Method for restricting and slowing oil heating furnace high-temperature molten salt corrosion
A high-temperature molten salt, heating furnace technology, used in the treatment of equipment corrosion/fouling inhibition, fuel, petroleum industry and other directions, can solve the problem of low combustion-promoting performance of additives, and achieve the purpose of enhancing combustion-promoting performance, inhibiting corrosion and prolonging service life. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
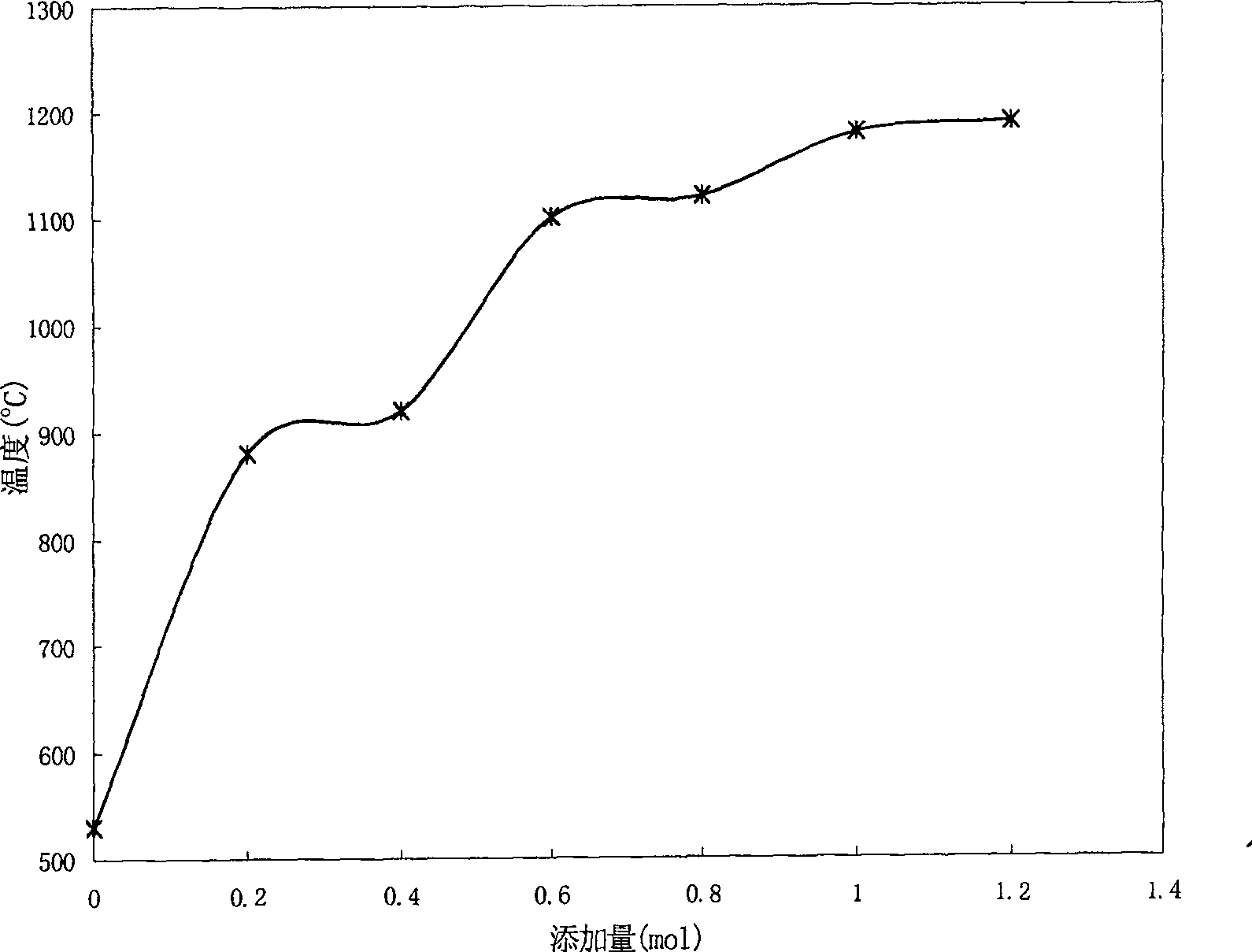
[0012] Preparation composition (lanthanum trioxide 70% by weight, cerium oxide 20% by weight, neodymium trioxide 10% by weight), with respect to simulated ash (50 mol% V 2 o 5 +50 mol%Na 2 The molar numbers of vanadium in O) are respectively 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2, mixed with simulated ash, made into 6 kinds of samples, ground, passed through a 100 mesh sieve, and put into a high-temperature box-type resistance furnace for heating , the initial temperature is 500°C, and the maximum temperature is 1200°C. The temperature interval is 20°C, and each temperature point is kept for 15 minutes to investigate the state of each sample at different temperatures and record the change of melting point; the temperature interval is 10°C near the melting point in order to determine the change of ash melting point more accurately. see test results figure 1 . figure 1 It shows that when the addition amount of the composition is 1.0, the simulated ash melting point increases to 1170°C...
Embodiment 2
[0014] Preparation composition (lanthanum trioxide 65% by weight, cerium oxide 30% by weight, neodymium trioxide 5% by weight), the simulated combustion ash composition is shown in Table 1, with the molar number of the composition relative to the vanadium in the simulated combustion ash The molar ratio is 1.0 and mixed with the simulated combustion ash, take 10g of the mixture, add 40-50ml of absolute alcohol, and stir evenly. Then 20g carbon steel is aluminized, Cr 5 The Mo aluminized test piece is immersed in the above suspension for several times, so that the bonded simulated dirt layer is about 20mg / cm 2 , high temperature test at 750°C, the test period is 96 hours, take out and weigh after the test, and calculate the corrosion rate by weight gain. Corrosion data results are shown in Table 2. The data in Table 2 shows that the composition can well inhibit the corrosion of simulated combustion ash.
[0015] Table 1 Composition of simulated combustion ash
[0016] ...
Embodiment 3
[0020] Weigh 2430g of 5% aqueous sodium hydroxide solution and 547.2g of isooctanoic acid, add them into the flask, heat to 75°C for 30 minutes, take 122.7g of lanthanum chloride, 73.98g of cerous chloride, and 50.14g of neodymium chloride to prepare 4950g of aqueous solution was added to the reaction flask together with 2748g of diesel oil, heated to 75°C for 30 minutes, and the oil phase was separated to prepare additive composition A.
[0021] The synthetic additive composition A was mixed into the vacuum residue (specific gravity 0.951g / cm2) with a content of 30 μg / g 3 , freezing point 44°C, residual carbon 19.07%, sulfur content 0.06%), use a thermal analyzer to heat to 550°C under the conditions of 30ml / min air flow and a heating rate of 85°C / min, and keep warm to measure the DTA curve . Calculate the half-life of the carbonaceous body from the DTA curve, and then use the formula of Shibata et al. to calculate the burning rate:
[0022] 1 / (σm)·(dm / dt)=1 / (tσ)·ln(m1 / m2) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com