Bio-preserving fungus agent and its preparation method
A technology for biological preservation and inoculum is applied in the field of agricultural biology to achieve the effects of simple production and use methods, easy technology and delaying fruit ripening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
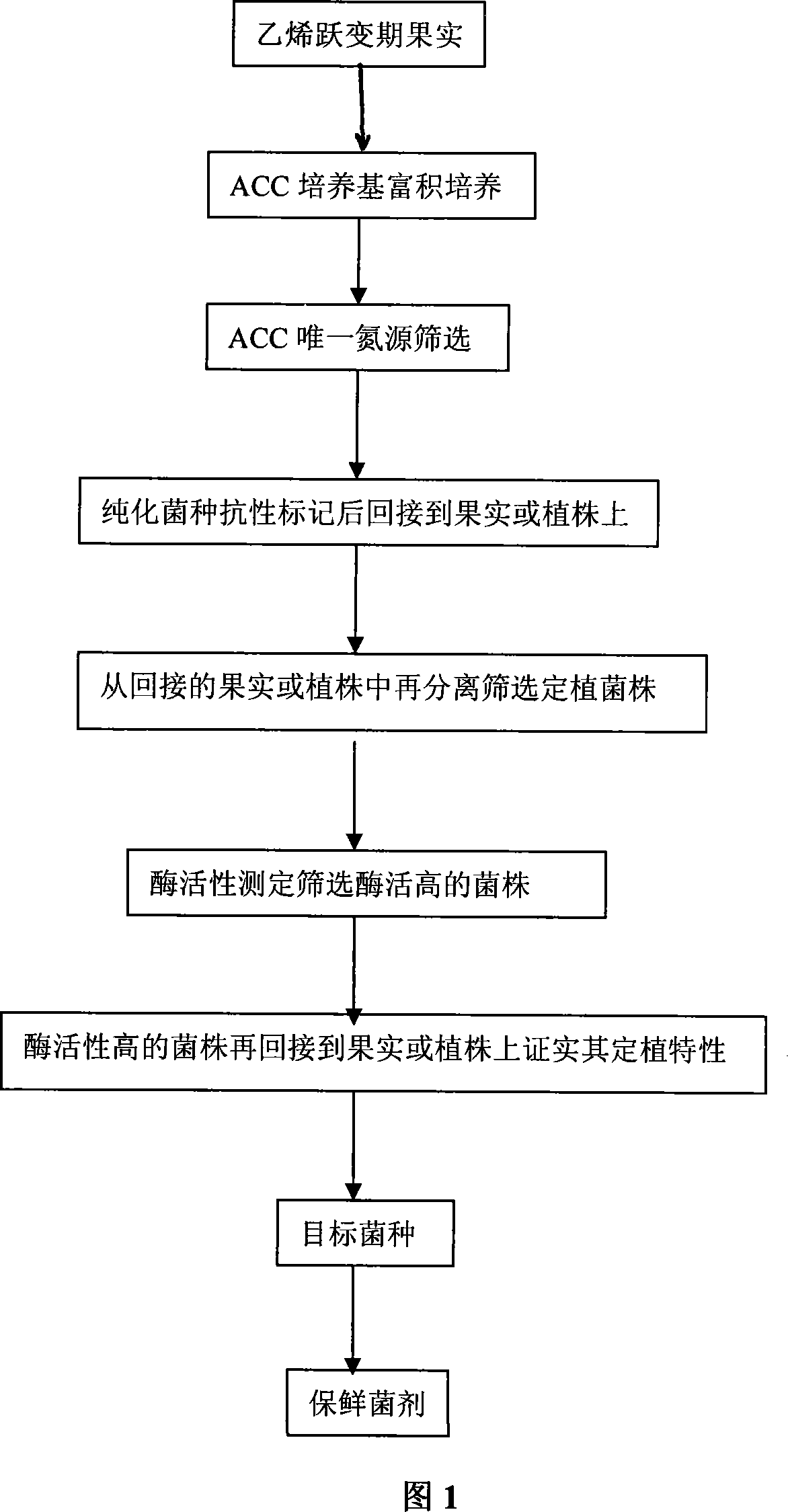
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Preparation of Banana Biological Preservative
[0023] 1. Preliminary screening of banana endogenous enzyme live strains:
[0024] Soak the yellow bananas in the transition period of ethylene with 70% ethanol for 15 minutes. Then sterilize with 1% sodium hypochlorite for 15 minutes, wash thoroughly with sterile water, and blot dry with sterile filter paper. Weigh 10g of banana inner skin, grind it into a slurry in a sterile homogenizer, place it in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask filled with 90mL of sterile water (with an appropriate amount of glass beads inside), and vibrate to make a suspension. Transfer 1mL suspension per sample to 50mL PAF culture medium (peptone 10g, casein hydrolyzate 10g, MgSO 4 1.5g, K 2 HPO 4 1.5 g, glycerol 10 mL, pH 7.0), and cultivated at 28°C for 24 hours on a rotary shaker at 200 r / min. Then, transfer 1mL of the bacterial suspension to another 50mL of PAF culture medium, and cultivate under the same conditions for 24h. On the third day, t...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Preparation of Strawberry Biological Preservative
[0039] 1. Preliminary screening of strawberry endogenous enzyme active strains:
[0040] Soak the ripe strawberries with 70% ethanol for 15 minutes. Then sterilize with 1% sodium hypochlorite for 15 minutes, wash thoroughly with sterile water, and blot dry with sterile filter paper. Weigh 10 g of the pericarp and pulp about 2 mm thick, grind it into a slurry in a sterile homogenizer, place it in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask filled with 90 mL of sterile water (with an appropriate amount of glass beads), and shake to make a suspension. All the other methods refer to embodiment 1.
[0041] 34 active strains were obtained.
[0042] 2. Screening of colonization strains on strawberry epidermis:
[0043] Method is with embodiment 1.
[0044] The above-mentioned bacterial strains with enzymatic activity were reattached to the growing strawberry fruit after being labeled with anti-rifampicin, and after 7 days, it was detected...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Embodiment 3: prepare tomato biological antistaling agent
[0051] 1. Acquisition of tomato endogenous enzyme live strains:
[0052] Ripe tomatoes were soaked in 70% ethanol for 15 minutes. Then sterilize with 1% sodium hypochlorite for 15 minutes, wash thoroughly with sterile water, and blot dry with sterile filter paper. After removing the wax of the outer skin under aseptic conditions, weigh 10 g of the outer skin of the tomato, grind it into a slurry in a sterile homogenizer, place it in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask filled with 90 mL of sterile water (with an appropriate amount of glass beads), shake it to make a buoyant liquid. See embodiment 1 for all the other methods.
[0053] Obtained 41 active enzyme strains.
[0054] 2. Screening of tomato colonization strains:
[0055] In order to reduce the cumbersomeness of strains resistant to rifampicin markers and reduce operating procedures, the screening of tomato colonization strains was first screened by the inocu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com