Method for reducing energy consumption during wet refining of mechanical pulp
A mechanical pulping and refining technology, applied in pulp beating/refining methods, textiles and papermaking, fiber raw material treatment, etc., can solve the problems of high energy consumption for refining, poor whiteness stability, and low physical strength of pulping
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
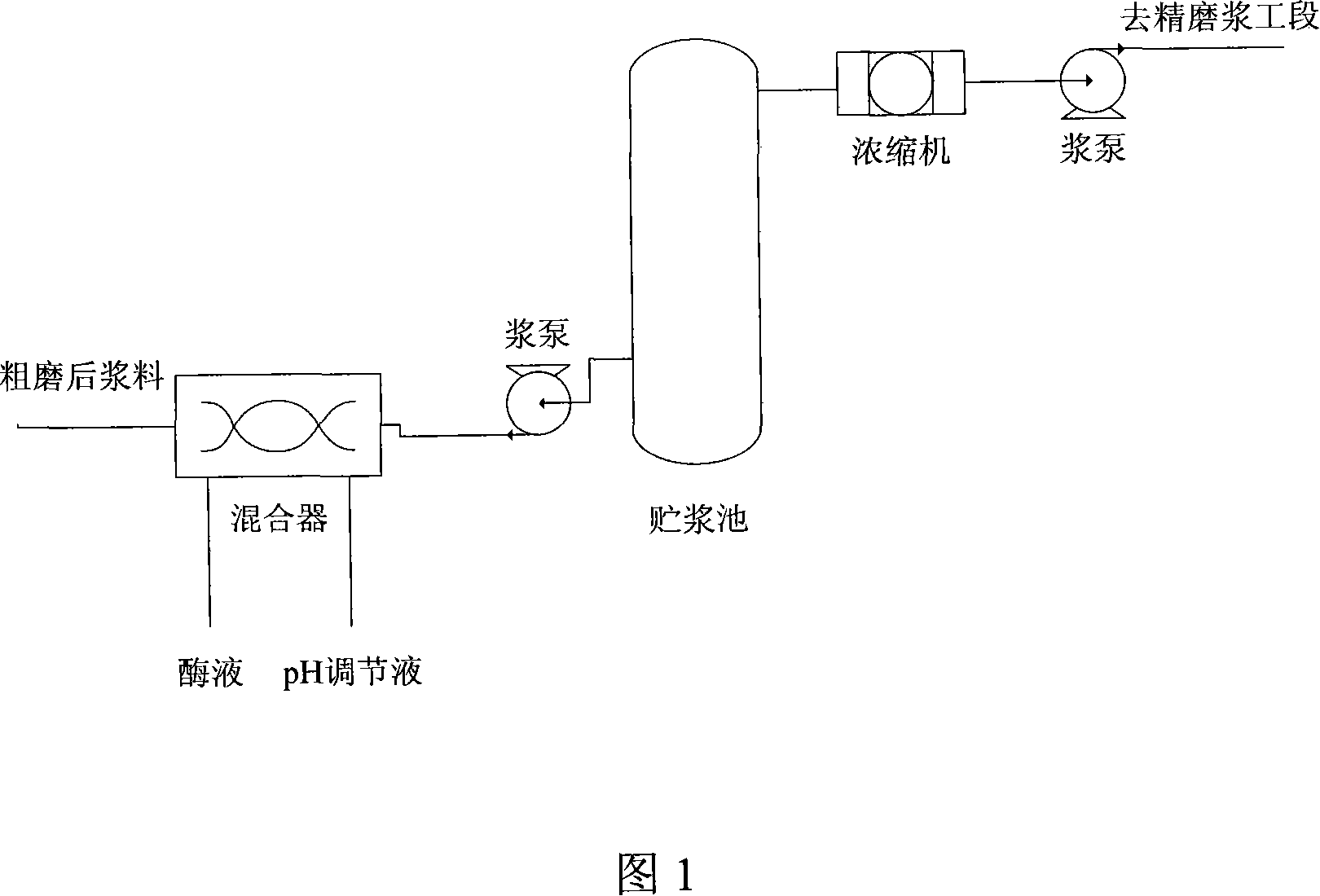
[0053] The refining energy consumption of conventional masson pine thermomechanical pulp (TMP) is 1350kW·h / t pulp, and the beating degree of pulp after refining is 50.2 0 SR, fiber bundle content 6.3%, bulk 2.73cm 3 g -1 , whiteness 45.7% ISO, burst index 1.26KPa m 2 g -1 , Fracture length 3.21km, tear index 2.45mN m 2 g -1 .
[0054] Adopt this method to produce masson pine TMP, carry out laccase treatment after the rough refining section, the treatment conditions are laccase dosage 32IU / g pulp, temperature 40 ℃, time 60min, pulp concentration 5%, pH value 5.0~7.5, After the treatment, the slurry is concentrated to a pulp concentration of 25%, and then finely refined. The energy consumption of refining in the refining section is 999kW·h / t pulp, and the energy consumption of refining is reduced by 26.0%. The beating degree of pulp is 50.8 0 SR, 5.0% tow content, 1.3% lower, bulk 2.65cm 3 g -1 , whiteness 47.1% ISO, burst index 1.34KPa m 2 g -1 , Fracture length 3.47...
Embodiment 2
[0056] The refining energy consumption of conventional eucalyptus bleached chemical thermomechanical pulp (BCTMP) is 1230kW·h / t pulp, and the beating degree of pulp after refining is 50.2 0 SR, fiber bundle content 6.1%, bulk 2.35cm 3 g -1 , whiteness 78.1% ISO, burst index 2.56KPa m 2 g -1 , Fracture length 4.54km, tear index 5.45mN m 2 g -1 . The ratio of producing newsprint eucalyptus BCTMP is 45%, and the ratio of deinking pulp is 55%.
[0057] Eucalyptus CTMP is prepared by this method, and xylanase treatment is carried out after the rough refining section. The treatment conditions are xylanase dosage 40IU / g pulp, temperature 50°C, time 60min, pulp concentration 8%, pH value 6 to 8. After the treatment, the pulp is concentrated to a pulp concentration of 25%, and then finely refined. The energy consumption of pulp in the fine grinding section is 929kW·h / t pulp, and the energy consumption of pulp is reduced by 24.5%. After fine grinding The beating degree of the ref...
Embodiment 3
[0059] The refining energy consumption of conventional poplar alkaline hydrogen peroxide mechanical pulp (APMP) is 960kW·h / t pulp, and the beating degree of pulp after refining is 48.5 0 SR, fiber bundle content 5.2%, bulk 2.23cm 3 g -1 , whiteness 77.3% ISO, burst index 2.35KPa m 2 g -1 , Fracture length 4.31km, tear index 5.33mN m 2 g -1 . The ratio of poplar APMP to produce low basis weight coated paper is 80%, and the ratio of bleached kraft pulp is 20%.
[0060] Adopt this method to prepare poplar APMP, carry out white rot fungus crude enzyme solution treatment after the rough refining section, the treatment condition is enzyme solution dosage 6ml / kg pulp, temperature 40 ℃, time 60min, pulp concentration 6%, pH value 5.0~7.0, after the treatment, the pulp is concentrated to a pulp concentration of 25%, and then finely refined. The beating degree of the refined pulp is 49.1 0 SR, 4.1% tow content, 1.1% lower, bulk 2.09cm 3 g -1 , whiteness 79.2% ISO, burst index ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Burst index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tear index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com