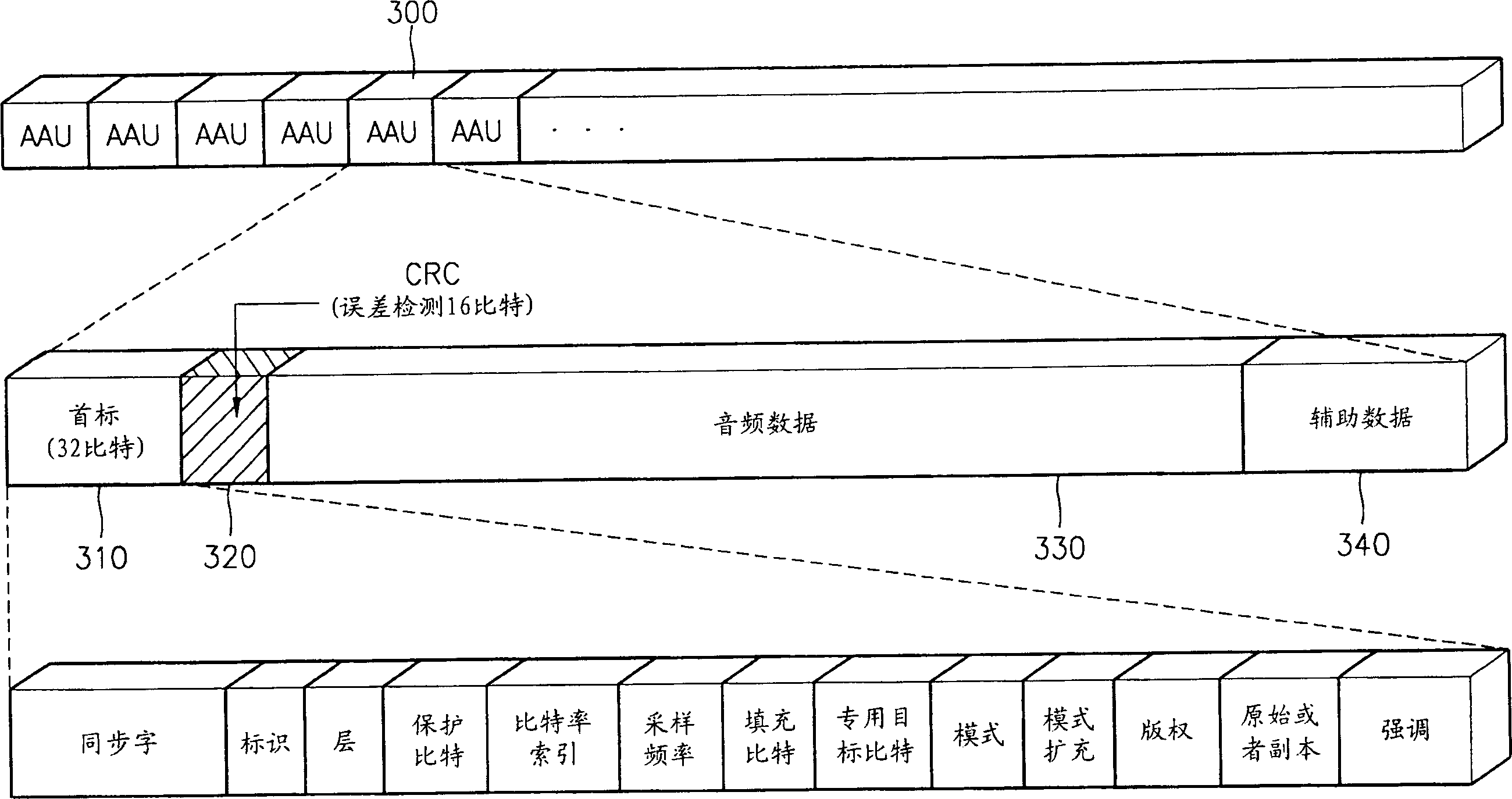
Audio decoding method and apparatus which recover high frequency component with small computation
InactiveUS7328161B2Reduce the amount presentElectrophonic musical instrumentsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsDecoding methodsMPEG-1
A method and apparatus for performing audio post processing using mode information that indicates the degree of similarity between a right channel signal and a left channel signal in MPEG-1 layer 3 audio data, are provided. If the difference between the two channel signals is small, a first mode is used in which the high frequency component of only one channel is recovered and the recovered high frequency component is used to recover the high frequency component of the other channel. If the difference between the two channel signals is large, a second mode is selected in which the high frequency component in only one of every two frames is recovered alternately in the left channel and the right channel and the high frequency component of each of the skipped frames is interpolated based on the high frequency components of the previous frame and the next frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Audio decoding method and apparatus which recover high frequency component with small computation
InactiveCN1467703ASmall amount of calculationElectrophonic musical instrumentsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsDecoding methodsMPEG-1
A method and apparatus for reducing the amount of computation in audio post processing, and more particularly, a method and apparatus for performing audio post processing using mode information that indicates the degree of similarity between a right channel signal and a left channel signal in MPEG-1 layer 3 audio data, are provided. If the difference between the two channel signals is small, a first mode is used in which the high frequency component of only one channel is recovered and the recovered high frequency component is used to recover the high frequency component of the other channel, and if the difference between the two channel signals is large, a second mode is selected in which the high frequency component in only one of every two frames is recovered alternately in the left channel and the right channel and the high frequency component of each of the skipped frames is interpolated based on the high frequency components of the previous frame and the next frame. By doing so, the new audio decoding method and apparatus recover high frequency components with a small amount of computation. The method reduces the amount of computation to less than half the amount of computation used in the prior art in recovering high frequency components.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
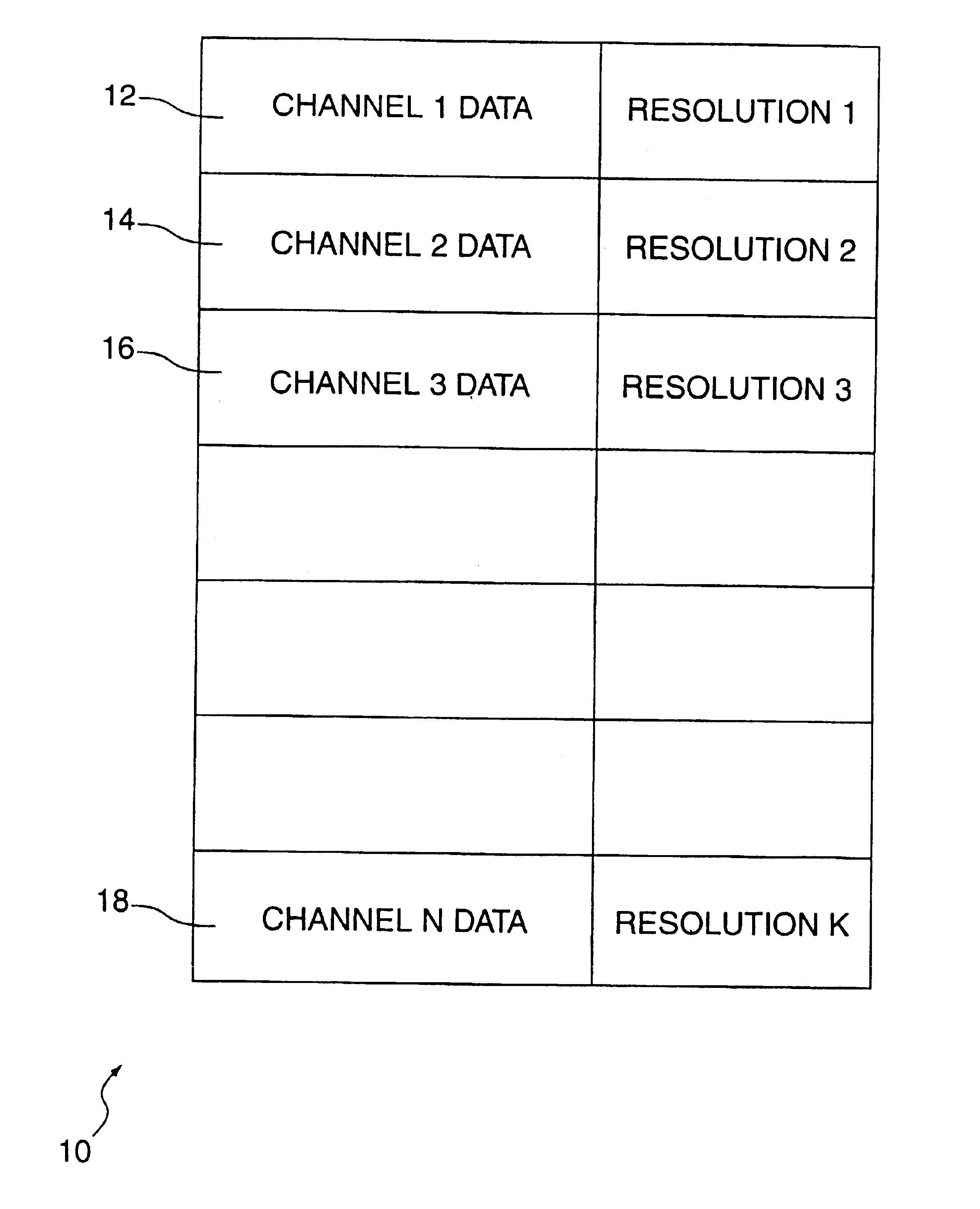
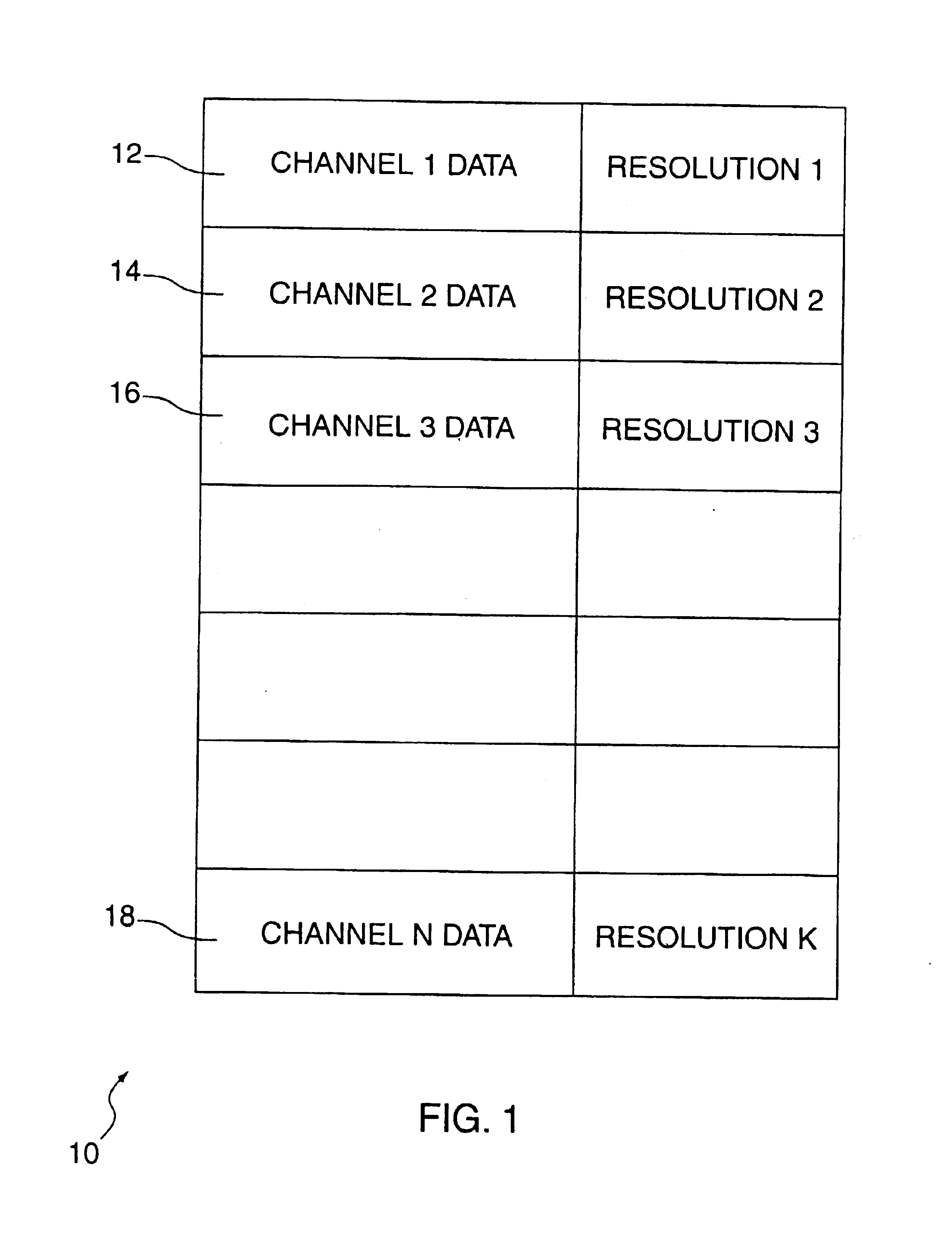
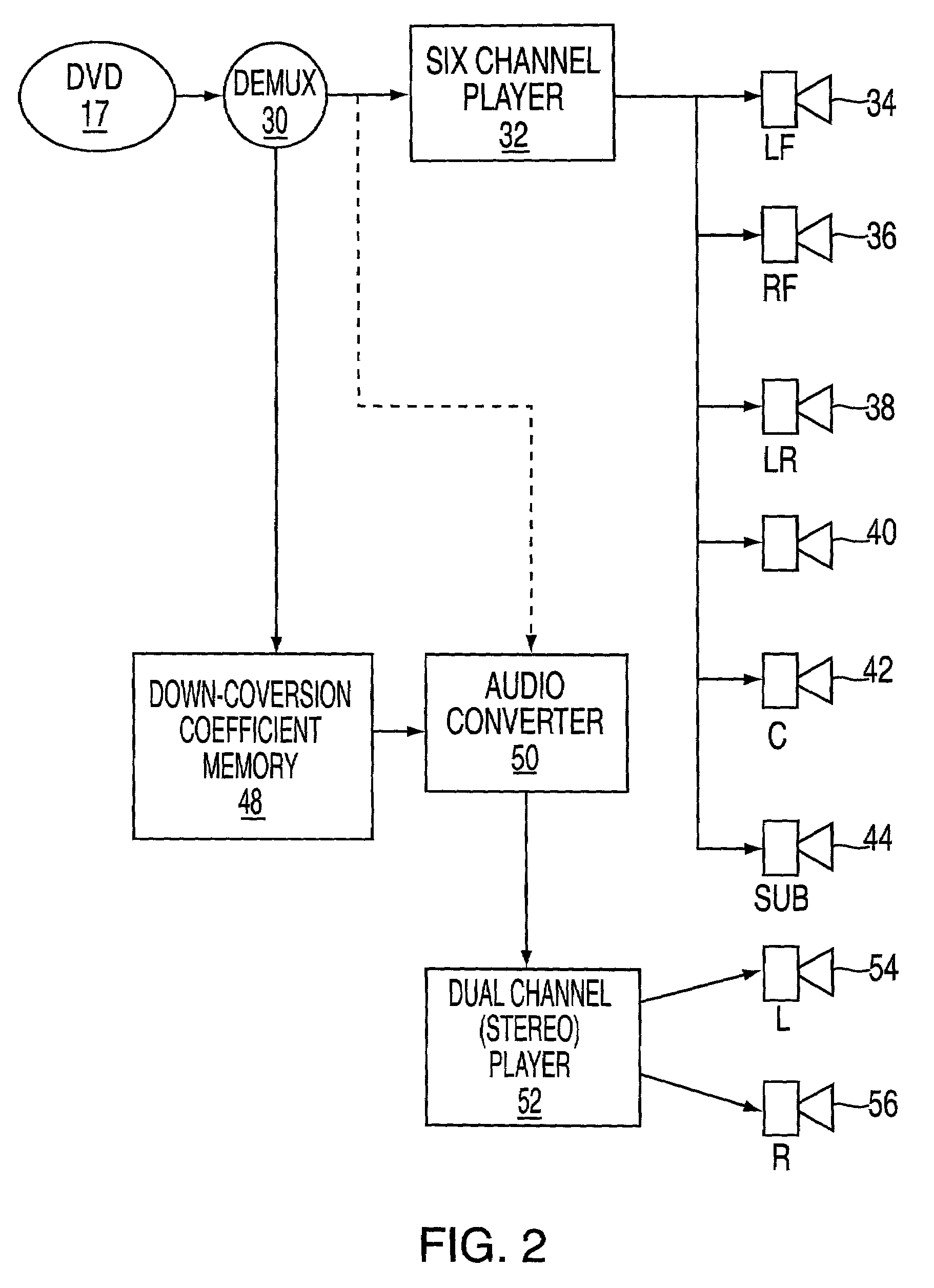
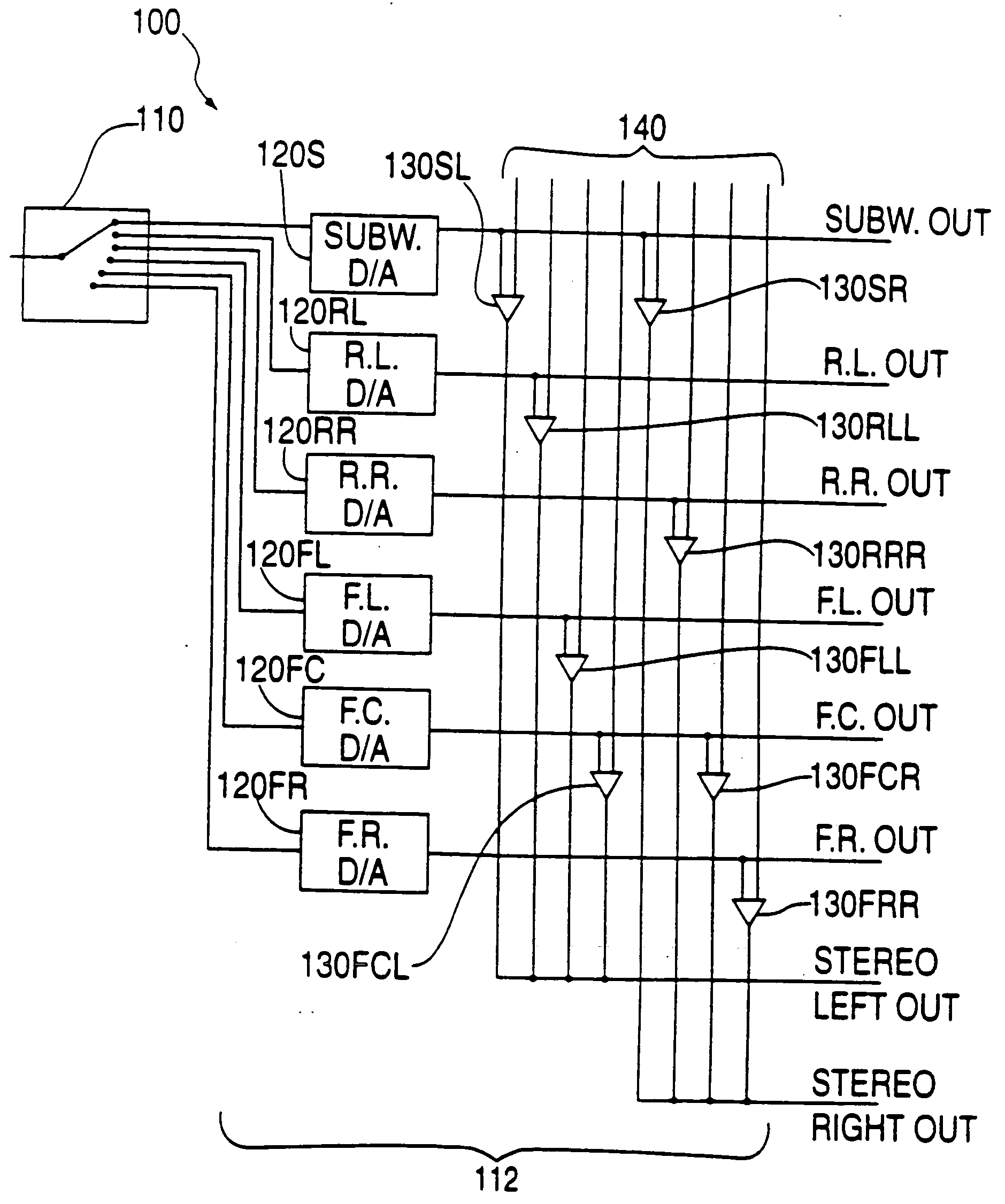
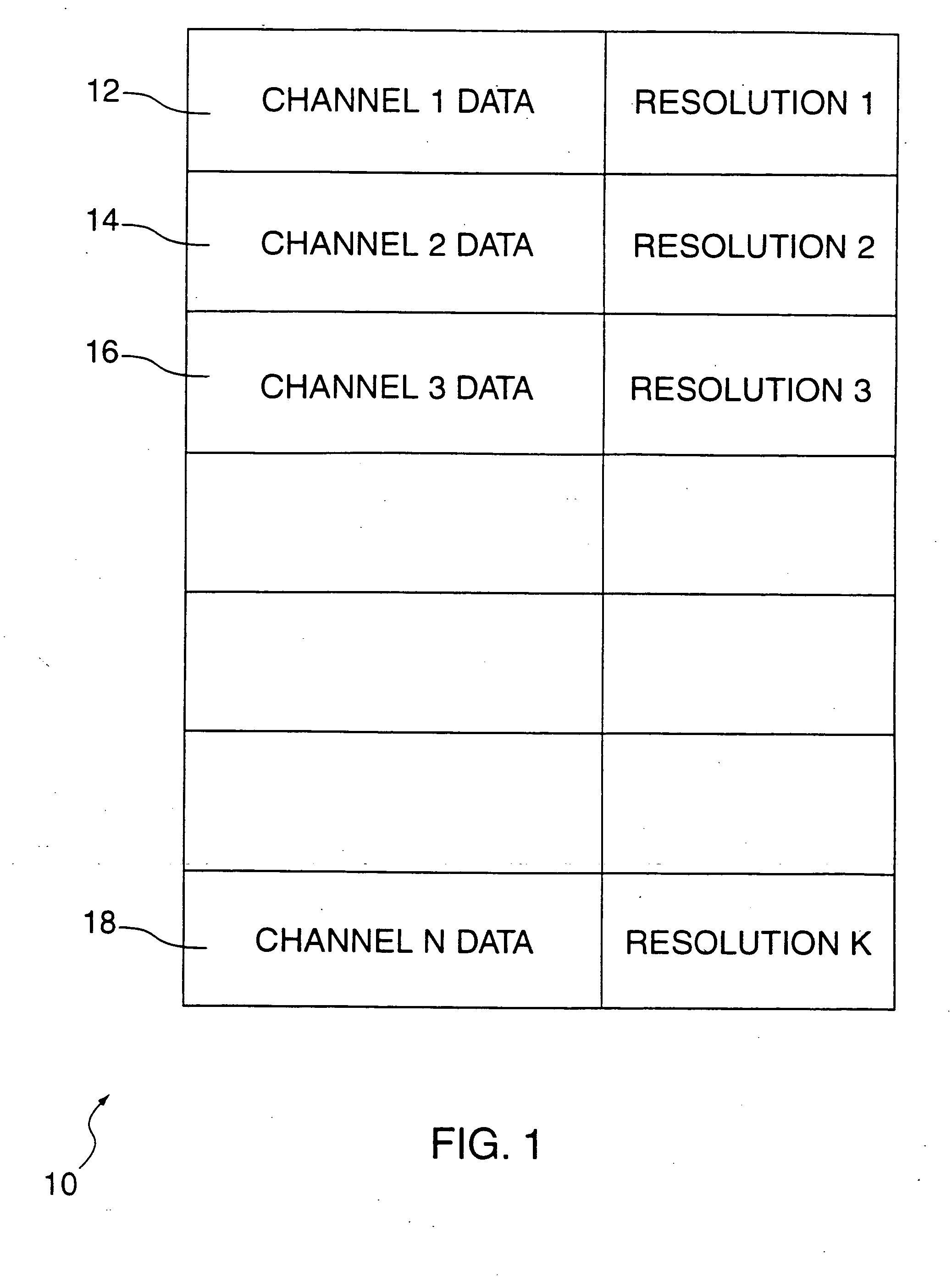
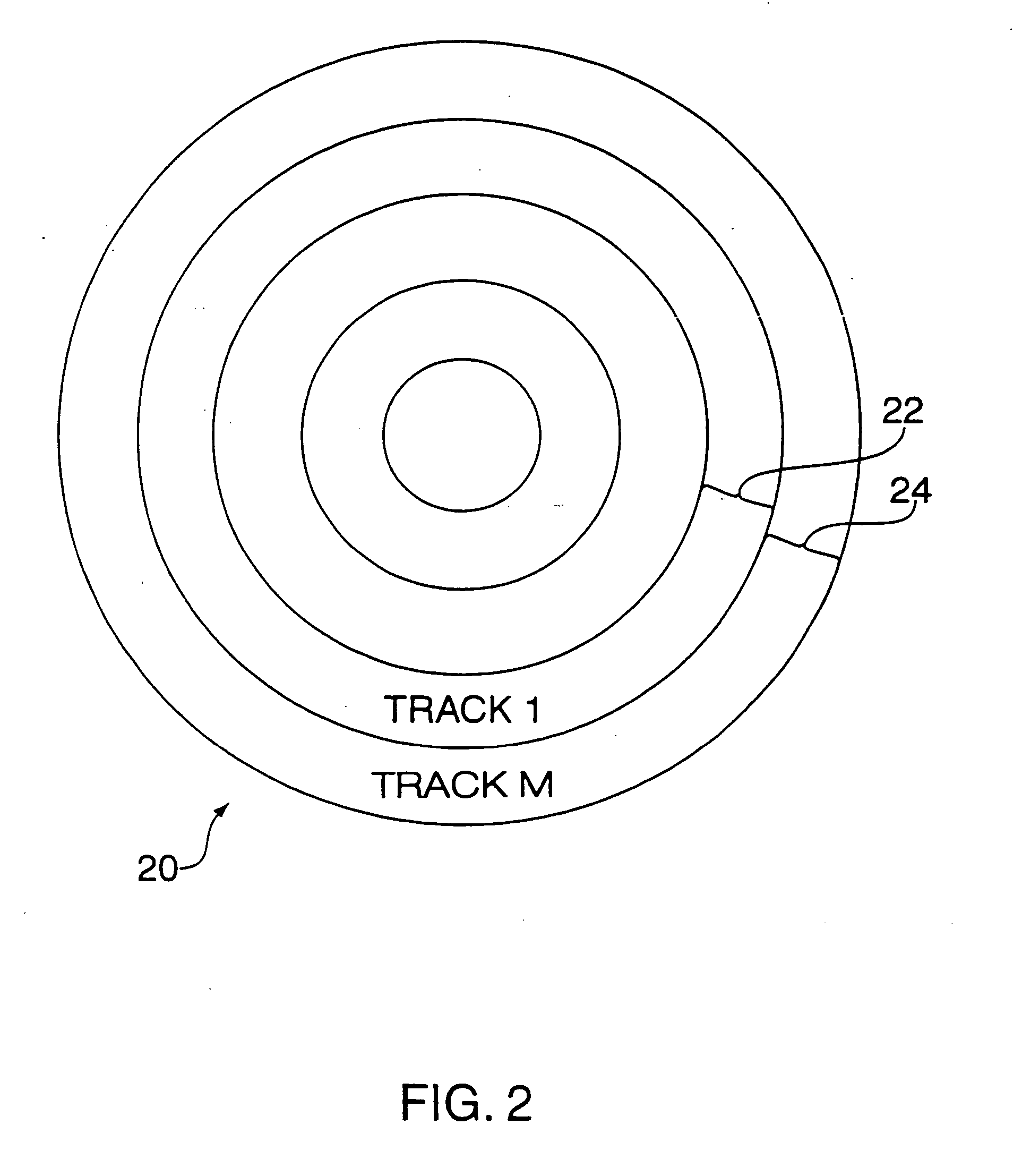
Recording and playback of multi-channel digital audio having different resolutions for different channels
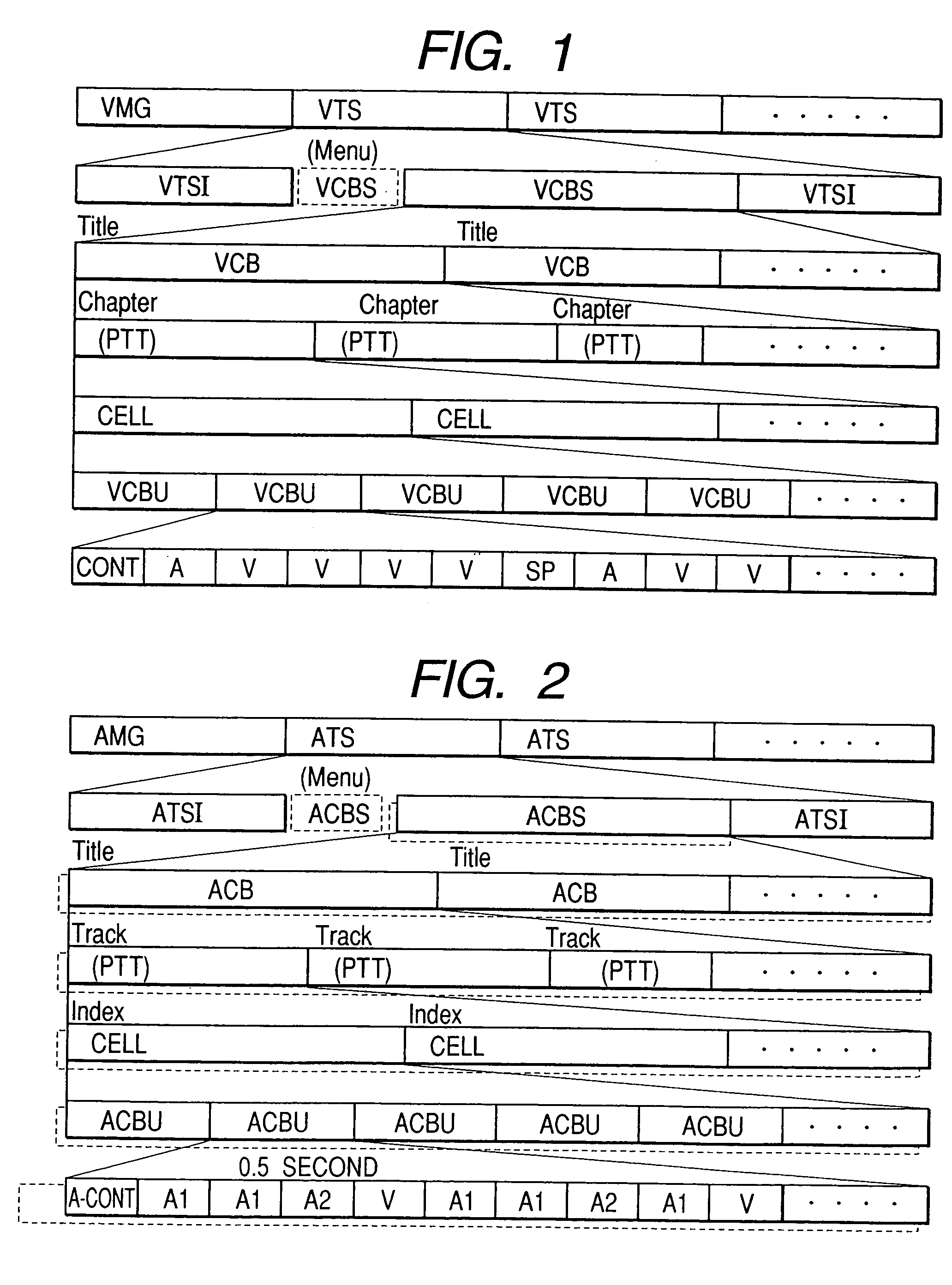
InactiveUS6898173B2Television system detailsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsComputer hardwareData stream
Methods and apparatus for recording on DVD-like recording media in which audio content is stored in a high-capacity multi-channel (e.g., six-channel) format are provided. Various channels may use various resolutions. A two-channel audio output may be derived from the multi-channel audio data stream during playback. To facilitate an accurate derivation, the mixing coefficients to be used in generating the derivation can be supplied along with the six-channel audio data.
Owner:WARNER MUSIC GROUP
Information processing device, information processing method, and program
InactiveUS20100254678A1Television system detailsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsComputer graphics (images)Graphics
An information processing device includes an API (Application Programming Interface) only for reading / writing of an offset value, which is data providing disparity to a graphics image to generate an image for the left eye and an image for the right eye from the original image, arranged to store the offset value in an internal storage region that is a storage region inside of a reproducer configured to reproduce images, and to read out the offset value stored in the internal storage region.
Owner:SONY CORP
Multi-channel compatible stereo recording
ActiveUS20050259828A1Improve time-stretchingImprove pitch shiftingElectrophonic musical instrumentsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsComputer hardwareEncoder
An encoder for mixing a plurality of independent mono audio channels into a stereo recording and generating a restricted set of additional parameters used to master an audio track of a storage device is described. The plurality of independent mono audio channels are constructed such that the storage device can be played using an optical disk player so that in a first mode all of the plurality of independent mono audio channels are played as the stereo recording and in a second mode at least one of the plurality of independent mono audio channels can be unmixed and the stereo recording played with at least one mono audio channel removed. A corresponding decoder and an audio system comprising such encoder and decoder are also described.
Owner:AURO TECH
Optical disc playback apparatus
InactiveUS20060044976A1Television system detailsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsUsabilityExecution control
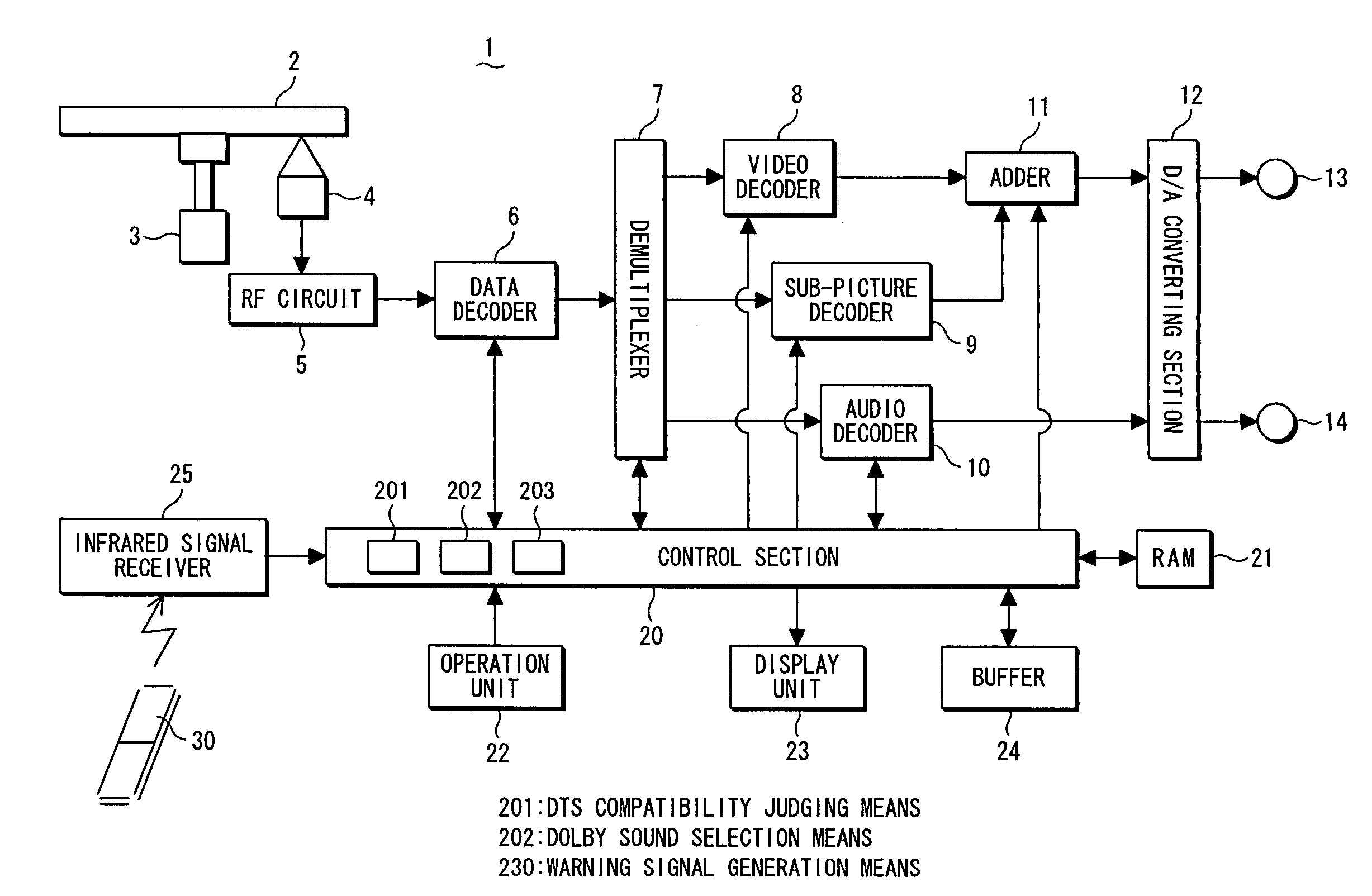
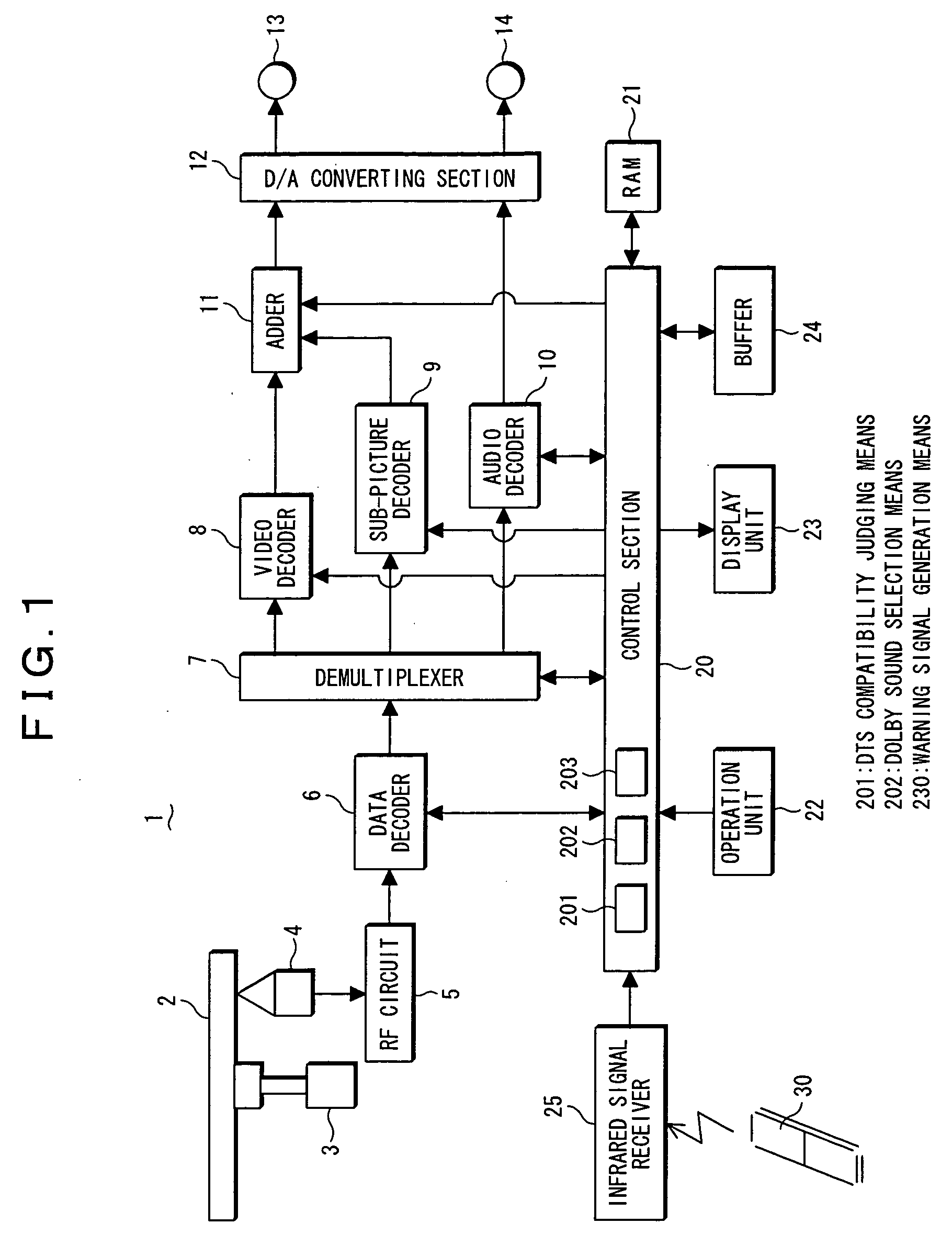
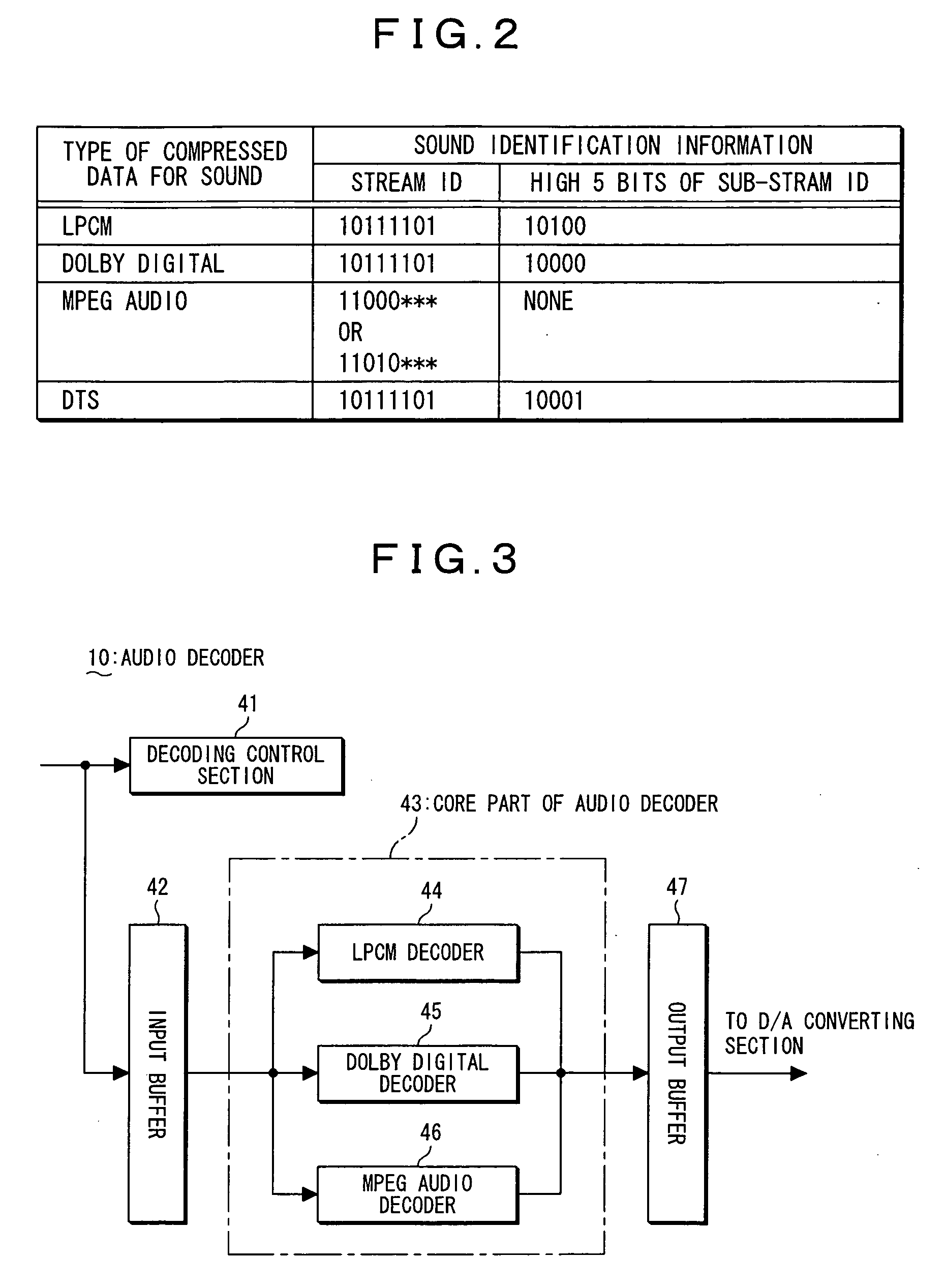
An optical disc playback apparatus having DTS sound incompatible function is provided, which apparatus is capable of automatically playing back the Dolby sound without selecting the Dolby sound in the menu setting, when an optical disc including the DTS content is played back. When the playback of the optical disc including the DTS content is started, DTS compatibility judging means judges whether or not the setting function of the apparatus is set in the DTS sound compatible state. In the case when the result of judgment indicates the DTS sound incompatible state, Dolby sound selection means carries out a control in such a manner that a Dolby sound is compulsively selected, so that the Dolby sound is output instead of the DTS sound. Accordingly, a user is able to listen a comfortable sound and no operation for selecting the Dolby sound is required as for the type of sound to be listened, thereby enabling the usability to be enhanced in the operation of the apparatus.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
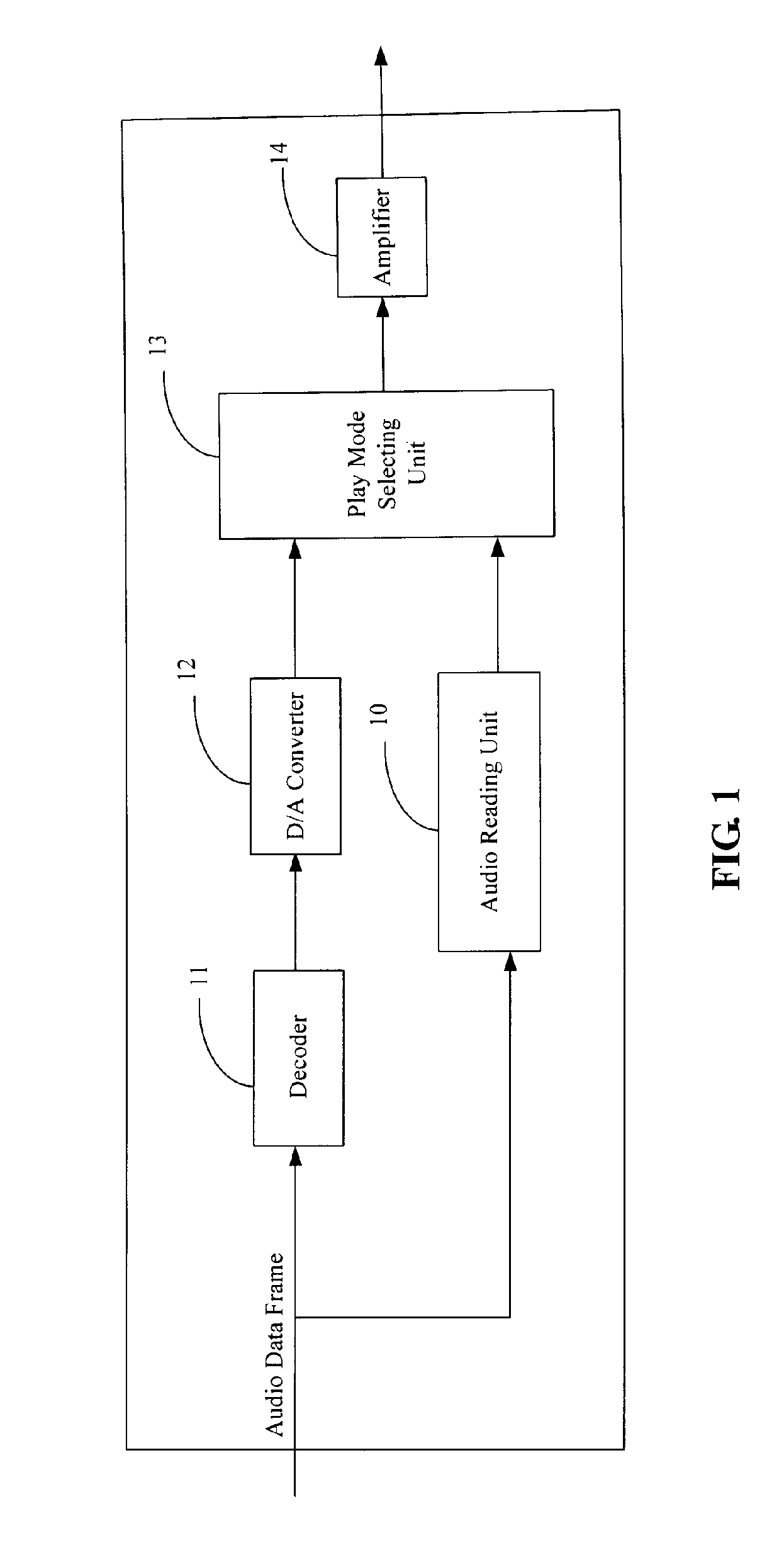
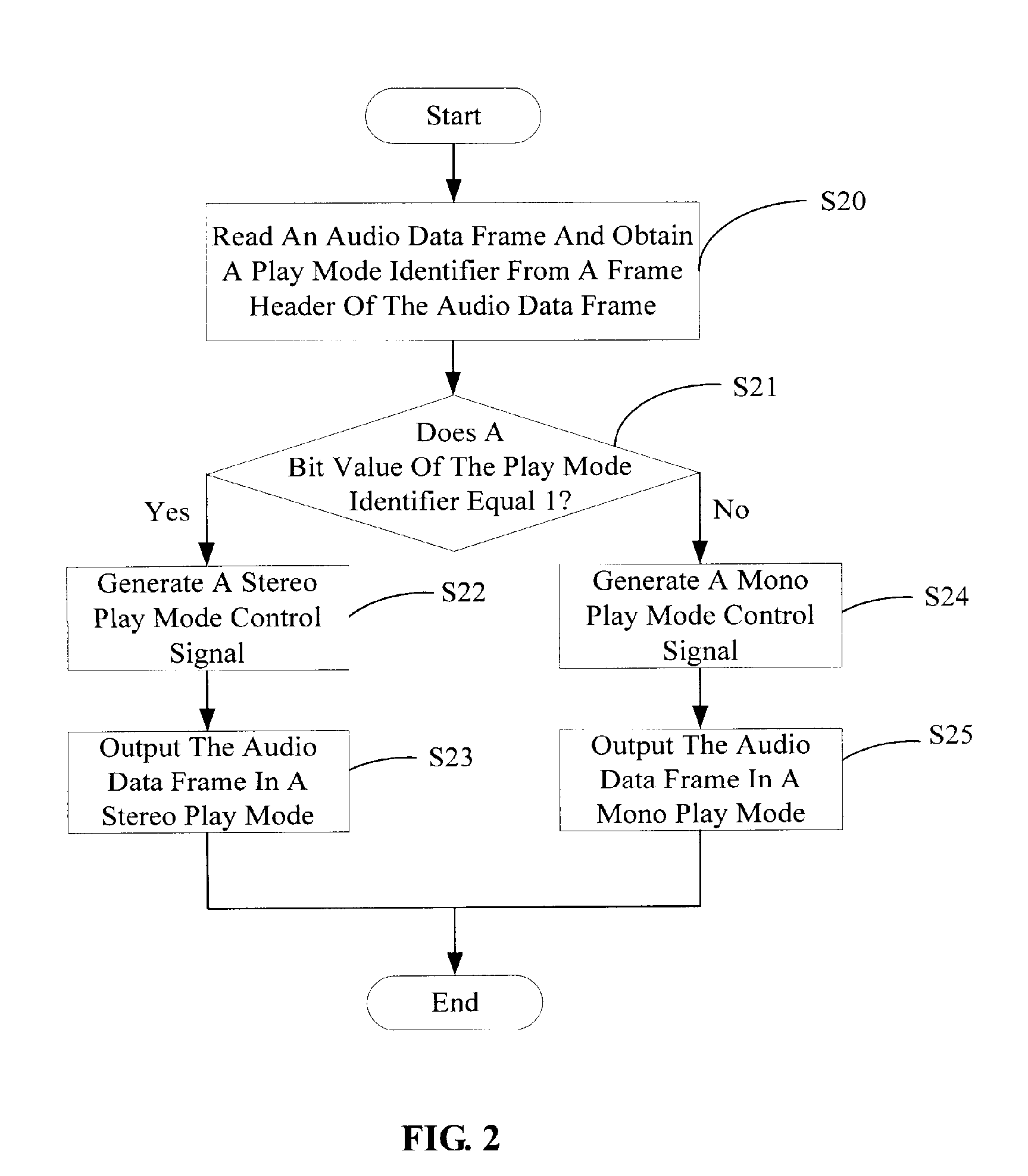
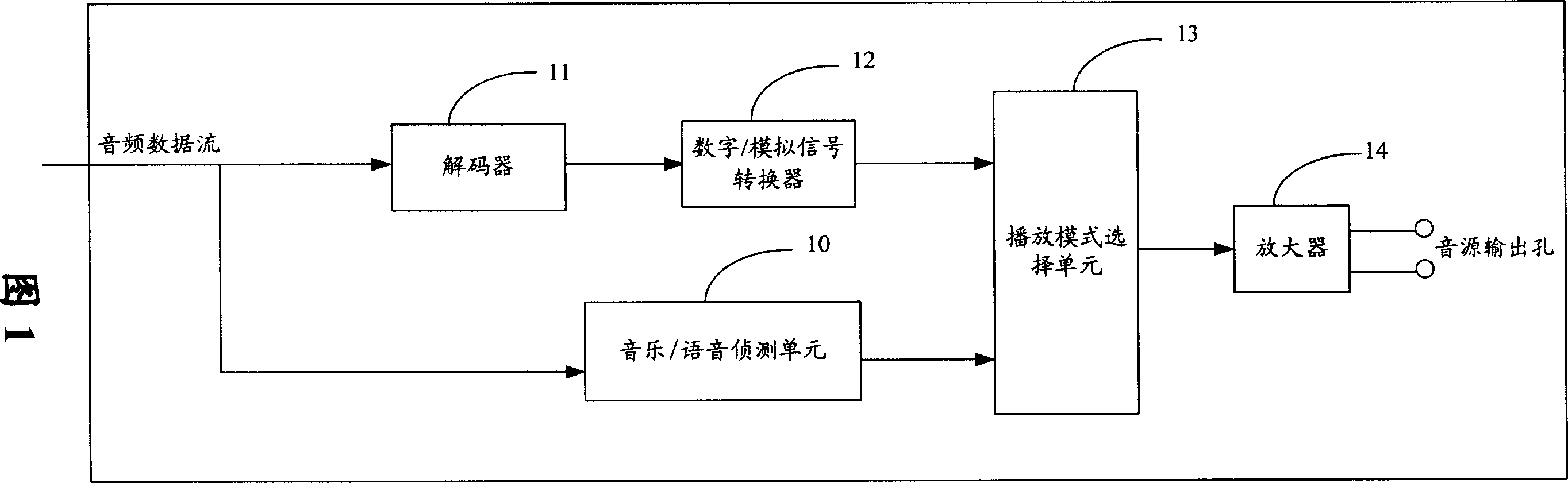
Apparatus and method for automatically selecting an audio play mode
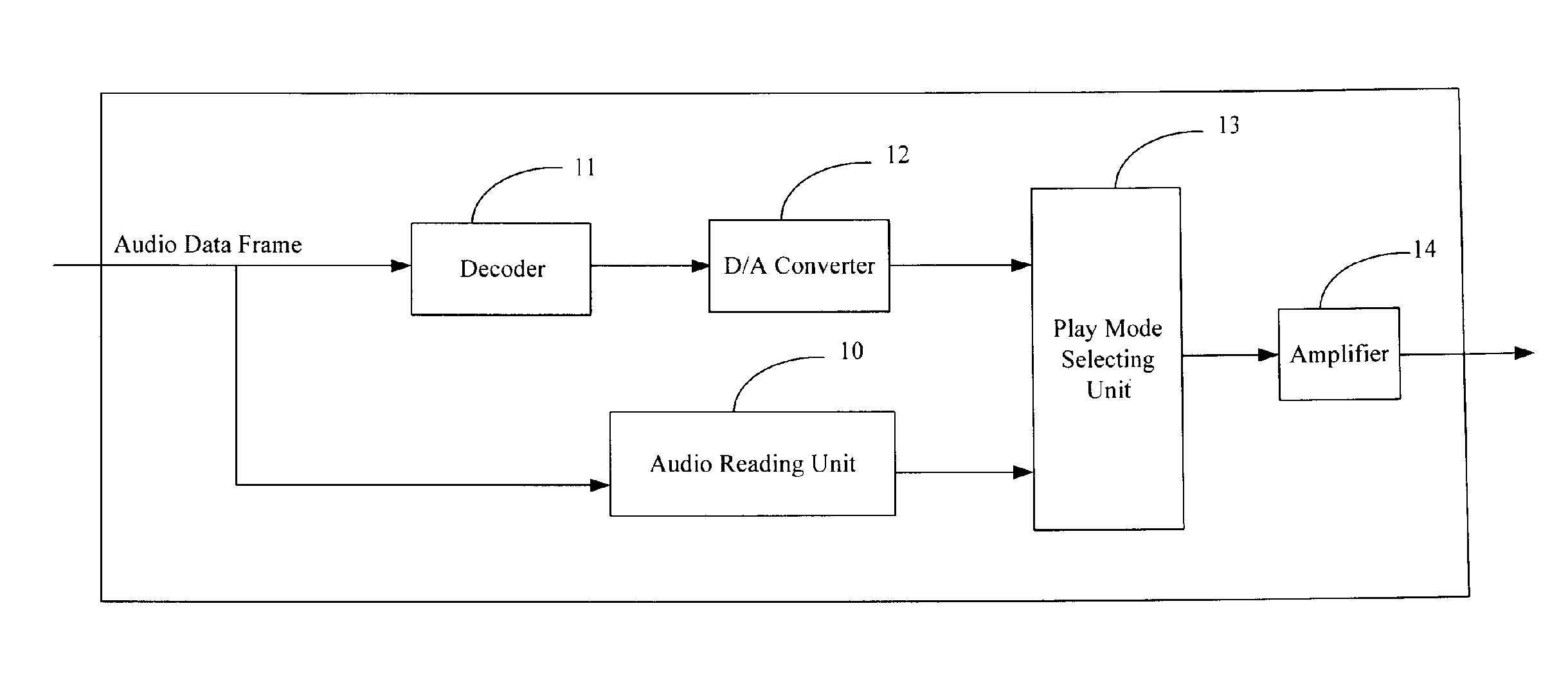
InactiveUS20070079241A1Stereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsRecord information storageMode controlPattern selection
An apparatus and method for automatically selecting an audio play mode mainly is provided. The apparatus includes an audio reading unit and a play mode selecting unit. The audio reading unit reads an audio data frame, obtains and recognizes a play mode identifier from a frame header of the audio data frame, and generates an associated play mode control signal according to the recognized play mode identifier. The play mode selecting unit selects a corresponding play mode to output the audio data frame according to the play mode control signal from the audio reading unit. A related method is also provided.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
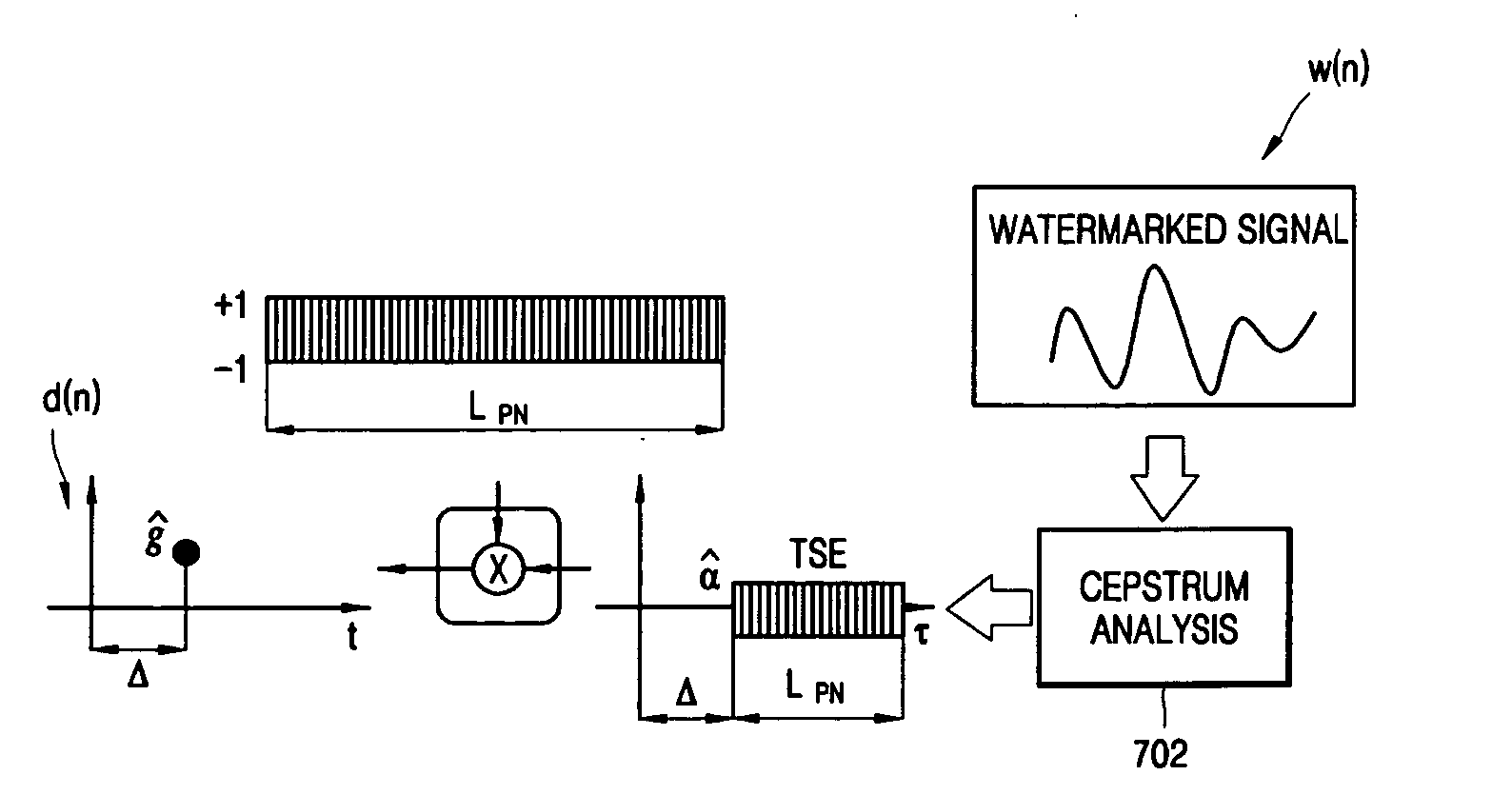
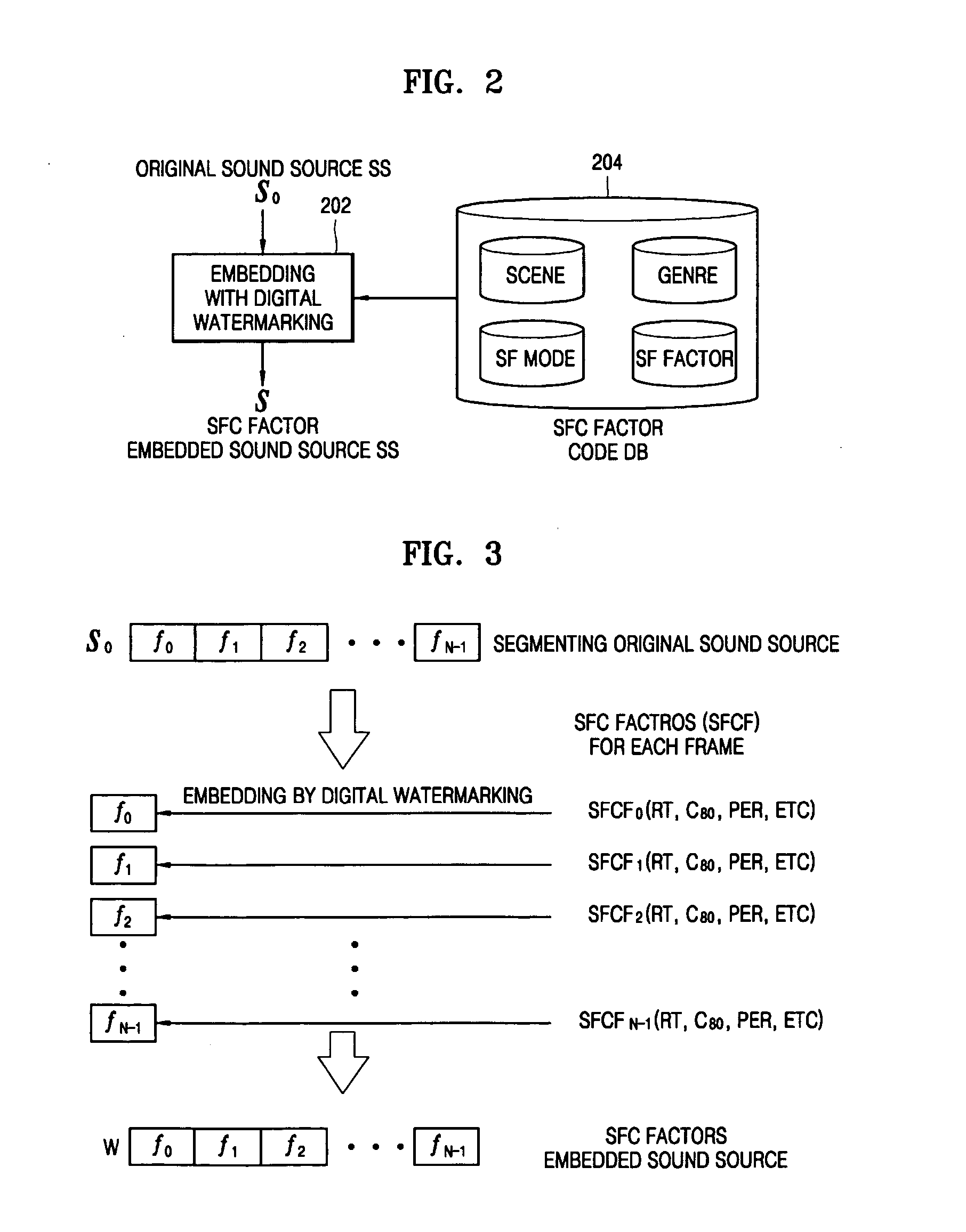
Method of embedding sound field control factor and method of processing sound field
InactiveUS20060059001A1Reliable transmissionTelevision system detailsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsSound sourcesData type
A method of embedding sound field control factors (SFC factors) into a sound source. The method includes coding sound field factors and sound field information to obtain sound field control factors for the sound source in a binary data type, and the sound field factors represent an acoustic characteristic of the sound source and the sound field information represents an environment under which the sound source is decoded, and watermarking the sound field control factors into the sound source without compressing the sound source. In this method, the SFC factors that represent characteristics of the sound source are embedded into the sound source itself using a digital watermarking technology. Therefore, the SFC factors need not be manually set by a user. In addition, the SFC factors can be reliably transmitted, irrespective of header corruption caused by format conversion and transmission of a compressed sound source.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
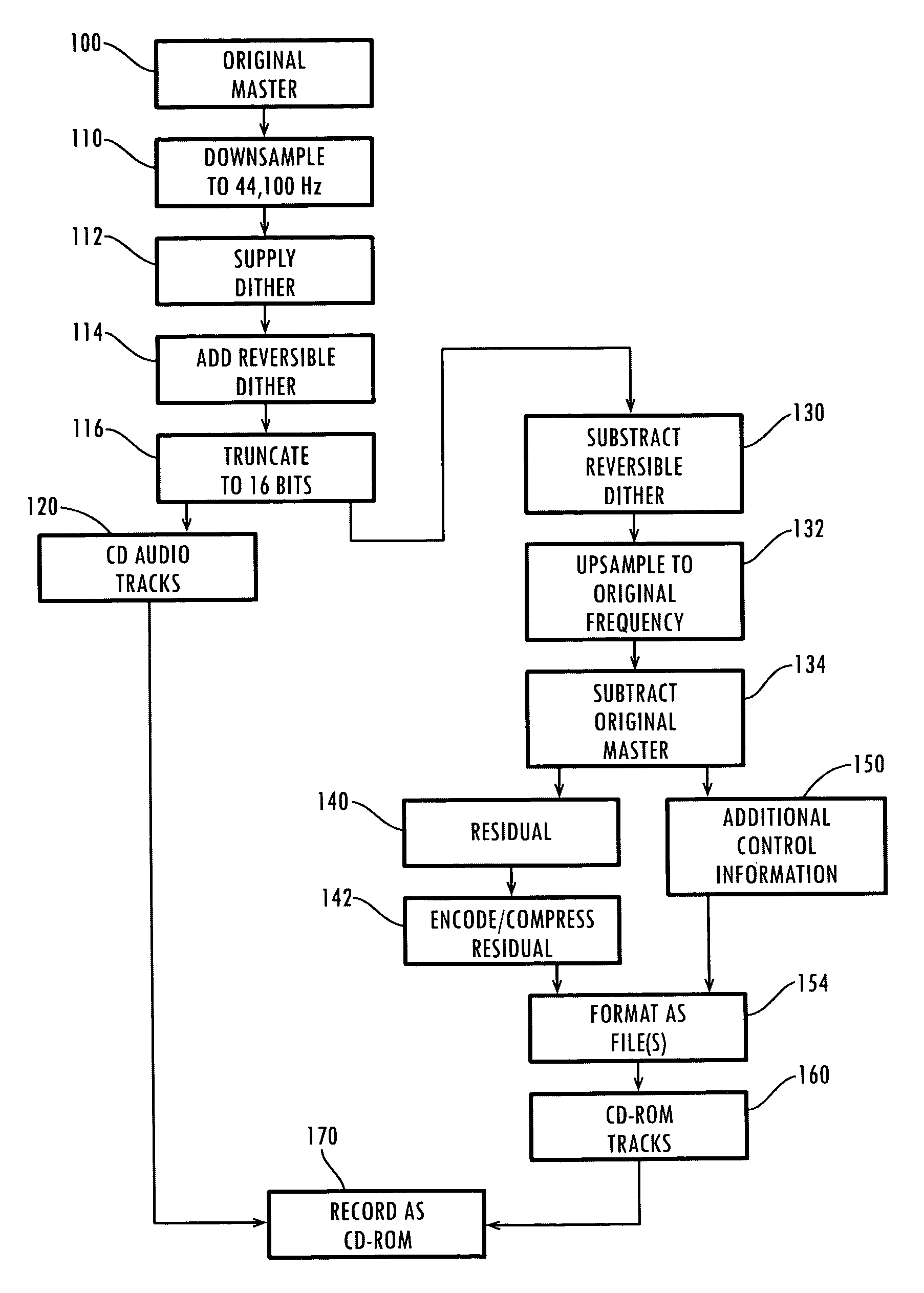
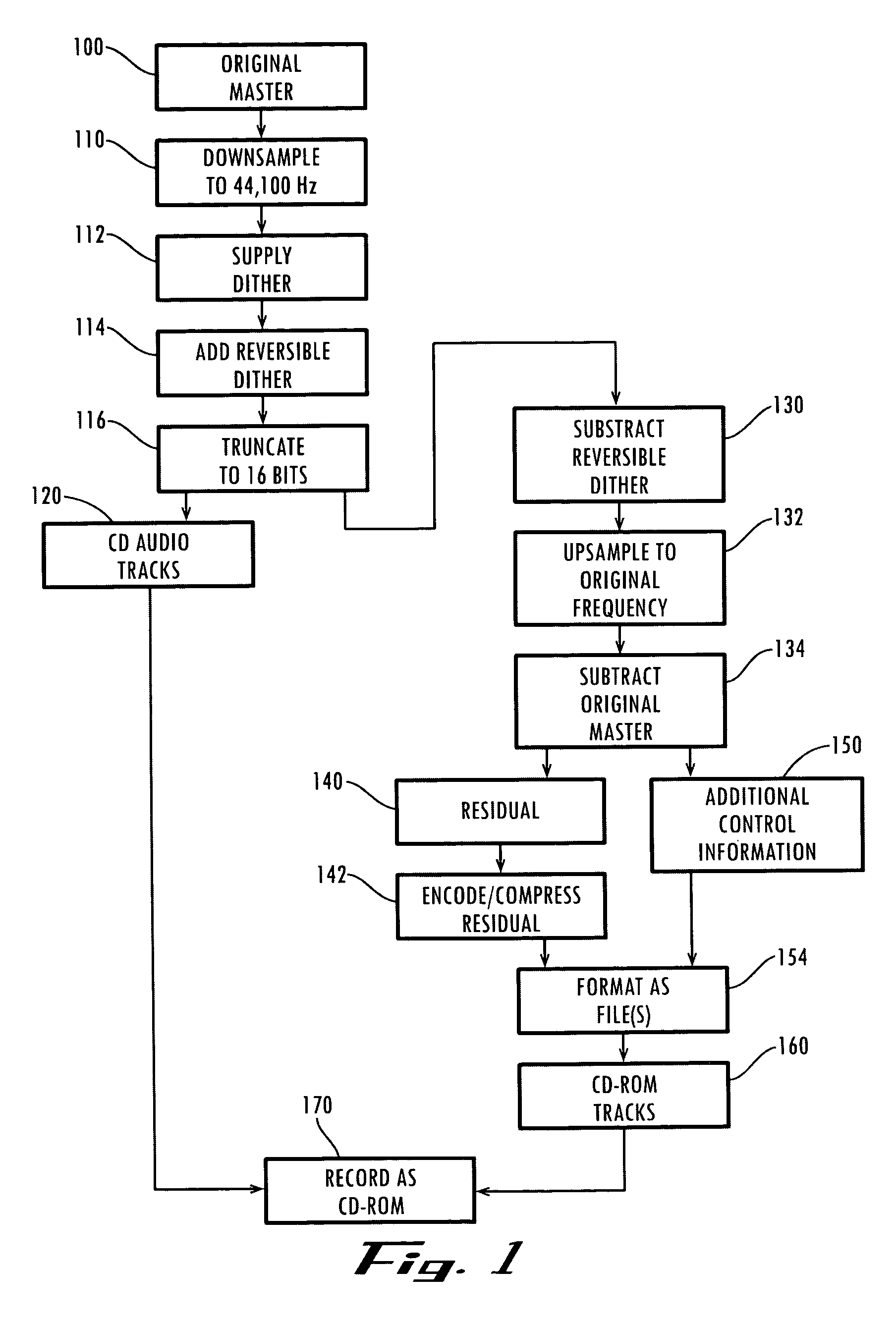
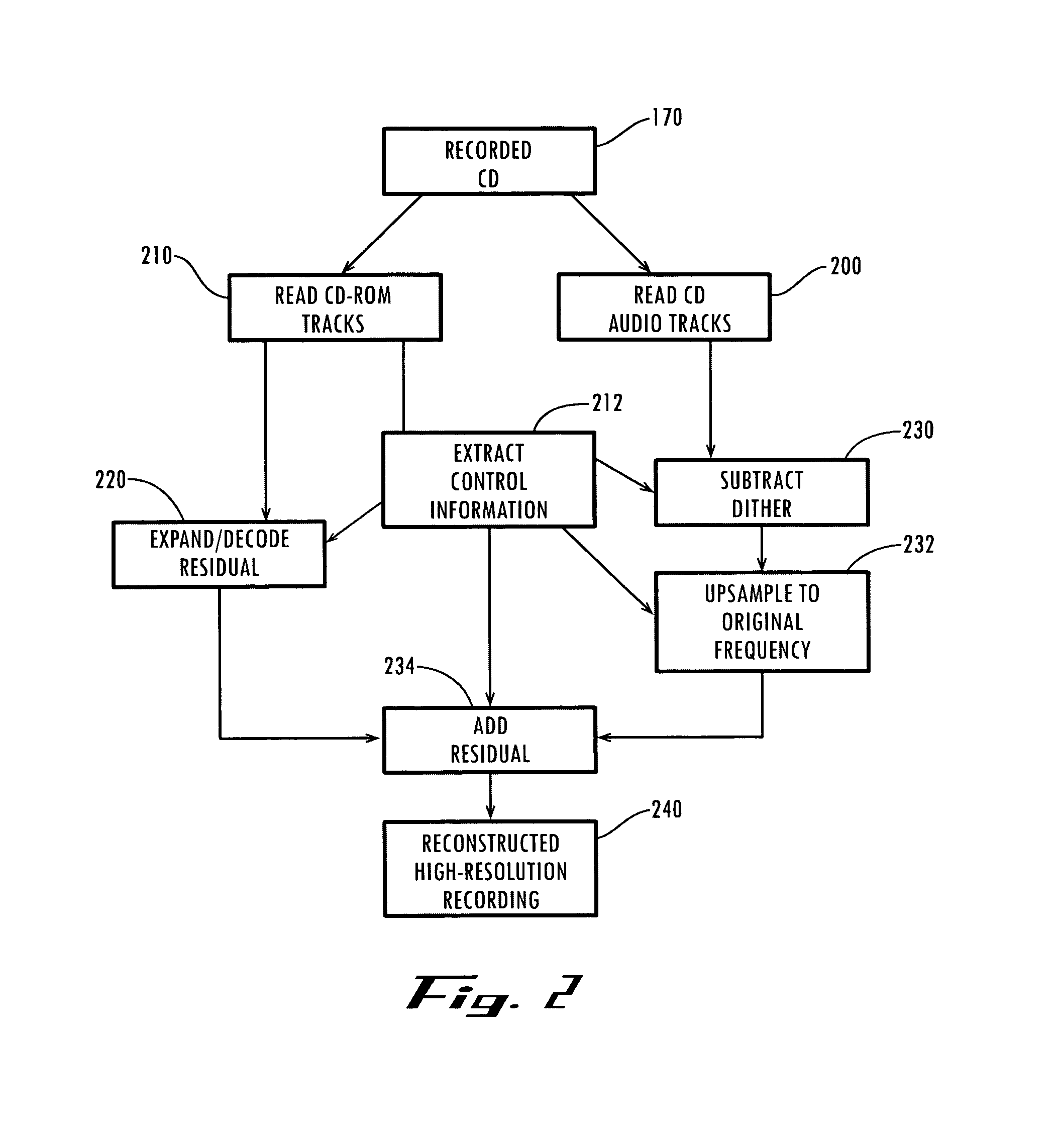
CD playback augmentation for higher resolution and multi-channel sound
InactiveUS7043312B1Improve playbackIncrease the number ofStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsRecord information storageCD-ROMCD player
The present invention presents a way to augment the playback of a compact disk by increasing the resolution, the number of channel, or both during reproduction, while still allowing the resultant CD to be playable on a standard CD player. From a high quality original master or other source, it produces a set of conventional two track audio signals and a set of residual or additional audio data derived from the original master using this conventional stereo audio signal. Additionally, it extracts a set of control information relating this additional audio data to the conventional stereo signals. This additional audio data contains information from the original master that would otherwise be lost when encoded onto a conventional CD. Upon playback, the control information allows the additional audio data to be recombined with the conventional stereo signal in order to reconstruct the original master. A single CD embodiment places the conventional stereo tracks in the audio portion of a compact disk, with the residual or additional audio data and control information stored in the CD-ROM portion of the same disk. The described techniques extend to more general embodiments, since once the original signal is separated into a conventional stereo portion and the additional information, these may be delivered and stored independently in media other than a CD, with the conventional stereo portion usable by itself and only recombined with the additional information when augmented playback is desired.
Owner:S AQUA SEMICONDUCTOR LLC
Audio file playing method and device
ActiveCN104867507AQuality improvementGood sense of spaceModification of read/write signalsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsComputer terminalComputer science
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CHINA R&D CENT +1
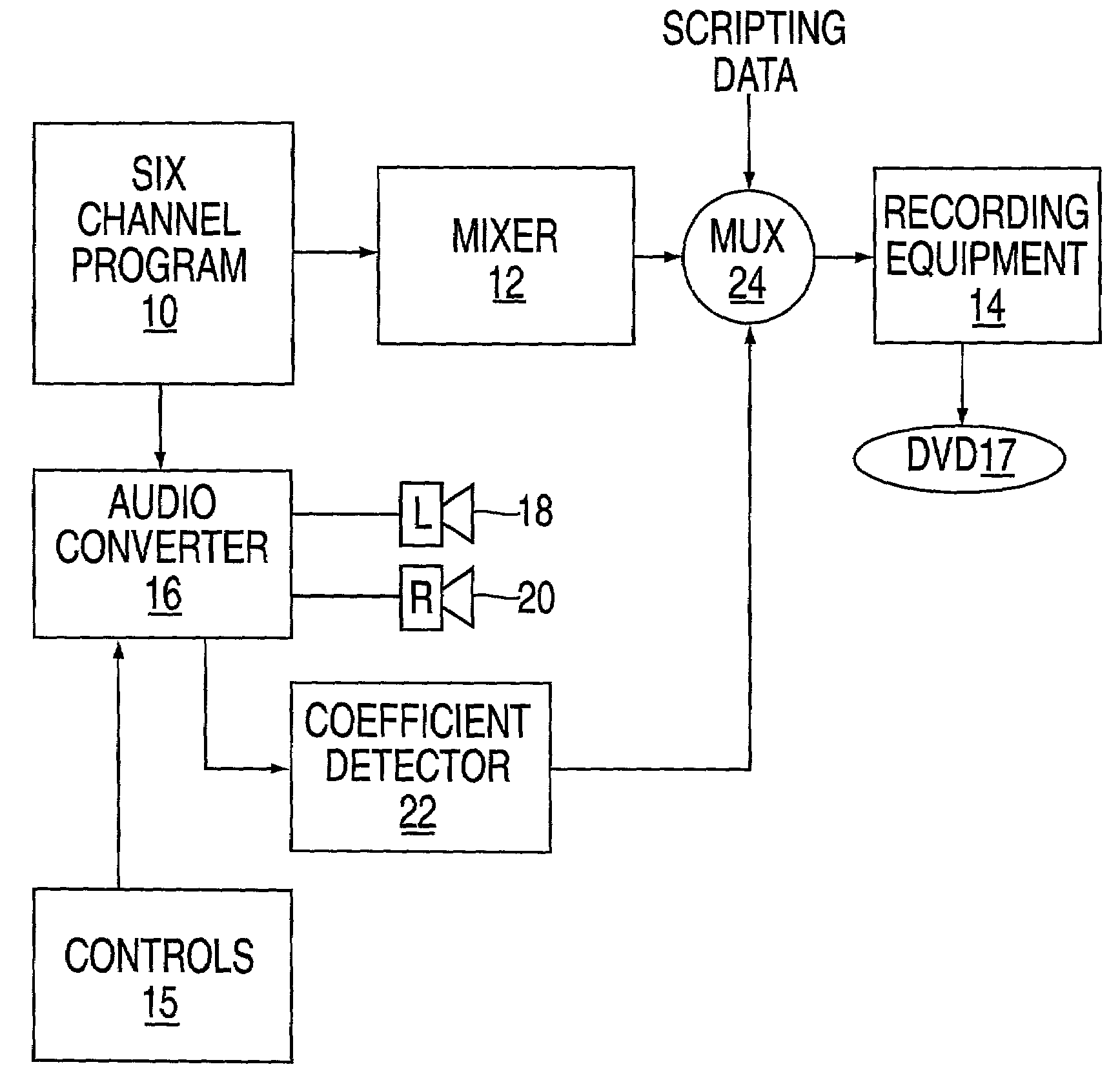
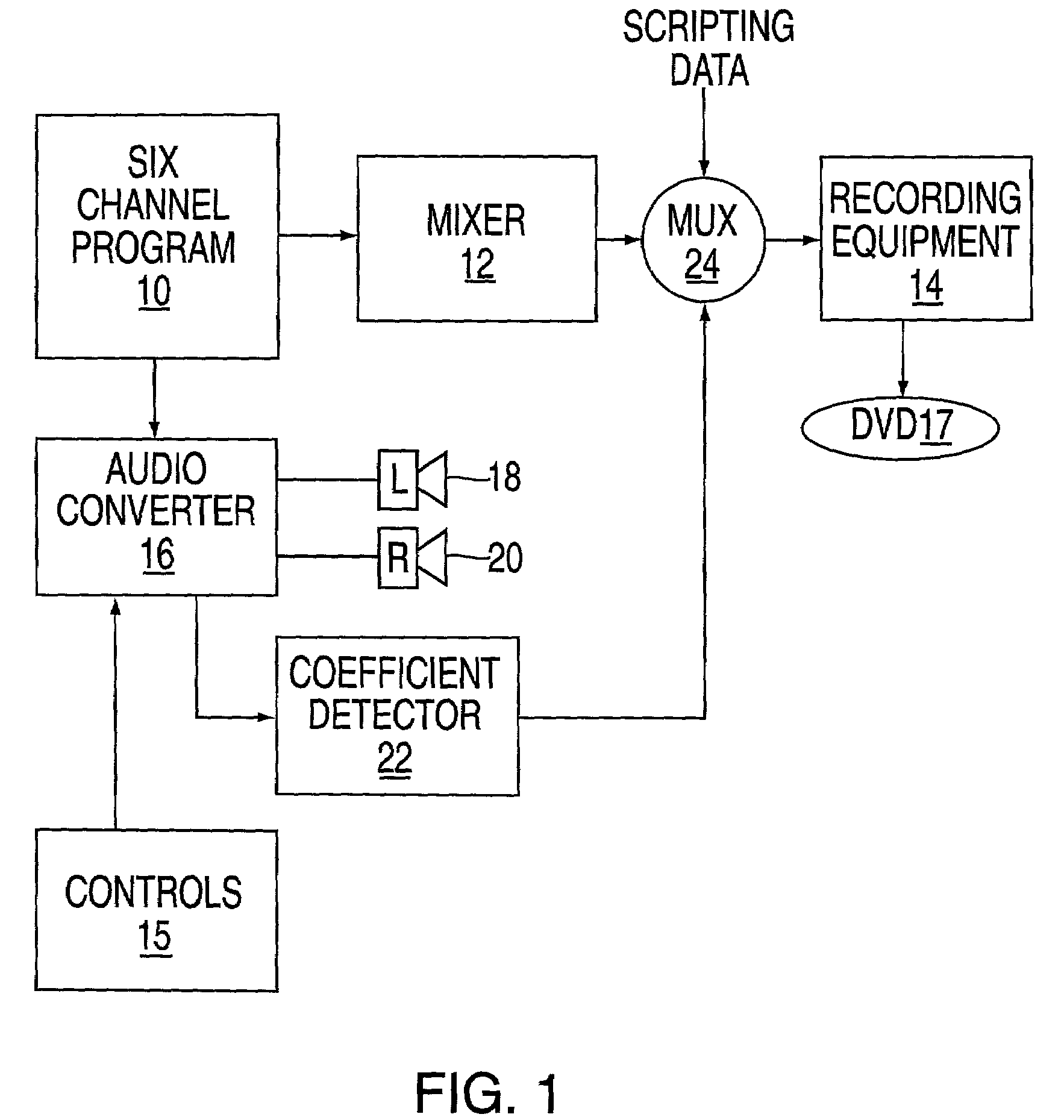
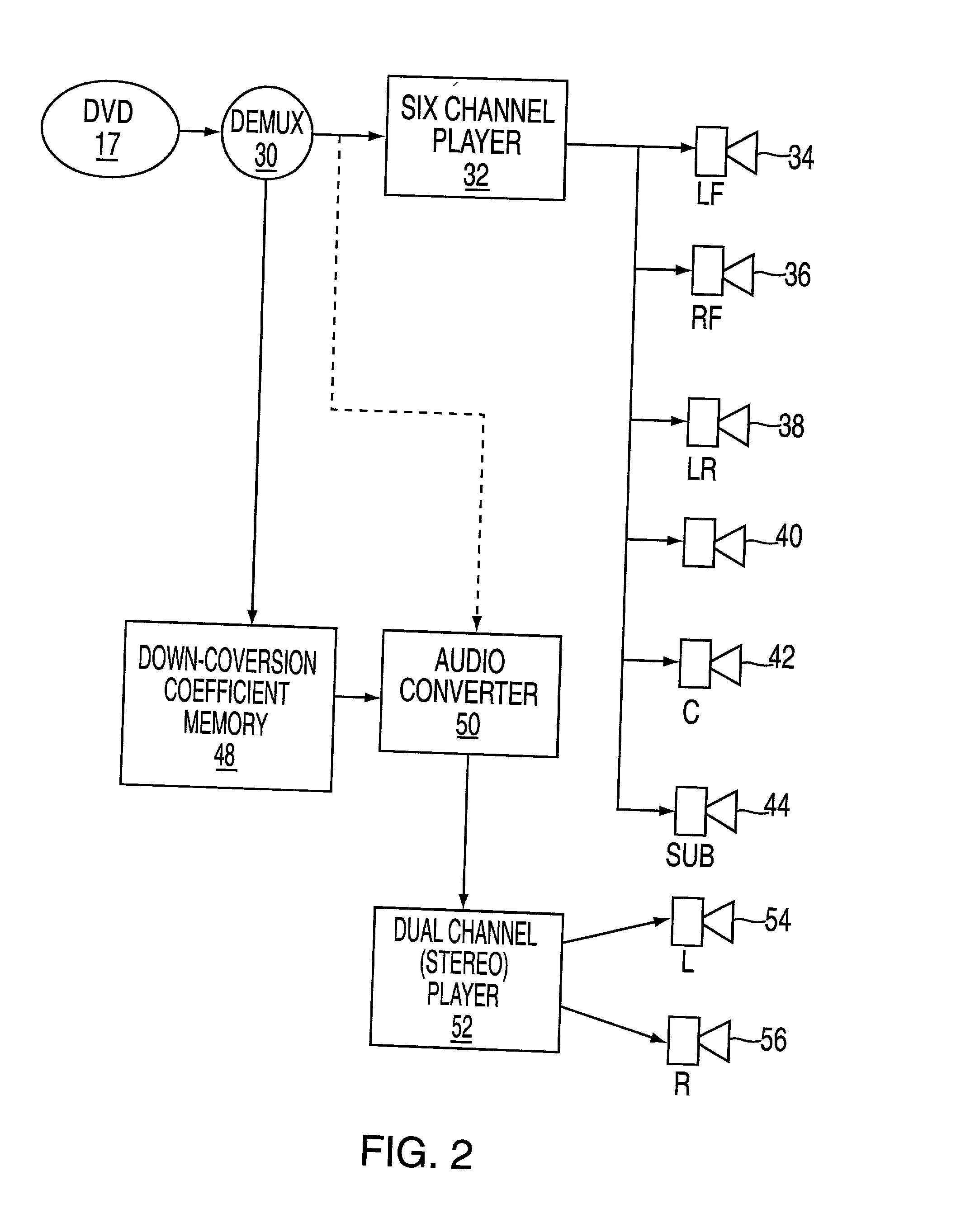
Apparatus and method for down converting multichannel programs to dual channel programs using a smart coefficient generator
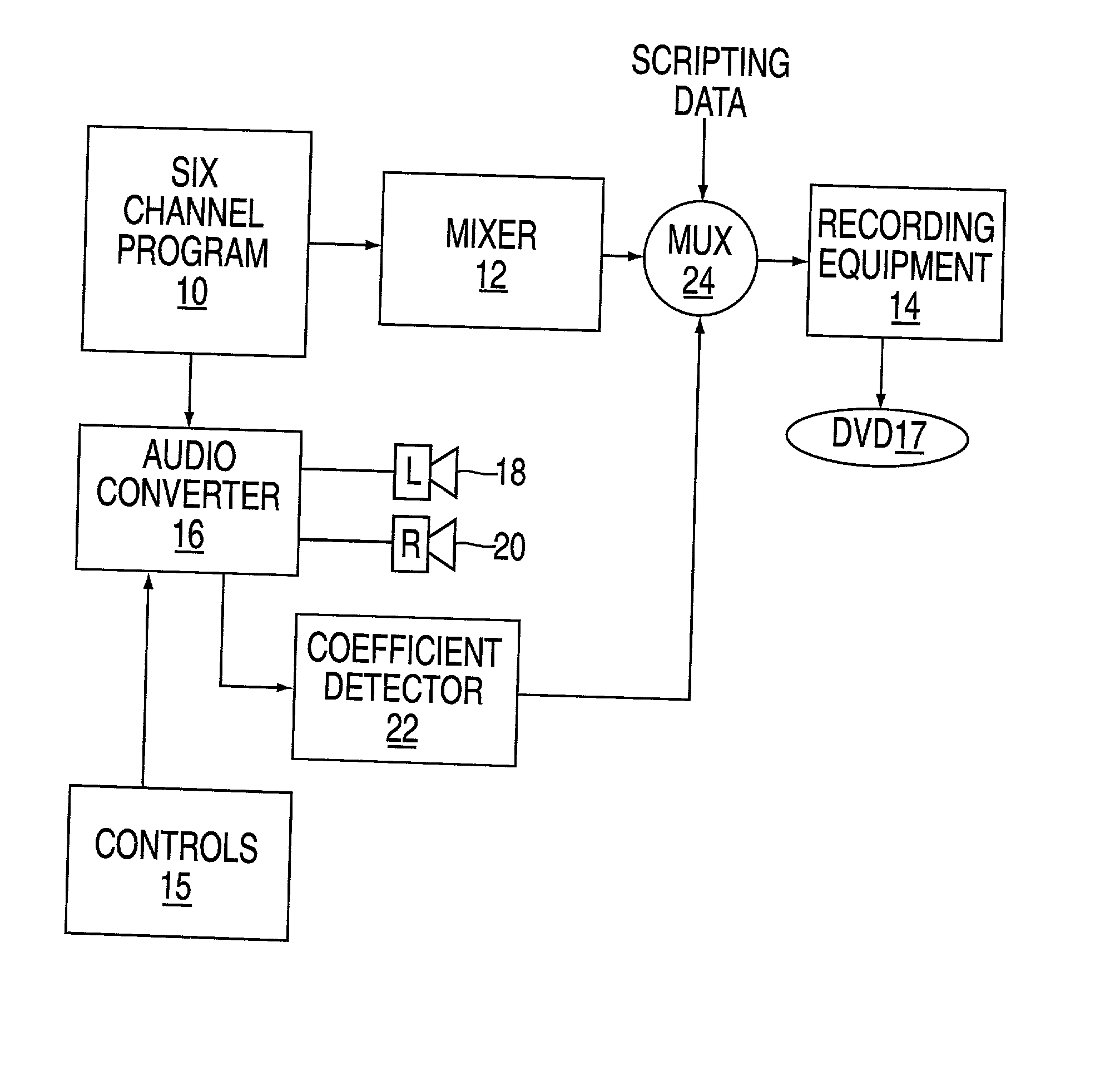
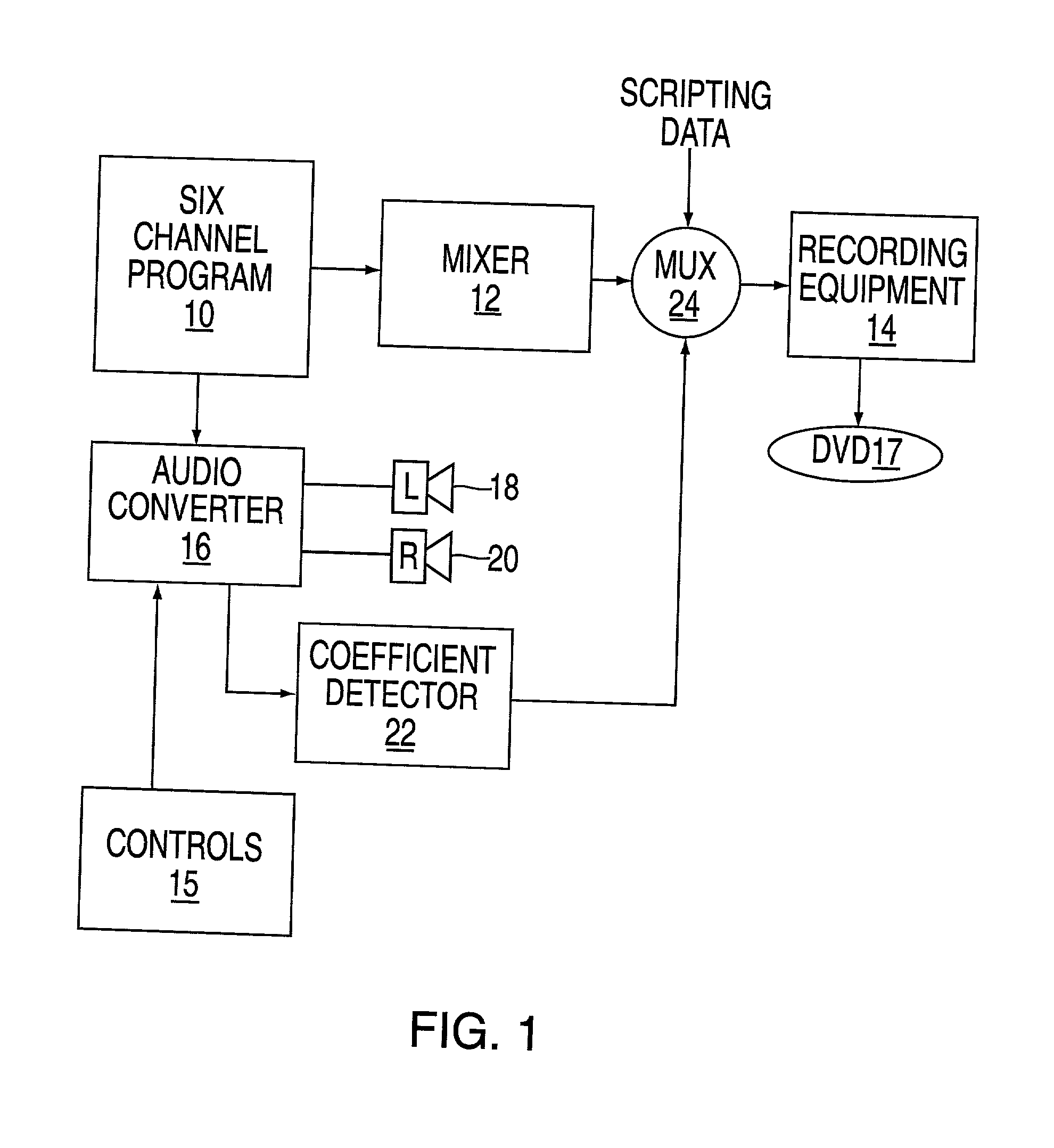
ActiveUS7454257B2Stereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsBroadcast information characterisationTheoretical computer scienceComputer science
An apparatus for recording a multichannel program includes an audio converter adapted to convert said multichannel program at least partially into a modified program requiring less channels than said multichannel program. The audio converter including control elements used to modify the conversion process used to generate said modified program. A coefficient generator coupled to said converter to generate a coefficient indicative of the operation of said controls. A mixer is arranged to mix the coefficient with program data. A recorder is arranged to record the mixed data on a medium, whereby the medium can be played either using a multichannel player device or a reduced channel player device by using said coefficient.
Owner:WARNER MUSIC GROUP
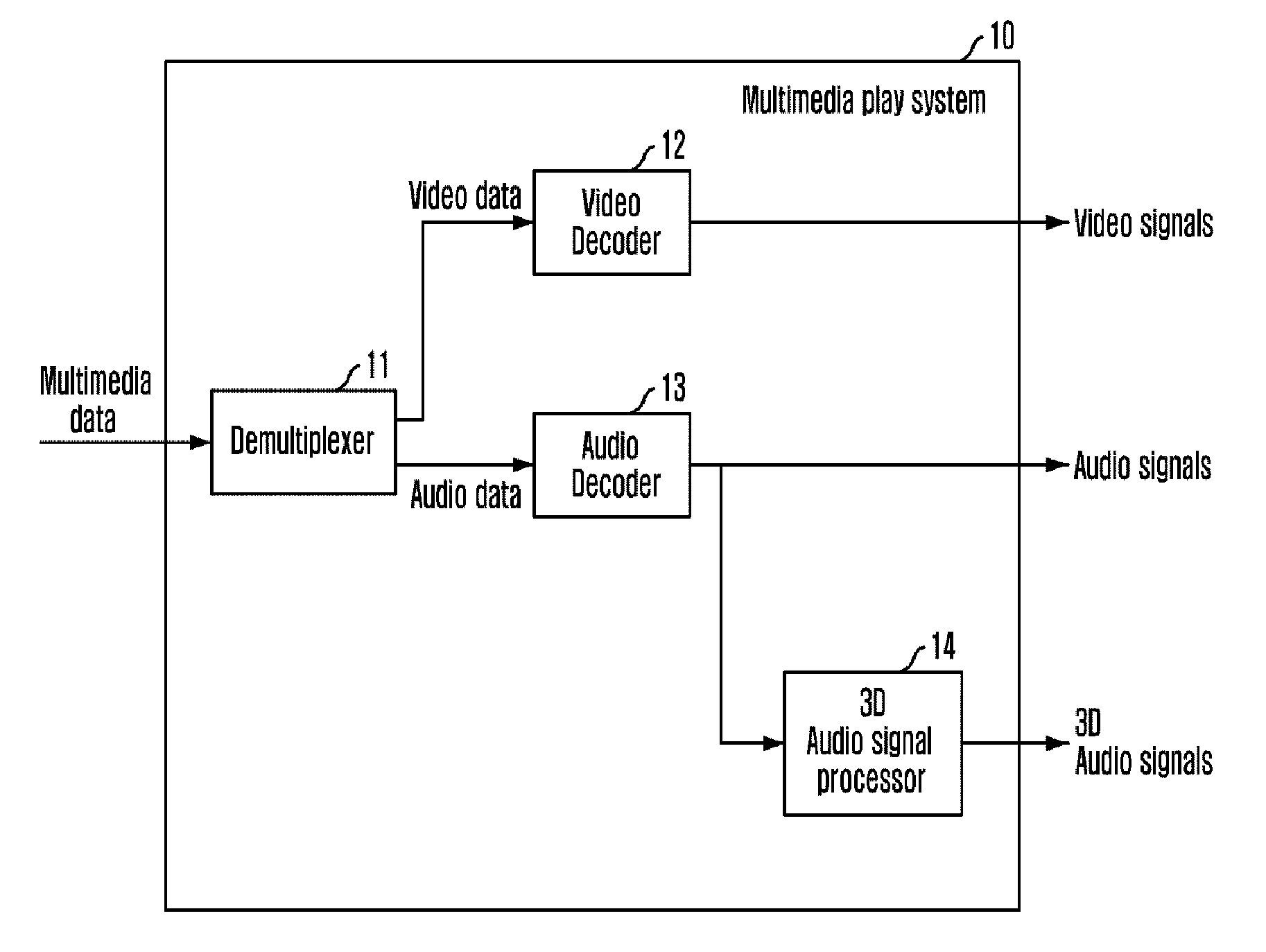
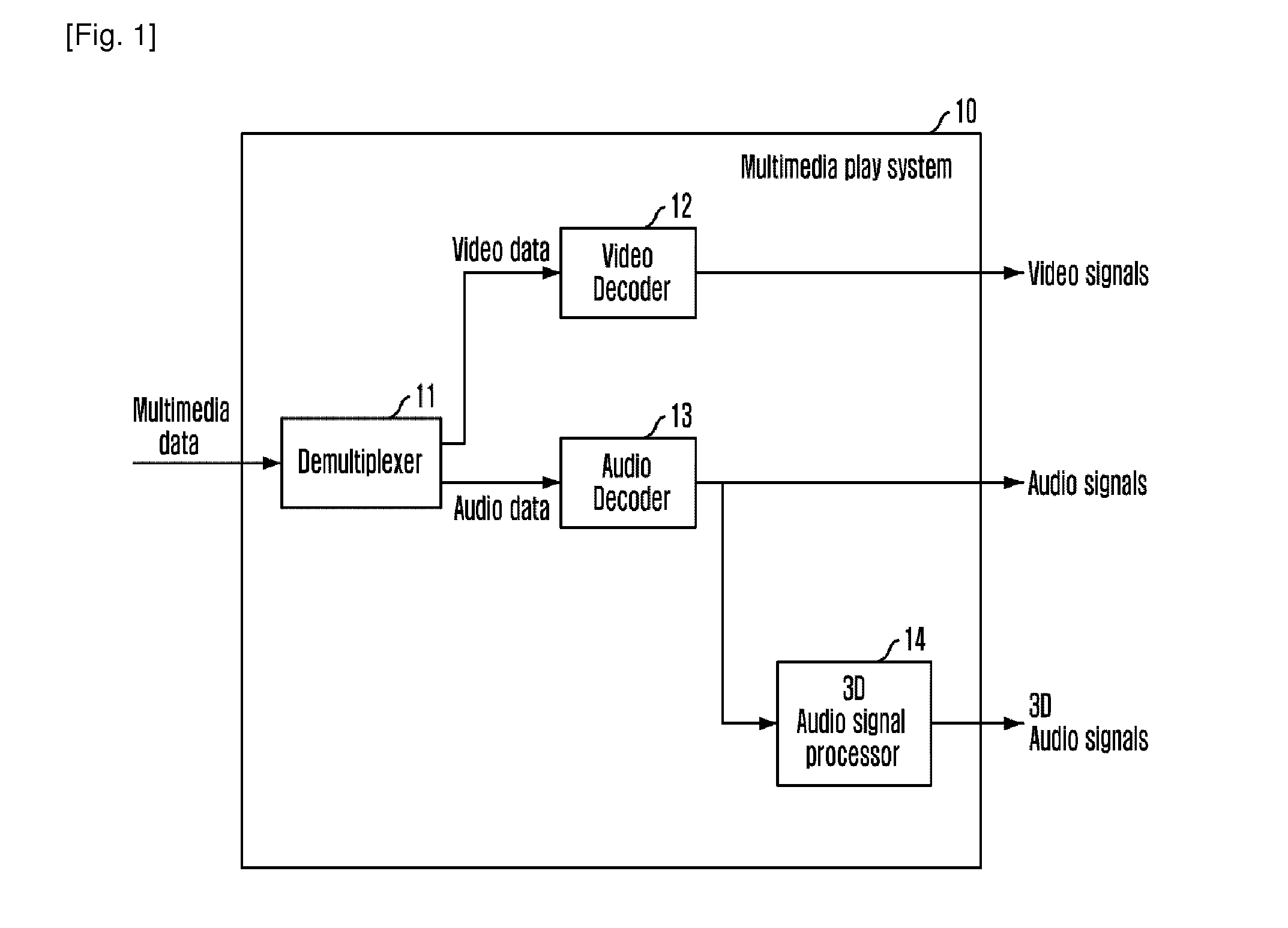
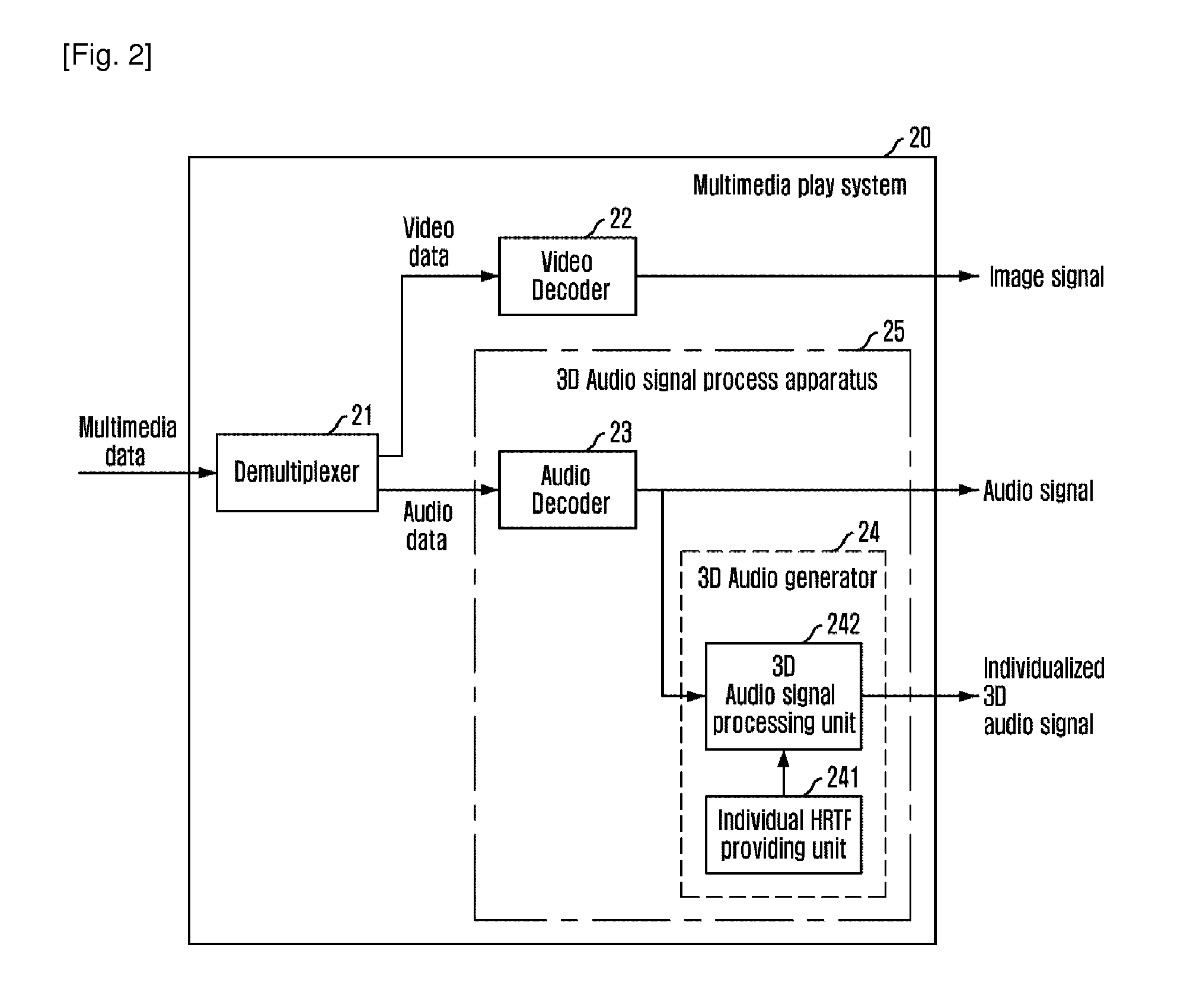
Apparatus and method for processing 3D audio signal based on hrtf, and highly realistic multimedia playing system using the same
InactiveUS20110150098A1Stereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPersonalizationComputer science
A three-dimensional audio signal processing apparatus using a Head Related Transfer Function (HRTF) includes an audio decoder for decoding audio data to restore original audio signals and a three-dimensional audio generator for generating three-dimensional signals corresponding to the audio signals restored by using the HRTF modeled according to physical characteristics of an user, wherein the HRTF modeled according to physical characteristics of an user is an individualized HRTF.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
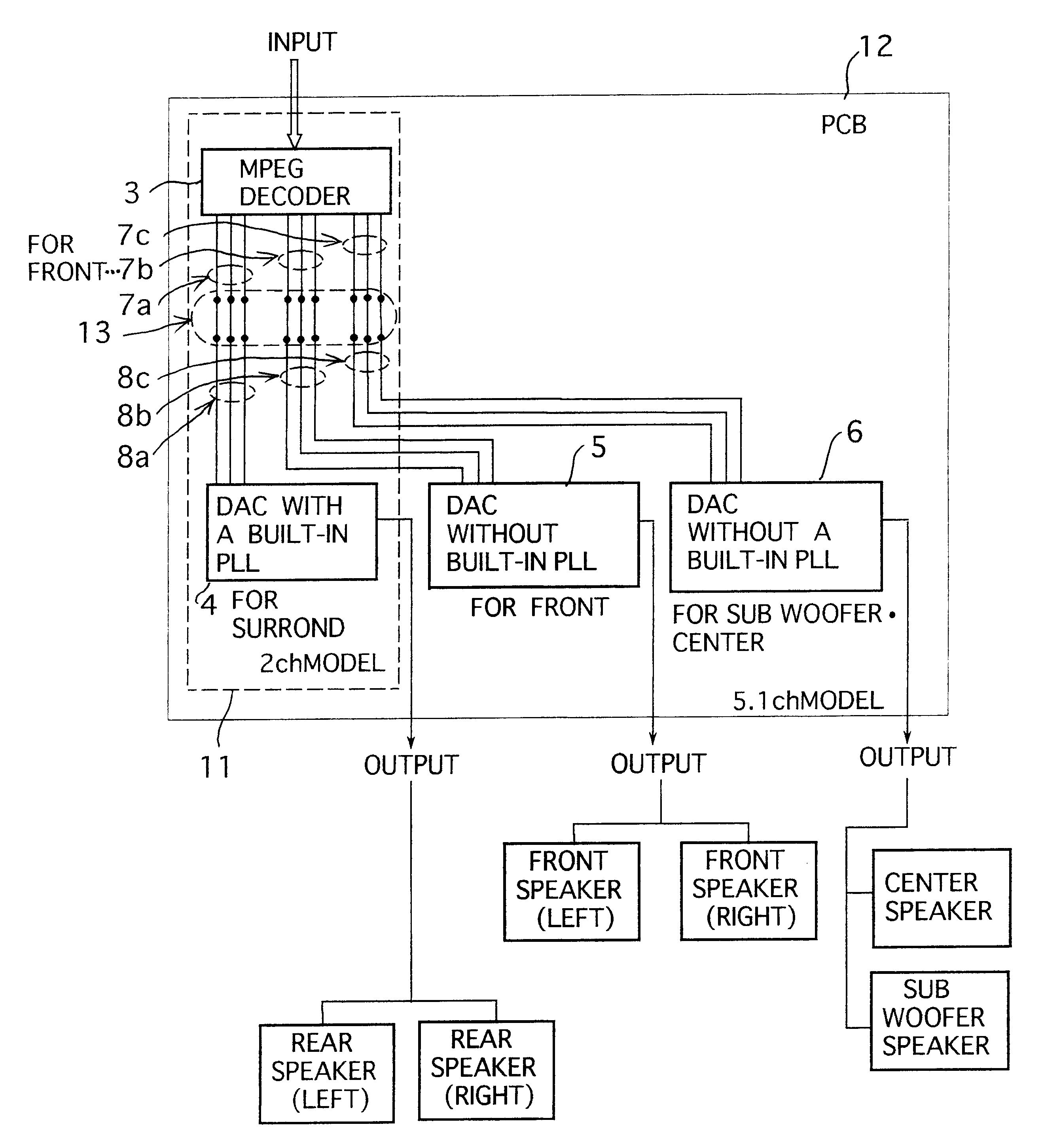
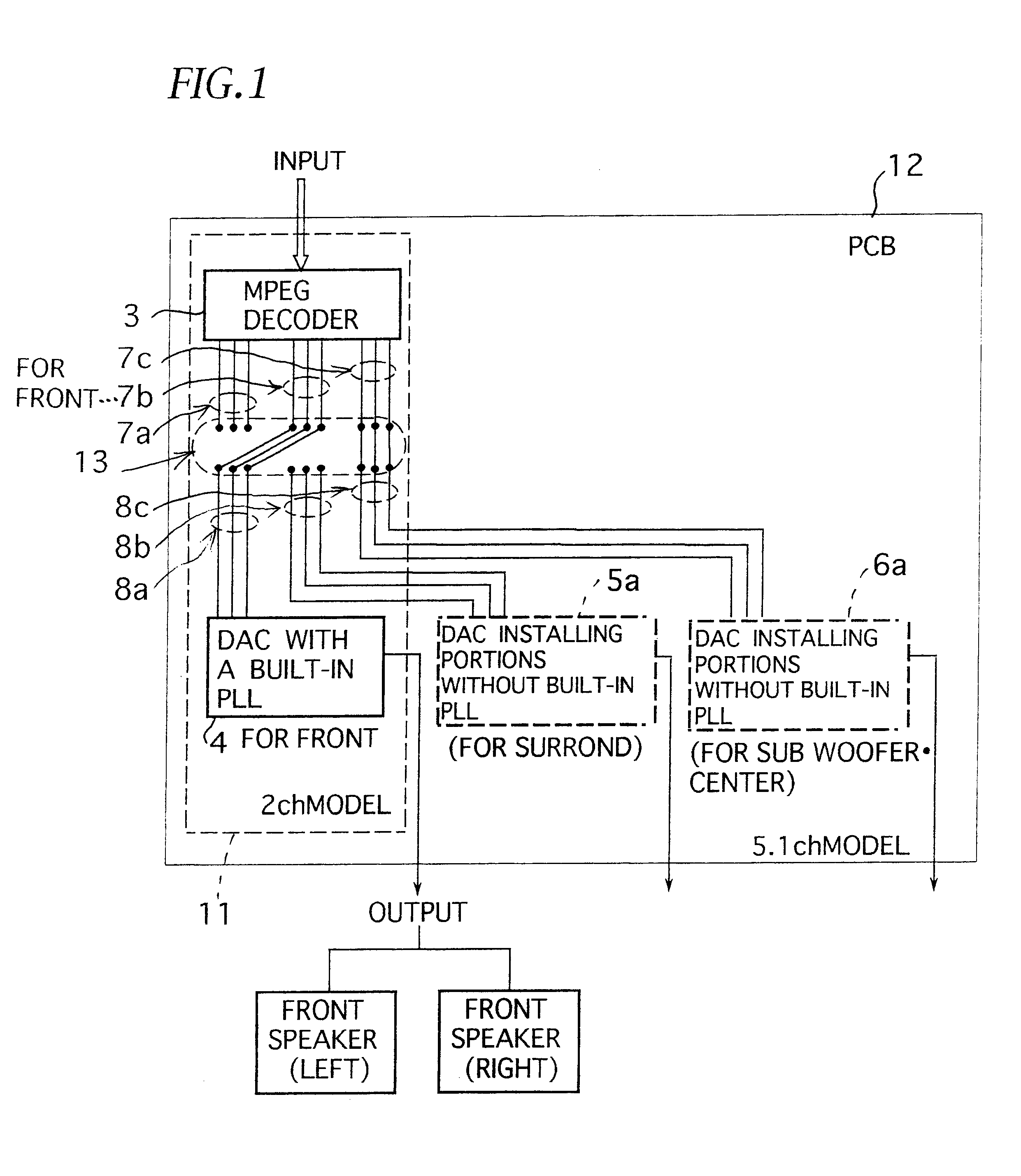
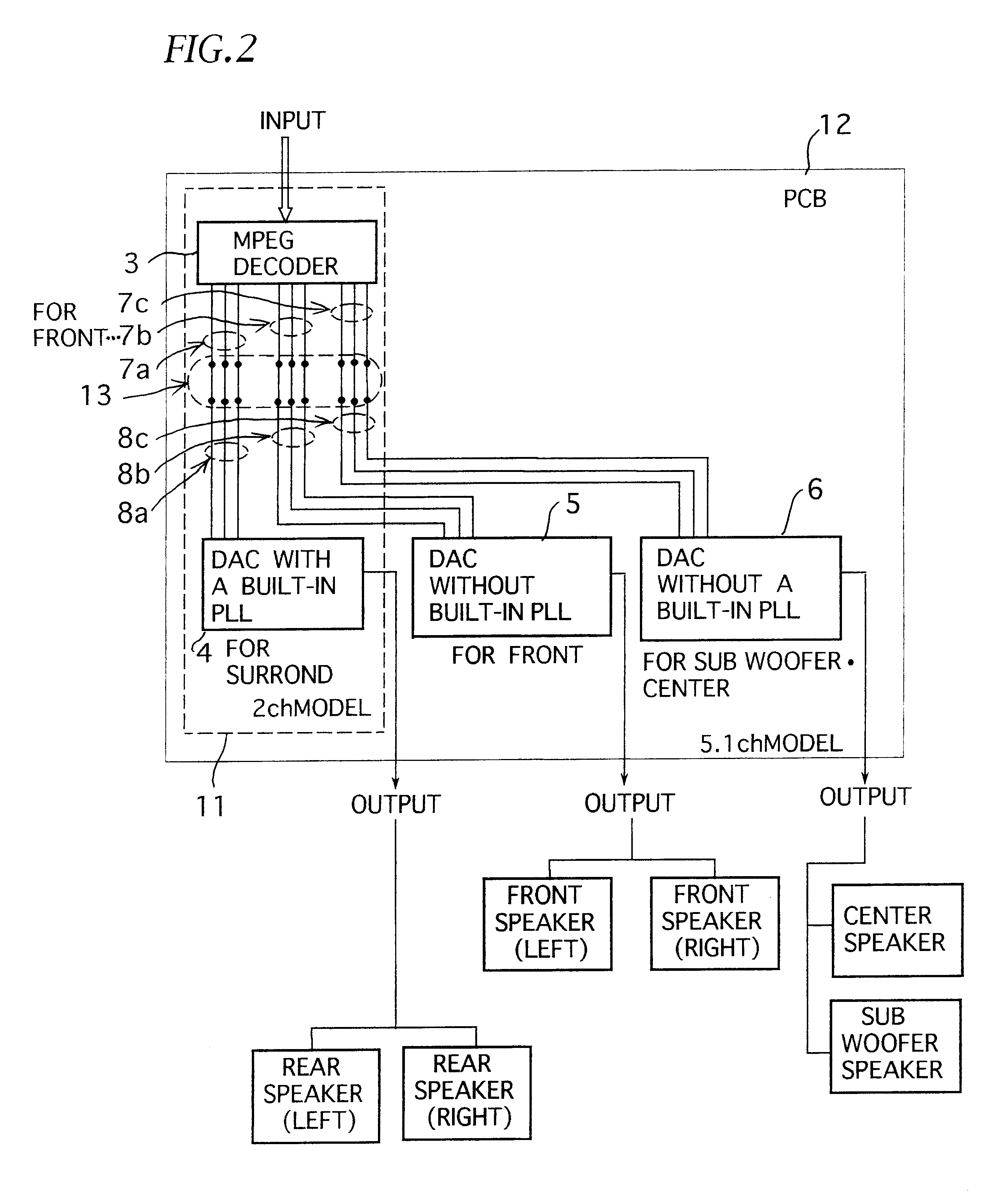
Audio-decoder apparatus using a common circuit substrate for a plurality of channel models
InactiveUS6839676B2Advantageous in fabrication costAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsEngineeringAudio frequency
In audio-decoder apparatus, a circuit substrate common to a 2-channel model and a 5.1-channel model, on which a decoder and a D / A converter with built-in PLL are installed, and which has installing portions and for enabling installation of D / A converters without built-in PLL. The line connection modes of signal lines connecting the output terminal of the decoder to the input terminals of each D / A converter can be changed by a switching apparatus, corresponding to the channel model, thus it becomes possible to realize D / A converters without built-in PLL having better audio performance under a line connection mode desired for an improved audio performance. Therefore, a good audio performance can be secured, while a common circuit substrate can be used for a variety of channel models, which is advantageous in view of fabrication cost.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Multi-channel compatible stereo recording
ActiveUS8009837B2Sufficient informationImprove time-stretching and/or pitch shiftingElectrophonic musical instrumentsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsComputer hardwareEncoder
An encoder for mixing a plurality of independent mono audio channels into a stereo recording and generating a restricted set of additional parameters used to master an audio track of a storage device is described. The plurality of independent mono audio channels are constructed such that the storage device can be played using an optical disk player so that in a first mode all of the plurality of independent mono audio channels are played as the stereo recording and in a second mode at least one of the plurality of independent mono audio channels can be unmixed and the stereo recording played with at least one mono audio channel removed. A corresponding decoder and an audio system comprising such encoder and decoder are also described.
Owner:AURO TECH
Recording medium and audio-signal processing apparatus
InactiveUS7006422B2Television system detailsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsDigital audio signalsAudio frequency
A digital signal recording disc has a first area and a second area. The second area differs from the first area. The first area stores a first-channel digital audio signal and a second-channel digital audio signal. The first-channel digital audio signal results from quantizing a first-channel analog audio signal with a first quantization bit number. The second-channel digital audio signal results from quantizing a second-channel analog audio signal with a second quantization bit number. The second area stores information of the first and second quantization bit numbers.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP
Apparatus and method for down converting multichannel programs to dual channel programs using a smart coefficient generator
ActiveUS20020106088A1Stereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsBroadcast information characterisationTheoretical computer science
An apparatus for recording a multichannel program includes an audio converter adapted to convert said multichannel program at least partially into a modified program requiring less channels than said multichannel program. The audio converter including control elements used to modify the conversion process used to generate said modified program. A coefficient generator coupled to said converter to generate a coefficient indicative of the operation of said controls. A mixer is arranged to mix the coefficient with program data. A recorder is arranged to record the mixed data on a medium, whereby the medium can be played either using a multichannel player device or a reduced channel player device by using said coefficient.
Owner:WARNER MUSIC GROUP
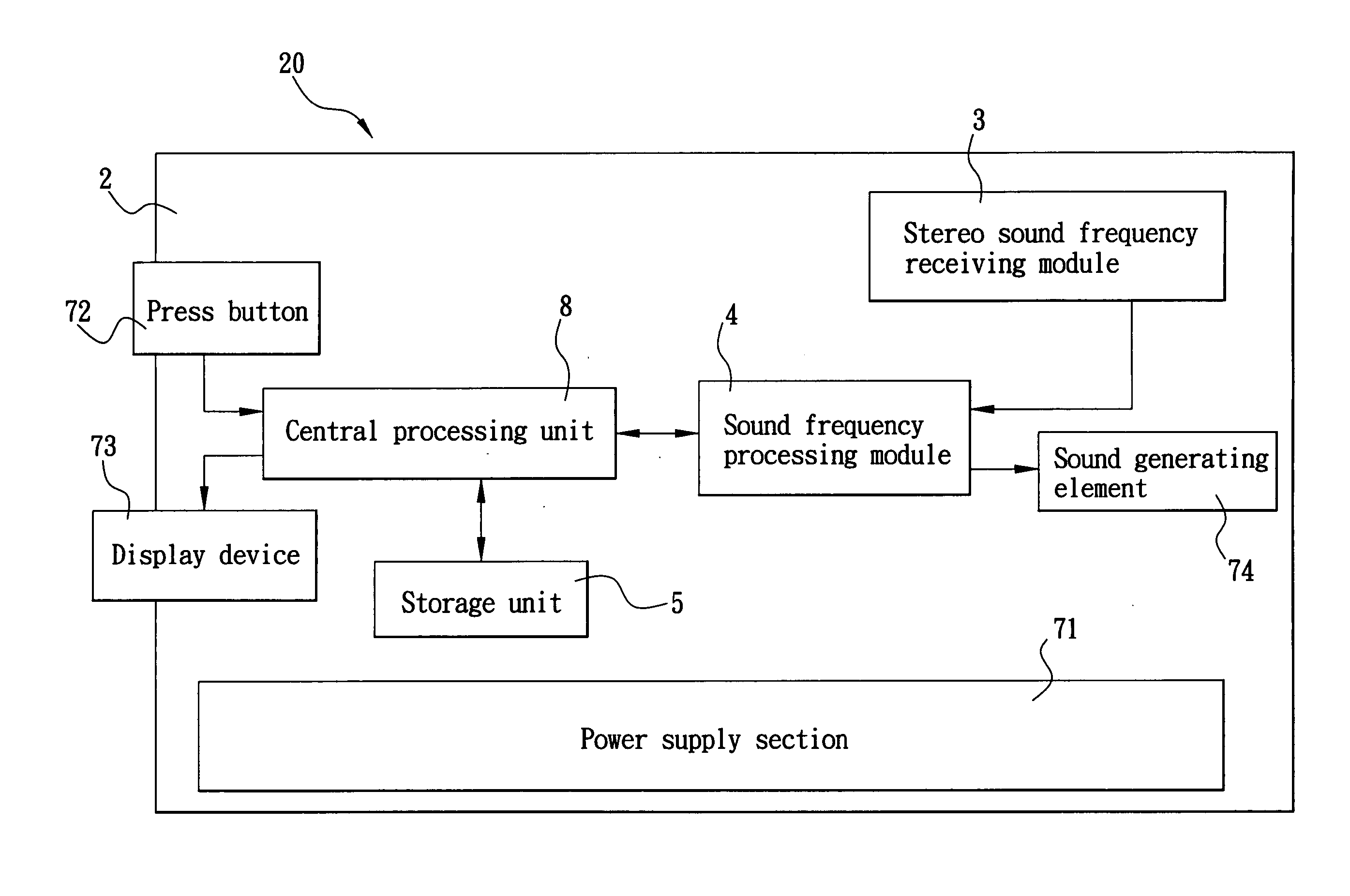
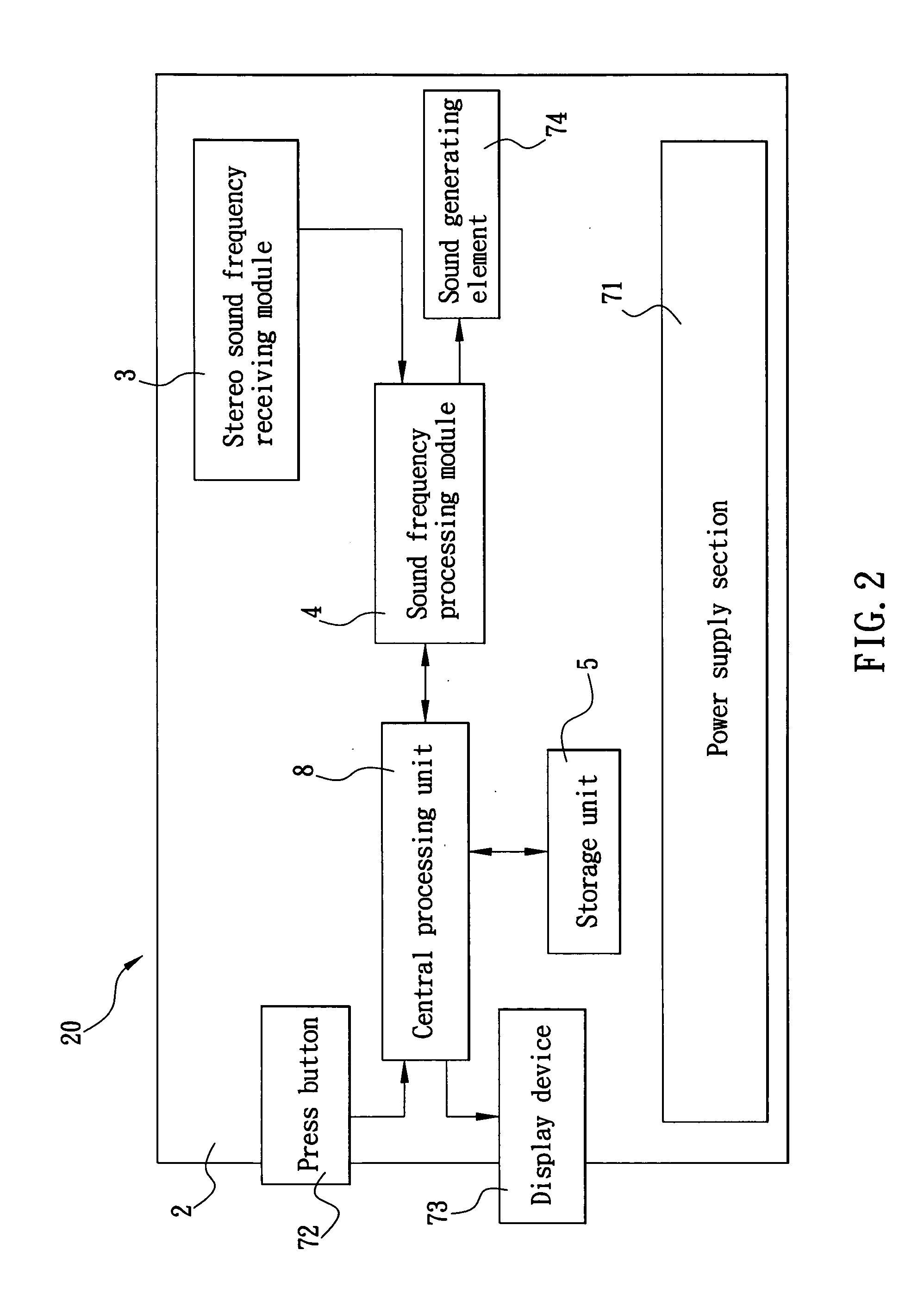
Mobile phone with a stereo recording function
InactiveUS20060040703A1Stereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsSubstation speech amplifiersComputer scienceMobile phone
The present invention relates to a mobile phone with a stereo recording function, which includes a stereo sound frequency receiving module including sound receiving components for receiving sounds from different places within a sound field and converting the received sounds into a digital signal, a central processing unit (CPU) for encoding and compressing the digital signal, and a storage unit for storing the digital signal therein as an audio file having a stereo effect during being played back by the mobile phone.
Owner:INVENTEC APPLIANCES CORP
Recording and playback of multi-channel digital audio having different resolutions for different channels
InactiveUS20050088934A1Recording carrier detailsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsComputer hardwareData stream
Methods and apparatus for recording on DVD-like recording media in which audio content is stored in a high-capacity multi-channel (e.g., six-channel) format are provided. Various channels may use various resolutions. A two-channel audio output may be derived from the multi-channel audio data stream during playback. To facilitate an accurate derivation, the mixing coefficients to be used in generating the derivation can be supplied along with the six-channel audio data.
Owner:WARNER MUSIC GROUP
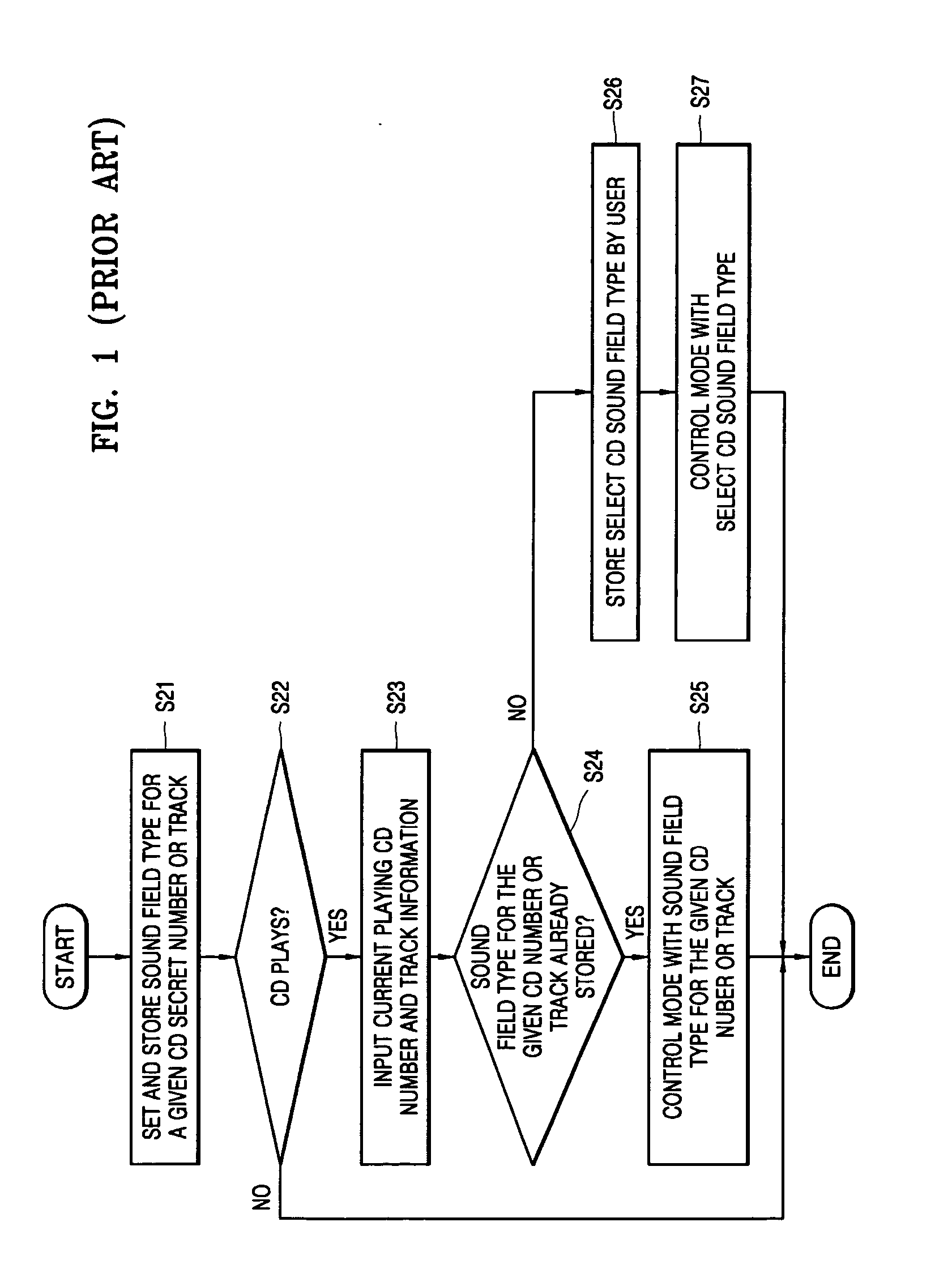
Device and method for automatically selecting audio-frequency play mode
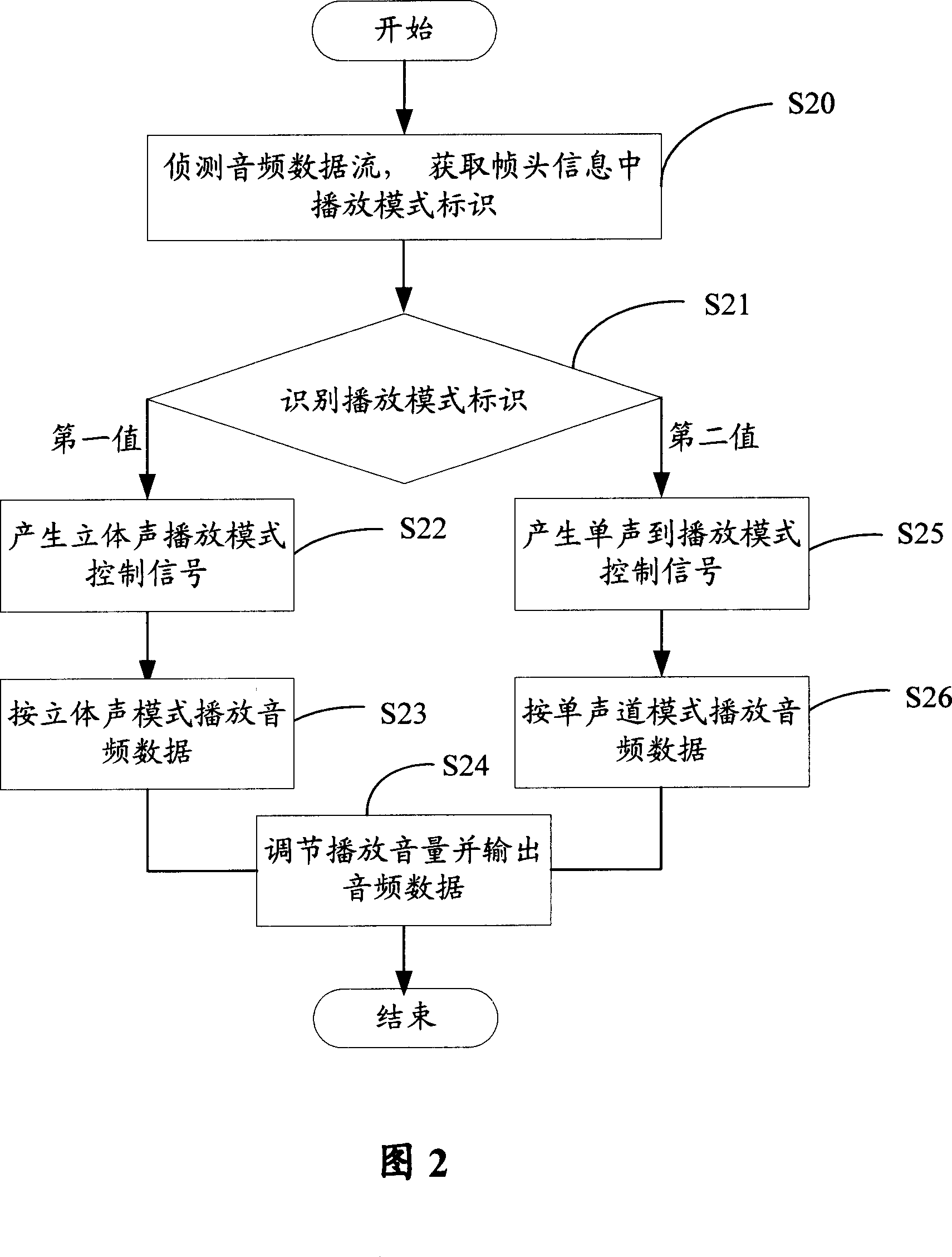
InactiveCN1941160AMeet the sound quality effectImprove the sound effectStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsRecord information storageAudio power amplifierControl signal
This invention is an automatically choose device of audio playing mode and its working method. The device receives audio stream and output the processed data as data frame. The data frame includes frame head information which has an identification of playing mode. The device includes an audio detection unit, a decoder, a D / A converter, a playing mode choosing unit and an amplifier. The audio detecting unit acquires and identifies the playing mode in the frame head. In case the playing mode is the first value, a control signal of stereo playing mode is generated. In case the playing model is the second value, a control signal of single track playing mode is generated. The playing mode choosing unit outputs the corresponding analog signals according to the control signal.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com