Transfer belt for image forming apparatus
A technology of an imaging device and a transfer belt, applied in the direction of electrorecording process applying charge pattern, equipment for applying charge pattern electrorecording process, electrorecording technique, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
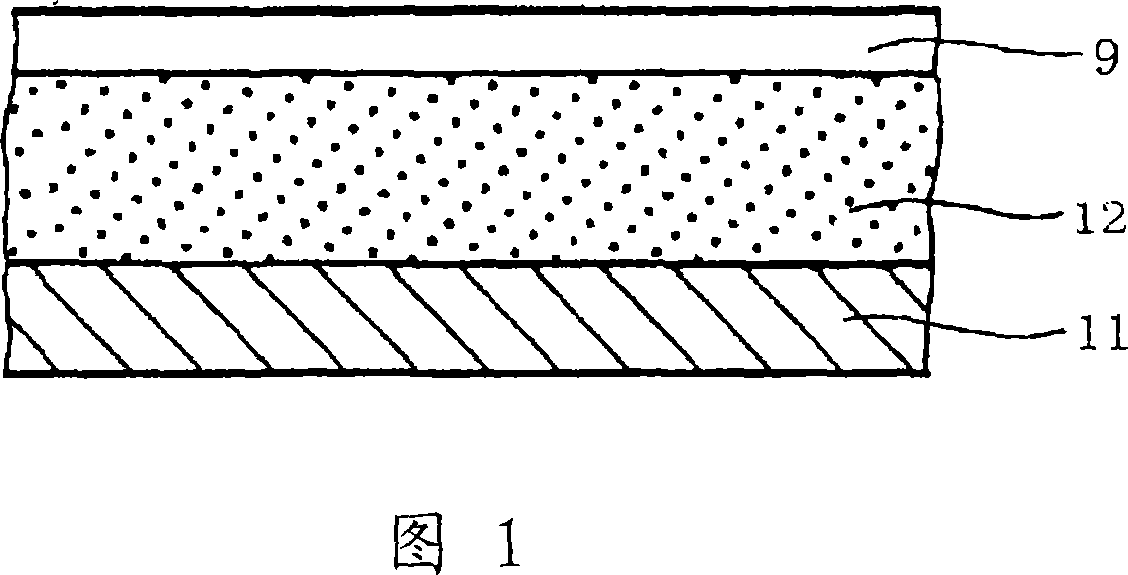
[0156] While rotating the drum mold, polyimide varnish is coated on its outer surface, and then the mold is heated to perform imidation reaction, thereby obtaining a 60 μm thick polyimide covering the periphery of the mold layer (bottom layer). Then adjust the viscosity of aqueous polyurethane (aqueous urethane) to a viscosity of about 10 Pa·s by adding a viscosifier, and perform defoaming, and apply the aqueous polyurethane to the polyimide layer by dip coating . After coating, it was dried at normal temperature to remove water, and annealed at 160° C. to obtain a 200 μm thick polyurethane layer (elastic layer) on the polyimide layer.
[0157] Then, on the polyurethane layer, the THV solution was sprayed under the condition that a thickness of 5 μm after drying and annealing was obtained. It was then dried and annealed at 160°C to form a surface layer, thereby obtaining the transfer belt of the present invention.
Embodiment 2
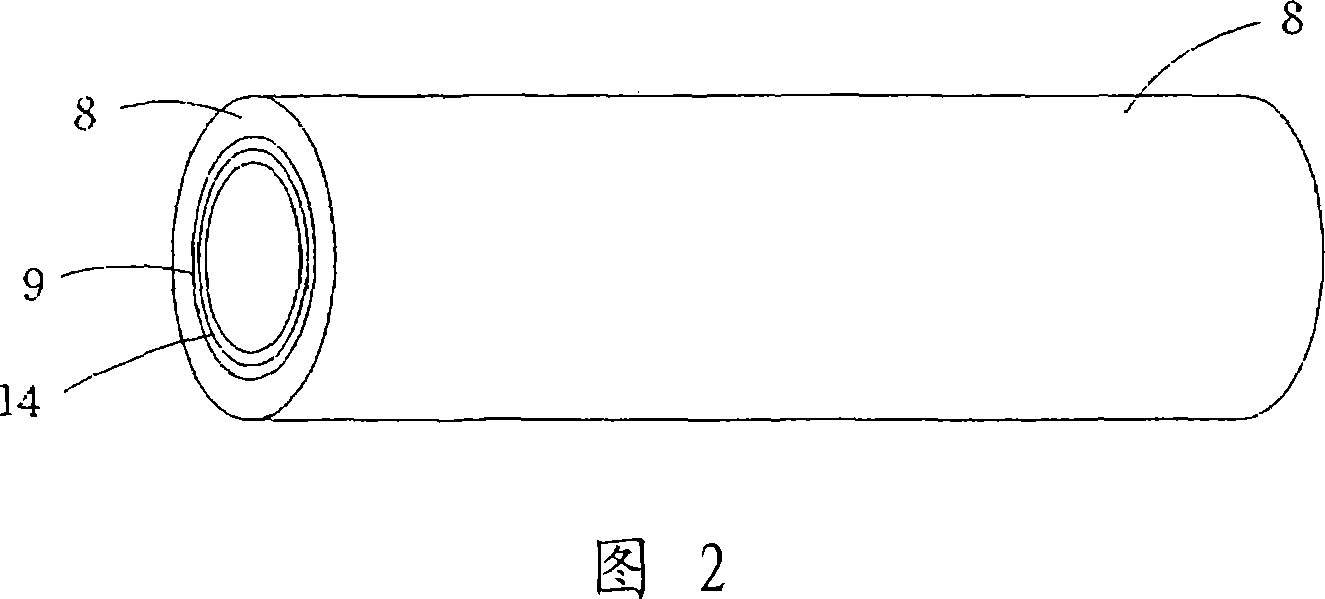
[0159] First, as shown in Figure 2, with 1.76×10 -5 On the inner surface of the steel outer tube 8 with a thermal expansion coefficient of / °C and a mirror-polished inner surface, a dispersion of PTFE (melting point 327°C, thermal decomposition point 400°C) is coated by dip coating, and sintered at 380°C , so as to obtain the surface layer 9.
[0160] THV (melting point: 120° C., thermal decomposition point: 400° C.) was then dissolved in butyl acetate to form a film on surface layer 9 by dip coating and dried to obtain adhesive layer 14 . The adhesive layer 14 is then heated at a temperature above the melting point of PTFE and THV, ie 350° C., thereby bonding the adhesive layer 14 to the skin 9 .
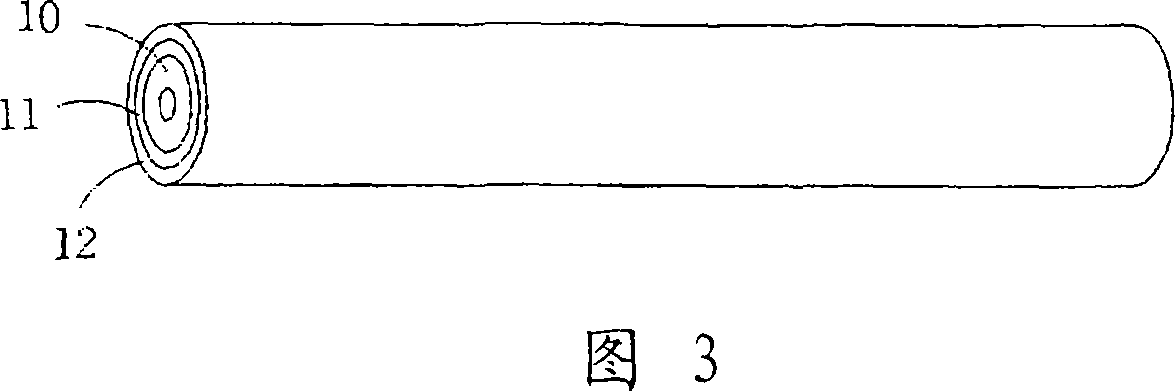
[0161] Then, as shown in FIG. 3 , polyimide subjected to conductive carbon treatment to adjust the volume resistivity was formed into a film on the surface of the drum mold 10 and sintered at 380° C. to obtain the bottom layer 11 .
[0162] Then, water-based polyurethane (melting...
Embodiment 3
[0170] Process in the same manner as in Example 2, except that the amount of THV dissolved in butyl acetate is changed to change the thickness of the adhesive layer 14, and the water-based polyurethane coated on the bottom layer 11 is changed A transfer belt for an image forming device is obtained for ion-conducting polyurethane, which consists of a 200-μm-thick elastic layer (polyurethane) on a 60-μm-thick base layer (polyimide), and a 3-μm-thick adhesive layer (THV) and a 5 μm thick surface layer (PTFE). The ion conductive treatment is performed by dispersing an ionic conductive agent in aqueous polyurethane, and its volume resistivity is adjusted to be 10 times that of the base layer 11 .
[0171] The thus-obtained transfer belt for an image forming apparatus has excellent surface resistivity, toner releasing properties, and non-staining properties. And the volume resistivity of the transfer belt for image forming apparatus is controlled in a stable manner by the elastic l...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Volume resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com