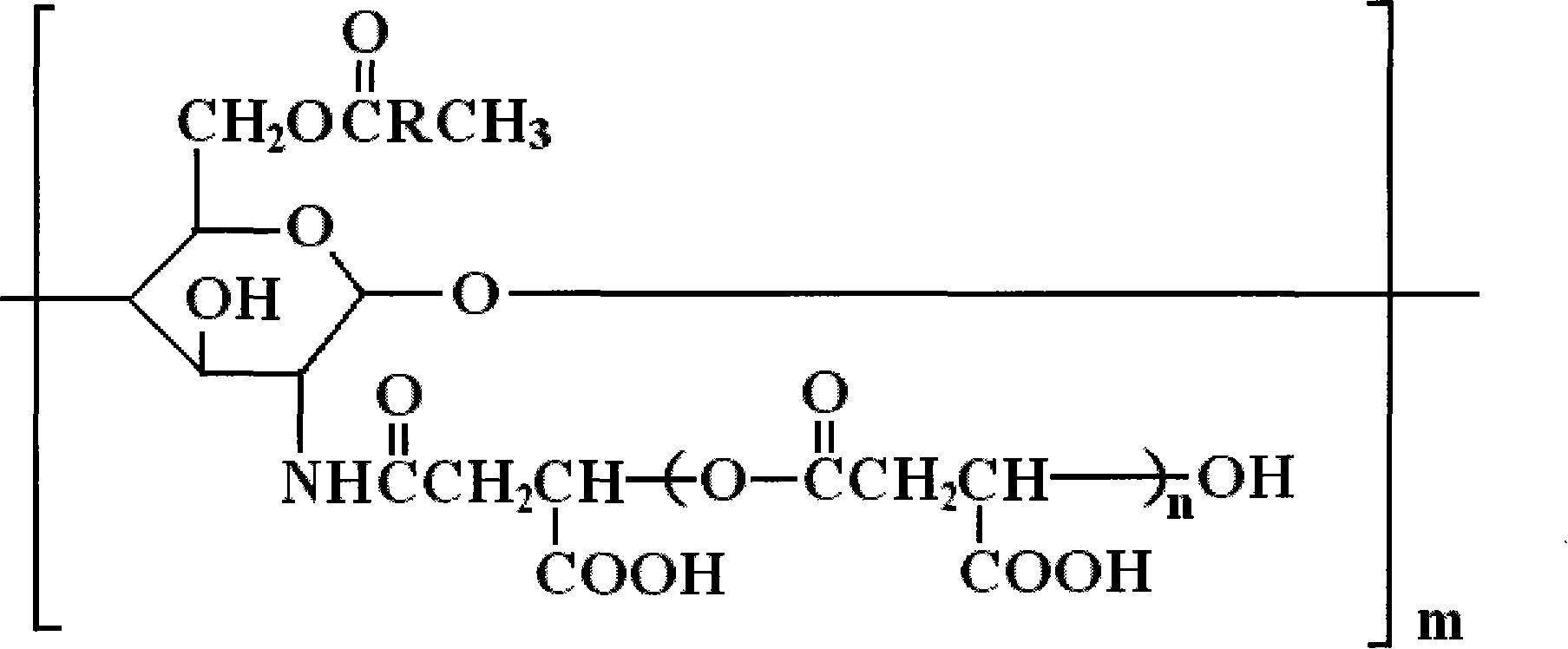
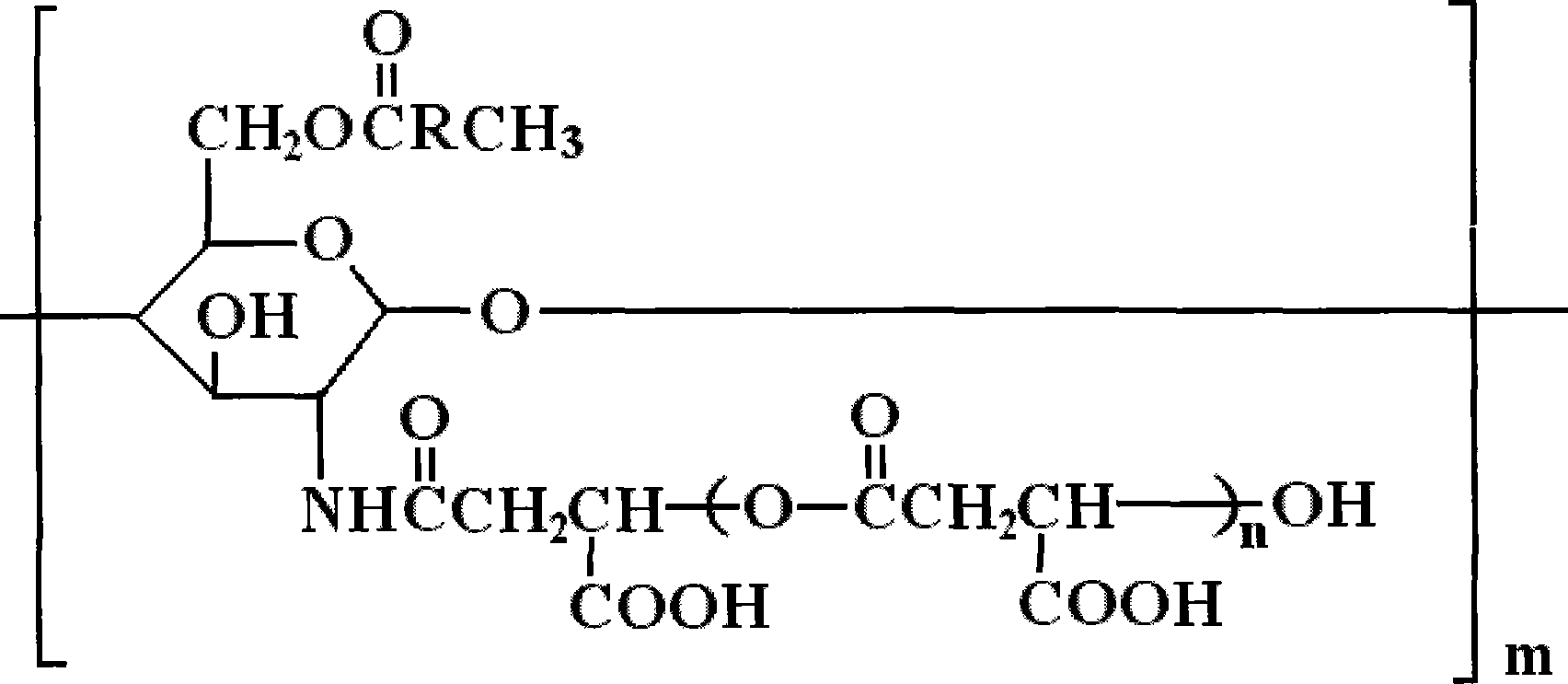
Derivative of amphoteric chitosan, preparation method, and application in pharmacy
A technology of chitosan derivatives and amphiphilicity, which is applied in the field of amphiphilic chitosan derivatives and its preparation, can solve problems such as unclear degradation mechanisms, achieve long circulation, good biocompatibility, reduce devouring effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: Preparation of O-oleic acid-N-polymalic acid chitosan nanoparticles
[0030] One, the preparation of oleic acid chloride
[0031] Dissolve oleic acid (2.82 g) in 20 mL of dry dichloromethane under a nitrogen atmosphere, stir in an ice bath, slowly add dropwise a solution of 2 mL of oxalyl chloride dissolved in 10 mL of dry dichloromethane, continue stirring at room temperature for 5 hours, and The excess oxalyl chloride and solvent were removed under reduced pressure to obtain 3 g of oleic acid chloride.
[0032] 2. Preparation of O-oleic acid chitosan
[0033] Take the molecular weight as 2×10 5 Add chitosan (0.8 g) with a degree of deacetylation above 90% into the solvent and stir until completely dissolved. According to the molar ratio of oleic acid chloride and chitosan unit 3:1 feed intake, at room temperature and N 2 Reacted for 8h under protection, and then added 20g of crushed ice to terminate the reaction. This mixture was dialyzed for 1 day ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: Preparation of O-oleic acid-N-polymalic acid chitosan nanoparticles
[0041] One, the preparation of oleic acid chloride
[0042] Dissolve oleic acid (2.82g) in 20mL of dry dichloromethane under a nitrogen atmosphere, stir in an ice bath, slowly add dropwise a solution of 2mL oxalyl chloride dissolved in 10mL of dry dichloromethane, continue to stir at room temperature for 1 hour, and dry in the tower The excess oxalyl chloride and solvent were removed under reduced pressure to obtain 3 g of oleic acid chloride.
[0043] 2. Preparation of O-oleic acid chitosan
[0044] Take the molecular weight as 5×10 4 Add chitosan (0.8 g) with a degree of deacetylation above 90% into the solvent and stir until completely dissolved. According to the molar ratio of oleic acid chloride and chitosan unit 5:1 feed intake, at room temperature and N 2 Reacted for 8h under protection, and then added 20g of crushed ice to terminate the reaction. This mixture was dialyzed fo...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment 3: Preparation of O-oleic acid-N-polymalic acid chitosan nanoparticles
[0050] One, the preparation of oleic acid chloride
[0051] Dissolve oleic acid (2.82 g) in 20 mL of dry dichloromethane under a nitrogen atmosphere, stir in an ice bath, slowly add dropwise a solution of 2 mL of oxalyl chloride dissolved in 10 mL of dry dichloromethane, continue stirring at room temperature for 8 hours, and dry The excess oxalyl chloride and solvent were removed under reduced pressure to obtain 3 g of oleic acid chloride.
[0052] 2. Preparation of O-oleic acid chitosan
[0053] Take the molecular weight as 1×10 6 Add chitosan (0.8 g) with a degree of deacetylation above 90% into the solvent and stir until completely dissolved. According to the molar ratio of oleic acid chloride and chitosan unit 1:1 feed intake, at room temperature and N 2 Reacted for 8h under protection, and then added 20g of crushed ice to terminate the reaction. This mixture was dialyzed for 1 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com