Antihuman CD146 monoclone antibody, composition containing the same, and method for testing dissolubility CD146
An antibody and human body technology, applied in the fields of molecular biology and biology, can solve problems such as differences in the exposure of antibody binding epitopes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
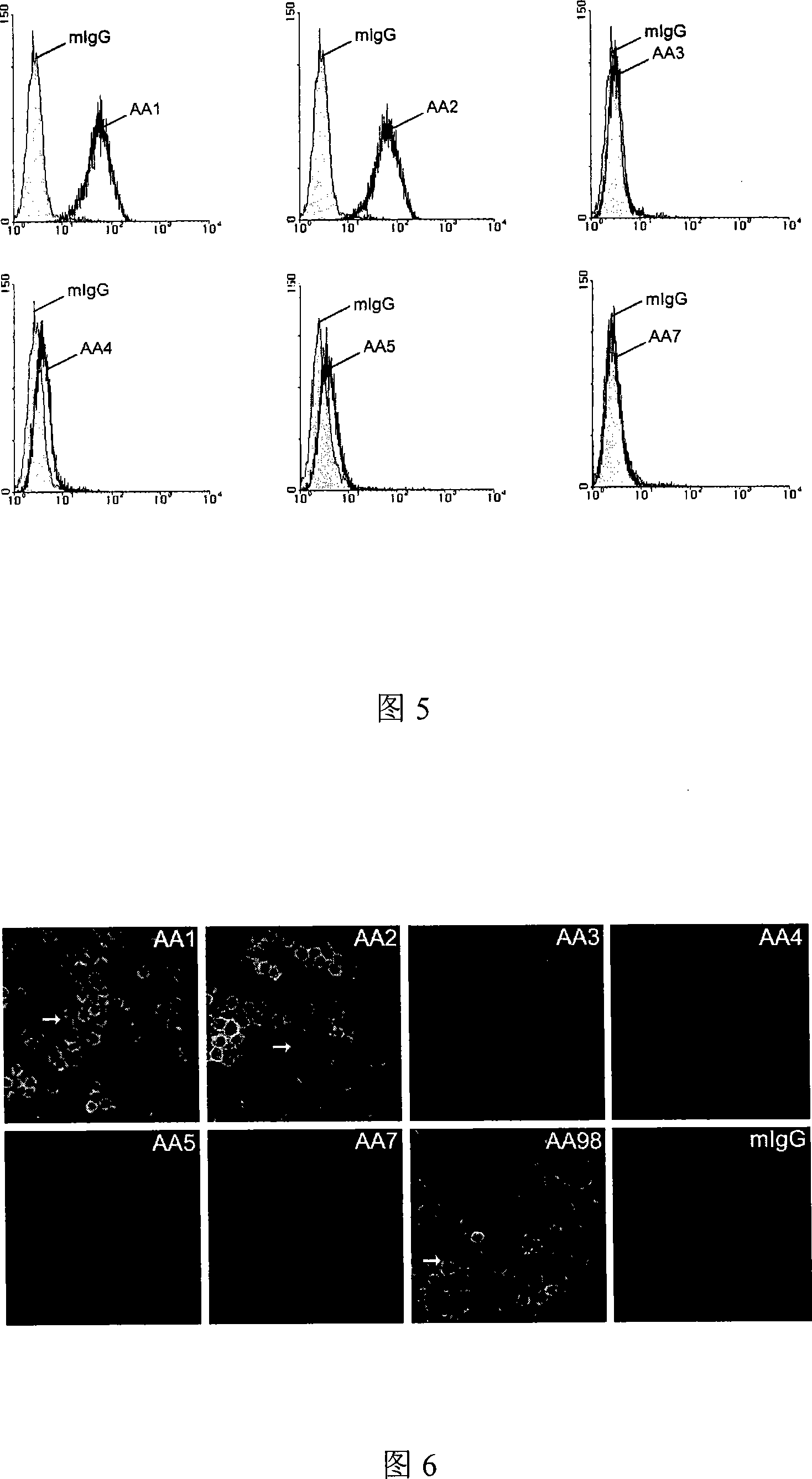
[0054] Example 1: Preparation and identification of monoclonal antibodies AA1-AA5 and AA7.
[0055] Application of hybridoma technology (Kohler and Milstein 1975; Yeh, Hellstrom et al.1979; Yeh, Hellstrom et al.1982) produced and screened to obtain antibodies AA1-AA6 and AA7. Briefly described as follows: Isolate natural CD146 protein (its amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2) from human umbilical cord vein endothelial cells, according to (Yan, Lin et al.2003 ) to purify the monoclonal antibody AA98 antigen, and use it as an immunogen to immunize BALB / C mice (Beijing Experimental Animal Center), inject 100 μg protein / mouse intraperitoneally, once every two weeks, for a total of three times. Before the splenocytes were collected, immunization was boosted once, and 100 μg protein / mouse was injected intraperitoneally. Three days after the booster immunization, the spleen was taken, and the splenocytes were suspended ...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Example 2: Epitope identification of monoclonal antibodies AA1-AA5 and AA7.
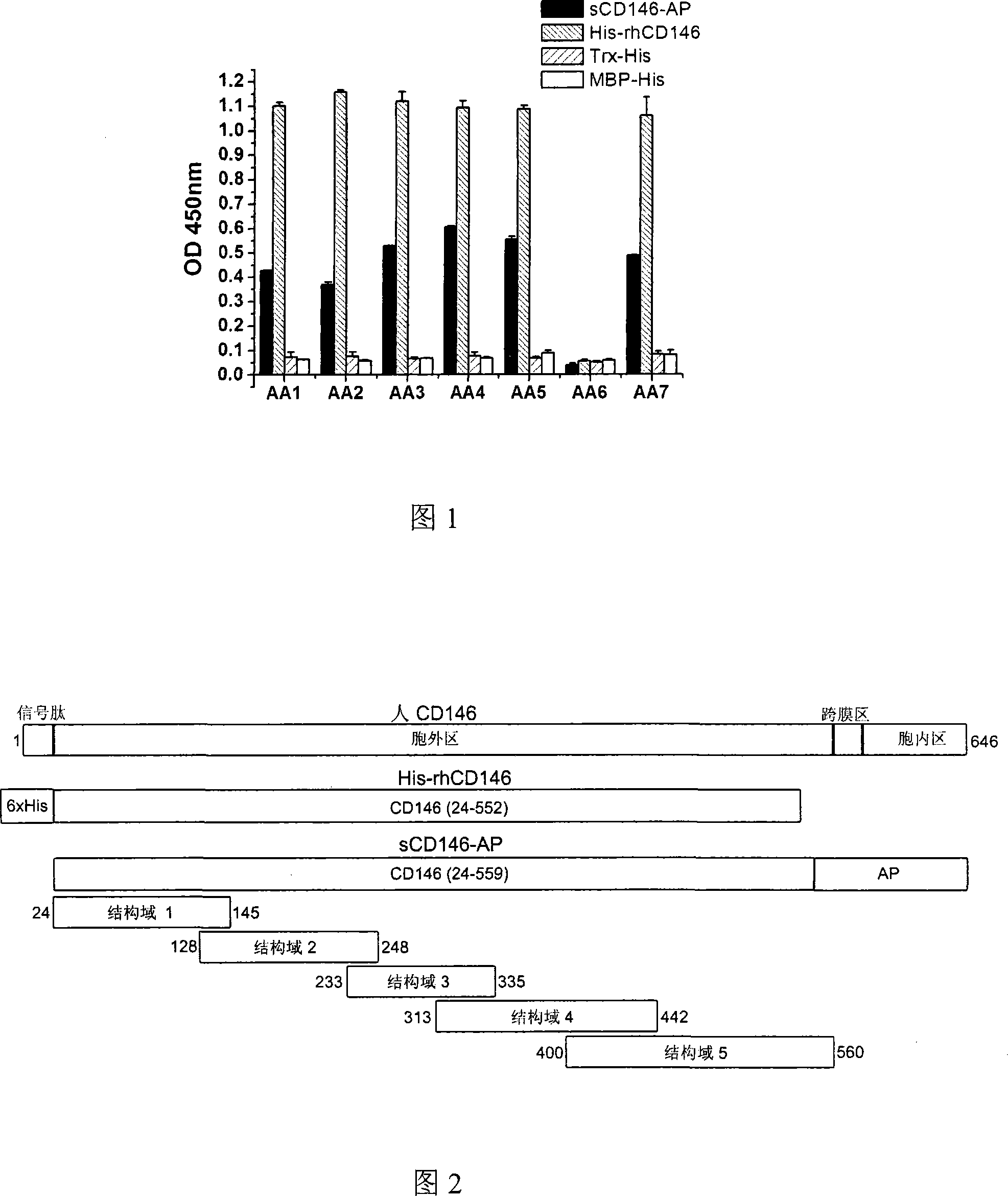
[0080] The antigenic epitopes of the six antibodies described in the present invention were identified by recombinantly expressing the five domain proteins of the extracellular region of human CD146 and immunoblotting.
[0081] As shown in Figure 2, domains 1-5 respectively represent the five domains V-V-C2-C2-C2 of CD146 from the extracellular to the transmembrane region. Overlapping sequences were designed to prevent possible loss of epitopes. Domain 1 (sequence is the amino acid at position 24-145 in the human CD146 sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, as shown in SEQ ID NO: 9) is cloned on pET30a (Novagen), and what is expressed is His6-Stag fusion His6 - S-D1 protein. Structural domain 2 (sequence is the amino acid of position 128-248 in the human CD146 sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, as shown in SEQ ID NO: 10), structural domain 3 (sequence is the human CD146 sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 The amino acid of...
Embodiment 3
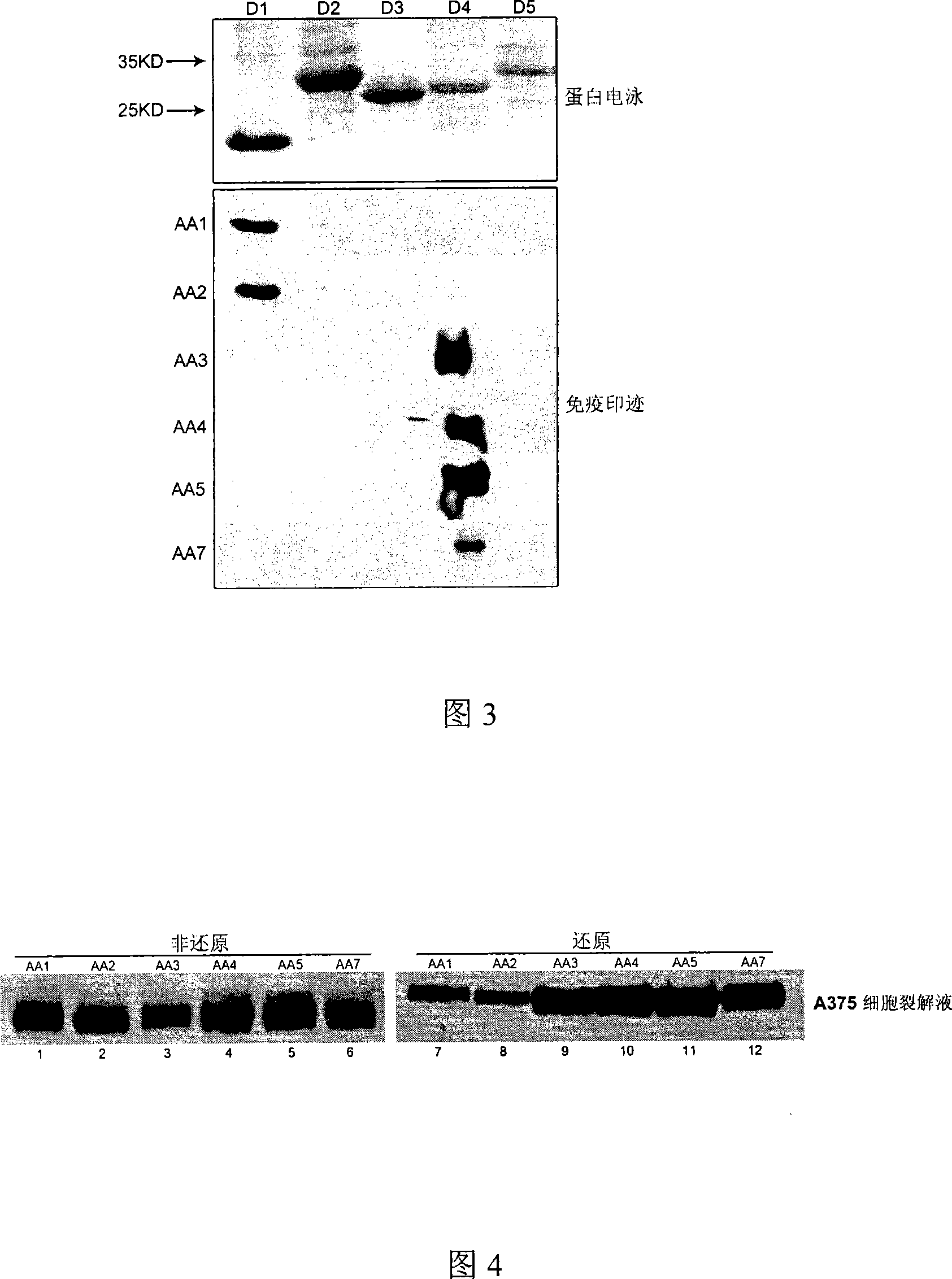
[0092] Example 3: Detection of human CD146 using monoclonal antibodies AA1-AA5 and AA7
[0093] The anti-human CD146 mouse monoclonal antibody of the present invention can detect human CD146 protein at molecular, cell and tissue levels.
[0094] In whole-cell western blot experiments, both AA1-AA5 and AA7 could recognize CD146 protein in both reduced and non-reduced states. The specific experimental method is as follows: collect human melanoma cells A375 (ATCC) highly expressing CD146, wash the cells twice with pre-cooled PBS, centrifuge at 800 rpm at 4°C for 5 minutes, and use lysate (Tris-HCl 50mM pH8. 0, NaCl 150mM, EDTA 1mM, NP-40 1%, Glycerol 10%, PMSF 100μg / ml) to lyse the cells, centrifuge at 12000g at 4°C for 15 minutes, collect the supernatant, add DTT (final concentration 100mM) (dithiothreose) Alcohol) and DTT-free loading buffer (5x loading buffer: 0.313M Tris-HCl, pH6.8, 10% SDS, 0.05% bromophenol blue, 50% glycerol), cook at 100°C. Whole-cell proteins were sepa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com