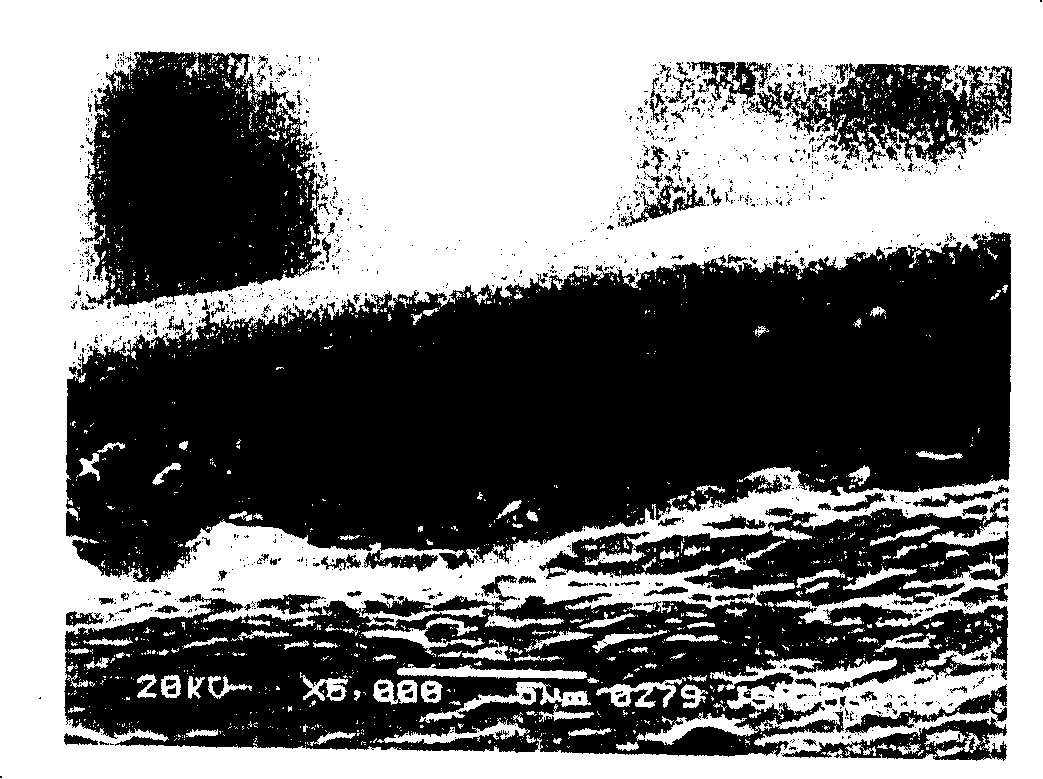
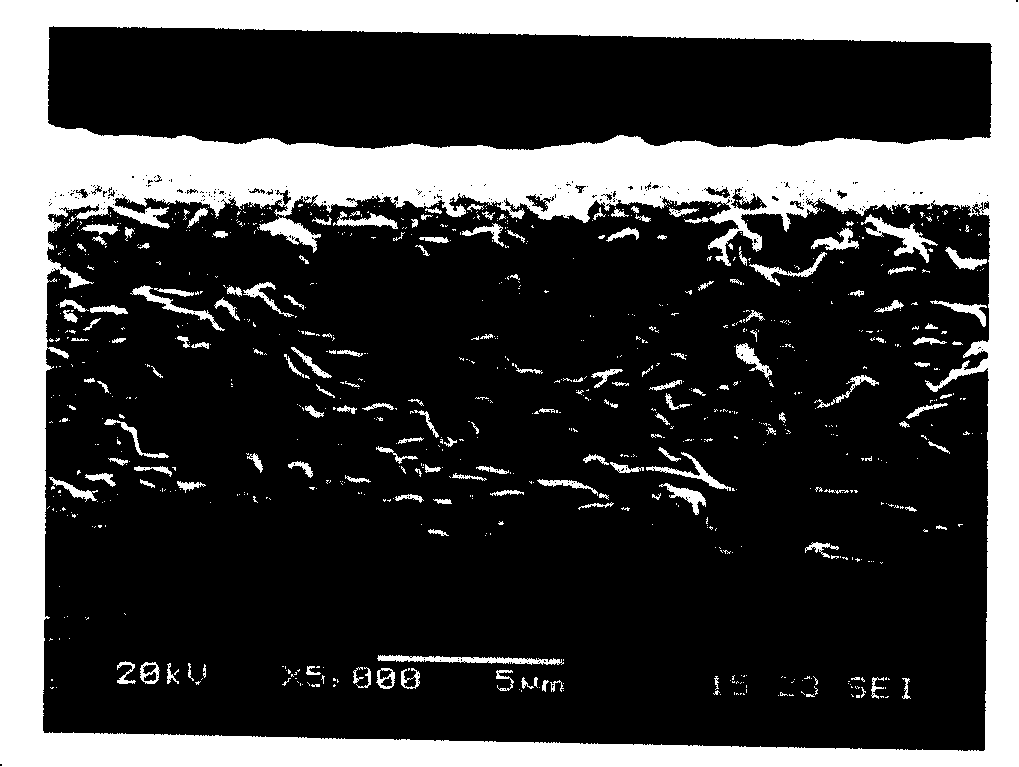
Preparation process of composite proton exchanging member based on hydrophilic porous poly tetrafluoro ethylene matrix
A technology of polytetrafluoroethylene membrane and polytetrafluoroethylene, which is applied in the field of preparation of composite proton exchange membranes, can solve problems such as the difficulty of perfluorosulfonic acid resin solution entering porous polytetrafluoroethylene, and achieve low gas permeability and mechanical The effect of high performance and strong proton conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Take a porous polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membrane with a thickness of 10 microns, a pore size of 0.05 to 2 microns, and a porosity of 85%, and use Ar gas to treat the surface of PTFE. The free radicals generated by Ar gas can react with oxygen or water in the air. The reaction forms peroxide, which further cross-links and polymerizes with the functional monomer-acrylic acid to obtain a hydrophilic surface. The porous polytetrafluoroethylene membrane after hydrophilic treatment is placed in the isopropanol solution of 5% (mass) perfluorinated proton conductive resin (Nafion, EW value 1100) and soaked for 10 minutes, then taken out and rolled by two wheels Press once, put the rolled film into a vacuum drying oven, adjust the temperature to 160°C, heat-treat for 60 seconds, repeat the above dipping process 4 times to obtain a transparent composite film; soak the film in isopropanol for 5 minutes Remove organic impurities, then soak in boiling deionized water for 10 min...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Take a porous polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membrane with a thickness of 12 microns, a pore size of 0.05 to 2 microns, and a porosity of 85%, pretreat the PTFE membrane with Ar plasma, and then use hydrophilic functional monomers such as acrylic acid and sodium styrene sulfonate The graft copolymerization reaction of salt, N,N-dimethylacetamide and glycidyl methacrylate aqueous solution was induced by near ultraviolet light. Place the porous polytetrafluoroethylene membrane after hydrophilic treatment in 5% (mass) sulfonated polyetheretherketone resin (s-PEEK, EW value 900) and 2% (mass) Trinton-100 ethanol solution for immersion Take it out for 10 minutes, then take it out and roll it again with double-wheel rollers, put the rolled film into a vacuum drying oven, adjust the temperature to 230°C, heat treatment for 50 seconds, repeat the above impregnation process 5 times, and obtain a transparent composite film; Soak the film in isopropanol for 5 minutes to remove org...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com